Abstract
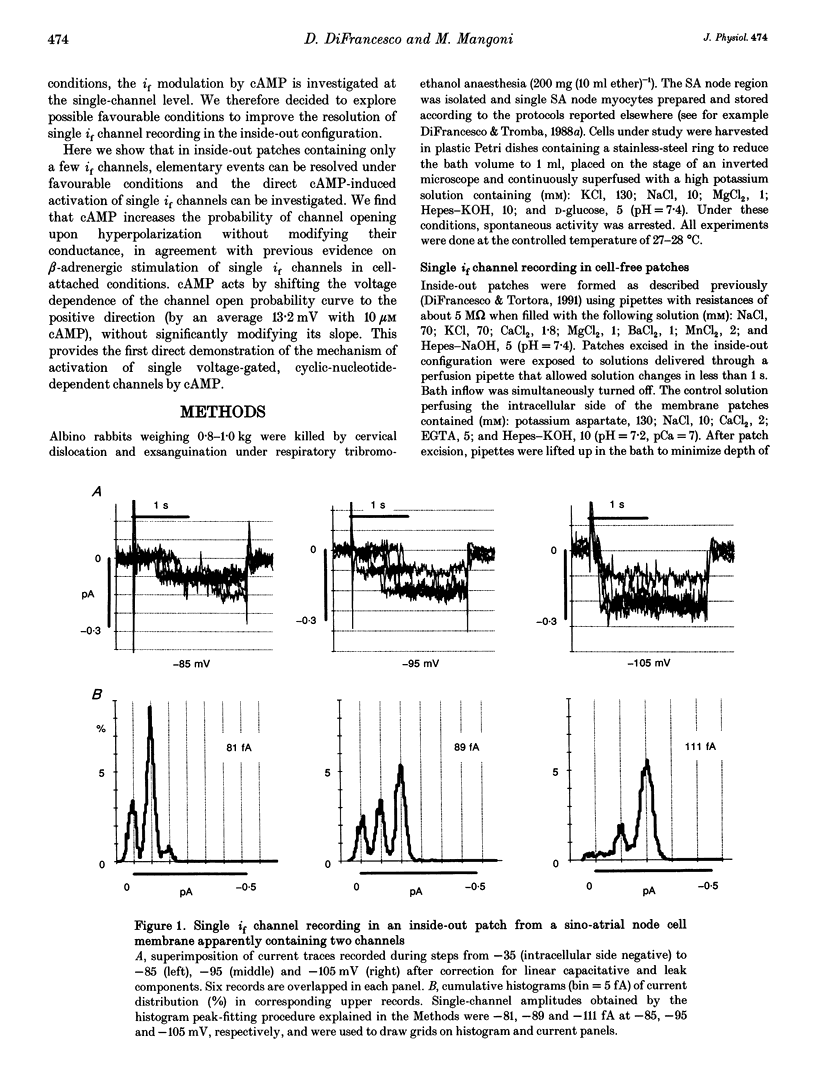
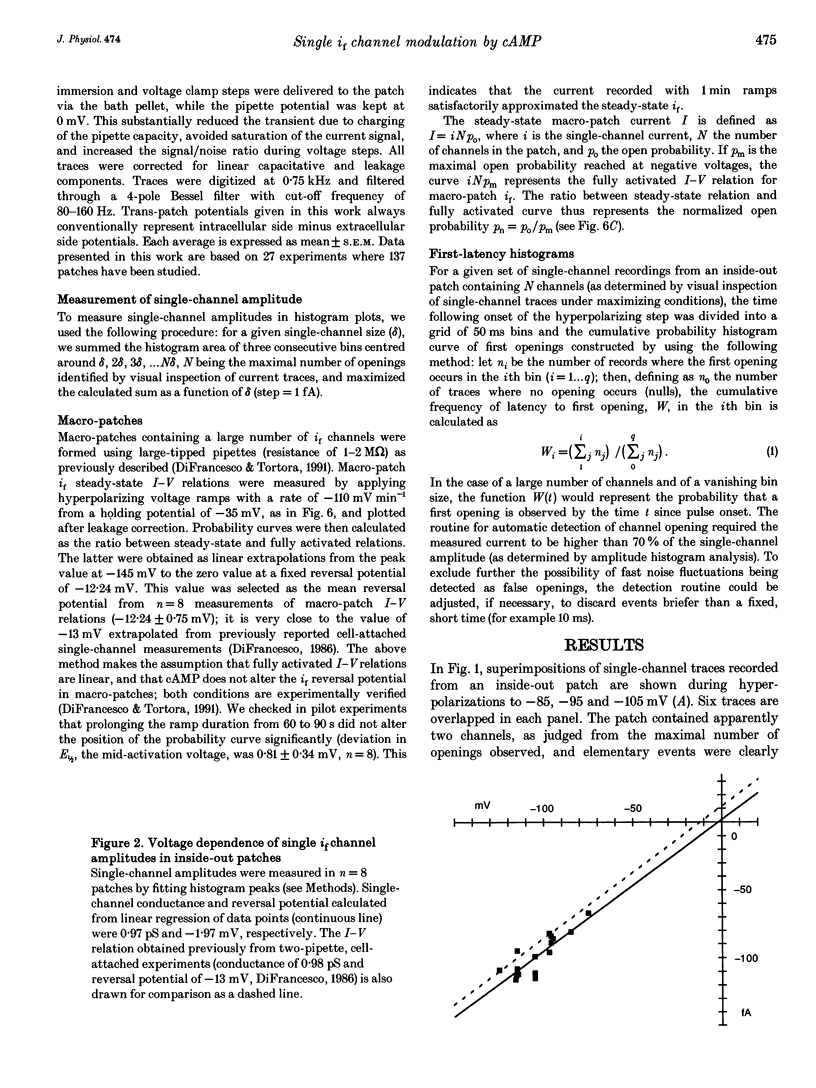
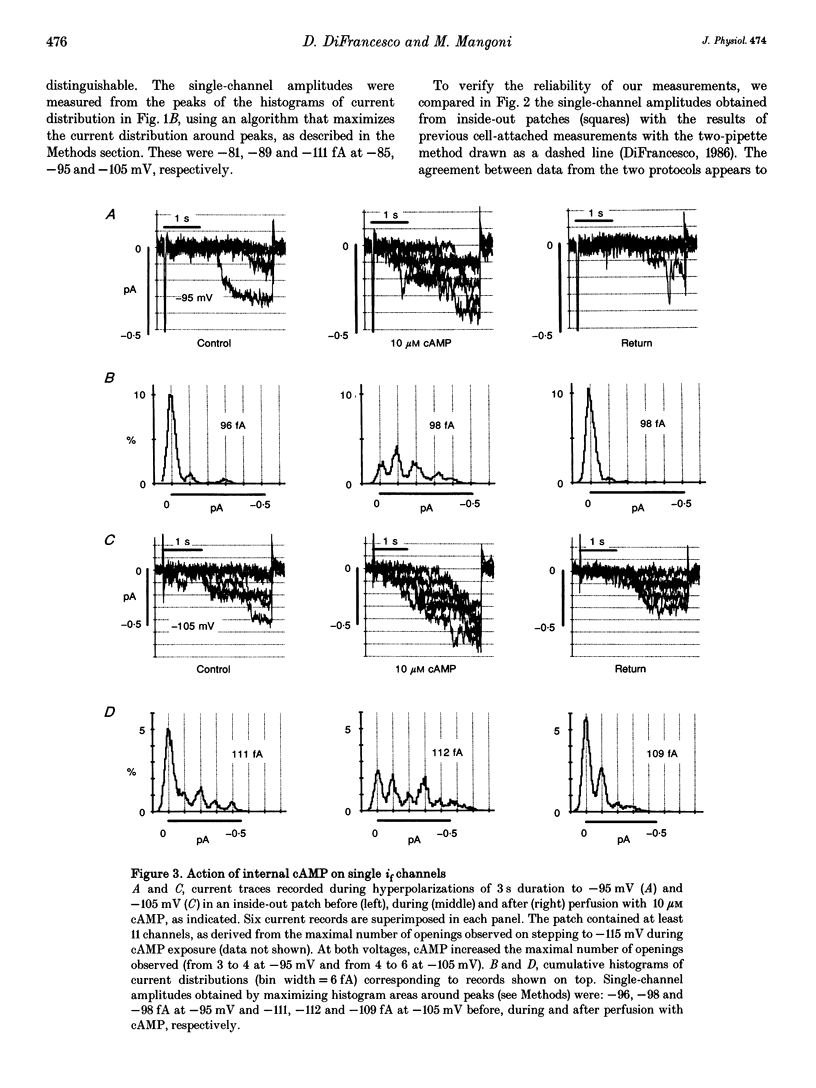
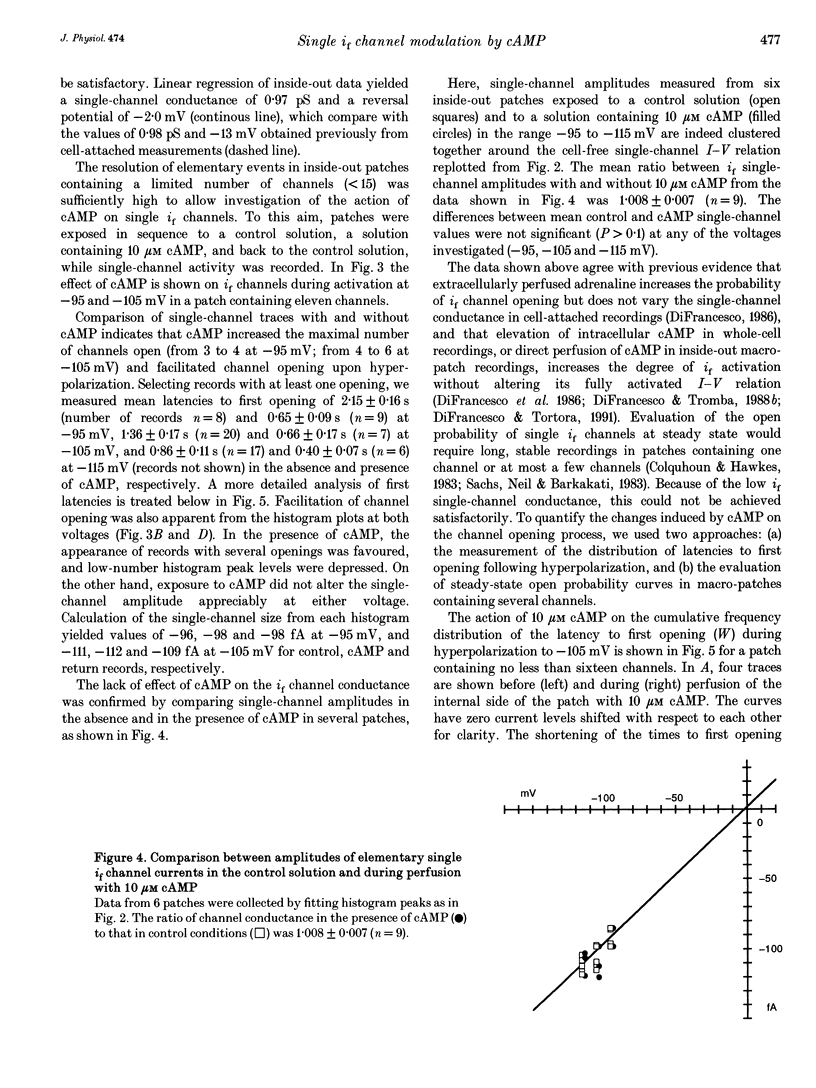
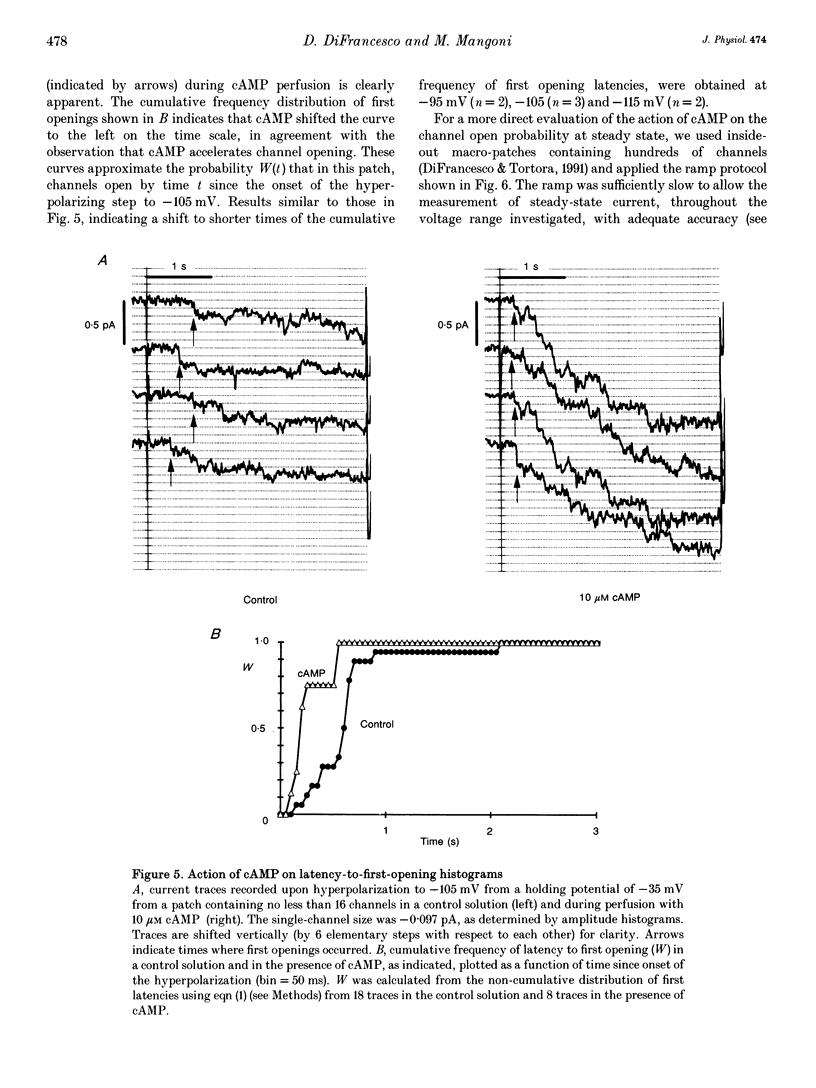
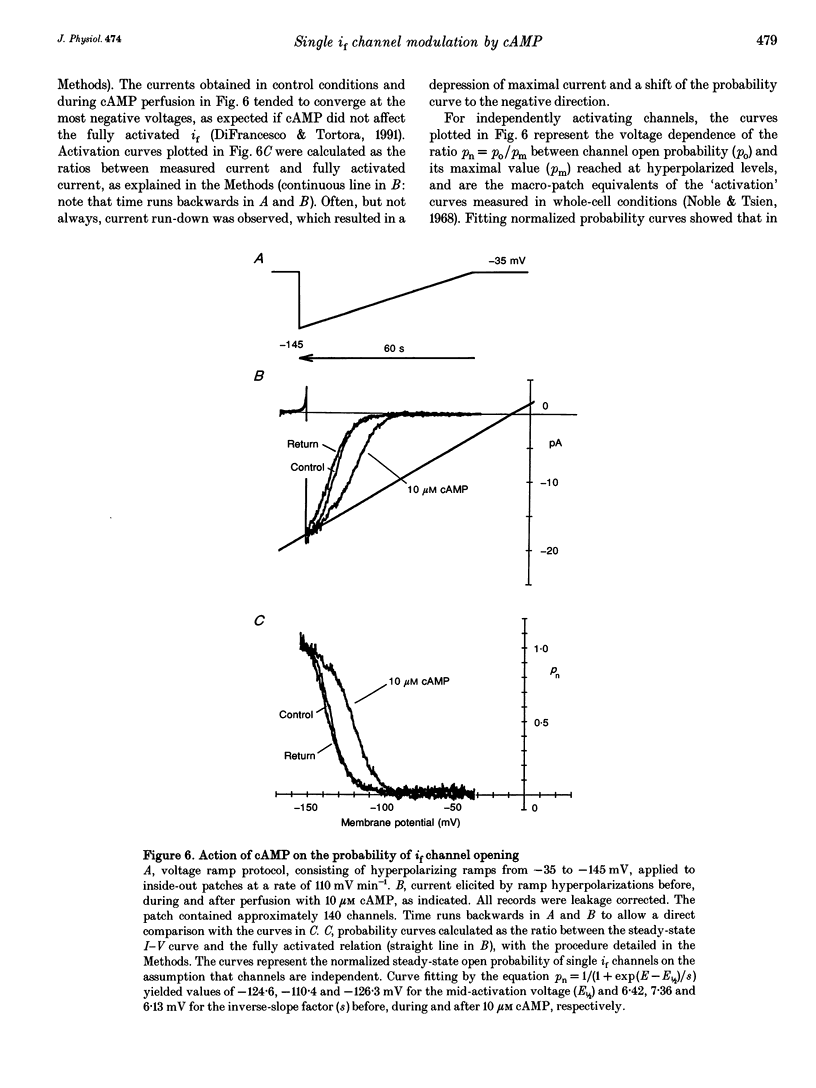
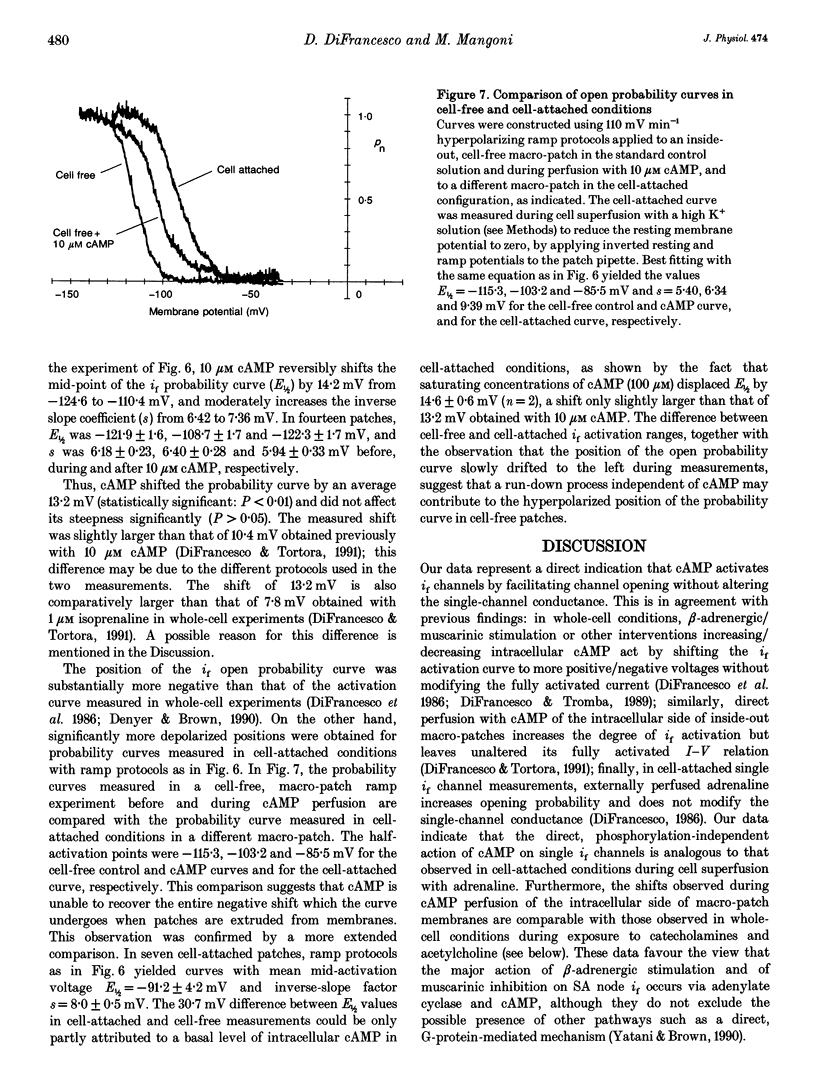
1. The hyperpolarization-activated 'pacemaker' current (i(f)) was recorded in inside-out patches excised from rabbit sino-atrial (SA) node cell membranes. 2. Single-channel activity could be resolved in patches containing only a few channels; the voltage dependence of single-channel size and single-channel conductance (0.97 pS) were similar to those measured previously in cell-attached conditions. 3. Perfusion of the intracellular side of the patch membrane with 10 microM cAMP facilitated the opening of single i(f) channels on hyperpolarization. The cAMP-induced i(f) current activation occurred without modification of the single-channel conductance. 4. Modification by cAMP of the probability of channel opening was investigated with respect to the latency to first opening during hyperpolarization and in patches containing a large number of channels (macro-patches). First-latency histograms showed that cAMP shifts the probability curve of first