Abstract
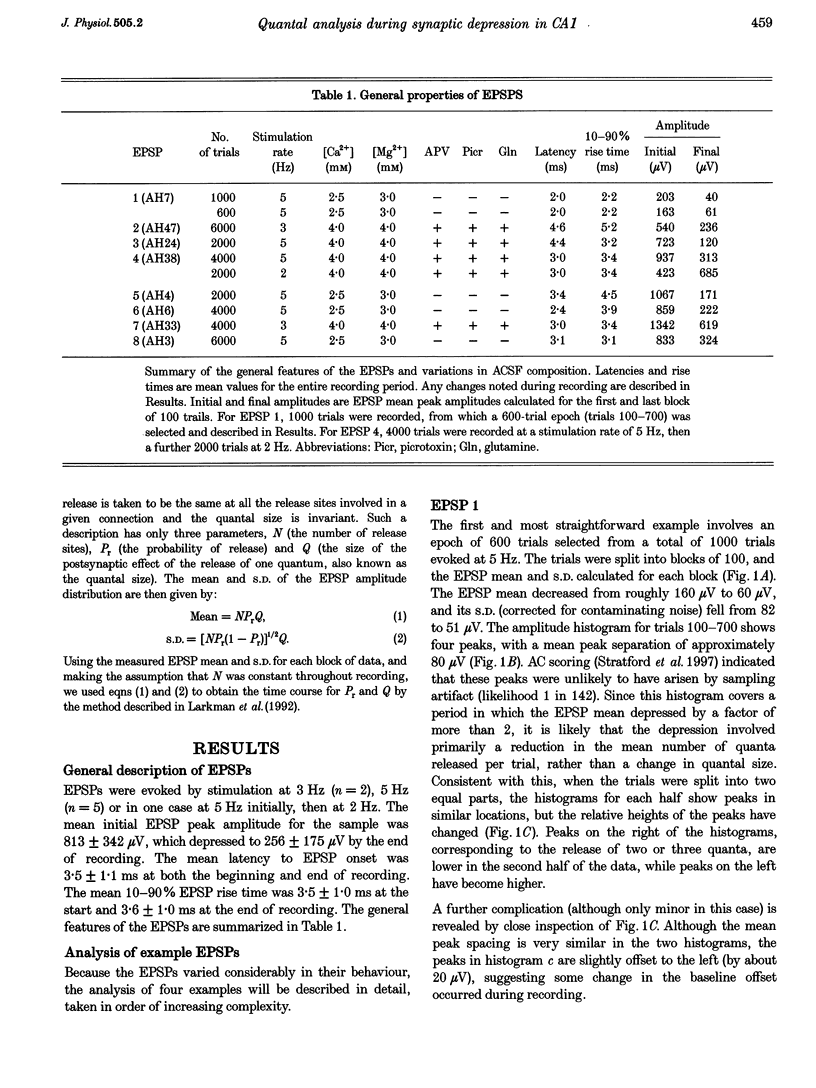
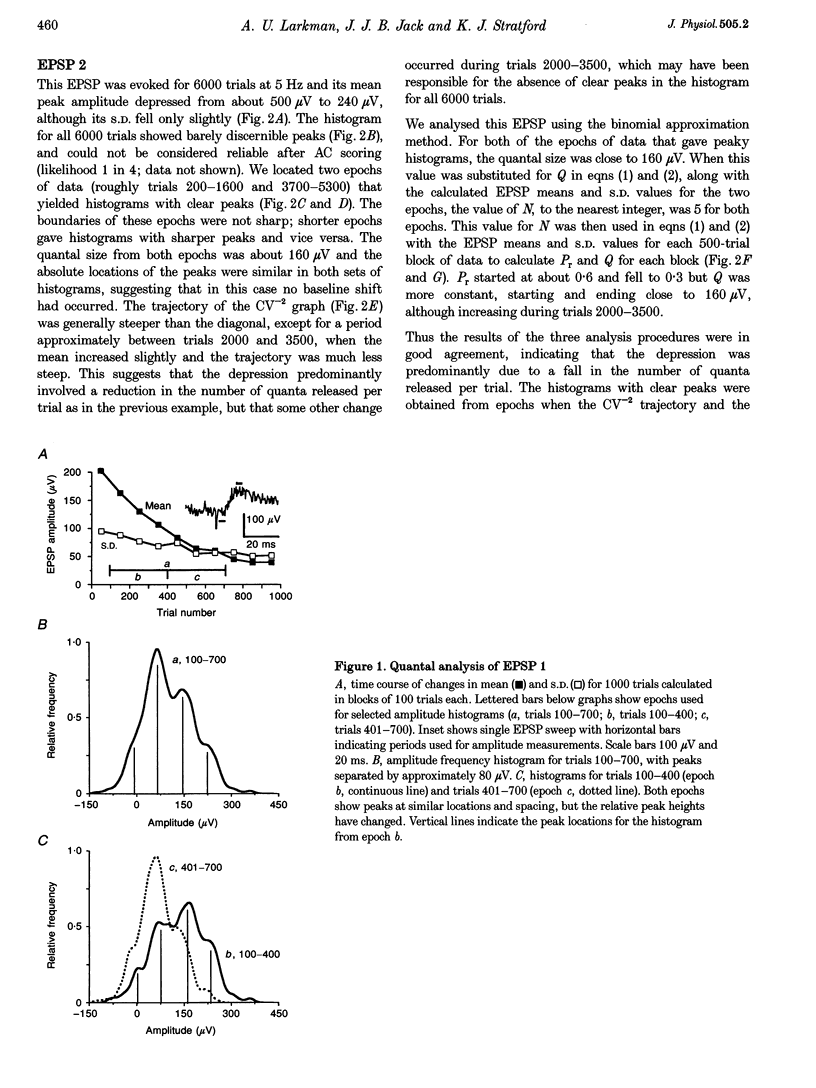
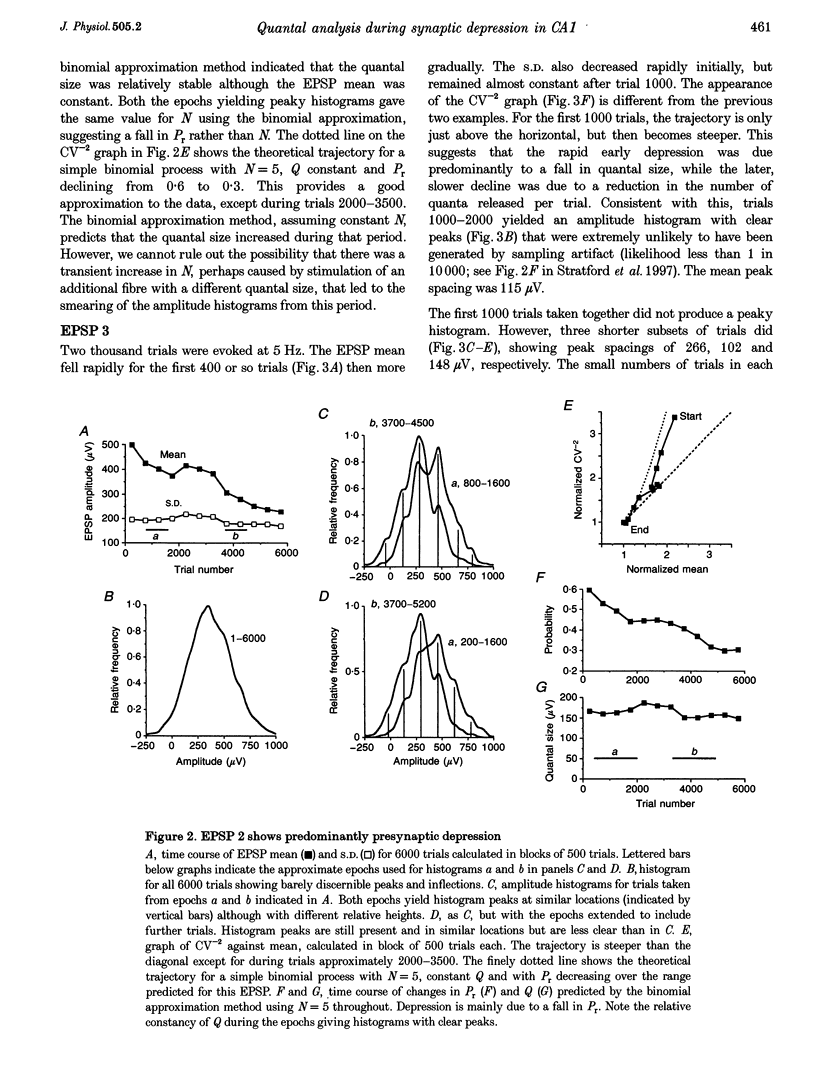
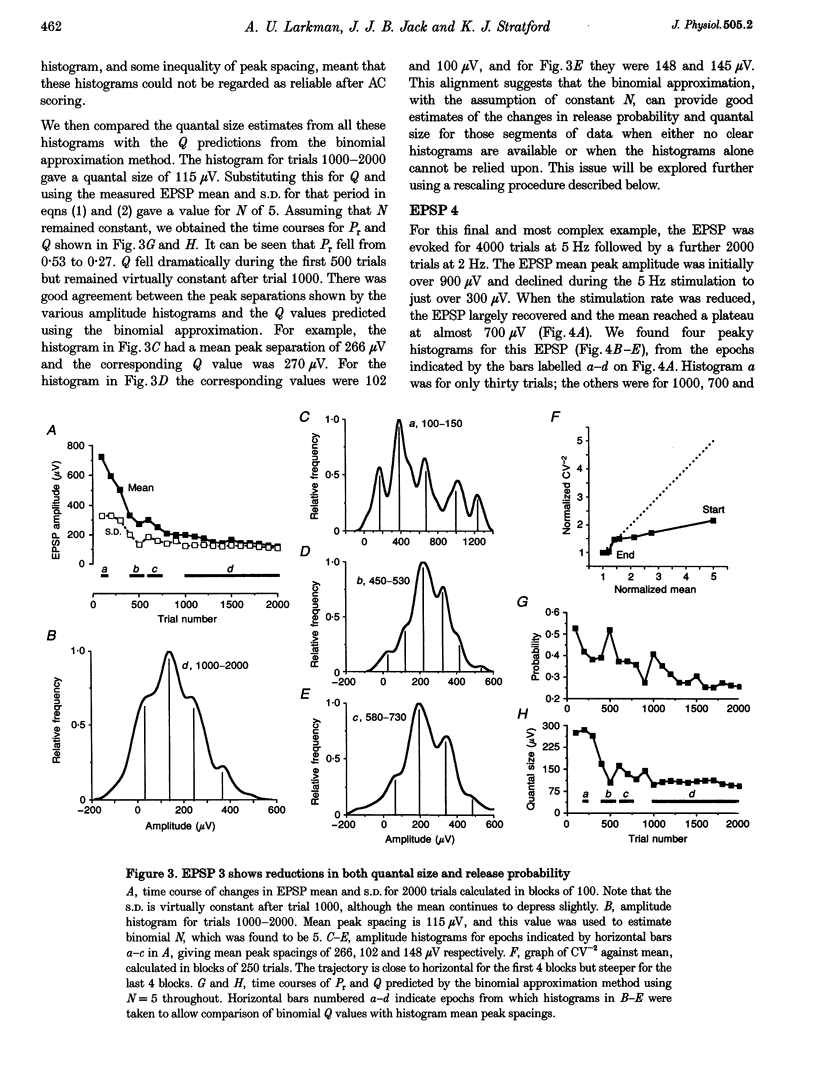
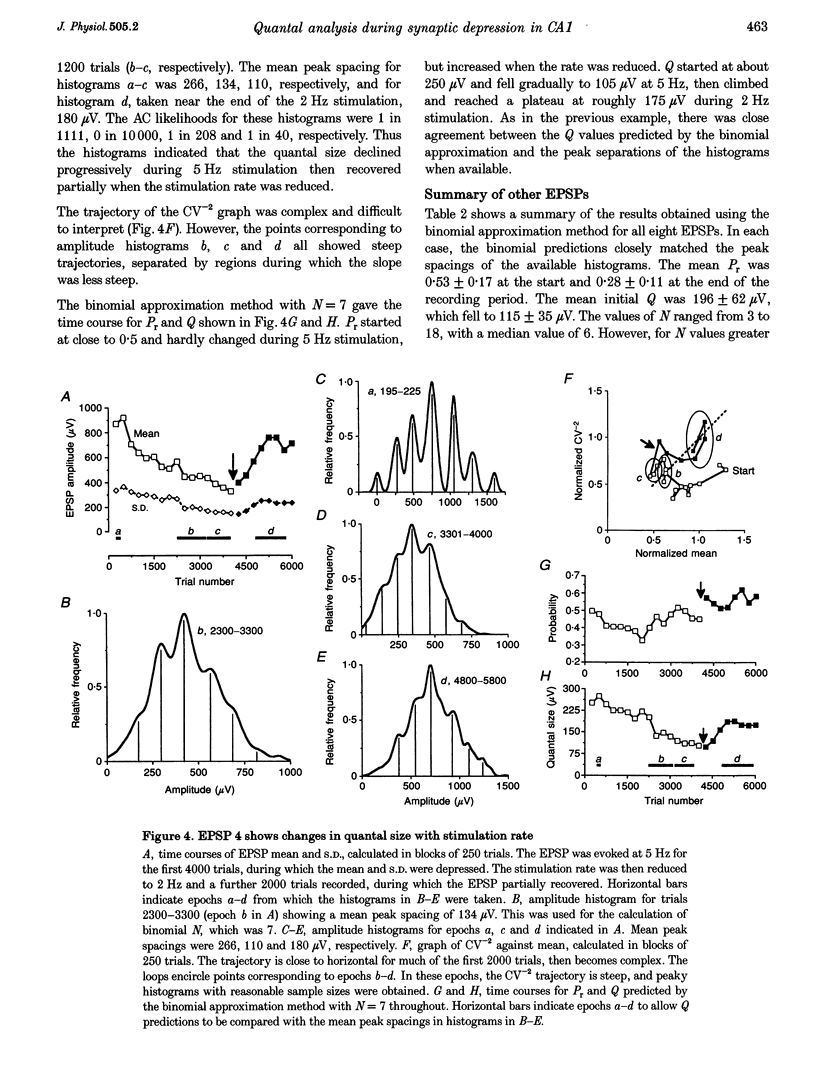
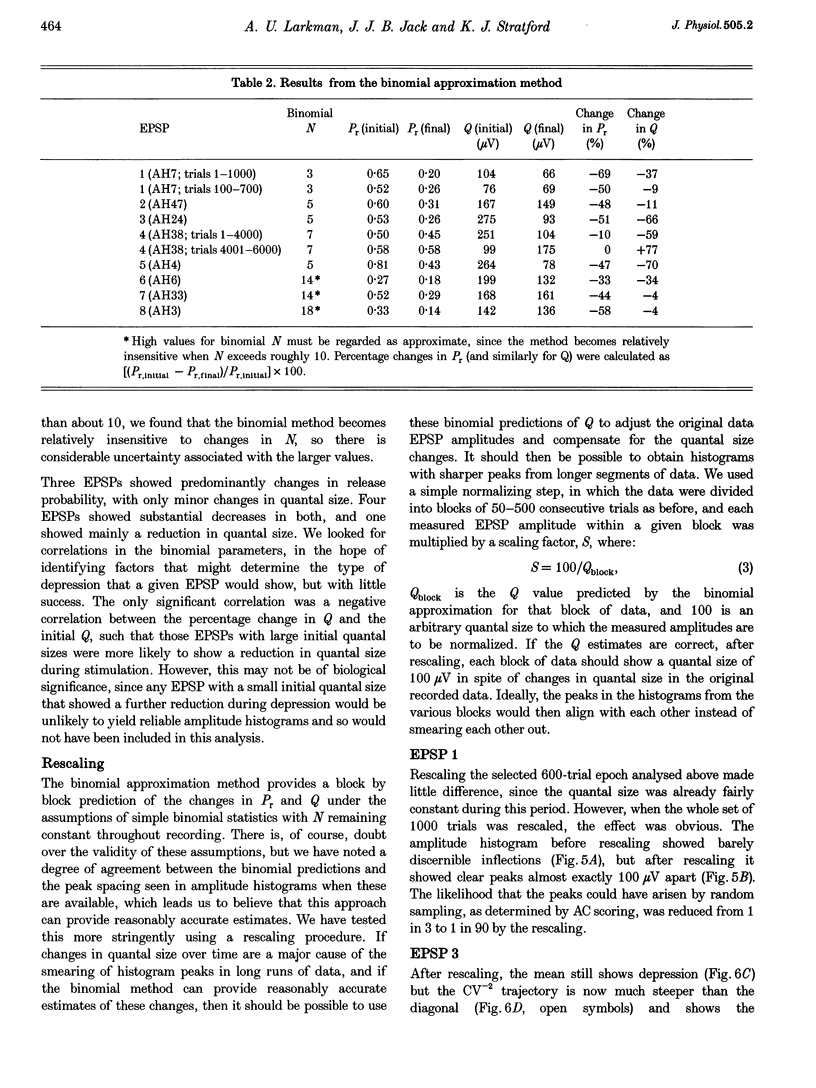
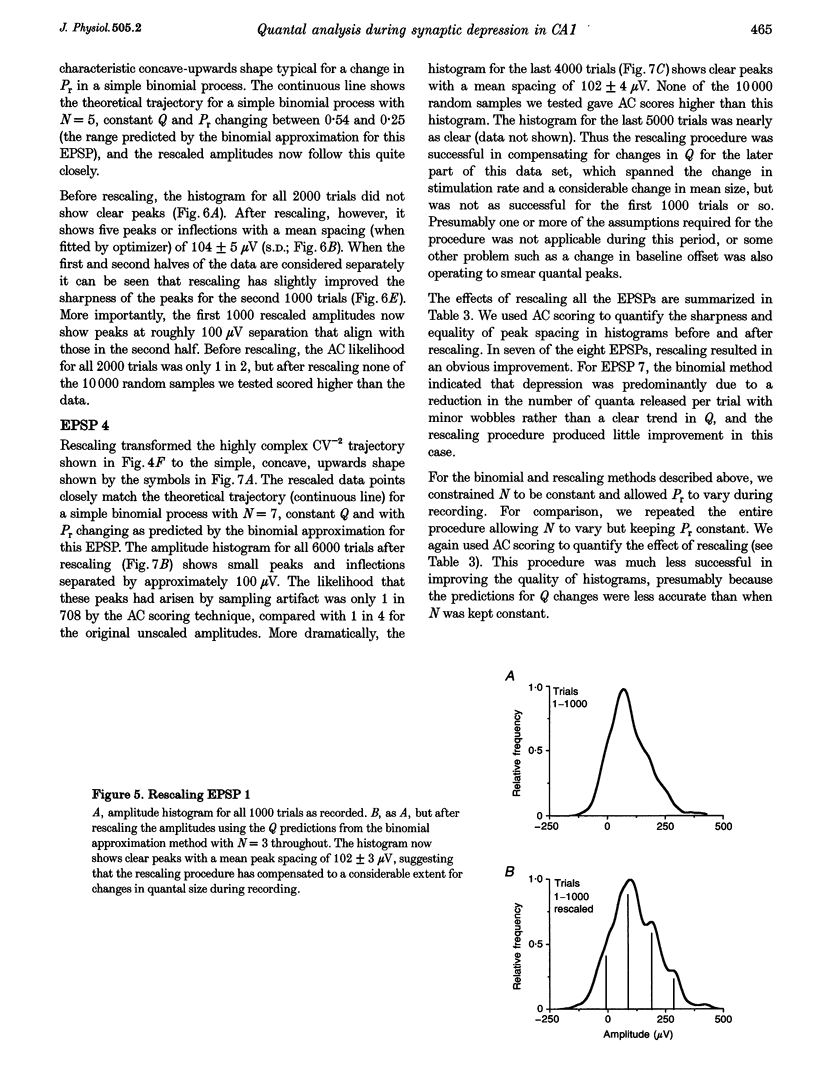
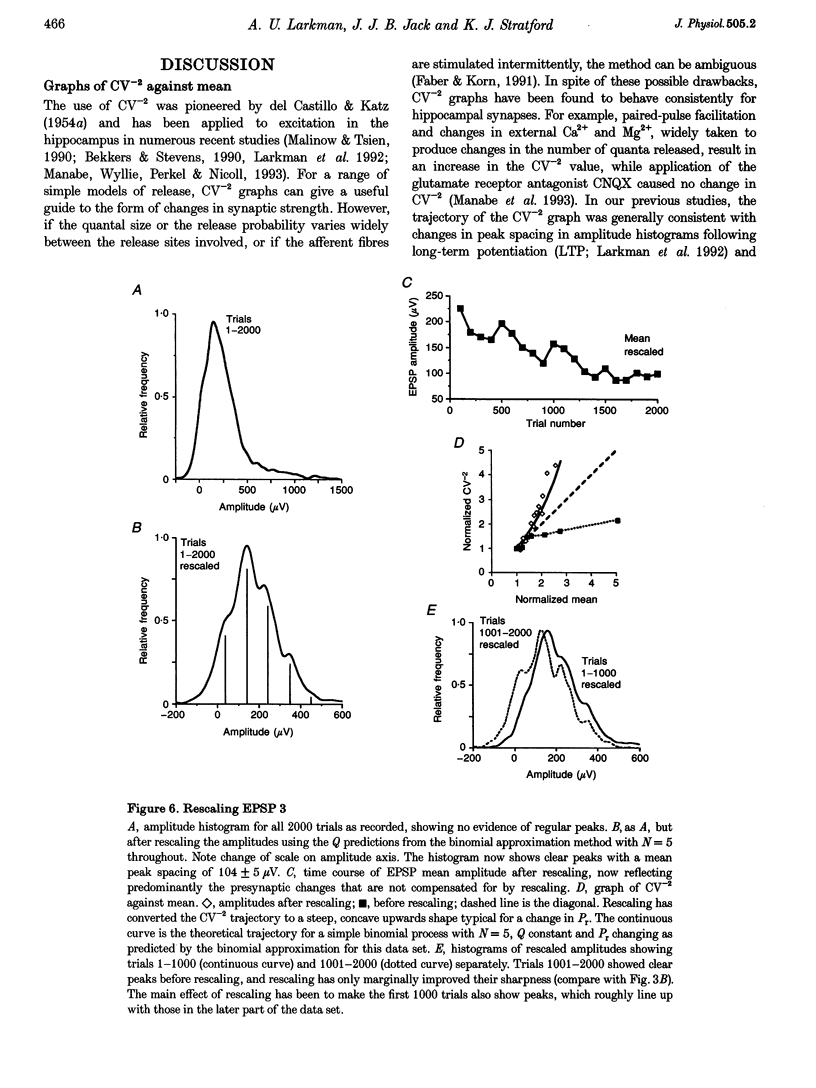
1. We have performed a detailed quantal analysis of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) evoked by minimal extracellular stimulation in the CA1 region of slices of adult rat hippocampus maintained in vitro. 2. EPSPs were evoked at 2-5 Hz, and the eight that were analysed all showed at least a 50% depression of mean peak amplitude during recording. 3. EPSP amplitude fluctuations were analysed by three methods: the use of amplitude frequency histograms with clear and reliable peaks where available, graphs of the EPSP (coefficient of variation)-2 against EPSP mean, and analysis of EPSP mean and standard deviation assuming simple binomial statistics with the number of release sites (N) kept constant but the quantal size (Q) and the release probability (Pr) allowed to vary over time. 4. The results of the three analysis procedures were in good agreement. Seven EPSPs showed a substantial reduction in the mean number of quanta released per trial, and in three cases this was the predominant mechanism of the depression. Five EPSPs showed a substantial decrease in Q. Values for N ranged between 3 and 18, with a median of 6; Pr ranged between 0.14 and 0.81 and Q between 66 and 275 microV. 