Abstract
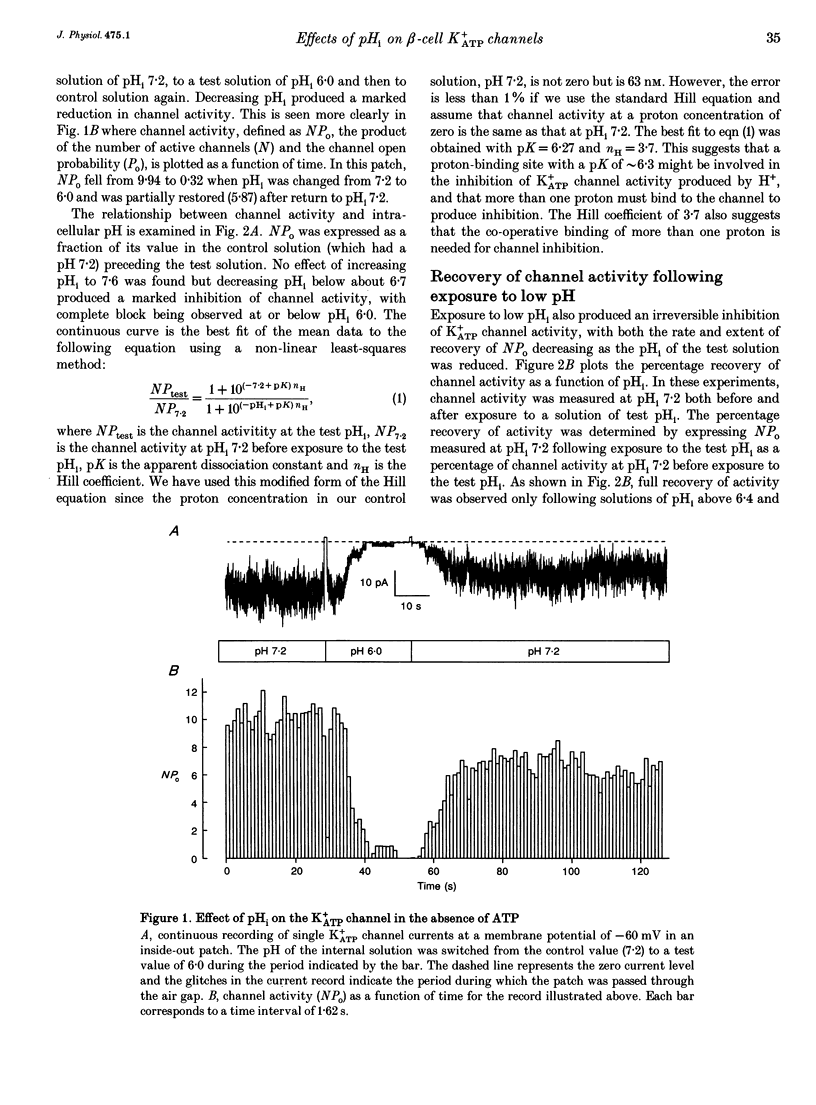
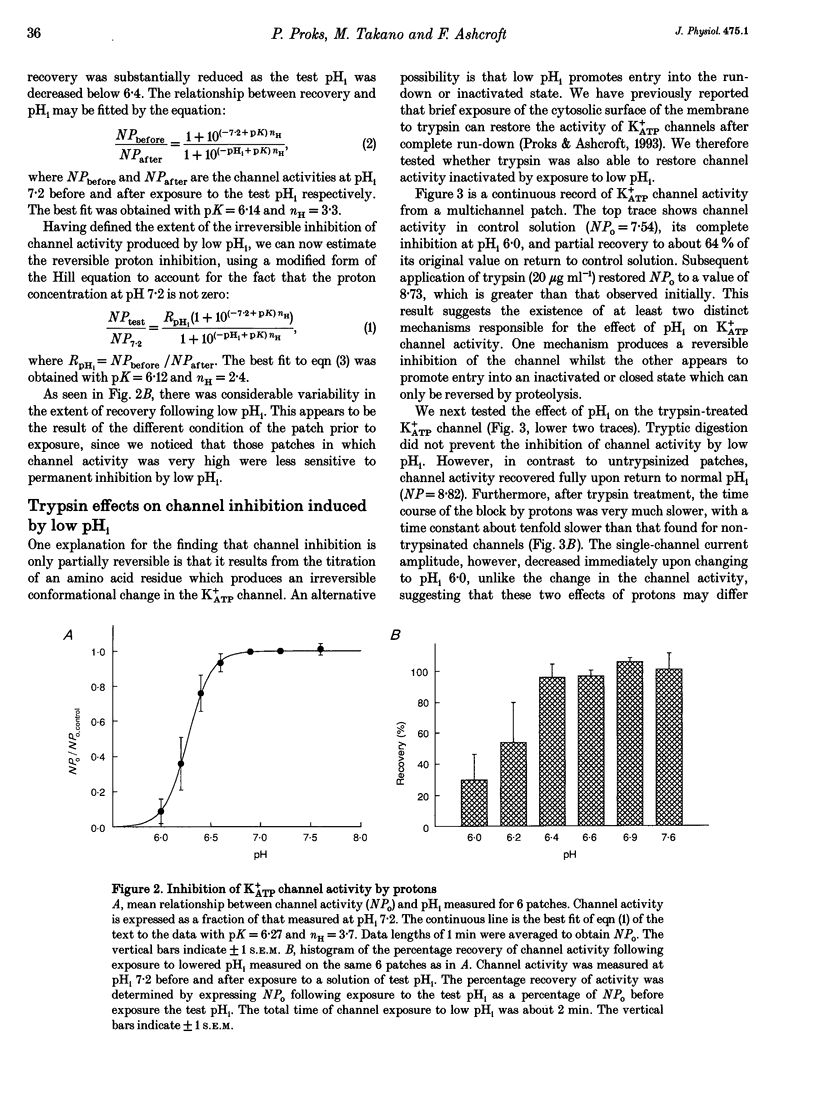
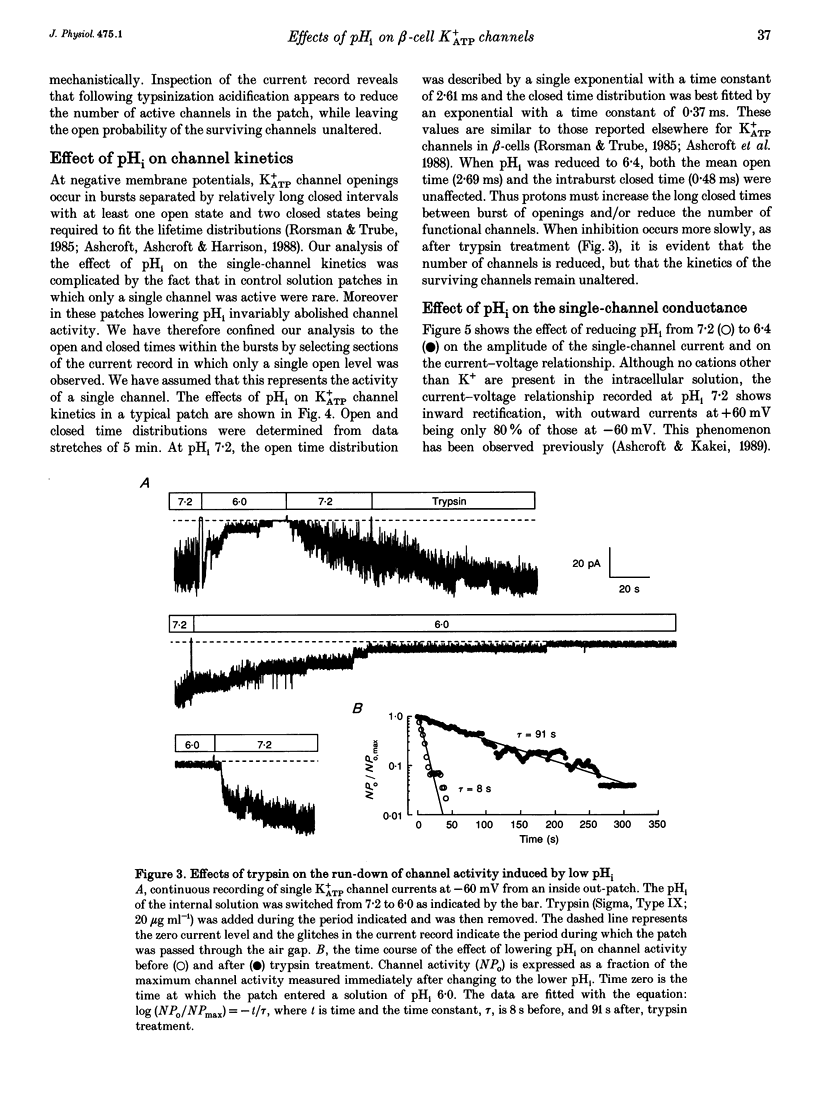
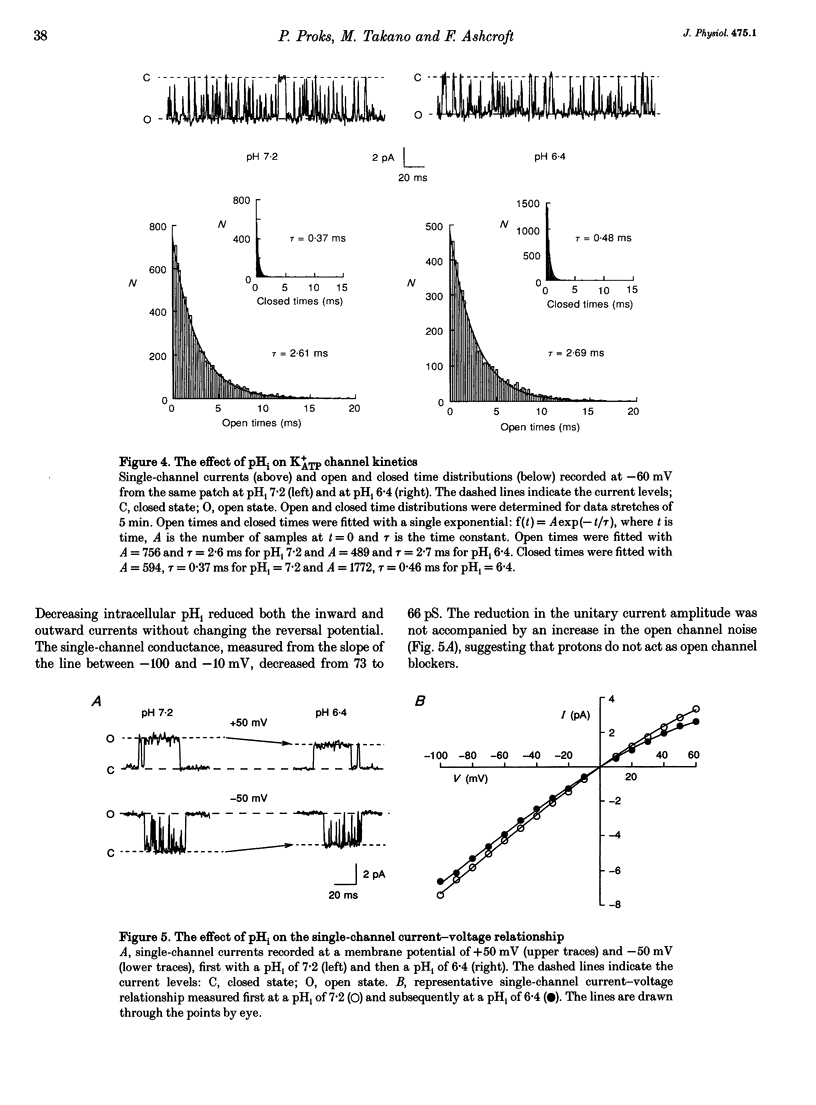
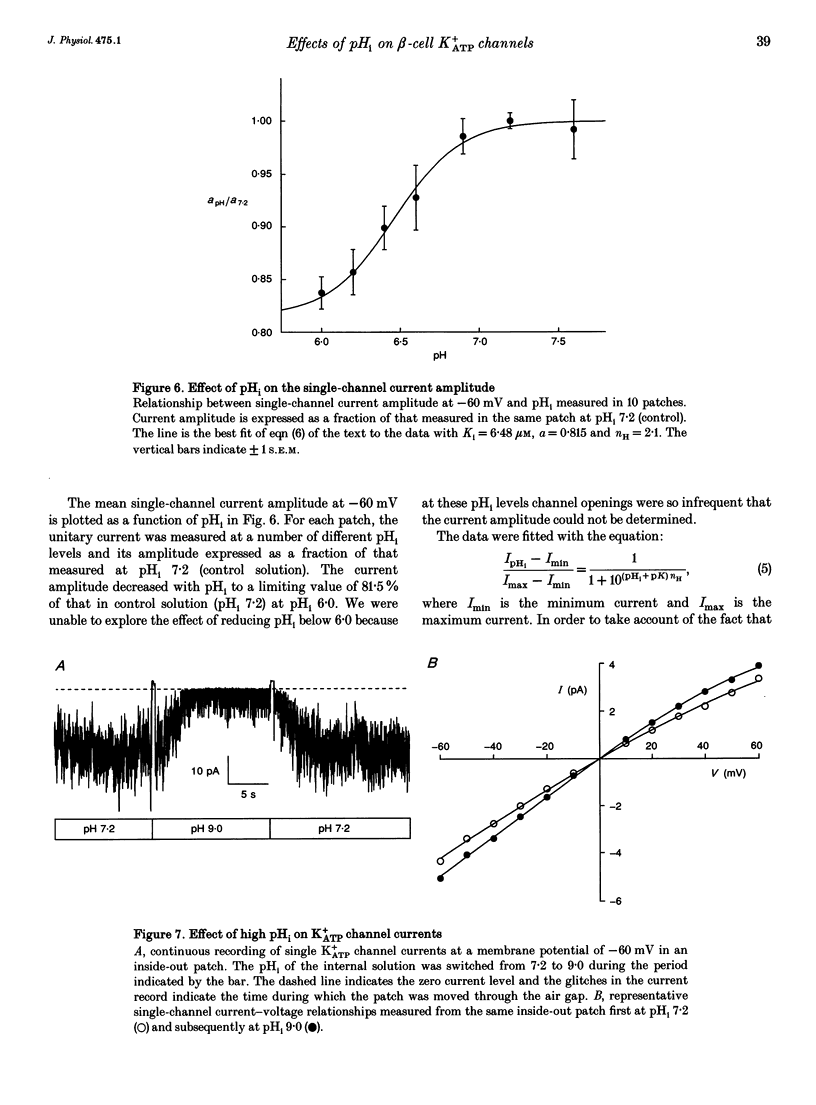
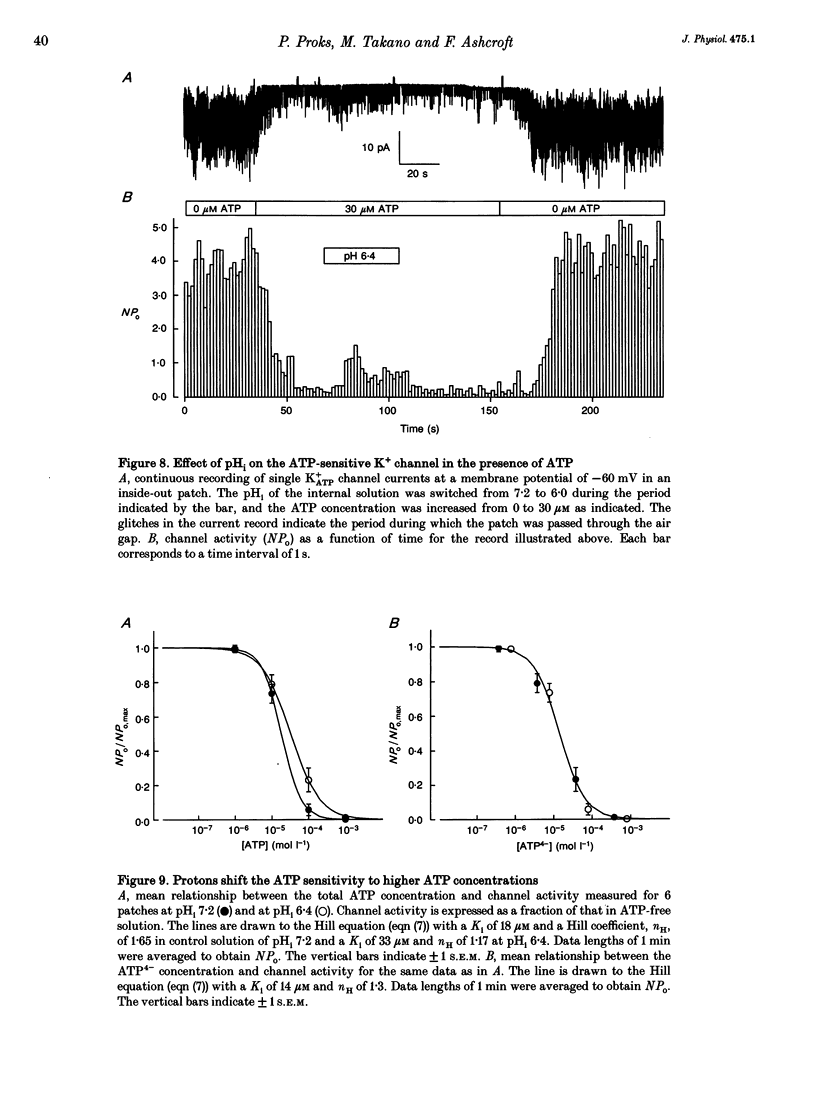
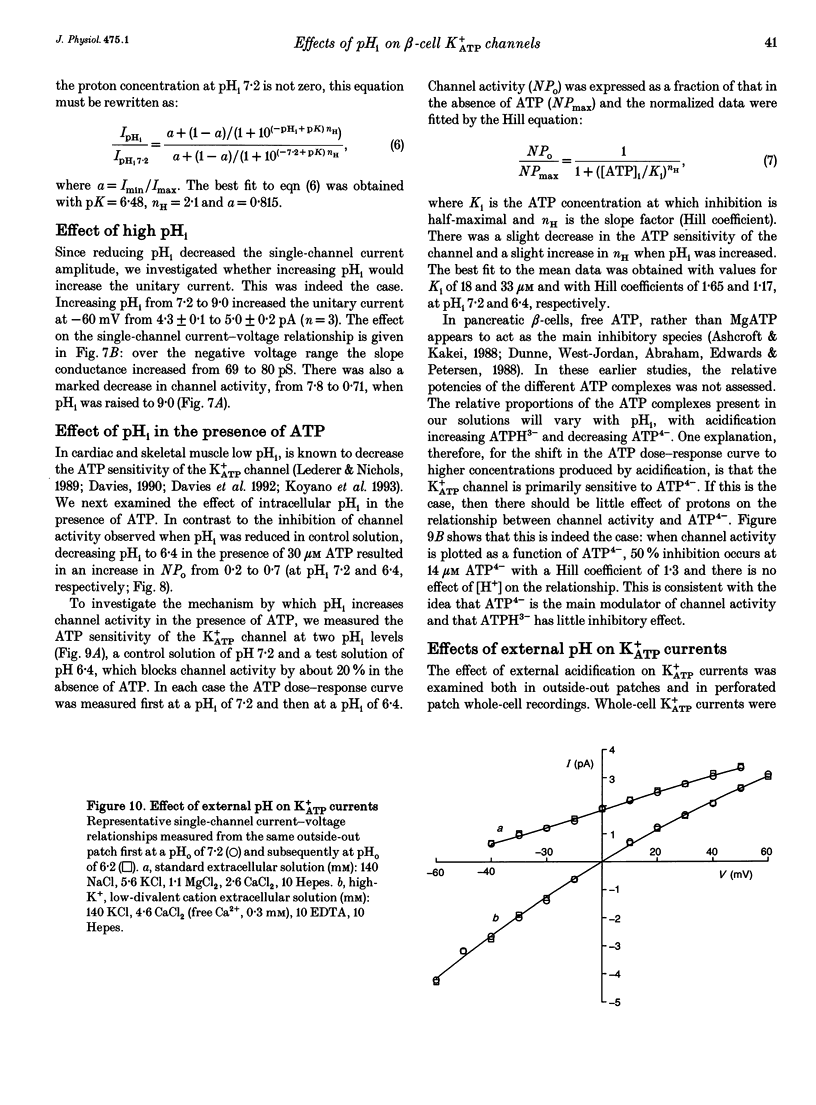
1. The effects of intracellular pH (pHi) on the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (K+ATP channel) from mouse pancreatic beta-cells were examined in inside-out patches exposed to symmetrical 140 mM K+ solutions. 2. The relationship between channel activity and pHi was described by the Hill equation with half-maximal inhibition (Ki) at pHi 6.25 and a Hill coefficient of 3.7. 3. Following exposure to pHi < 6.8, channel activity did not recover to its original level. Subsequent application of trypsin to the intracellular membrane surface restored channel activity to its initial level or above. 4. At -60 mV the relationship between pHi and the single-channel current amplitude was described by a modified Hill equation with a Hill coefficient of 2.1, half-maximal inhibition at pHi 6.48 and a maximum inhibition of 18.5%. 5. A decrease in pHi reduced the extent of channel inhibition by ATP: Ki was 18 microM at pH 7.2 and 33 microM at pH 6.4. The Hill coefficient was also reduced, being 1.65 at pH 7.2 and 1.17 at pH 6.4. 