openings to shorter times, in agreement with a cAMP-induced facilitation of channel opening. In macro-patches, measurement of the voltage dependence of the open probability by a slow voltage ramp protocol showed that cAMP shifts the probability curve to more positive voltages without modifying its shape. 5. In cell-free macro-patches the normalized open probability curve in control solutions was centred around -121.9 mV, a voltage some 30 mV more negative than in cell-attached macro-patches. Negative shifting of the curve after patch excision could only partly be explained by the removal of intracellular cAMP, and progressed with time during the ramp protocol, suggesting the presence of a run-down process independent from cAMP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belles B., Malécot C. O., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. "Run-down" of the Ca current during long whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosphorylation and intracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00587713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., DiFrancesco D., Noble S. J. How does adrenaline accelerate the heart? Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):235–236. doi: 10.1038/280235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Cohen I. S., DiFrancesco D., Rosen M. R., Tromba C. Effects of protein kinase inhibitors on canine Purkinje fibre pacemaker depolarization and the pacemaker current i(f). J Physiol. 1991;440:367–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denyer J. C., Brown H. F. Rabbit sino-atrial node cells: isolation and electrophysiological properties. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:405–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. Characterization of single pacemaker channels in cardiac sino-atrial node cells. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):470–473. doi: 10.1038/324470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ducouret P., Robinson R. B. Muscarinic modulation of cardiac rate at low acetylcholine concentrations. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):669–671. doi: 10.1126/science.2916119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ferroni A., Mazzanti M., Tromba C. Properties of the hyperpolarizing-activated current (if) in cells isolated from the rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. The contribution of the 'pacemaker' current (if) to generation of spontaneous activity