Abstract
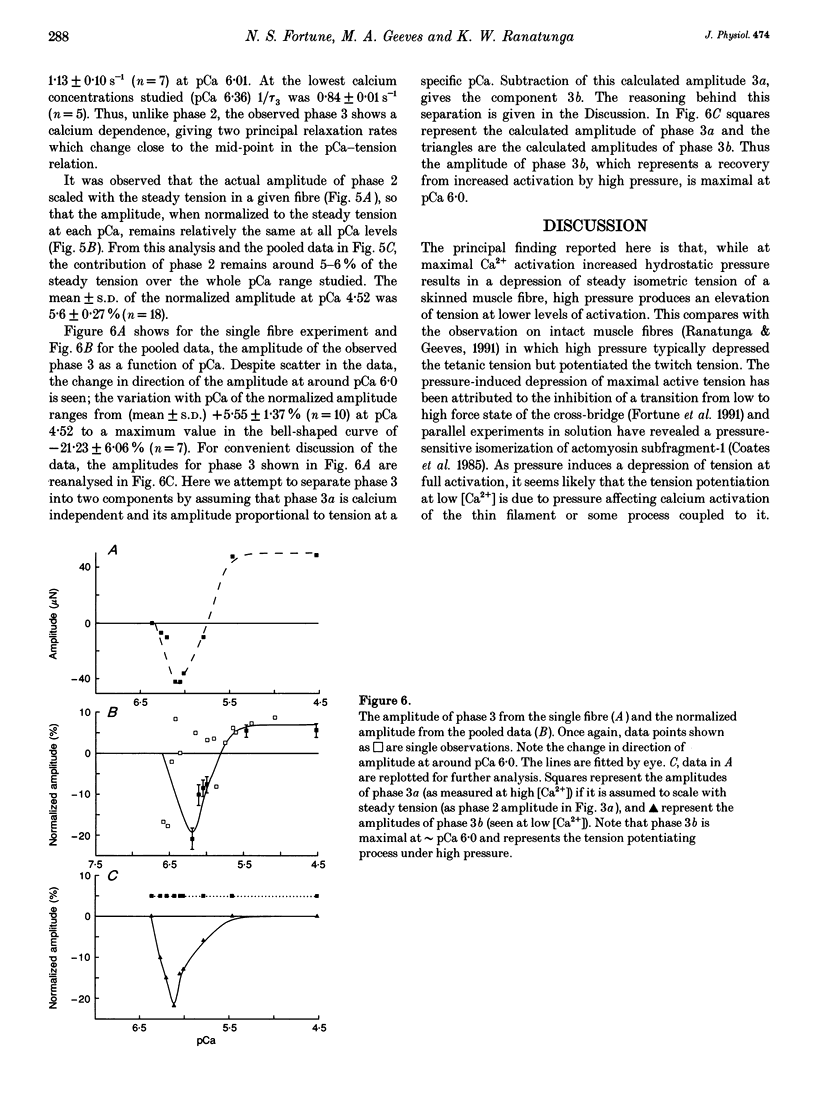
1. Effects of hydrostatic pressure (range 0.1-10 MPa) on the isometric tension of skinned (rabbit psoas) muscle fibres were examined at 12 degrees C and at different levels of Ca2+ activation (pCa range 4-7); the effects on both the steady tension and the tension transients induced by rapid pressure release (< 1 ms) are described. 2. The steady tension was depressed by increased pressure (approximately 1% MPa-1) at a high level of Ca2+ activation (pCa approximately 4) whereas it was potentiated at lower Ca2+ levels (pCa > 6); the effects were reversible. 3. At maximal Ca2+ activation, the tension recovery following pressure release (10 MPa to atmospheric) consisted of a fast (approximately 30 s-1) and a slow (2-3 s-1) phase; the rate and the normalized amplitude (normalized to the steady tension at atmospheric pressure for a particular pCa) of the fast phase were invariant with changes in Ca2+ level. 4. The effects of changing Ca2+ level on the slow phase were complex; its positive amplitude at high Ca2+ levels changed to negative and the rate decreased to approximately 1 s-1 at low Ca2+ levels (pCa > 6.0). 5. Results are discussed in relation to previous studies on the effect of pressure on intact muscle fibres and the actin-myosin interaction. This work supports calcium regulation of cross-bridge recruitment rather than calcium regulation of the rate of a specific step in the cross-bridge cycle.
