Abstract
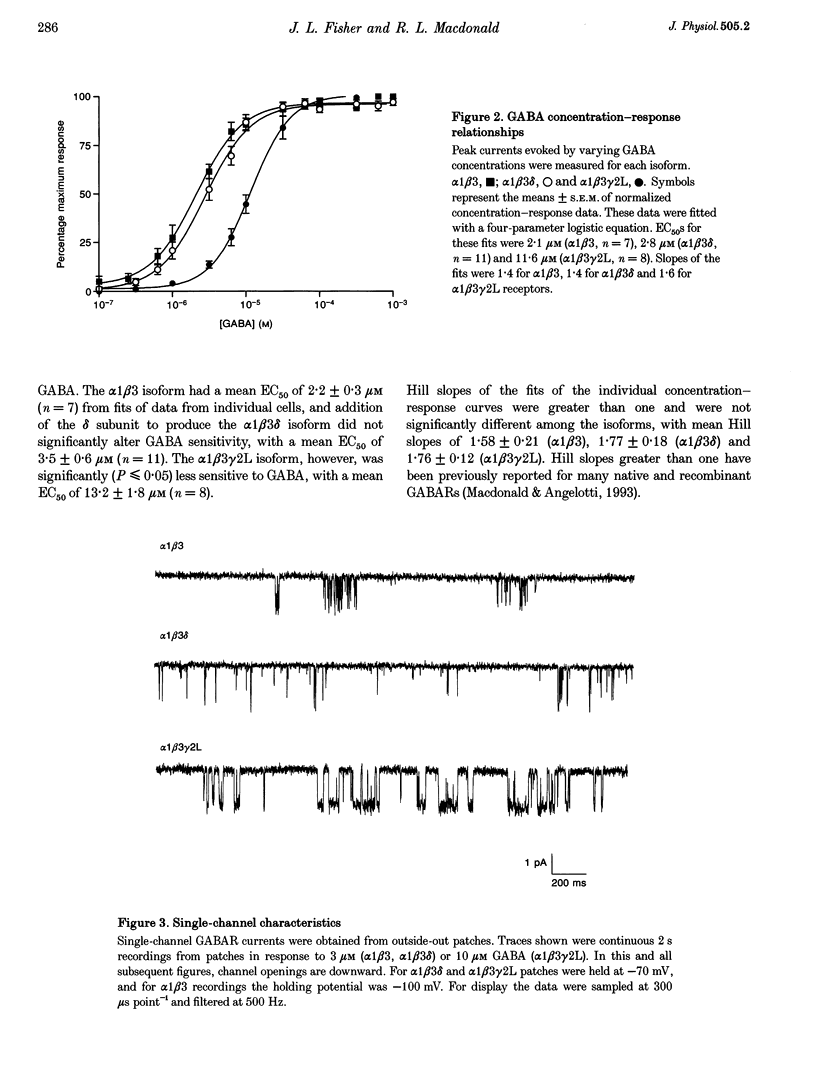
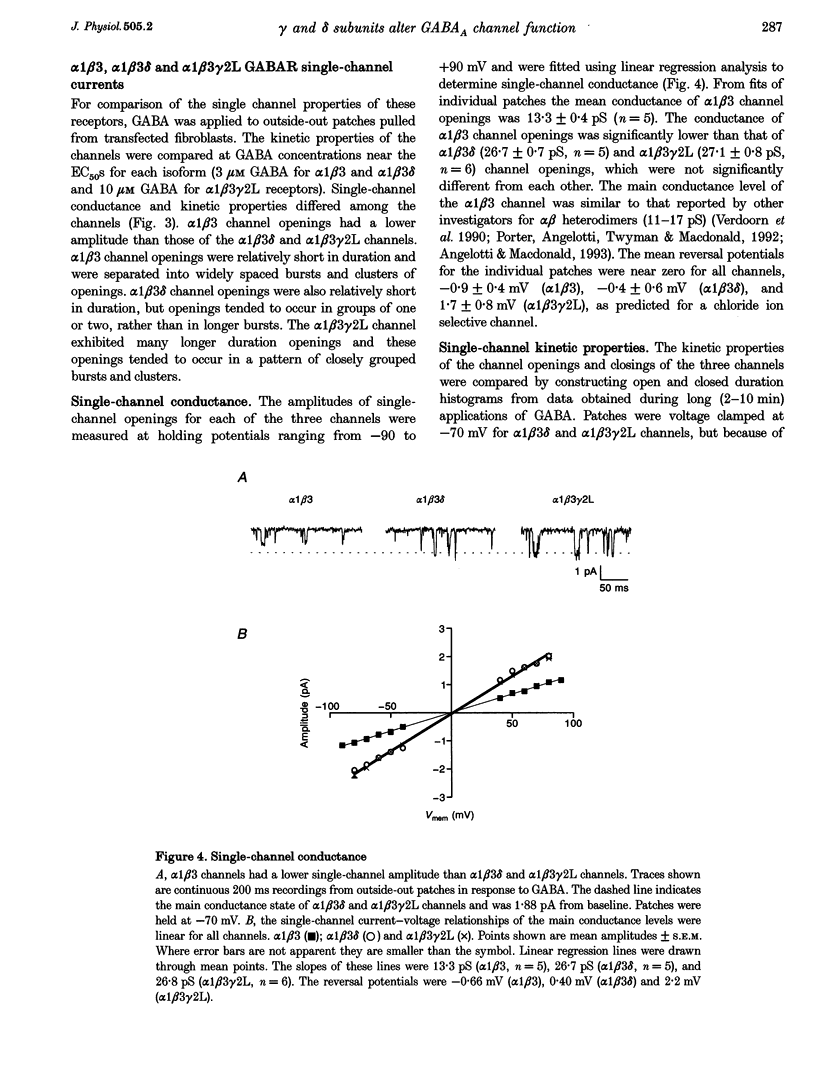
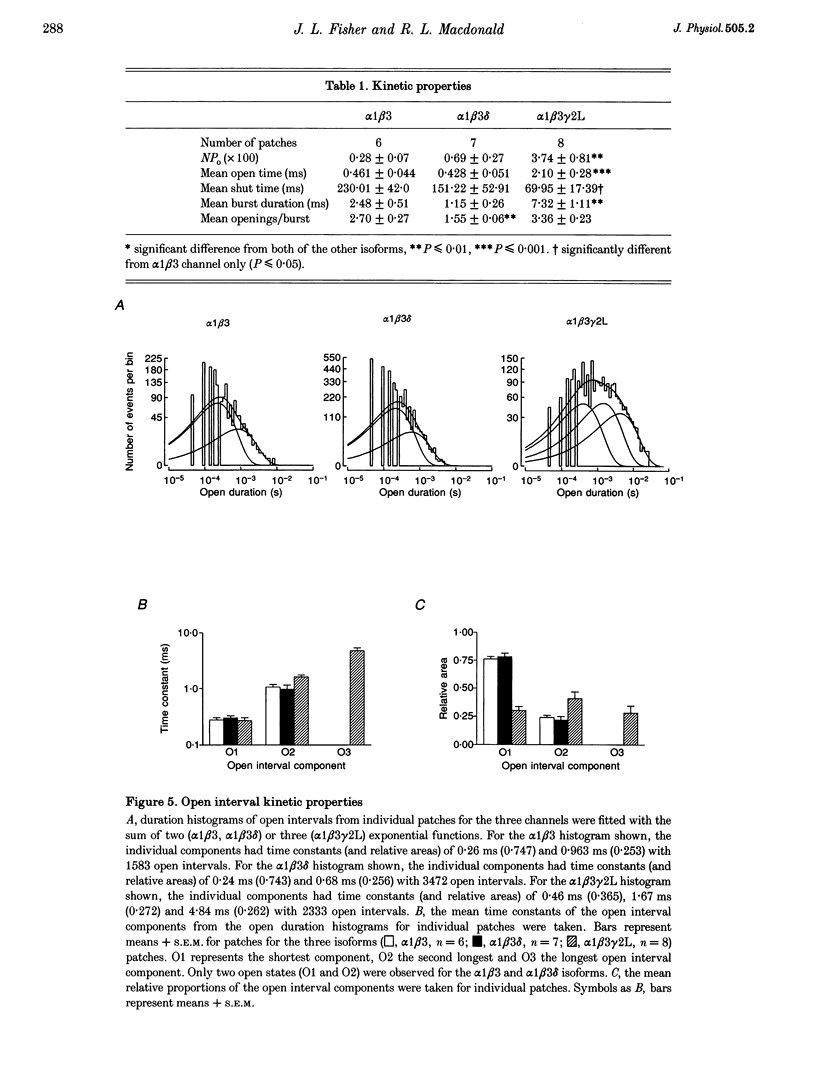
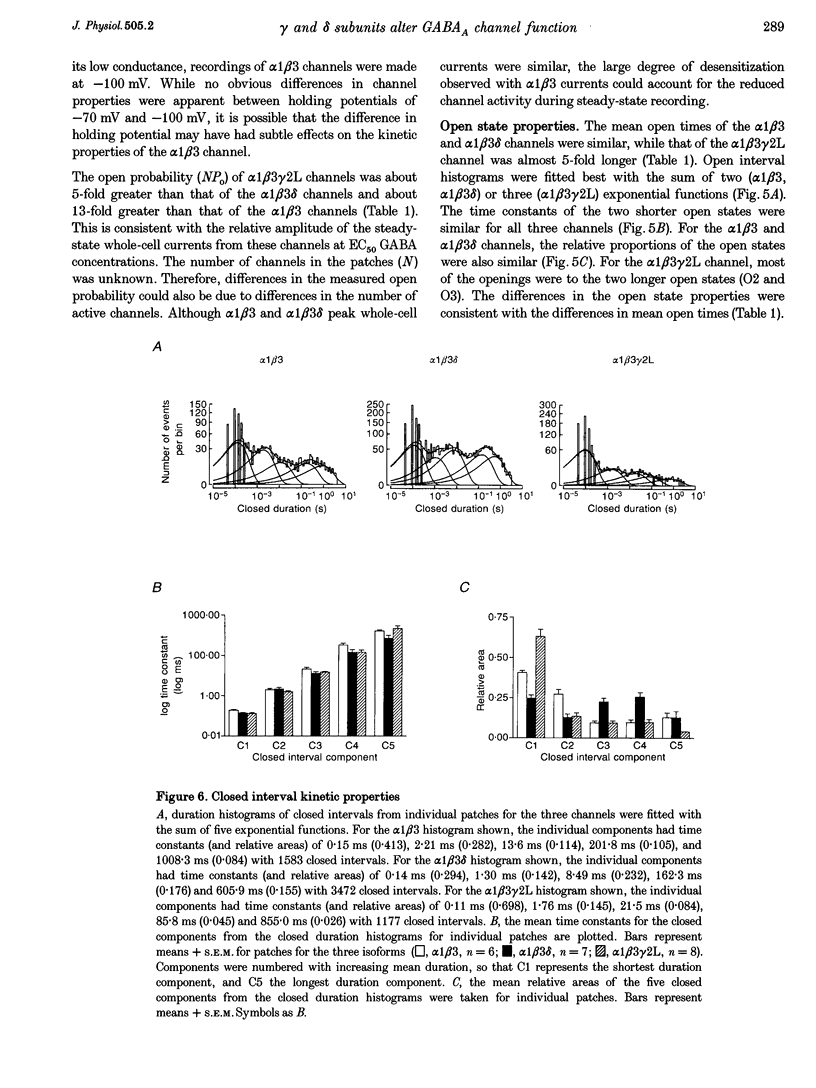
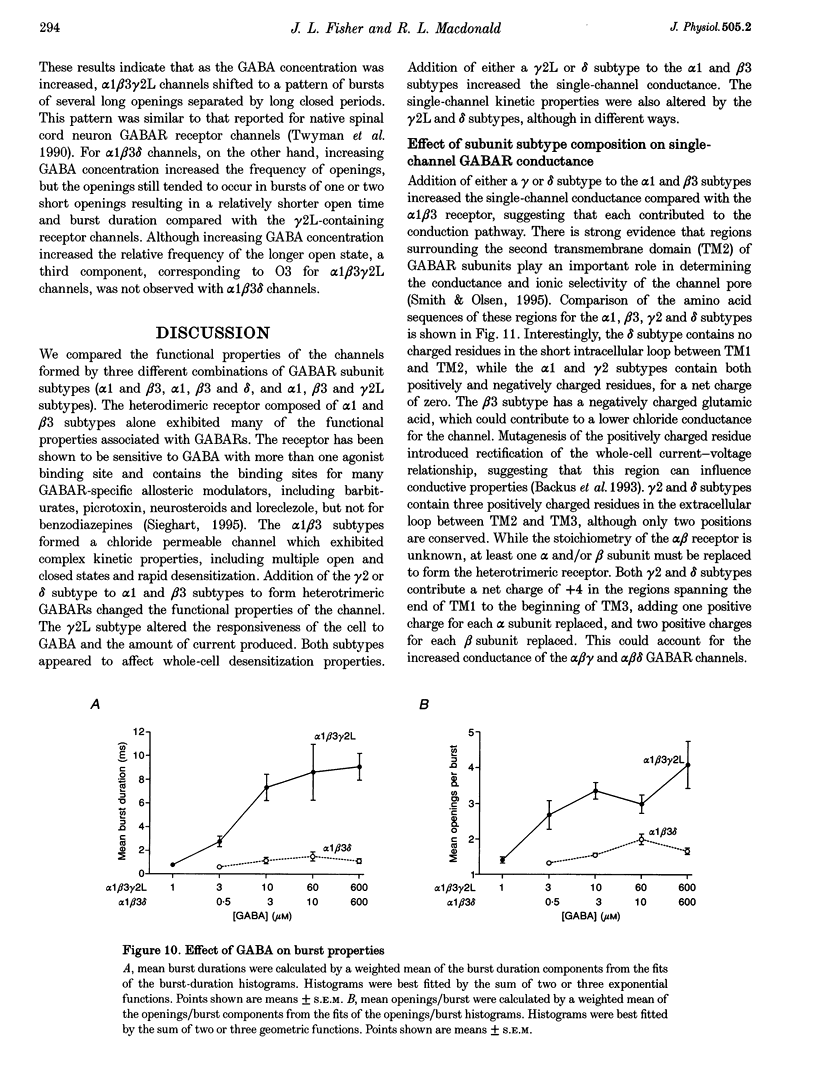
1. To determine their contributions to GABAA receptor (GABAR) channel properties, rat gamma 2L and delta subunits were acutely co-expressed with alpha 1 and beta 3 subtypes in mouse L929 fibroblasts to produce alpha 1 beta 3, alpha 1 beta 3 delta or alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L GABAR isoforms. 2. With whole-cell recording, the alpha 1 beta 3 isoform had relatively high sensitivity to GABA (EC50 2.1 microM) and low maximum current amplitude. The alpha 1 beta 1 delta isoform had similar sensitivity to GABA (EC50 2.8 microM) and low current amplitude. The alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L isoform had lower sensitivity to GABA (EC50 11.6 microM) and higher maximum current amplitude. 3. The single channel conductance of alpha 1 beta 3 channels was low (13 pS) compared with that of alpha 1 beta 3 delta and alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L channels (27 pS). 4. The single channel kinetic properties of the channels also differed. The alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L channel exhibited three open states, while the alpha 1 beta 3 and alpha 1 beta 3 delta channels exhibited only two open states with mean dwell times similar to those of the two shorter open states of the alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L channel. All three channels exhibited at least five closed states. Bursts of alpha 1 beta 3 delta channels consisted primarily of only one or two openings, while those of alpha 1 beta 3 channels contained multiple openings. alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L channels exhibited burst kinetics typical for native GABARs with several long openings per burst. 5. These results show that the alpha 1 beta 3 heterodimer formed a GABA-sensitive channel with complex gating kinetics. Addition of a delta subunit to form the alpha 1 beta 3 delta heterotrimer altered the single channel conductance and the kinetic properties of the closed components, but did not affect the GABA sensitivity of the receptor nor the open state kinetics. In contrast, addition of a gamma subunit (gamma 2L subtype) to produce the alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2L heterotrimer affected the GABA sensitivity, channel conductance and kinetic properties of both open and closed states.
