Abstract
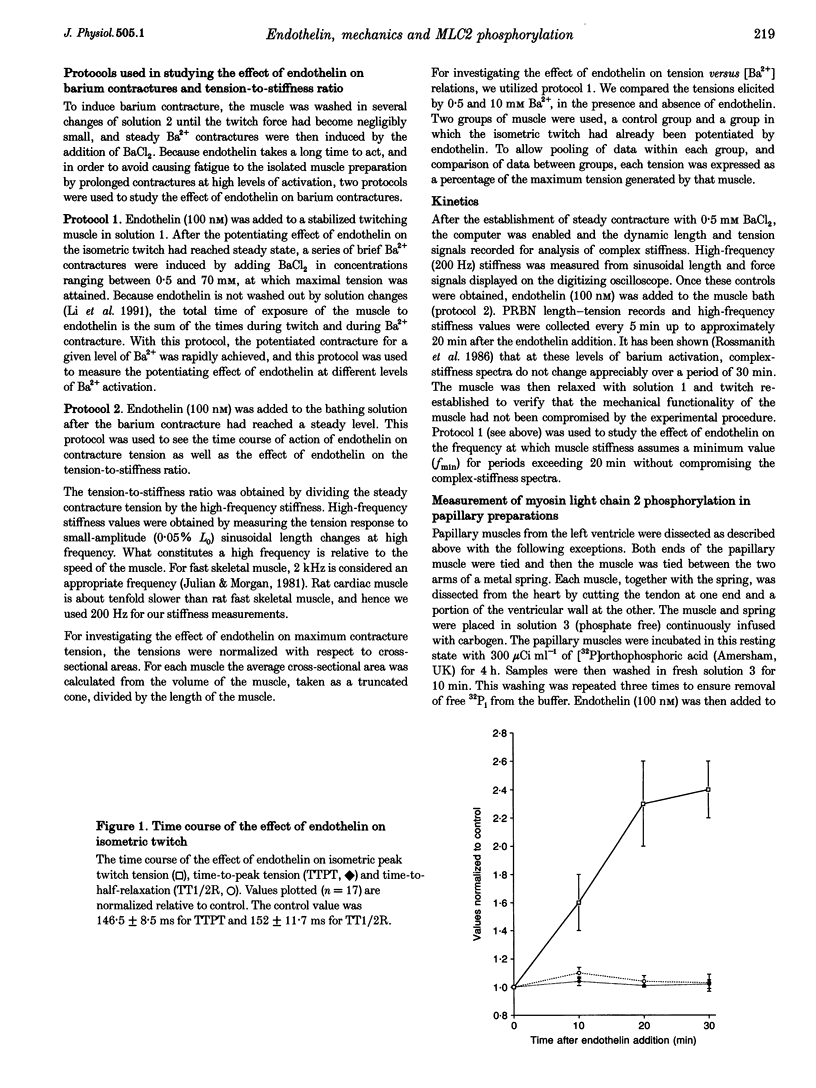
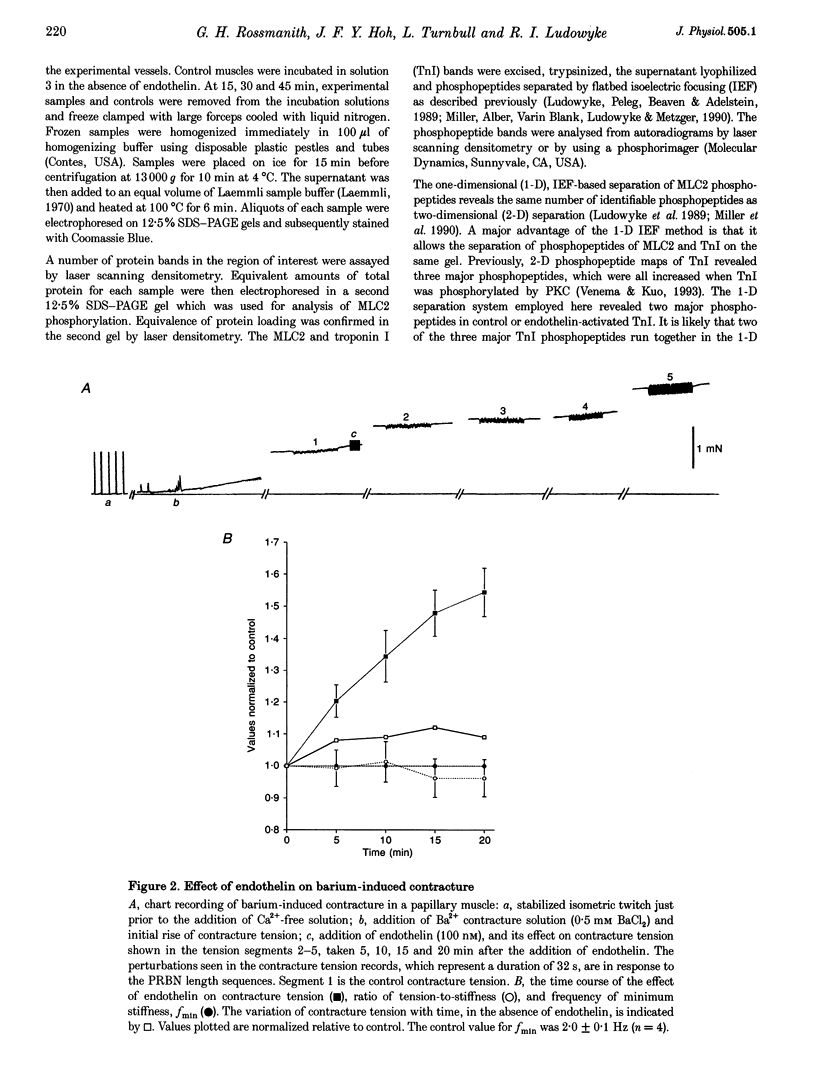
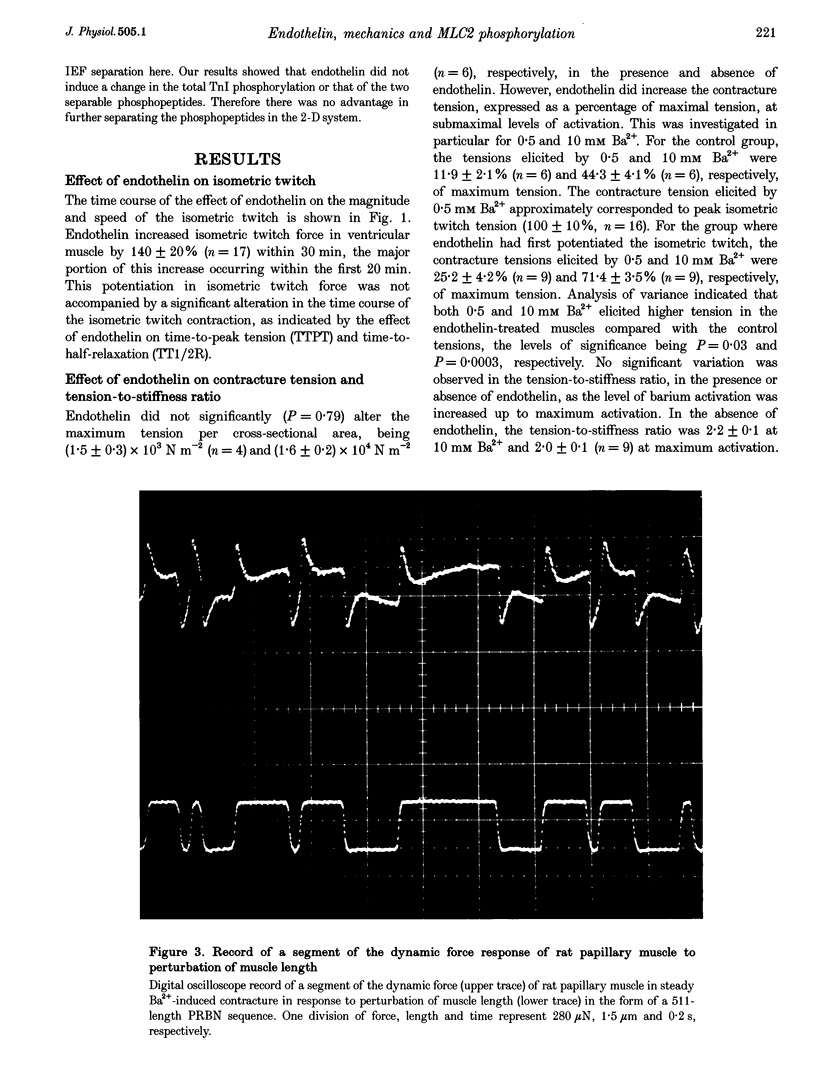
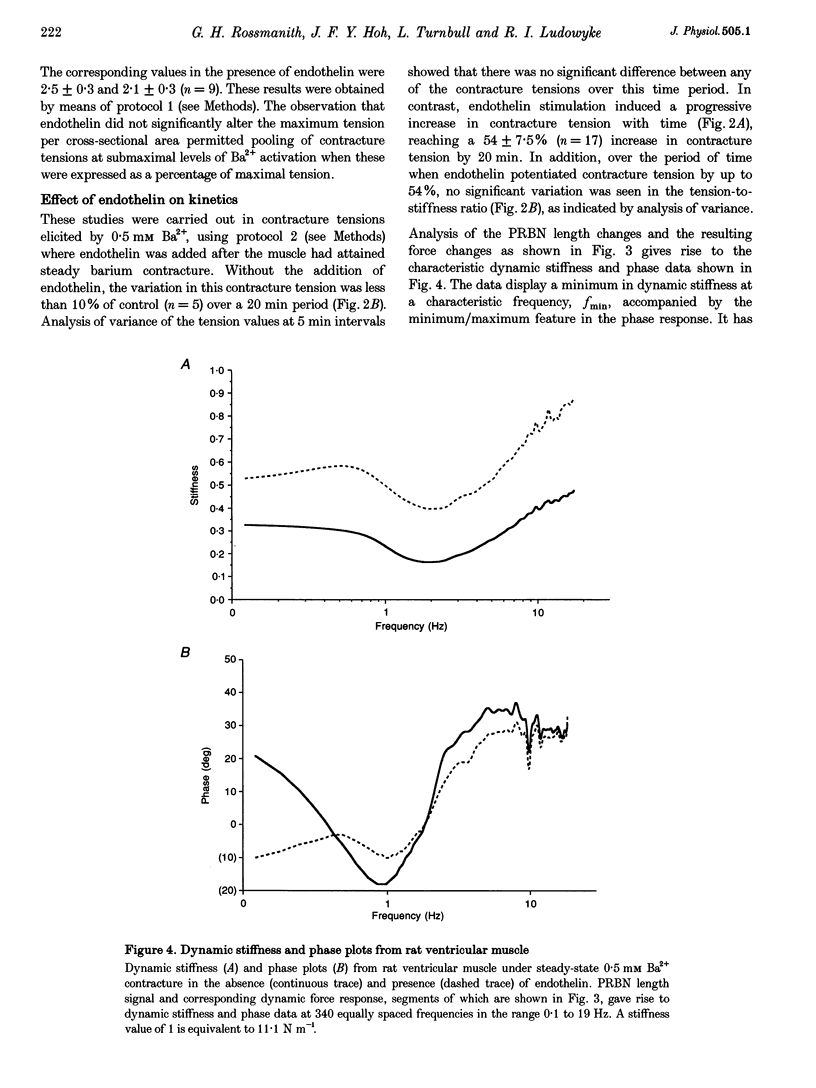
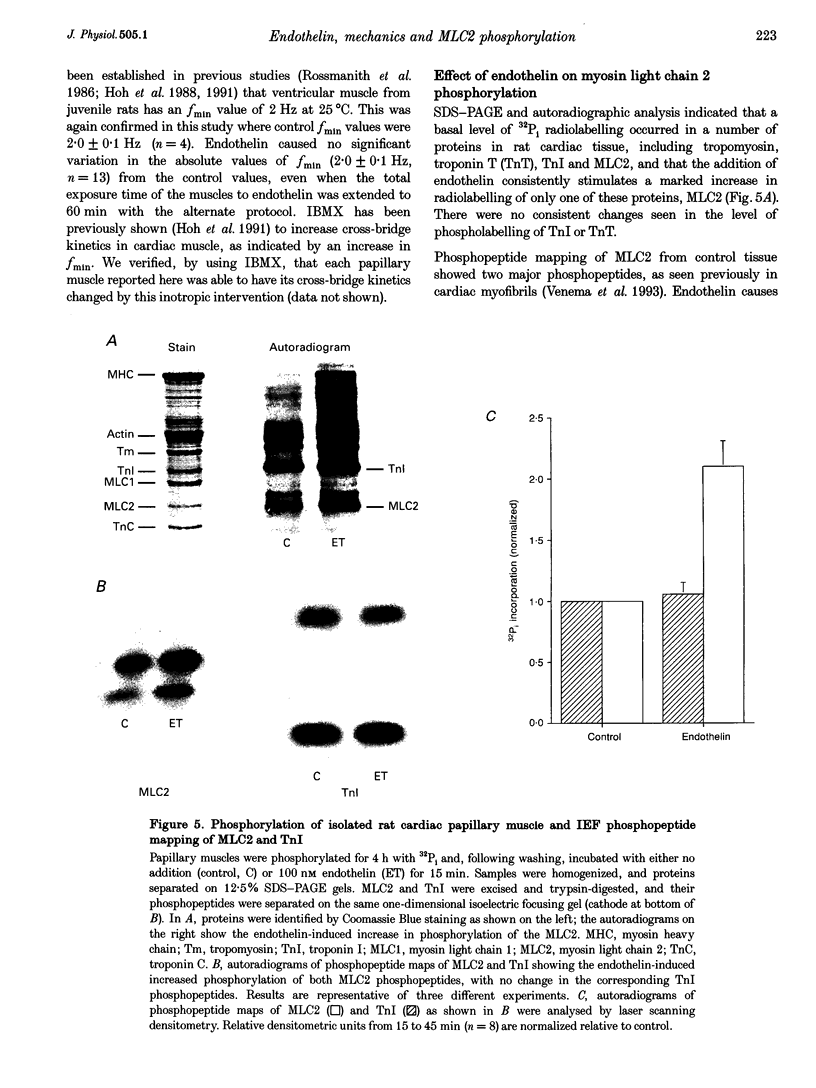
1. The molecular mechanism of inotropic action of endothelin was investigated in rat ventricular muscle by studying its effects on characteristics of isometric twitch, barium-induced steady contracture and the level of incorporation of 32Pi into myosin light chain 2. 2. Exposure of rat papillary muscle to endothelin caused an increase in isometric twitch force but did not alter the twitch-time parameters. 3. Endothelin did not significantly change the maximum contracture tension but did cause an increase in contracture tension at submaximal levels of activation, without changes in the tension-to-stiffness ratio and kinetics of attached cross-bridges. Kinetics of attached cross-bridges were deduced during steady contracture from complex-stiffness values, and in particular from the frequency at which muscle stiffness assumes a minimum value, fmin. Endothelin did not alter fmin. 4. Endothelin caused an increase in the level of incorporation of 32Pi into myosin light chain 2 without a concurrent change in the level of incorporation of 32Pi into troponin I. 5. We conclude that the inotropic action of endothelin is not due to an increase in the kinetics of attached cross-bridges, nor due to a change in the force per unit cross-bridge, but may result from an increased divalent cation sensitivity caused by elevated myosin light chain 2 phosphorylation, resembling post-tetanic potentiation in fast skeletal muscle fibres.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R. Calcium transients in aequorin-injected frog cardiac muscle. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):509–513. doi: 10.1038/273509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyevitch M. A., Parker P. J., Sugden P. H. Characterization of protein kinase C isotype expression in adult rat heart. Protein kinase C-epsilon is a major isotype present, and it is activated by phorbol esters, epinephrine, and endothelin. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):757–767. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Alpha 1-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):532–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement O., Puceat M., Walsh M. P., Vassort G. Protein kinase C enhances myosin light-chain kinase effects on force development and ATPase activity in rat single skinned cardiac cells. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):311–317. doi: 10.1042/bj2850311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R., Hoh J. F. The after-effects of repetitive stimulation on the isometric twitch contraction of rat fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):461–477. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damron D. S., Darvish A., Murphy L., Sweet W., Moravec C. S., Bond M. Arachidonic acid-dependent phosphorylation of troponin I and myosin light chain 2 in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1995 Jun;76(6):1011–1019. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.6.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gando S., Nishihira J., Hattori Y., Kanno M. Endothelin-1 does not phosphorylate phospholamban and troponin I in intact beating rat hearts. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Tsuda T., Alexander R. W. Endothelin stimulates diacylglycerol accumulation and activates protein kinase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8237–8240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring B. P., England P. J. The turnover of phosphate bound to myosin light chain-2 in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):205–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2400205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F. Muscle fiber types and function. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;4(6):801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., Rossmanith G. H., Hamilton A. M. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic AMP, ouabain, and xanthine derivatives on crossbridge kinetics in rat cardiac muscle. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):702–713. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., Rossmanith G. H., Kwan L. J., Hamilton A. M. Adrenaline increases the rate of cycling of crossbridges in rat cardiac muscle as measured by pseudo-random binary noise-modulated perturbation analysis. Circ Res. 1988 Mar;62(3):452–461. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Positive inotropic action of novel vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin on guinea pig atria. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H970–H973. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura K., Hori M., Watanabe Y., Kitabatake A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Yoshida H., Kamada T. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation increases intracellular pH and Ca2+ in cardiomyocytes through Na+/H+ and Na+/Ca2+ exchange. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 4;186(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Morgan D. L. Variation of muscle stiffness with tension during tension transients and constant velocity shortening in the frog. J Physiol. 1981;319:193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. A., Eid H., Krämer B. K., O'Neill M., Liang B. T., Reers M., Smith T. W. Endothelin enhances the contractile responsiveness of adult rat ventricular myocytes to calcium by a pertussis toxin-sensitive pathway. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1164–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI114822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer B. K., Smith T. W., Kelly R. A. Endothelin and increased contractility in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Role of intracellular alkalosis induced by activation of the protein kinase C-dependent Na(+)-H+ exchanger. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):269–279. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li K., Stewart D. J., Rouleau J. L. Myocardial contractile actions of endothelin-1 in rat and rabbit papillary muscles. Role of endocardial endothelium. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):301–312. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludowyke R. I., Peleg I., Beaven M. A., Adelstein R. S. Antigen-induced secretion of histamine and the phosphorylation of myosin by protein kinase C in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12492–12501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayoux E., Coutry N., Lechêne P., Marotte F., Hoffmann C., Ventura-Clapier R. Effects of acidosis and alkalosis on mechanical properties of hypertrophied rat heart fiber bundles. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):H2051–H2060. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.5.H2051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan G., Weisberg A., Rose D., Winegrad S. Endothelial cell storage and release of endothelin as a cardioregulatory mechanism. Circ Res. 1994 Jul;75(1):85–96. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan G., Weisberg A., Winegrad S. Effect of endothelin-1 on actomyosin ATPase activity. Implications for the efficiency of contraction. Circ Res. 1996 Jun;78(6):1044–1050. doi: 10.1161/01.res.78.6.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Variations in cross-bridge attachment rate and tension with phosphorylation of myosin in mammalian skinned skeletal muscle fibers. Implications for twitch potentiation in intact muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):855–883. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Alber G., Varin-Blank N., Ludowyke R., Metzger H. Transmembrane signaling in P815 mastocytoma cells by transfected IgE receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12444–12453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P., O'Reilly G., Sharkey A., Kuc R. E., Harding D. P., Plumpton C., Gresham G. A., Davenport A. P. Characterization and localization of endothelin receptor subtypes in the human atrioventricular conducting system and myocardium. Circ Res. 1993 Mar;72(3):526–538. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.3.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morano I., Bächle-Stolz C., Katus A., Rüegg J. C. Increased calcium sensitivity of chemically skinned human atria by myosin light chain kinase. Basic Res Cardiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;83(4):350–359. doi: 10.1007/BF02005820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Z., Wang J., Perreault C. L., Meuse A. J., Grossman W., Morgan J. P. Effects of endothelin on intracellular Ca2+ and contractility in single ventricular myocytes from the ferret and human. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 22;214(2-3):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90134-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmanith G. H., Hoh J. F., Kirman A., Kwan L. J. Influence of V1 and V3 isomyosins on the mechanical behaviour of rat papillary muscle as studied by pseudo-random binary noise modulated length perturbations. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Aug;7(4):307–319. doi: 10.1007/BF01753651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmanith G. H. Tension responses of muscle to n-step pseudo-random length reversals: a frequency domain representation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Aug;7(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF01753650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybin V. O., Steinberg S. F. Protein kinase C isoform expression and regulation in the developing rat heart. Circ Res. 1994 Feb;74(2):299–309. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki Y., Kato C., Totsuka T., Yanagisawa K. Mechanical properties and ATPase activity in glycerinated cardiac muscle of hyperthyroid rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(6):578–583. doi: 10.1007/BF00581159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. J., Stull J. T. Quantitation of myosin light chain phosphorylation in small tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6137–6144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Bowman B. F., Stull J. T. Myosin light chain phosphorylation in vertebrate striated muscle: regulation and function. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1085–C1095. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema R. C., Kuo J. F. Protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of troponin I and C-protein in isolated myocardial cells is associated with inhibition of myofibrillar actomyosin MgATPase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2705–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema R. C., Raynor R. L., Noland T. A., Jr, Kuo J. F. Role of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of cardiac myosin light chain 2. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):401–406. doi: 10.1042/bj2940401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. X., Paik G., Morgan J. P. Endothelin 1 enhances myofilament Ca2+ responsiveness in aequorin-loaded ferret myocardium. Circ Res. 1991 Sep;69(3):582–589. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.3.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Hess P. Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Effects of cardiotonic steroids on the intracellular [Ca2+] transient, membrane potential, and contraction. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):395–415. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]