6. When channel activity was plotted as a function of ATP4- (rather than total ATP) there was no effect of pHi on the relationship. This suggests that ATP4- is the inhibitory ion species and that the effects of reducing pHi are due to the lowered concentration of ATP4-. 7. Changes in external pH had little effect on either single-channel or whole-cell K+ATP currents. 8. The effects of pHi do not support a role for H+ in linking glucose metabolism to K+ATP channel inhibition in pancreatic beta-cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Rorsman P. Direct evidence for opposite effects of D-glucose and D-glyceraldehyde on cytoplasmic pH of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Biosci Rep. 1986 Apr;6(4):355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01116422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Ashcroft S. J., Harrison D. E. Effects of 2-ketoisocaproate on insulin release and single potassium channel activity in dispersed rat pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:517–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kakei M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells: modulation by ATP and Mg2+ ions. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:349–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas J., Bassett A. L., Cameron J. S., Furukawa T., Myerburg R. J., Kimura S. Effect of H+ on ATP-regulated K+ channels in feline ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H755–H761. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daumas P., Andersen O. S. Proton block of rat brain sodium channels. Evidence for two proton binding sites and multiple occupancy. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jan;101(1):27–43. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. W. Modulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in skeletal muscle by intracellular protons. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):375–377. doi: 10.1038/343375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. W., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. The effect of intracellular pH on ATP-dependent potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:549–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Findlay I., Petersen O. H., Wollheim C. B. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in an insulin-secreting cell line are inhibited by D-glyceraldehyde and activated by membrane permeabilization. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(3):271–279. doi: 10.1007/BF01871181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., West-Jordan J. A., Abraham R. J., Edwards R. H., Petersen O. H. The gating of nucleotide-sensitive K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells can be modulated by changes in the ratio ATP4-/ADP3- and by nonhydrolyzable derivatives of both ATP and ADP. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):165–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01870928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. ATP maintains ATP-inhibited K+ channels in an operational state. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):238–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00580683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grapengiesser E., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Regulation of pH in individual pancreatic beta-cells as evaluated by fluorescence ratio microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Vereecke J., Carmeliet E. Intracellular protons inhibit inward rectifier K+ channel of guinea-pig ventricular cell membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Dec;422(3):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00376214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyano T., Kakei M., Nakashima H., Yoshinaga M., Matsuoka T., Tanaka H. ATP-regulated K+ channels are modulated by intracellular H+ in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:747–766. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Ashford M. L. ATP-sensitive K(+)-channel run-down is Mg2+ dependent. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jun 22;240(1298):397–410. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Nichols C. G. Nucleotide modulation of the activity of rat heart ATP-sensitive K+ channels in isolated membrane patches. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:193–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström P., Sehlin J. Effect of glucose on the intracellular pH of pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):887–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2180887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström P., Sehlin J. Effect of intracellular alkalinization on pancreatic islet calcium uptake and insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):199–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2390199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch A. M., Trebilcock R., Tomlinson S., Best L. Studies of the mechanism of activation of HIT-T15 cells by lactate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 31;1091(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90053-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Gillis K., Tabcharani J. Modulation of gating of a metabolically regulated, ATP-dependent K+ channel by intracellular pH in B cells of the pancreatic islet. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01870852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notsu T., Tanaka I., Takano M., Noma A. Blockade of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel by 5-hydroxydecanoate in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):702–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Shosaku T., Zünkler B. J., Trube G. Dual effects of ATP on K+ currents of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00581342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proks P., Ashcroft F. M. Modification of K-ATP channels in pancreatic beta-cells by trypsin. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jun;424(1):63–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00375103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin D. Y., Noma A. A new oil-gate concentration jump technique applied to inside-out patch-clamp recording. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H980–H984. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Qin D. Y., Noma A. ATP-dependent decay and recovery of K+ channels in guinea pig cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):H45–H50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.1.H45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Hescheler J. Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00583879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