Full text
PDF


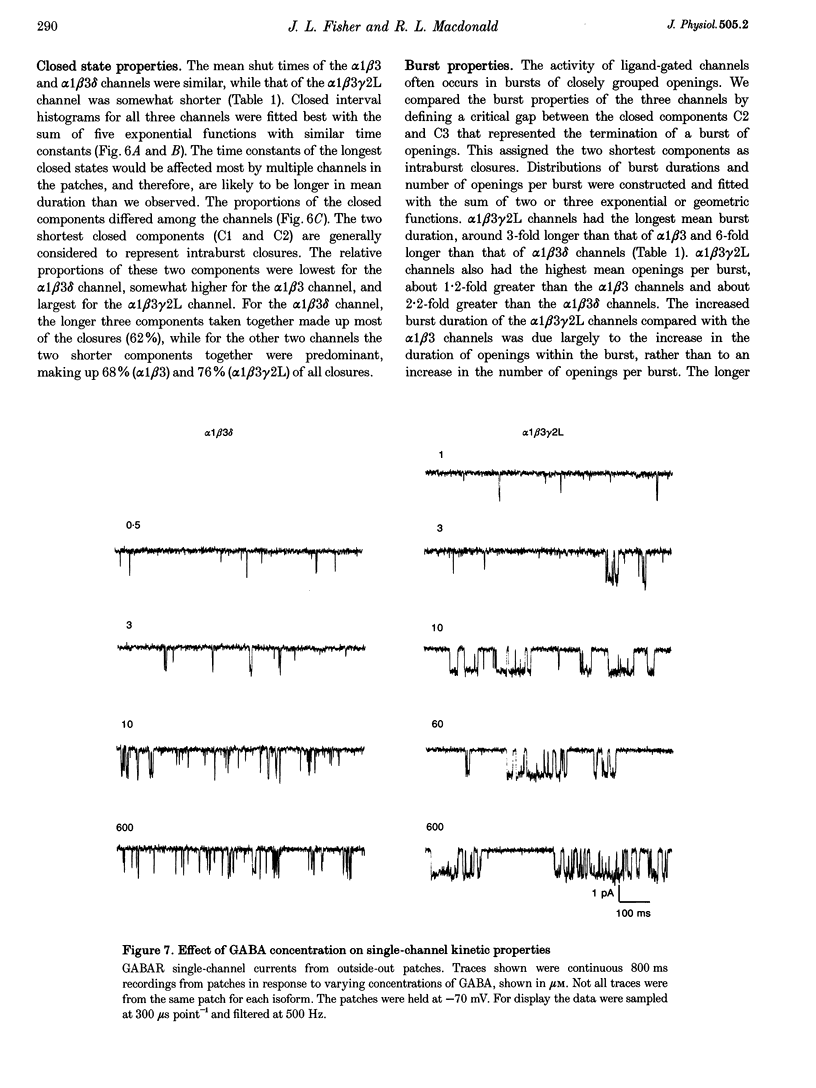
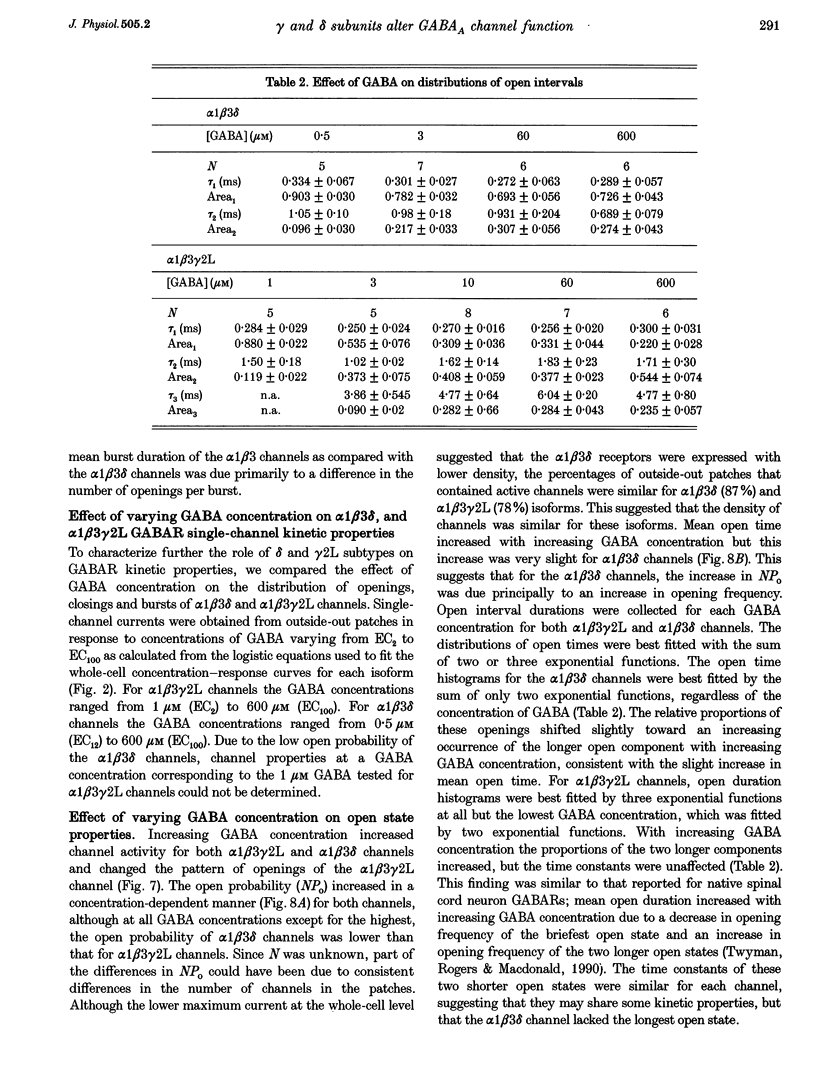
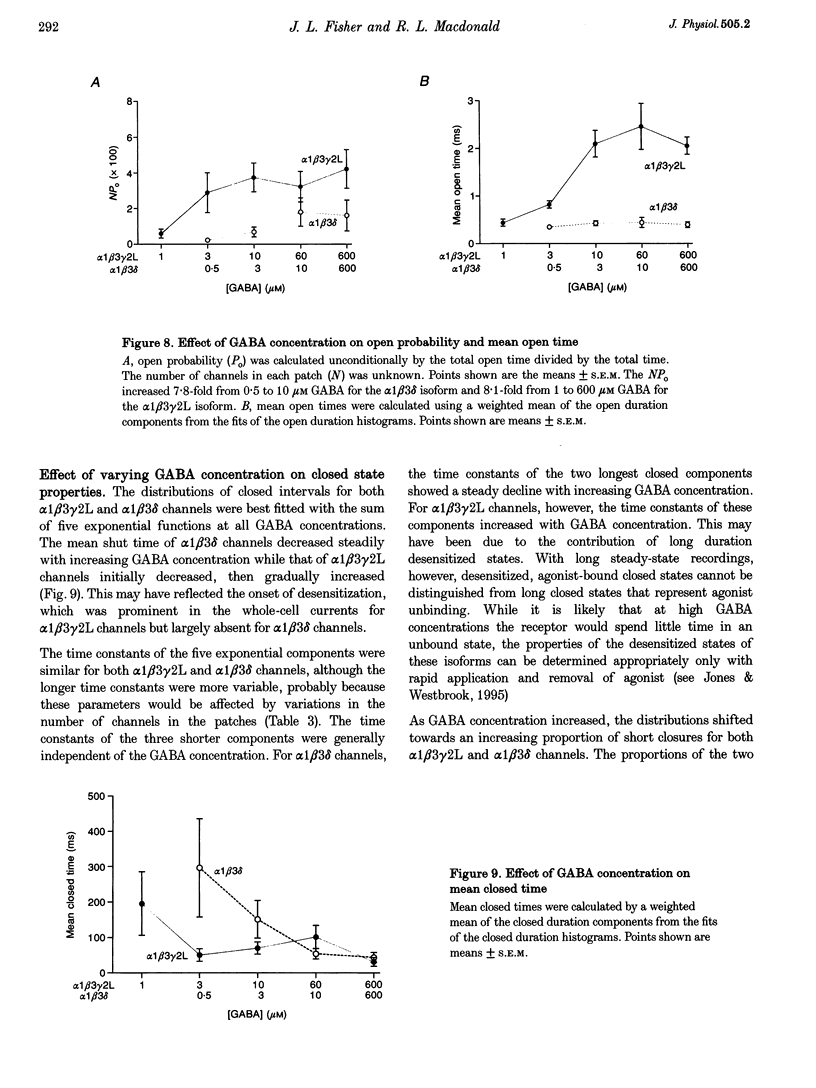
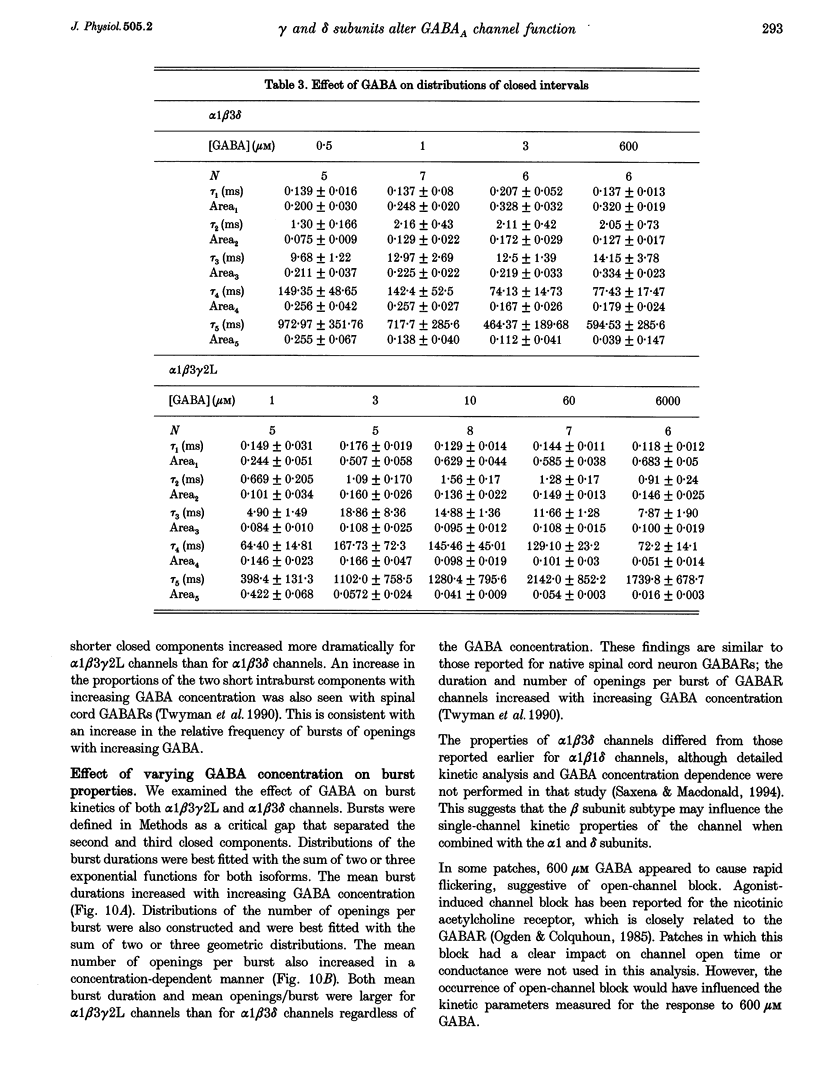



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelotti T. P., Macdonald R. L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits: alpha 1 beta 1 and alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2S subunits produce unique ion channels with dissimilar single-channel properties. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1429–1440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelotti T. P., Uhler M. D., Macdonald R. L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits: analysis of transient single-cell expression utilizing a fluorescent substrate/marker gene technique. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1418–1428. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01418.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backus K. H., Arigoni M., Drescher U., Scheurer L., Malherbe P., Möhler H., Benson J. A. Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor deduced from mutation-induced rectification. Neuroreport. 1993 Dec 13;5(3):285–288. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199312000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Perrot C., Feltz P., Poulter M. O. Recombinant GABAA receptor desensitization: the role of the gamma 2 subunit and its physiological significance. J Physiol. 