Abstract
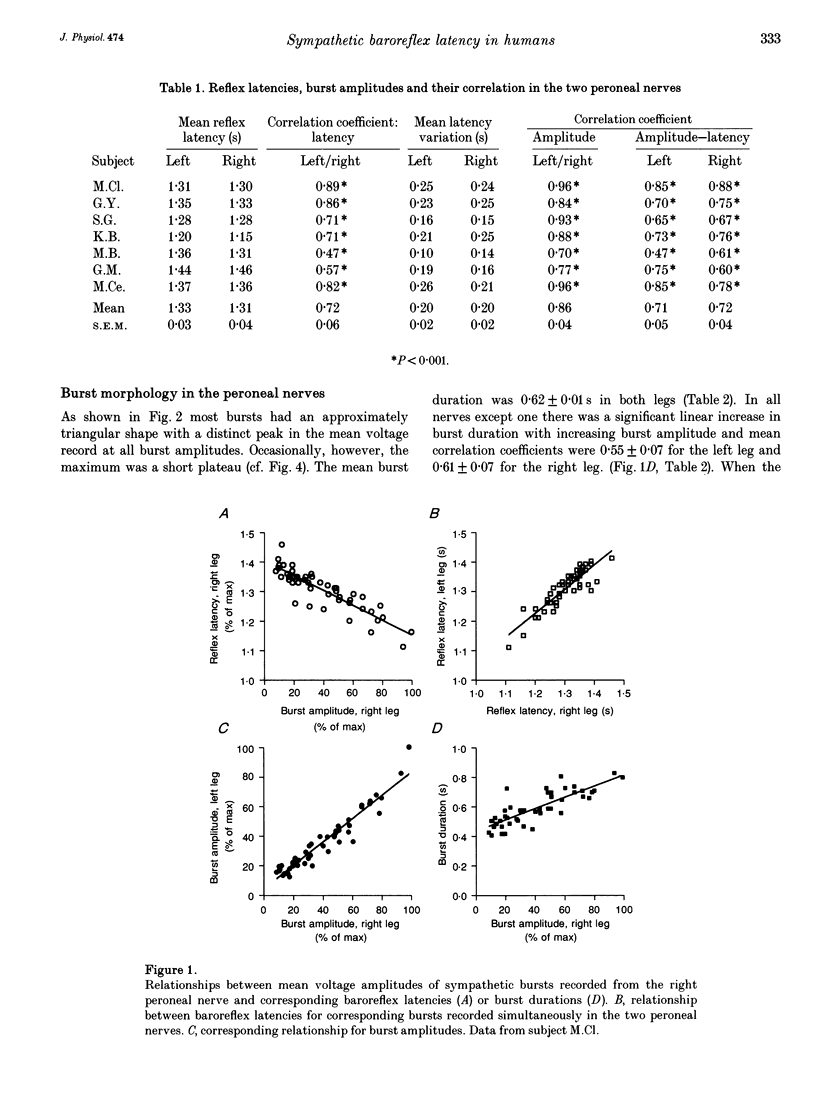
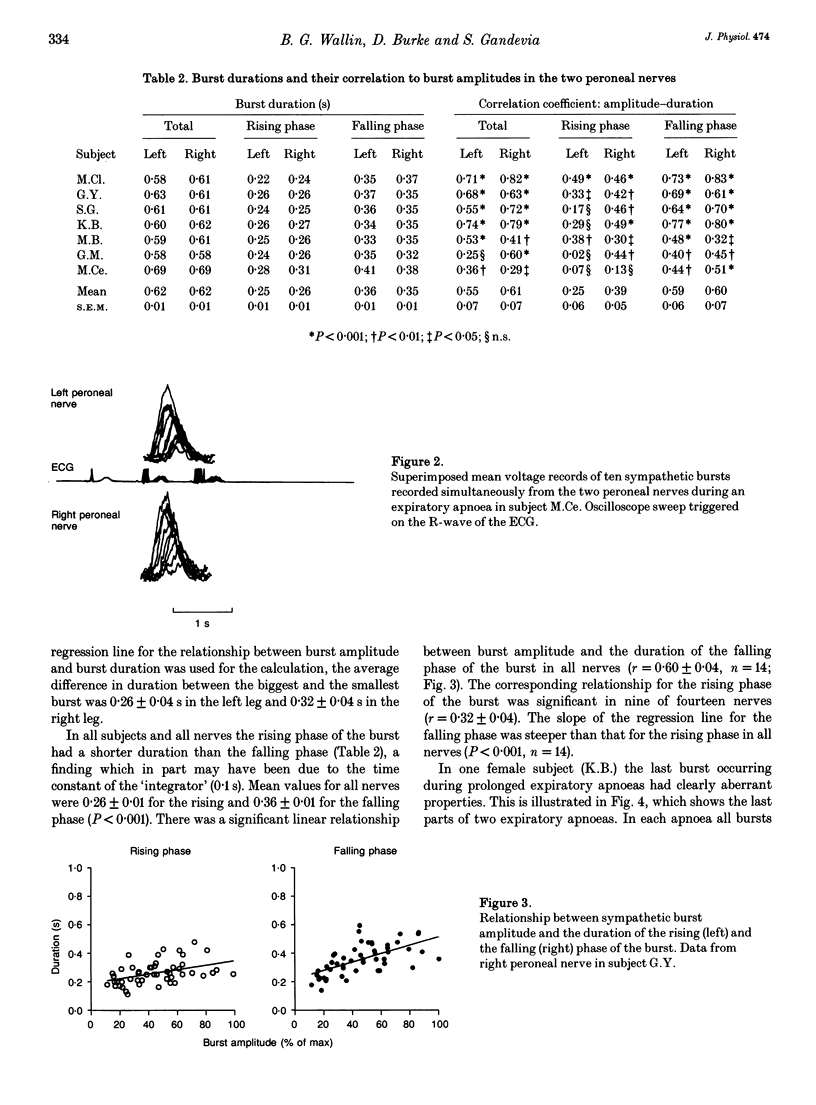
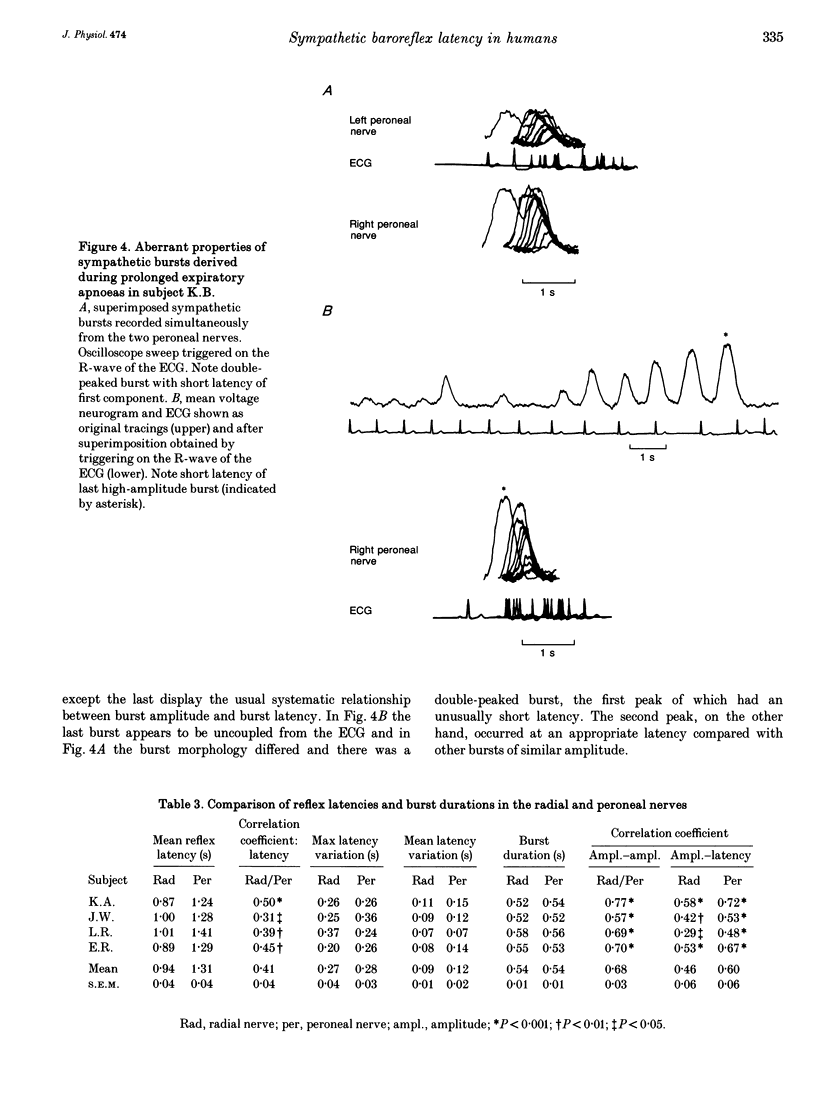
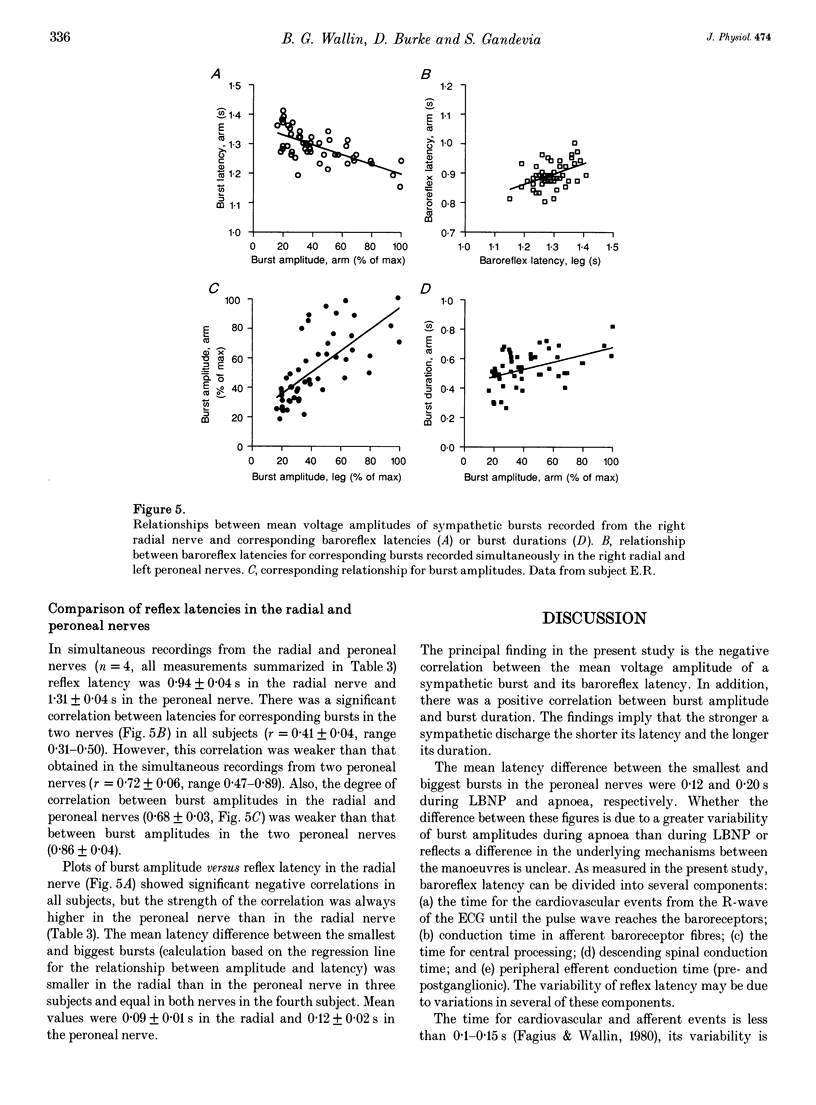
1. Pulse-synchronous multiunit muscle nerve sympathetic activity was recorded simultaneously from two nerves together with ECG in eleven healthy subjects; seven recordings were made from the two peroneal nerves during prolonged expiratory apnoeas and four from a radial and a peroneal nerve during lower body negative pressure of 10-40 mmHg. The neural records were displayed in mean voltage neurograms (time constant 0.1 s) and for each mean voltage burst the following measures were taken and related to each other: amplitude, duration, rise time, decay time and baroreflex latency (from the appropriate R-wave of the ECG to the peak of the burst). 2. Average baroreflex latencies were 1.3 s in the peroneal nerves and 0.9 s in the radial nerve. There were significant positive correlations between both the amplitudes and the baroreflex latencies of corresponding bursts in peroneal-peroneal recordings and in radial-peroneal recordings. 3. In all nerves baroreflex latency shortened significantly when burst amplitude increased. The correlation between burst amplitude and baroreflex latency was weaker in the radial than in the peroneal nerve. The average variation of baroreflex latency in peroneal-peroneal recordings was 0.20 +/- 0.02 s in both legs, and in radial-peroneal recordings the variation was 0.09 +/- 0.01 s in the radial nerve and 0.12 +/- 0.02 s in the peroneal nerve. 