Abstract
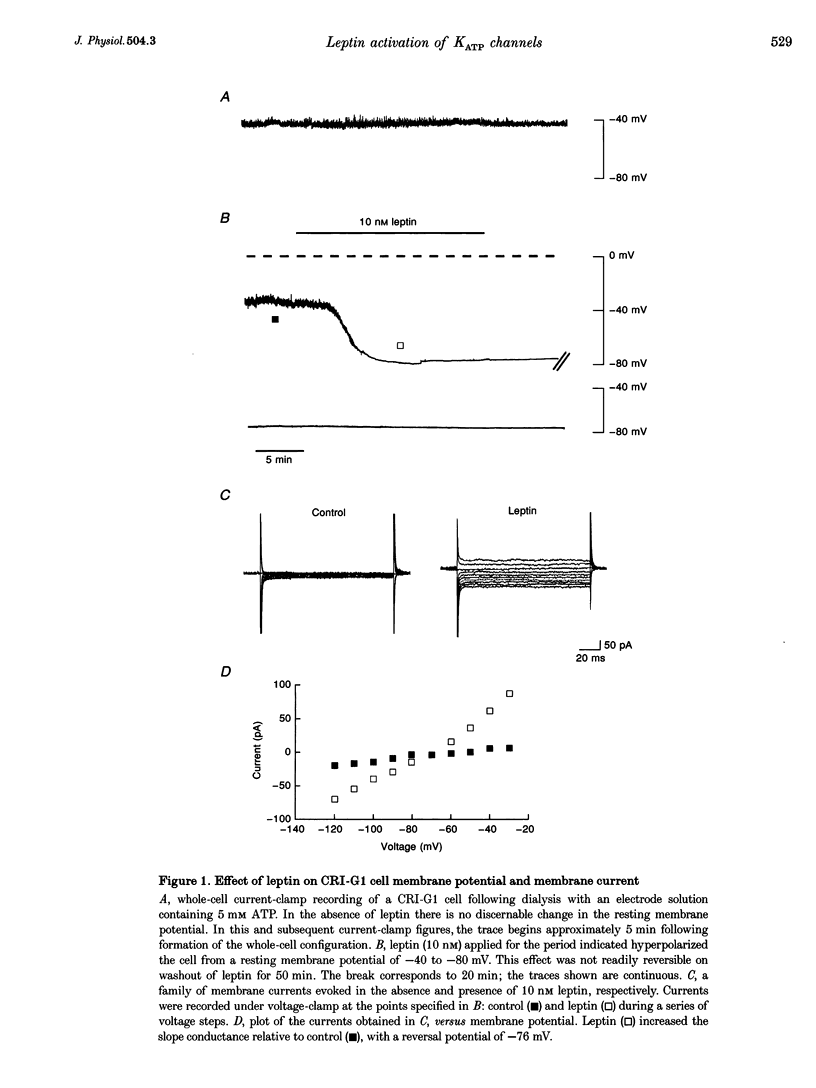
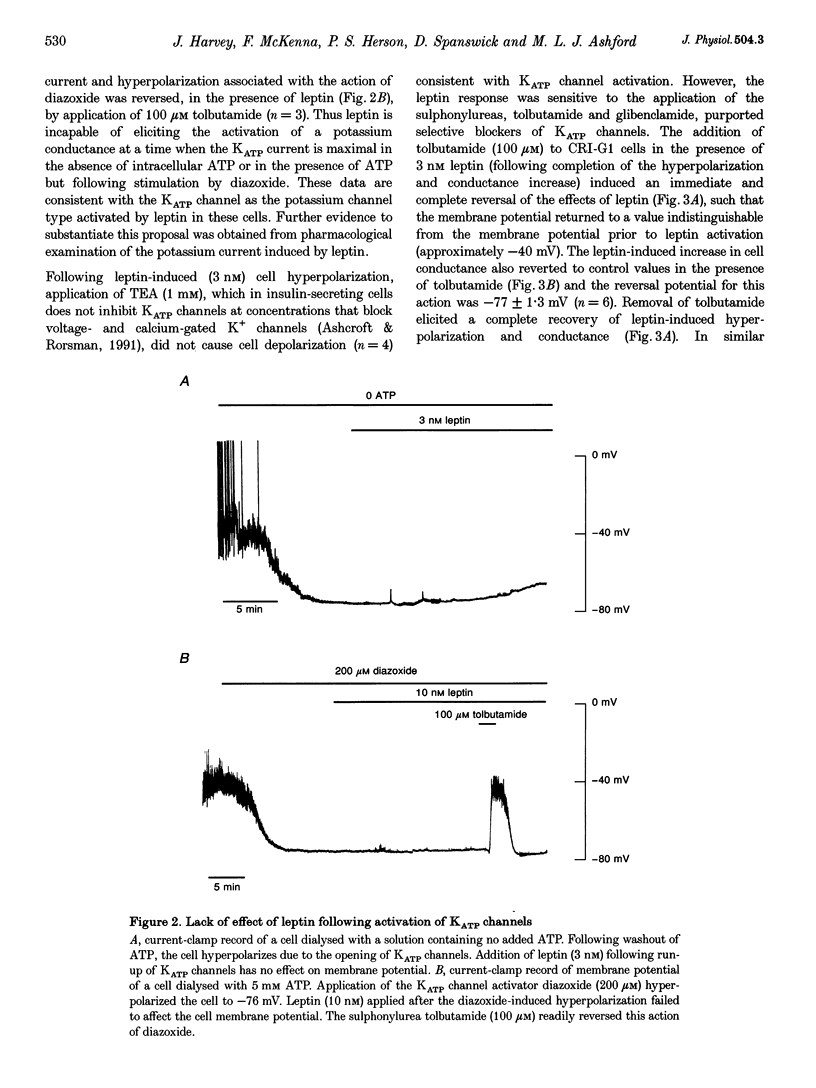
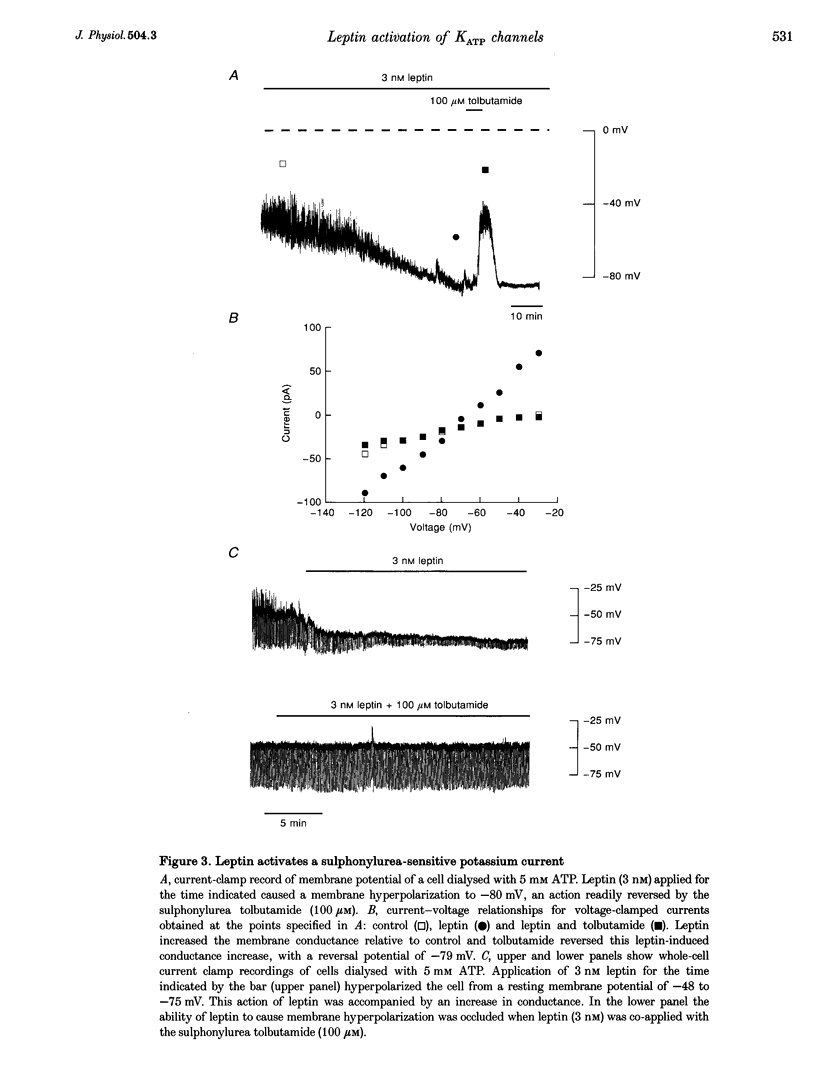
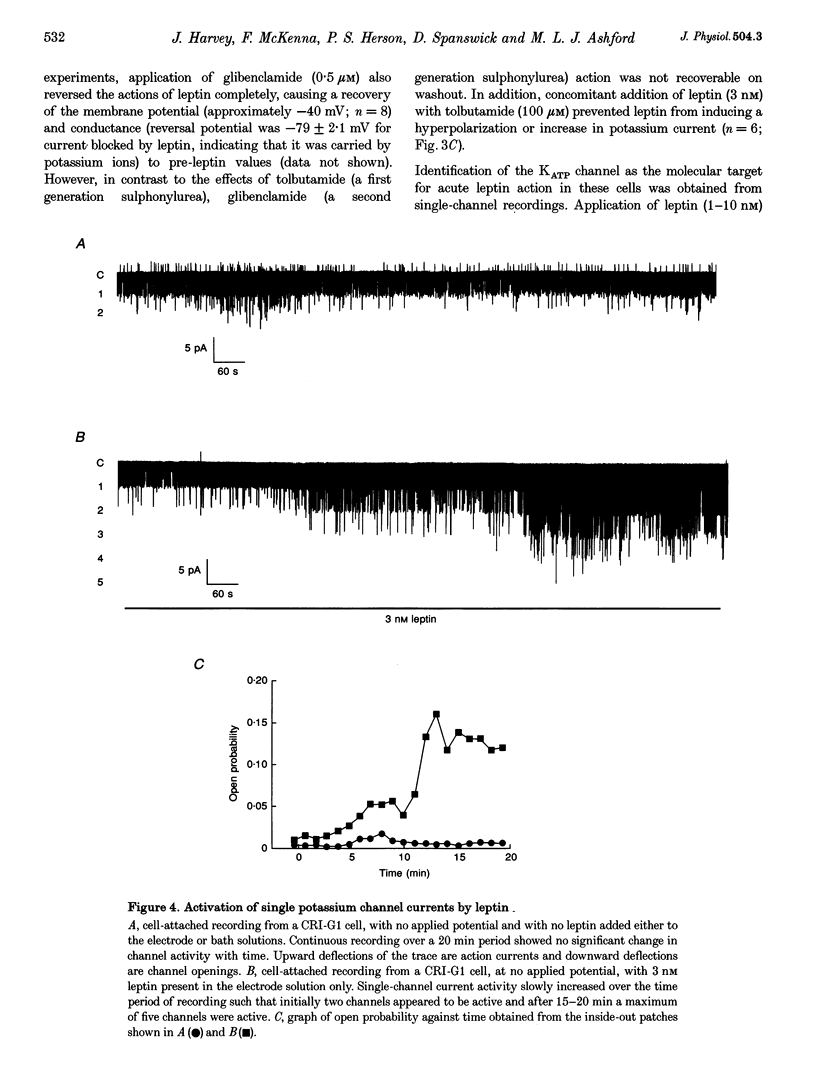
1. Whole-cell current-clamp recordings demonstrate that leptin (0.3-10 nm) hyperpolarizes CRI-G1 insulin-secreting cells. This effect is slow on onset and is not reversed on washout of the leptin. 2. Voltage-clamp recordings indicate that leptin activates a potassium conductance in the presence of intracellular ATP (5 mm), but has not effect in its absence. Following activation of ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) current by diazoxide (0.2 mm), addition of leptin did not alter cell membrane potential or potassium current further. 3. The leptin-induced hyperpolarization and increased potassium conductance are completely inhibited by the application of the sulphonylureas tolbutamide (100 microM) and glibenclamide (0.5 microM). 4. Cell-attached and inside-out single-channel recordings indicate that leptin activates tolbutamide-sensitive KATP channels in CRI-G1 insulin-secreting cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The sulfonylurea receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 15;1175(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Kolaczynski J. W., Zhang P. L., Considine R. V. Leptin: the tale of an obesity gene. Diabetes. 1996 Nov;45(11):1455–1462. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.11.