Abstract
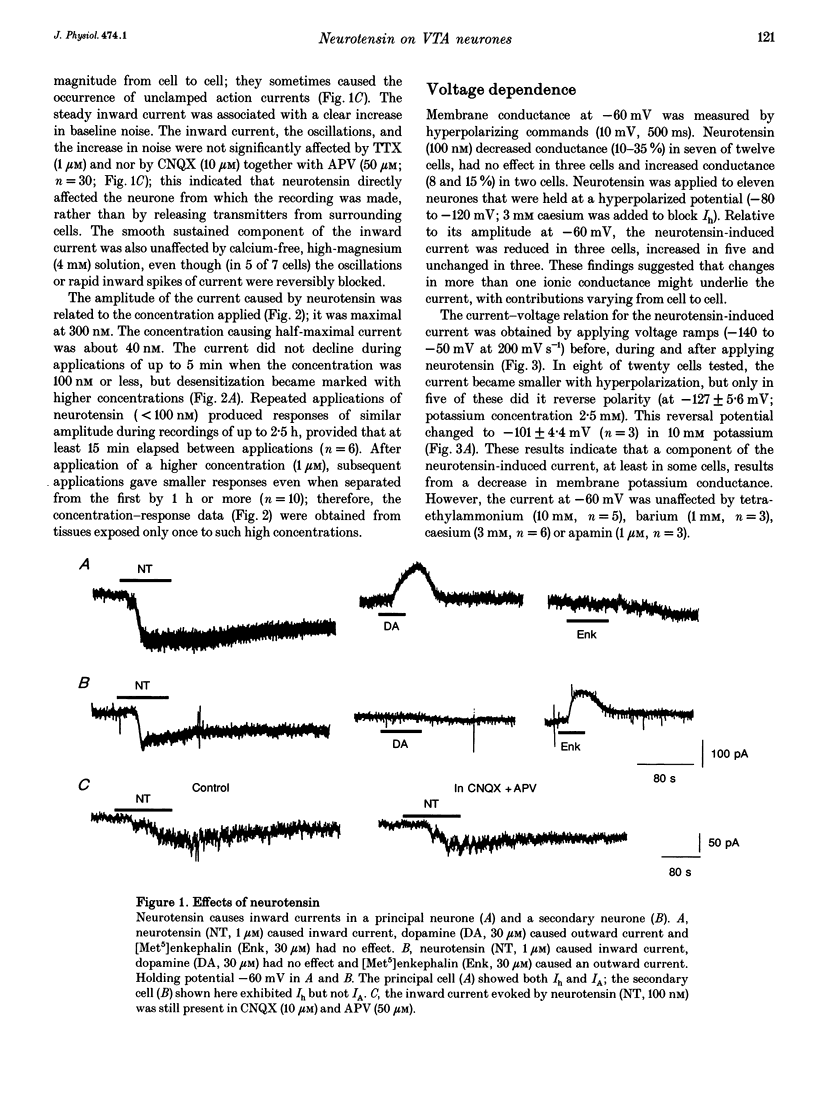
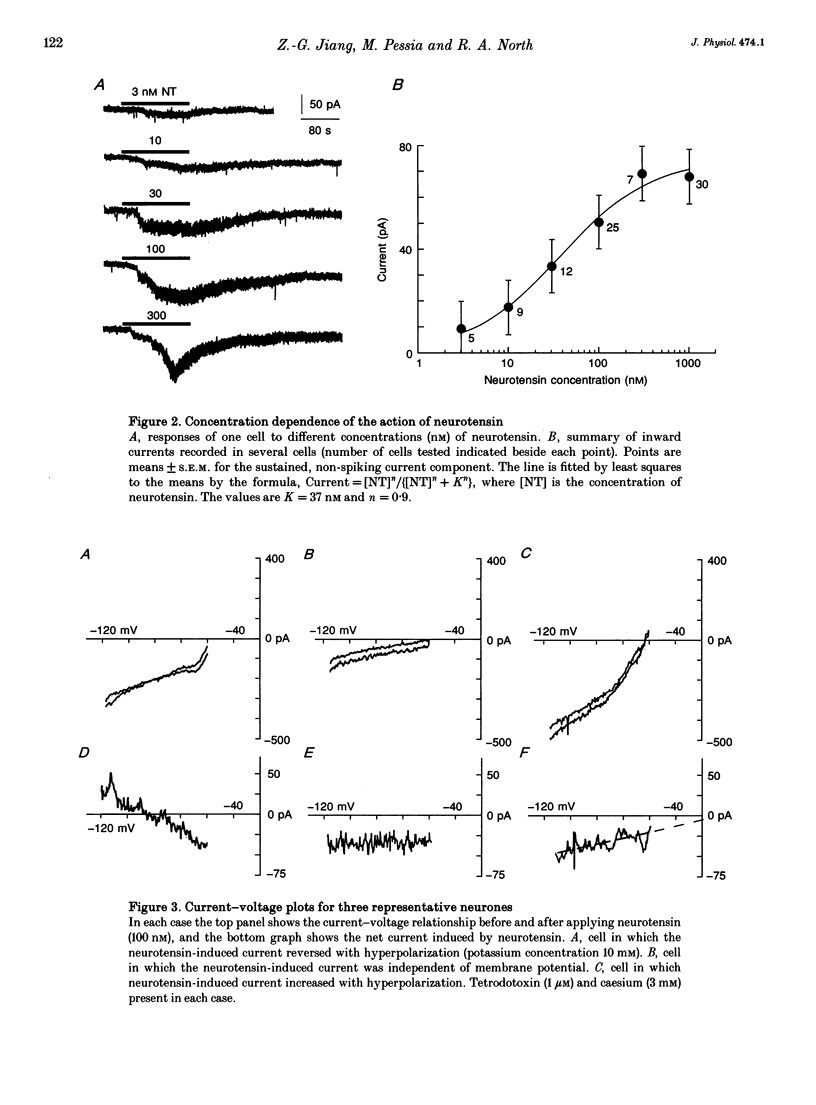
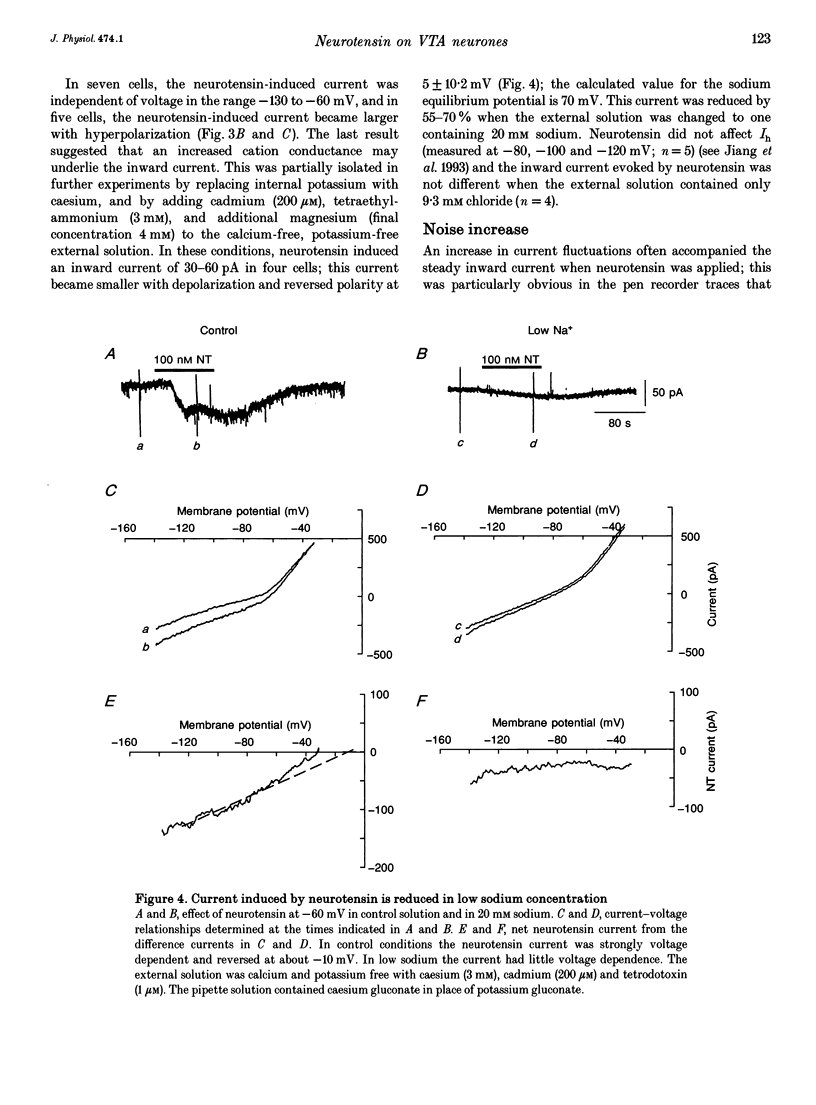
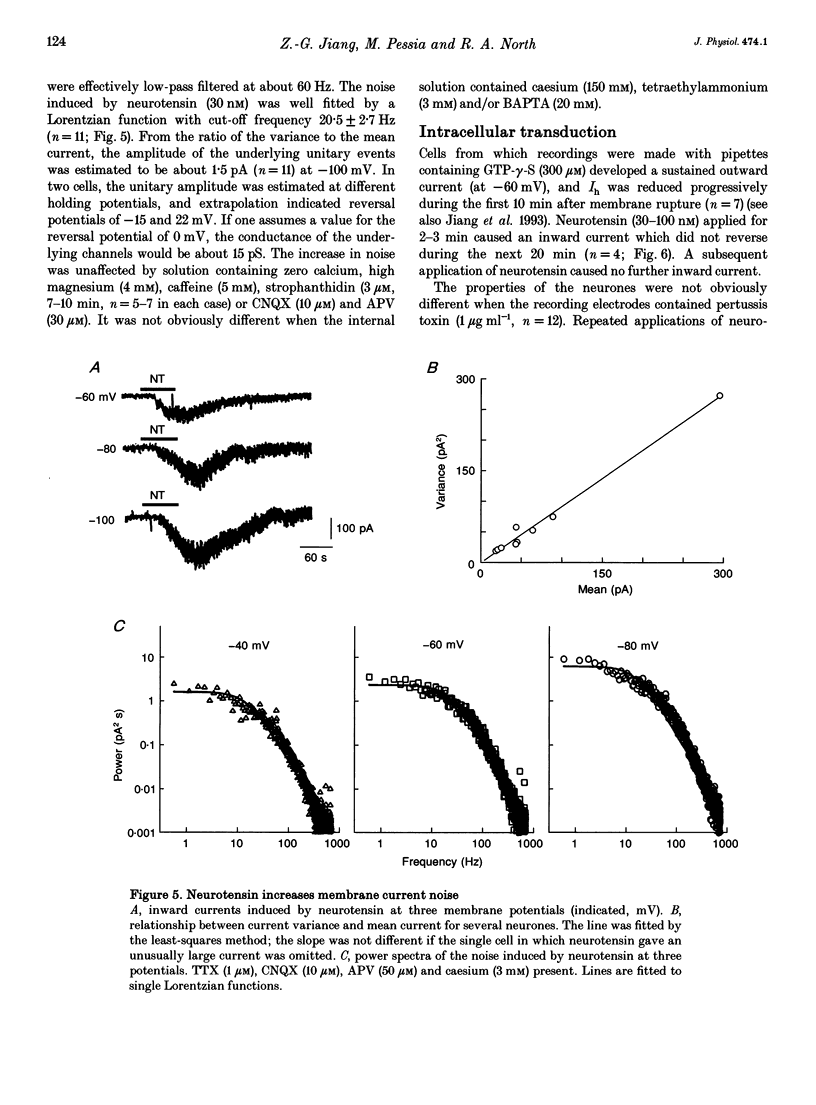
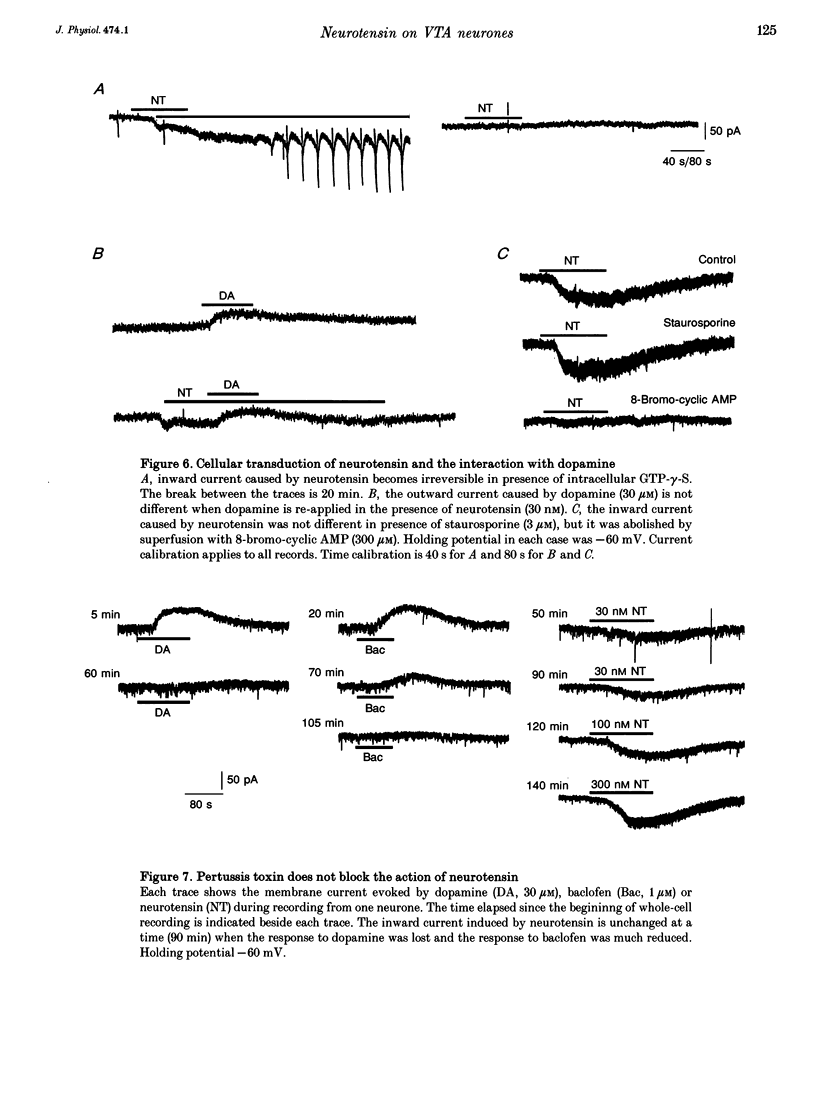
1. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from ventral tegmental area neurones in rat midbrain slices in vitro. In principal cells, which are presumed to contain dopamine, neurotensin (< or = 1 microM) caused an inward current at -60 mV in thirty of forty-seven neurones and had no effect on the remainder. In secondary neurones, neurotensin caused an inward current in twelve of thirty-three cells. 2. The inward current evoked by neurotensin reached a maximum amplitude of about 80 pA, and declined over several minutes when the application was discontinued. The current was most commonly accompanied by a decrease in membrane conductance and reversed polarity at a strongly hyperpolarized potential; this reversal potential was less negative in a higher extracellular potassium concentration. Neurotensin also caused an inward current even in potassium-free internal and external solutions; this current was accompanied by a conductance increase, reversed close to 0 mV and was inhibited by reduction of the extracellular sodium concentration (from 150 to 20 mM). 3. The inward current was associated with a large increase in noise; this persisted in calcium-free solutions but was inhibited by low sodium concentration. The increase in noise was more prominent at hyperpolarized potentials. The amplitude of the unitary current underlying the increase in noise was estimated from the ratio of the variance to the mean as about 1.5 pA at -100 mV. 4. When the recording was made with an electrode containing guanosine 5'-thio-triphosphate, the steady inward current evoked by neurotensin did not reverse when the application was discontinued. When the recording electrode contained pertussis toxin, the action of neurotensin was not different although outward currents evoked by dopamine and baclofen declined with time. 5. It is concluded that neurotensin excites ventral tegmental area neurones by activating a pertussis toxin-insensitive guanosine nucleotide-binding protein. This leads to a reduction in membrane potassium conductance and an increase in membrane sodium conductance, the relative contribution of which varies from cell to cell.