in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:23–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tortora P. Direct activation of cardiac pacemaker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):145–147. doi: 10.1038/351145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Inhibition of the hyperpolarization-activated current (if) induced by acetylcholine in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:477–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Muscarinic control of the hyperpolarization-activated current (if) in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:493–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanck D. A., Sheets M. F. Time-dependent changes in kinetics of Na+ current in single canine cardiac Purkinje cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):H1197–H1207. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.4.H1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. The kinetics and rectifier properties of the slow potassium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):185–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Kotake H., Irisawa H. Slow inward current and its role mediating the chronotropic effect of epinephrine in the rabbit sinoatrial node. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Oct;388(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00582621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Fozzard H. A., Hanck D. A. Mechanism of cAMP-dependent modulation of cardiac sodium channel current kinetics. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):807–815. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Fozzard H. A. Phosphorylation restores activity of L-type calcium channels after rundown in inside-out patches from rabbit cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:673–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieder W., Brum G., Hescheler J., Trautwein W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Injection of subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase into cardiac myocytes modulates Ca2+ current. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):576–578. doi: 10.1038/298576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster M. J., Camardo J. S., Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase closes the serotonin-sensitive K+ channels of Aplysia sensory neurones in cell-free membrane patches. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):392–395. doi: 10.1038/313392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Cyclic AMP and contractile activity in heart. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:363–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Effects of epinephrine on the pacemaker potassium current of cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Sep;64(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Brown A. M. Regulation of cardiac pacemaker current If in excised membranes from sinoatrial node cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):H1947–H1951. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.6.H1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Okabe K., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Heart rate regulation by G proteins acting on the cardiac pacemaker channel. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1163–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.1697697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Peyer J. E., Cachelin A. B., Levitan I. B., Reuter H. Ca2+ -activated K+ conductance in internally perfused snail neurons is enhanced by protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4207–4211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