5. We used the Q estimates from the binomial method to correct the recorded EPSP amplitudes for changes in quantal size over time. For seven out of the eight EPSPs, this rescaling procedure allowed histograms with clear peaks to be obtained from longer runs of data, or improved the sharpness of the peaks in histograms from all the recorded data. The improvement in peak sharpness was assessed using an autocorrelation-based method. The correction was much less successful if the Q estimates were obtained with a variant of the binomial method in which Pr was held constant and N was allowed to vary. 6. The only simple explanation for the success of the correction procedure is that changes in quantal size were a major factor in obscuring peaks in histograms based on large numbers of trials, and that the quantal size estimates from the binomial method with N held constant were reasonably accurate. 7. We conclude that transmission at these synapses was quantal with relatively low quantal variance, but repetitive stimulation often induced substantial changes in the quantal parameters that might prevent the success of conventional quantal analysis approaches.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. Presynaptic mechanism for long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):724–729. doi: 10.1038/346724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. Quantal analysis of EPSCs recorded from small numbers of synapses in hippocampal cultures. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Mar;73(3):1145–1156. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.3.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakov V. Y., Siegelbaum S. A. Regulation of hippocampal transmitter release during development and long-term potentiation. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1730–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.7569903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. Quantal synaptic transmission? Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):396–396. doi: 10.1038/353396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Jonas P., Sakmann B. Action of brief pulses of glutamate on AMPA/kainate receptors in patches from different neurones of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:261–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Korn H. Applicability of the coefficient of variation method for analyzing synaptic plasticity. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1288–1294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82162-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannay T., Larkman A., Stratford K., Jack J. A common rule governs the synaptic locus of both short-term and long-term potentiation. Curr Biol. 1993 Dec 1;3(12):832–841. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90217-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessler N. A., Shirke A. M., Malinow R. The probability of transmitter release at a mammalian central synapse. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):569–572. doi: 10.1038/366569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J., Wong K. The components of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:65–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Mallet A., Triller A., Faber D. S. Transmission at a central inhibitory synapse. II. Quantal description of release, with a physical correlate for binomial n. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Sep;48(3):679–707. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann D. M. Applications of the expectation-maximization algorithm to quantal analysis of postsynaptic potentials. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann D. M., Nicoll R. A. Long-term potentiation is associated with increases in quantal content and quantal amplitude. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):240–244. doi: 10.1038/357240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann D. M. Quantal variability of excitatory transmission in the hippocampus: implications for the opening probability of fast glutamate-gated channels. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Jul 22;253(1336):107–116. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman A. U., Jack J. J., Stratford K. J. Assessment of the reliability or amplitude histograms from excitatory synapses in rat hippocampal CA1 in vitro. J Physiol. 1997 Dec 1;505(Pt 2):443–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.443bb.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman A., Hannay T., Stratford K., Jack J. Presynaptic release probability influences the locus of long-term potentiation. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):70–73. doi: 10.1038/360070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman A., Stratford K., Jack J. Quantal analysis of excitatory synaptic action and depression in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):344–347. doi: 10.1038/350344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D., Jones A., Malinow R. Direct measurement of quantal changes underlying long-term potentiation in CA1 hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1089–1097. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90068-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Tsien R. W. Properties of synaptic transmission at single hippocampal synaptic boutons. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):404–408. doi: 10.1038/375404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupica C. R., Proctor W. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Presynaptic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by adenosine in rat hippocampus: analysis of unitary EPSP variance measured by whole-cell recording. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3753–3764. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03753.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Tsien R. W. Presynaptic enhancement shown by whole-cell recordings of long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):177–180. doi: 10.1038/346177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe T., Wyllie D. J., Perkel D. J., Nicoll R. A. Modulation of synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation: effects on paired pulse facilitation and EPSC variance in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Oct;70(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.4.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raastad Morten, Storm Johan F., Andersen Per. Putative Single Quantum and Single Fibre Excitatory Postsynaptic Currents Show Similar Amplitude Range and Variability in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Eur J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;4(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. Quantal analysis of synaptic potentials in neurons of the central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):165–198. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L. Nonuniform probability of glutamate release at a hippocampal synapse. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):754–757. doi: 10.1126/science.7901909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayer R. J., Redman S. J., Andersen P. Amplitude fluctuations in small EPSPs recorded from CA1 pyramidal cells in the guinea pig hippocampal slice. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):840–850. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00840.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorra K. E., Harris K. M. Occurrence and three-dimensional structure of multiple synapses between individual radiatum axons and their target pyramidal cells in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3736–3748. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03736.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F., Wang Y. Facilitation and depression at single central synapses. Neuron. 1995 Apr;14(4):795–802. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford K. J., Jack J. J., Larkman A. U. Calibration of an autocorrelation-based method for determining amplitude histogram reliability and quantal size. J Physiol. 1997 Dec 1;505(Pt 2):425–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.425bb.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker C., Field A. C., Redman S. J. Changes in quantal parameters of EPSCs in rat CA1 neurones in vitro after the induction of long-term potentiation. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 15;490(Pt 2):443–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker C., Field A. C., Redman S. J. Statistical analysis of amplitude fluctuations in EPSCs evoked in rat CA1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 15;490(Pt 2):419–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronin L. L., Kuhnt U., Hess G., Gusev A. G., Roschin V. Quantal parameters of "minimal" excitatory postsynaptic potentials in guinea pig hippocampal slices: binomial approach. Exp Brain Res. 1992;89(2):248–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00228242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley B., Edwards F. R., Tracey D. J. Nonuniform release probabilities underlie quantal synaptic transmission at a mammalian excitatory central synapse. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Sep;60(3):889–908. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.3.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Kelly P. T. Regulation of synaptic facilitation by postsynaptic Ca2+/CaM pathways in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1996 Jul;76(1):276–286. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.1.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Mennerick S., Que J. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by low concentrations of glutamate in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 1996 Jul 15;494(Pt 2):465–477. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:13–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