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi D. K., Kalivas P. W., Schenk J. O. Neurotensin binding to dopamine. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1321–1328. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audinat E., Hermel J. M., Crépel F. Neurotensin-induced excitation of neurons of the rat's frontal cortex studied intracellularly in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(2):358–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00228907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldino F., Jr, Wolfson B. Postsynaptic actions of neurotensin on preoptic-anterior hypothalamic neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1985 Jan 28;325(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer V. E., Towle A. C., Pickel V. M. Ultrastructural localization of neurotensin-like immunoreactivity within dense core vesicles in perikarya, but not terminals, colocalizing tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat ventral tegmental area. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Sep 8;311(2):179–196. doi: 10.1002/cne.903110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean A. J., During M. J., Roth R. H. Stimulation-induced release of coexistent transmitters in the prefrontal cortex: an in vivo microdialysis study of dopamine and neurotensin release. J Neurochem. 1989 Aug;53(2):655–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinaglia G., Probst A., Palacios J. M. Neurotensin receptors in Parkinson's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: an autoradiographic study in basal ganglia. Neuroscience. 1990;39(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana C., Vial M., Leonard K., Beauregard A., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P., Rostène W., Beaudet A. Electron microscopic localization of neurotensin binding sites in the midbrain tegmentum of the rat. I. Ventral tegmental area and the interfascicular nucleus. J Neurosci. 1989 Jul;9(7):2247–2257. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-07-02247.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Minota S. Effects of substance P on neurones of the inferior mesenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:259–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Goedert M., Horsfield P., Rioux F., St Pierre S. The regional distribution and chromatographic characterisation of neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1982 Apr;38(4):992–999. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb05340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Pinnock R. D., Downes C. P., Mantyh P. W., Emson P. C. Neurotensin stimulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 3;323(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Onn S. P. Morphology and electrophysiological properties of immunocytochemically identified rat dopamine neurons recorded in vitro. J Neurosci. 1989 Oct;9(10):3463–3481. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-10-03463.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Nedergaard S., Greenfield S. A. Electrophysiological localization of distinct calcium potentials at selective somatodendritic sites in the substantia nigra. Neuroscience. 1992 Oct;50(3):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90443-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Everitt B. J., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Goldstein M. Occurrence of neurotensinlike immunoreactivity in subpopulations of hypothalamic, mesencephalic, and medullary catecholamine neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Feb 1;222(4):543–559. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z. G., Pessia M., North R. A. Dopamine and baclofen inhibit the hyperpolarization-activated cation current in rat ventral tegmental neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:753–764. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. W., North R. A. Opioids excite dopamine neurons by hyperpolarization of local interneurons. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):483–488. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. W., North R. A. Two types of neurone in the rat ventral tegmental area and their synaptic inputs. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:455–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalivas P. W., Taylor S. Behavioral and neurochemical effect of daily injection with neurotensin into the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 9;358(1-2):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90949-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanba K. S., Kanba S., Okazaki H., Richelson E. Binding of [3H]neurotensin in human brain: properties and distribution. J Neurochem. 1986 Mar;46(3):946–952. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Synaptic events in sympathetic ganglia. Prog Neurobiol. 