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington C. A., Rubery E. D., Pearson E. C., Hales C. N. Five new insulin-producing cell lines with differing secretory properties. J Endocrinol. 1986 May;109(2):193–200. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1090193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Considine R. V., Considine E. L., Williams C. J., Nyce M. R., Zhang P., Opentanova I., Ohannesian J. P., Kolaczynski J. W., Bauer T. L., Moore J. H. Mutation screening and identification of a sequence variation in the human ob gene coding region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Mar 27;220(3):735–739. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilsson V., Liu Y. L., Cawthorne M. A., Morton N. M., Davenport M. Expression of the functional leptin receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets and direct inhibitory action of leptin on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1997 Feb;46(2):313–316. doi: 10.2337/diab.46.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., Rabinowitz D., Lallone R. L., Burley S. K., Friedman J. M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7624777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Dziura J., Medwick M. B., Leone P., Caprio S., During M., Shulman G. I., Sherwin R. S. The effect of leptin is enhanced by microinjection into the ventromedial hypothalamus. Diabetes. 1997 Jan;46(1):150–152. doi: 10.2337/diab.46.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer T. J., Heller R. S., Habener J. F. Leptin receptors expressed on pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Jul 16;224(2):522–527. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Ashford M. L. Nucleotide-dependent activation of KATP channels by diazoxide in CRI-G1 insulin-secreting cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):34–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. H., Proenca R., Montez J. M., Carroll K. M., Darvishzadeh J. G., Lee J. I., Friedman J. M. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature. 1996 Feb 15;379(6566):632–635. doi: 10.1038/379632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Rowe I. C., Ashford M. L. Characterization of an ATP-modulated large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel present in rat cortical neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Oct 15;488(Pt 2):319–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin N., Nelson C., Gurney A., Vandlen R., de Sauvage F. Decreased food intake does not completely account for adiposity reduction after ob protein infusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei M., Stoffel M., Barone M., Moon B., Dammerman M., Ravussin E., Bogardus C., Ludwig D. S., Flier J. S., Talley M. Absence of mutations in the human OB gene in obese/diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1996 May;45(5):679–682. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.5.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzaki H., Ogawa Y., Isse N., Satoh N., Okazaki T., Shigemoto M., Mori K., Tamura N., Hosoda K., Yoshimasa Y. Human obese gene expression. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1995 Jul;44(7):855–858. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.7.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):540–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7624776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevarskaya N. B., Skryma R. N., Vacher P., Daniel N., Djiane J., Dufy B. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation in potassium channel activation. Functional association with prolactin receptor and JAK2 tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24292–24299. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.24292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Opentanova I., Ohannesian J. P., Kolaczynski J. W., Heiman M. L., Hale J., Becker G. W., Bowsher R. R., Stephens T. W., Caro J. F. Evidence of free and bound leptin in human circulation. Studies in lean and obese subjects and during short-term fasting. J Clin Invest. 1996 Sep 15;98(6):1277–1282. doi: 10.1172/JCI118913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens T. W., Basinski M., Bristow P. K., Bue-Valleskey J. M., Burgett S. G., Craft L., Hale J., Hoffmann J., Hsiung H. M., Kriauciunas A. The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):530–532. doi: 10.1038/377530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Dembski M., Weng X., Deng N., Culpepper J., Devos R., Richards G. J., Campfield L. A., Clark F. T., Deeds J. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1263–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



