Abstract
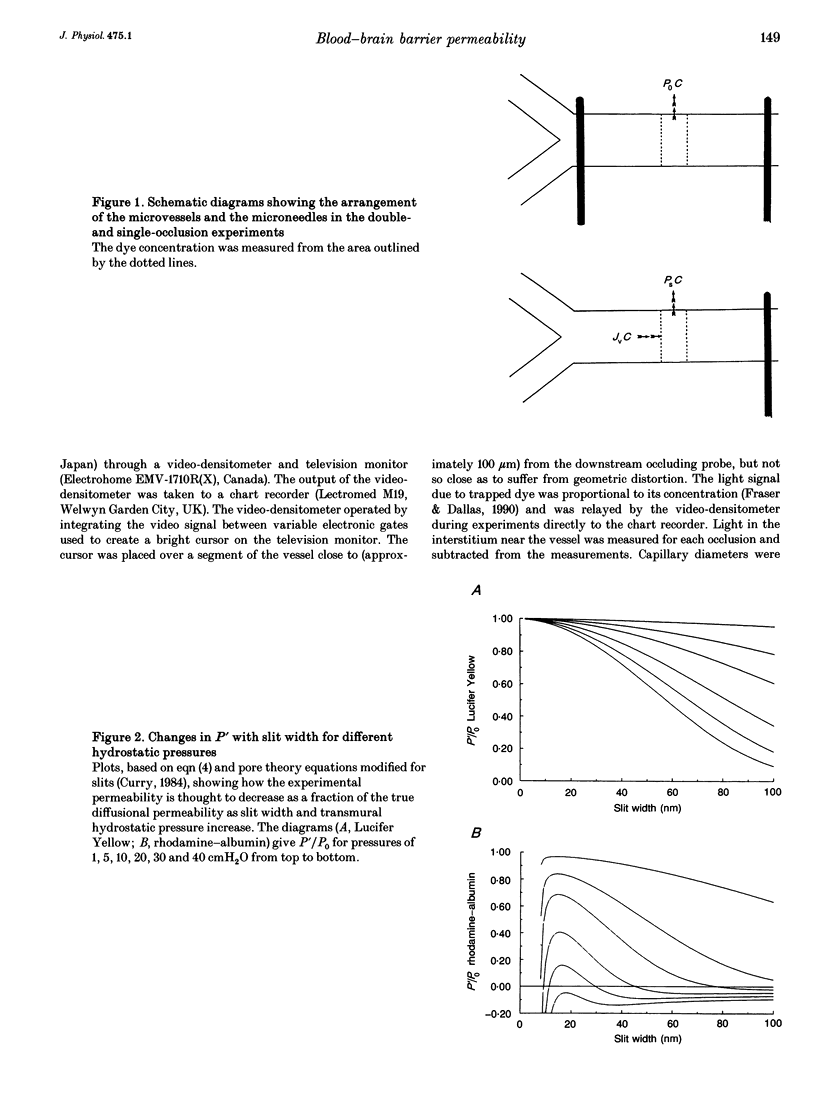