1996 Nov 15;497(Pt 1):145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draguhn A., Verdorn T. A., Ewert M., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90337-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L. J., Jr, Macdonald R. L. Whole-cell and single-channel alpha1 beta1 gamma2S GABAA receptor currents elicited by a "multipuffer" drug application device. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Oct;432(6):1080–1090. doi: 10.1007/s004240050238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L. J., Jr, Sun F., Neelands T. R., Burgard E. C., Donnelly J. L., MacDonald R. L. Expression of functional GABAA receptors in transfected L929 cells isolated by immunomagnetic bead separation. Neuropharmacology. 1997 Jan;36(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(96)00150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R. Statistical methods for model discrimination. Applications to gating kinetics and permeation of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83331-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggenvik J. I., Collard M. W., Stofko R. E., Seasholtz A. F., Uhler M. D. Regulation of the human enkephalin promoter by two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):921–930. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. V., Westbrook G. L. Desensitized states prolong GABAA channel responses to brief agonist pulses. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishek B. J., Amato A., Connolly C. N., Moss S. J., Smart T. G. Proton sensitivity of the GABA(A) receptor is associated with the receptor subunit composition. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 15;492(Pt 2):431–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Wisden W. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. II. Olfactory bulb and cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of thirteen GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. III. Embryonic and postnatal development. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4151–4172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Kinetic states and modes of single large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:79–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Ion channel block by acetylcholine, carbachol and suberyldicholine at the frog neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):329–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter N. M., Angelotti T. P., Twyman R. E., MacDonald R. L. Kinetic properties of alpha 1 beta 1 gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor channels expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells: regulation by pentobarbital and picrotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;42(5):872–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena N. C., Macdonald R. L. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits: role of the delta subunit. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 2):7077–7086. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-07077.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena N. C., Macdonald R. L. Properties of putative cerebellar gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor isoforms. Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;49(3):567–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Killisch I., Sprengel R., Sontheimer H., Köhler M., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Two novel GABAA receptor subunits exist in distinct neuronal subpopulations. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Structure and pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):181–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Sine S. M. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83298-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Rogers C. J., Macdonald R. L. Intraburst kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:193–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Draguhn A., Ymer S., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional properties of recombinant rat GABAA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Laurie D. J., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1040–1062. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01040.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