1978;11(2):77–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Mercuri N. B., North R. A. On the potassium conductance increase activated by GABAB and dopamine D2 receptors in rat substantia nigra neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:437–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Mercuri N. B., North R. A. Two cell types in rat substantia nigra zona compacta distinguished by membrane properties and the actions of dopamine and opioids. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1233–1241. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01233.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo P. M., Homburger V., Bockaert J., Vincent J. D. Differential G protein-mediated coupling of D2 dopamine receptors to K+ and Ca2+ currents in rat anterior pituitary cells. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90273-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai J. K., Triepel J., Metz J. Neurotensin in the human brain. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):499–524. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Fujimura K., Yoshida S. Two types of neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta studied in a slice preparation. Neurosci Res. 1987 Dec;5(2):172–179. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(87)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnock R. D. Neurotensin depolarizes substantia nigra dopamine neurones. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 8;338(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seutin V., Massotte L., Dresse A. Electrophysiological effects of neurotensin on dopaminergic neurones of the ventral tegmental area of the rat in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Sep;28(9):949–954. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Muscarine increases cation conductance and decreases potassium conductance in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:471–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Substance P opens cation channels and closes potassium channels in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard P. D., German D. C. Electrophysiological and pharmacological evidence for the existence of distinct subpopulations of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron in the rat. Neuroscience. 