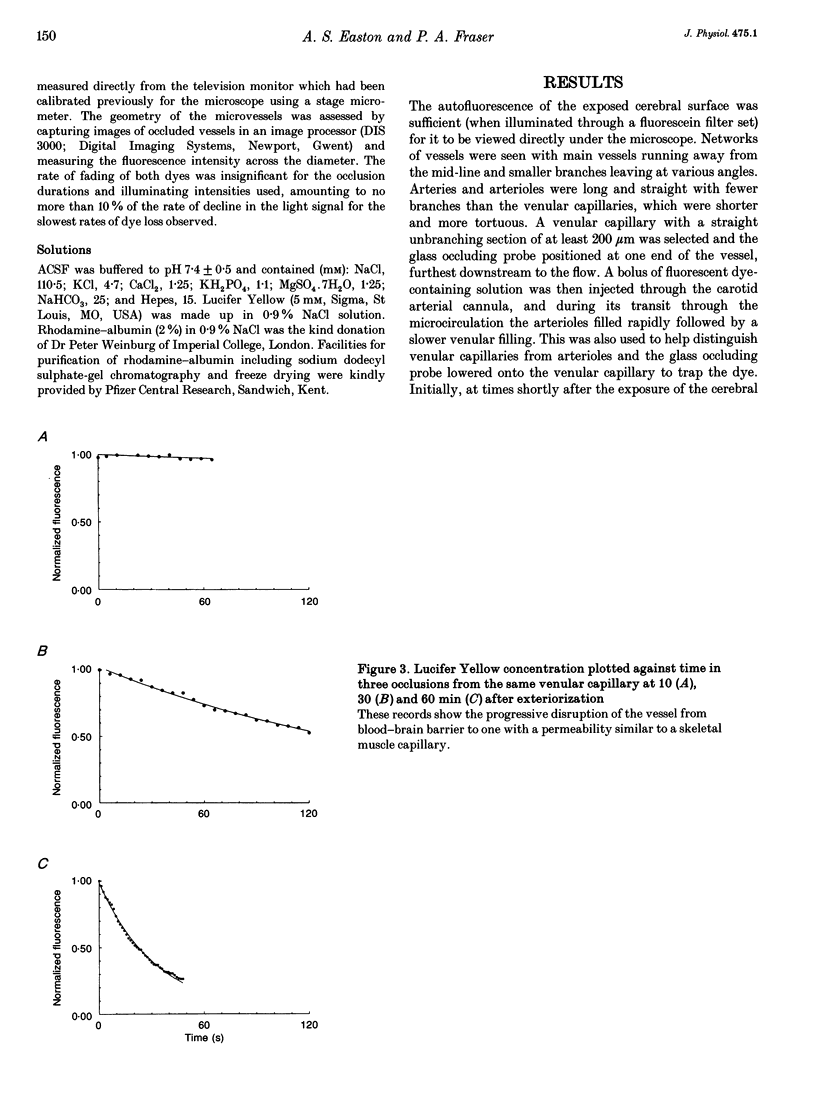
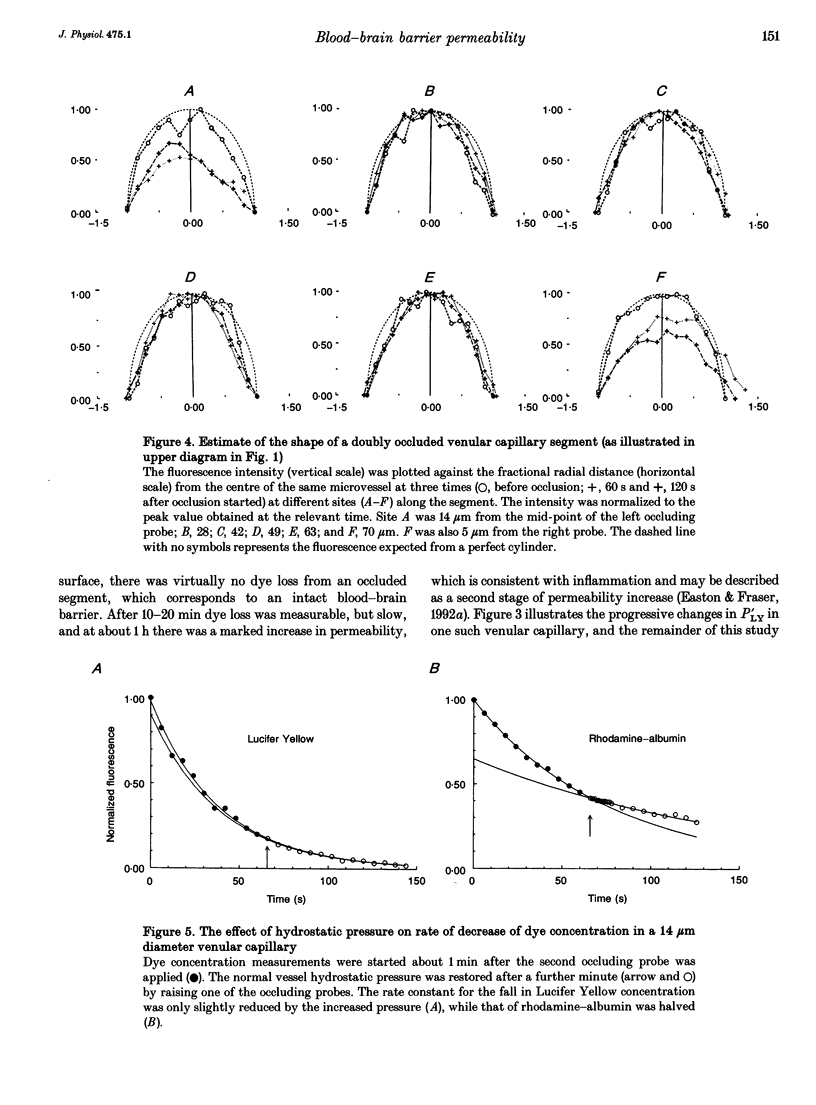