Full text
PDF
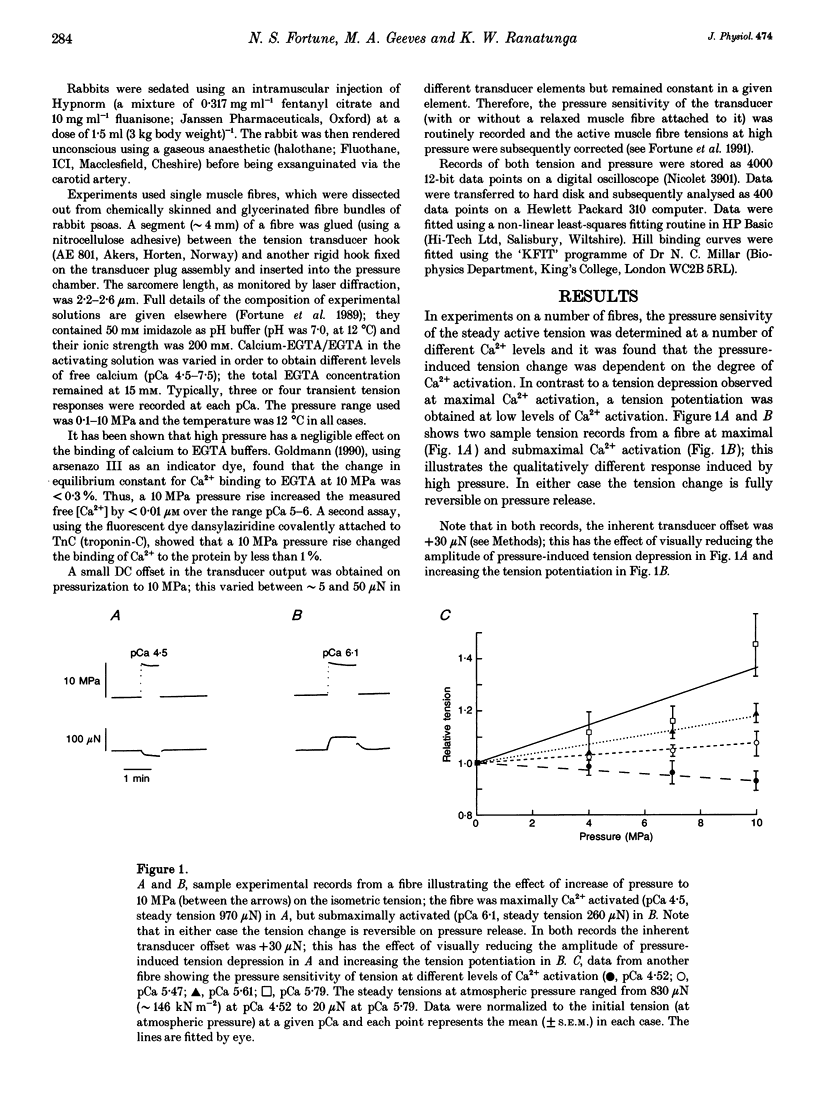
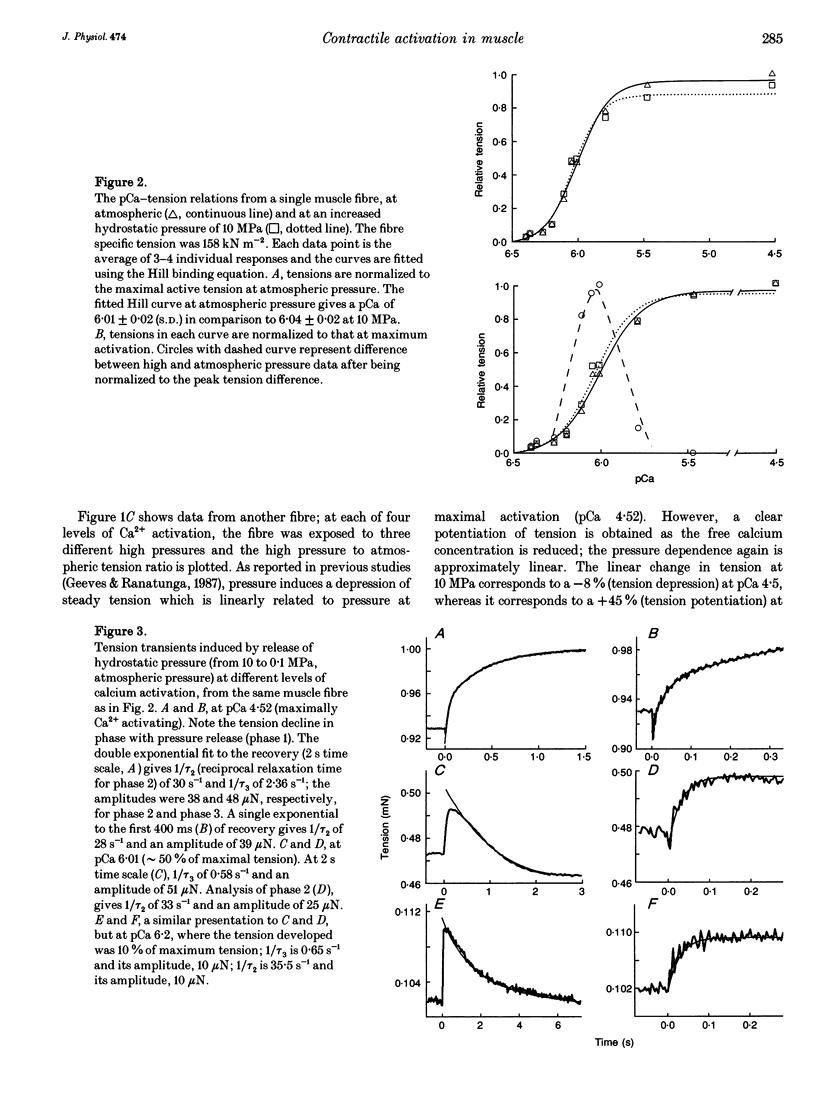
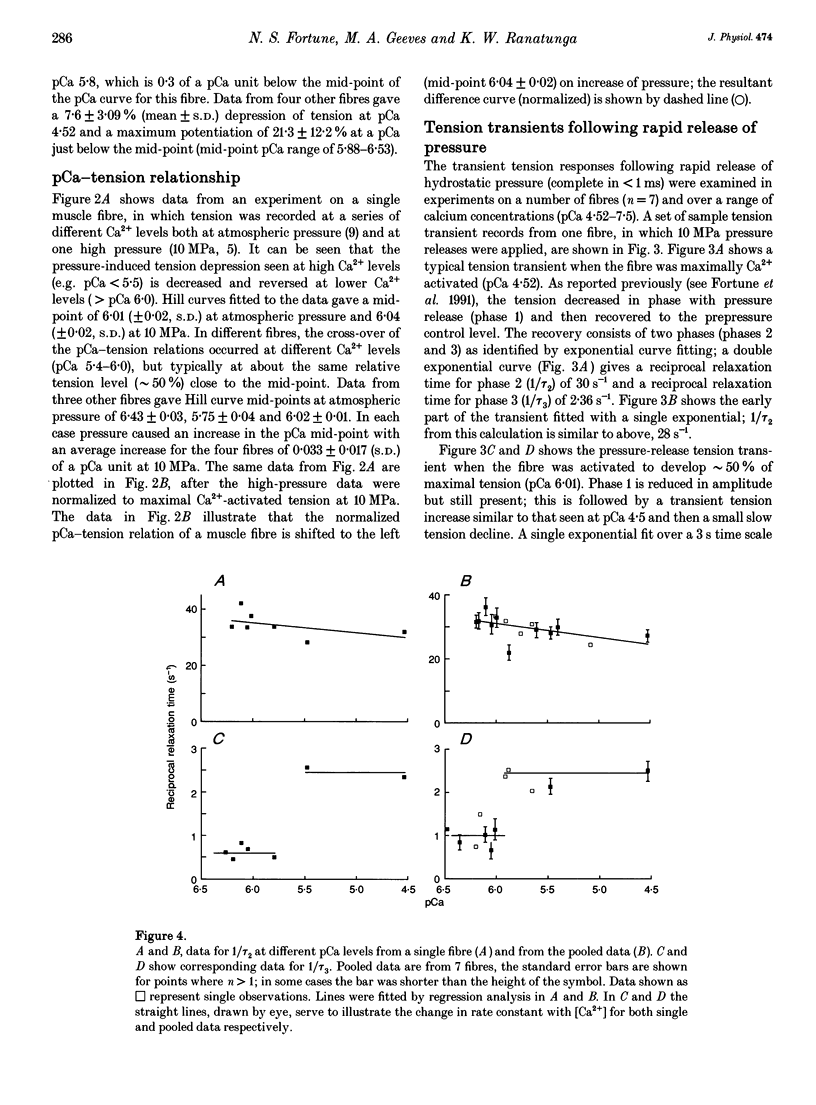
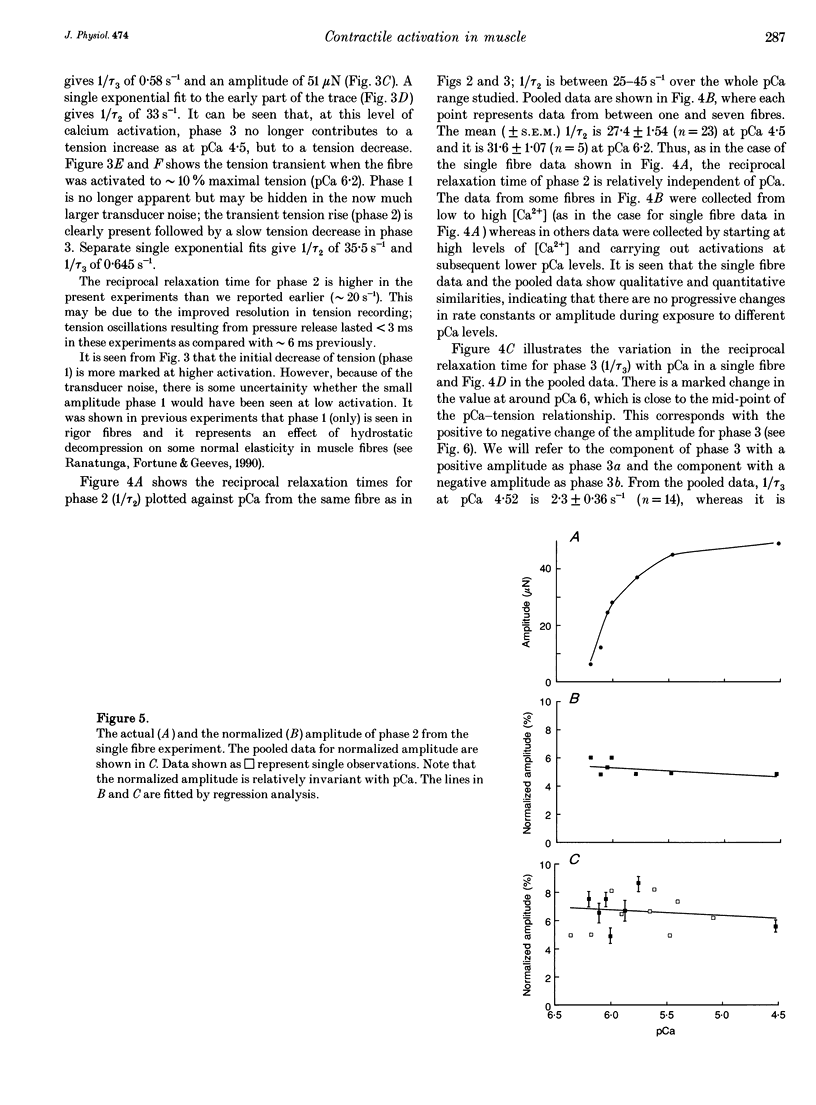


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on cross-bridge turnover kinetics in skinned single rabbit psoas fibers: implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2432–2437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates J. H., Criddle A. H., Geeves M. A. Pressure-relaxation studies of pyrene-labelled actin and myosin subfragment 1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for two states of acto-subfragment 1. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):351–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2320351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E., Millar N. C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Pressure sensitivity of active tension in glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle fibres: effects of ADP and phosphate. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Apr;10(2):113–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01739967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Tension responses to rapid pressure release in glycerinated rabbit muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A., Halsall D. J. Two-step ligand binding and cooperativity. A model to describe the cooperative binding of myosin subfragment 1 to regulated actin. Biophys J. 1987 Aug;52(2):215–220. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A., Ranatunga K. W. Tension responses to increased hydrostatic pressure in glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Nov 23;232(1267):217–226. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., McCray J. A., Ranatunga K. W. Transient tension changes initiated by laser temperature jumps in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:71–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cooperative binding of myosin subfragment-1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. Theoretical model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment 1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKillop D. F., Geeves M. A. Regulation of the acto.myosin subfragment 1 interaction by troponin/tropomyosin. Evidence for control of a specific isomerization between two acto.myosin subfragment 1 states. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):711–718. doi: 10.1042/bj2790711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Variations in cross-bridge attachment rate and tension with phosphorylation of myosin in mammalian skinned skeletal muscle fibers. Implications for twitch potentiation in intact muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):855–883. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Thin filament regulation of shortening velocity in rat skinned skeletal muscle: effects of osmotic compression. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:165–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranatunga K. W., Fortune N. S., Geeves M. A. Hydrostatic compression in glycerinated rabbit muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1401–1410. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82486-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranatunga K. W., Geeves M. A. Changes produced by increased hydrostatic pressure in isometric contractions of rat fast muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:423–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