1988 Nov;27(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. S., Bunney B. S. Neurotensin attenuates dopamine D2 agonist quinpirole-induced inhibition of midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1990 Nov;29(11):1095–1097. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(90)90119-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. X., Bunney B. S. Roles of intracellular cAMP and protein kinase A in the actions of dopamine and neurotensin on midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2433–2438. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02433.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva N. L., Pechura C. M., Barker J. L. Postnatal rat nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons exhibit five types of potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jul;64(1):262–272. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.1.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapelfeldt W. H., Szurszewski J. H. The electrophysiological effects of neurotensin on neurones of guinea-pig prevertebral sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:301–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szigethy E., Beaudet A. Correspondence between high affinity 125I-neurotensin binding sites and dopaminergic neurons in the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area: a combined radioautographic and immunohistochemical light microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jan 1;279(1):128–137. doi: 10.1002/cne.902790111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Euler G., Fuxe K. Neurotensin reduces the affinity of D-2 dopamine receptors in rat striatal membranes. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Dec;131(4):625–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Katayama Y., North R. A. The action of neurotensin on single myenteric neurones. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov 16;59(3-4):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Neurotensin receptor localization by light microscopic autoradiography in rat brain. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung W. H., Häusser M. A., Jack J. J. Electrophysiology of dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic neurones of the guinea-pig substantia nigra pars compacta in vitro. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:643–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