4. When peroneal burst amplitudes increased, burst duration increased. This was due to increases of both the rise time and the decay time of the burst, the latter being the greater.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borst C., Karemaker J. M. Time delays in the human baroreceptor reflex. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Nov;9(2-3):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Macleod V. H. Evidence for the involvement in the baroreceptor reflex of a descending inhibitory pathway. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):477–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius W., Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Wallin B. G. General characteristics of sympathetic activity in human muscle nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):65–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Sundlöf G., Wallin B. G. Variation of sympathetic reflex latency in man. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Dec;21(2-3):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Wallin B. G. Microneurographic evidence of excessive sympathetic outflow in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Brain. 1983 Sep;106(Pt 3):589–600. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Wallin B. G., Sundlöf G., Nerhed C., Englesson S. Sympathetic outflow in man after anaesthesia of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. Brain. 1985 Jun;108(Pt 2):423–438. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.2.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic reflex latencies and conduction velocities in normal man. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Sep;47(3):433–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornyak M., Cejnar M., Elam M., Matousek M., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic muscle nerve activity during sleep in man. Brain. 1991 Jun;114(Pt 3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.3.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The baroreceptor input to cardiac vagal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:365–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Potter E. K. Excitation and inhibition of cardiac vagal motoneurones by electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:163–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Iwase S., Mano T., Sugiyama Y., Watanabe T. Changes in muscle sympathetic nerve activity during sleep in humans. Neurology. 1991 Dec;41(12):1961–1966. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.12.1961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea R. F., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic nerve activity in arm and leg muscles during lower body negative pressure in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jun;66(6):2778–2781. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.6.2778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Reis D. J. Projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Dec 22;242(4):511–534. doi: 10.1002/cne.902420405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellgren J., Pontén J., Wallin B. G. Characteristics of muscle nerve sympathetic activity during general anaesthesia in humans. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1992 May;36(4):336–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1992.tb03478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellgren J., Pontén J., Wallin B. G. Percutaneous recording of muscle nerve sympathetic activity during propofol, nitrous oxide, and isoflurane anesthesia in humans. Anesthesiology. 1990 Jul;73(1):20–27. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199007000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernberg L., Blumberg H., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic activity in man after spinal cord injury. Outflow to muscle below the lesion. Brain. 1986 Aug;109(Pt 4):695–715. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundlöf G., Wallin B. G. The variability of muscle nerve sympathetic activity in resting recumbent man. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):383–397. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Burke D., Gandevia S. C. Coherence between the sympathetic drives to relaxed and contracting muscles of different limbs of human subjects. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:219–233. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Rea R. Spinal sympathetic conduction velocity in humans. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Oct;24(3):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Victor R. G., Mark A. L. Sympathetic outflow to resting muscles during static handgrip and postcontraction muscle ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):H105–H110. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.1.H105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