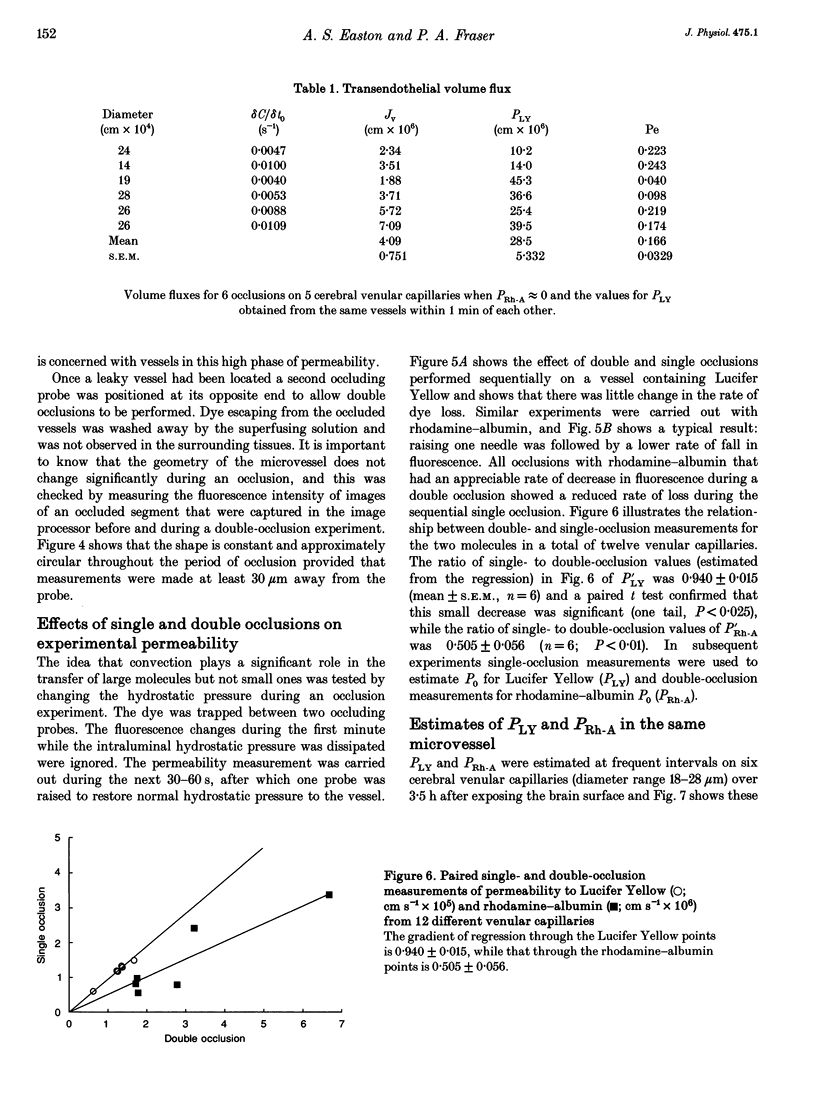
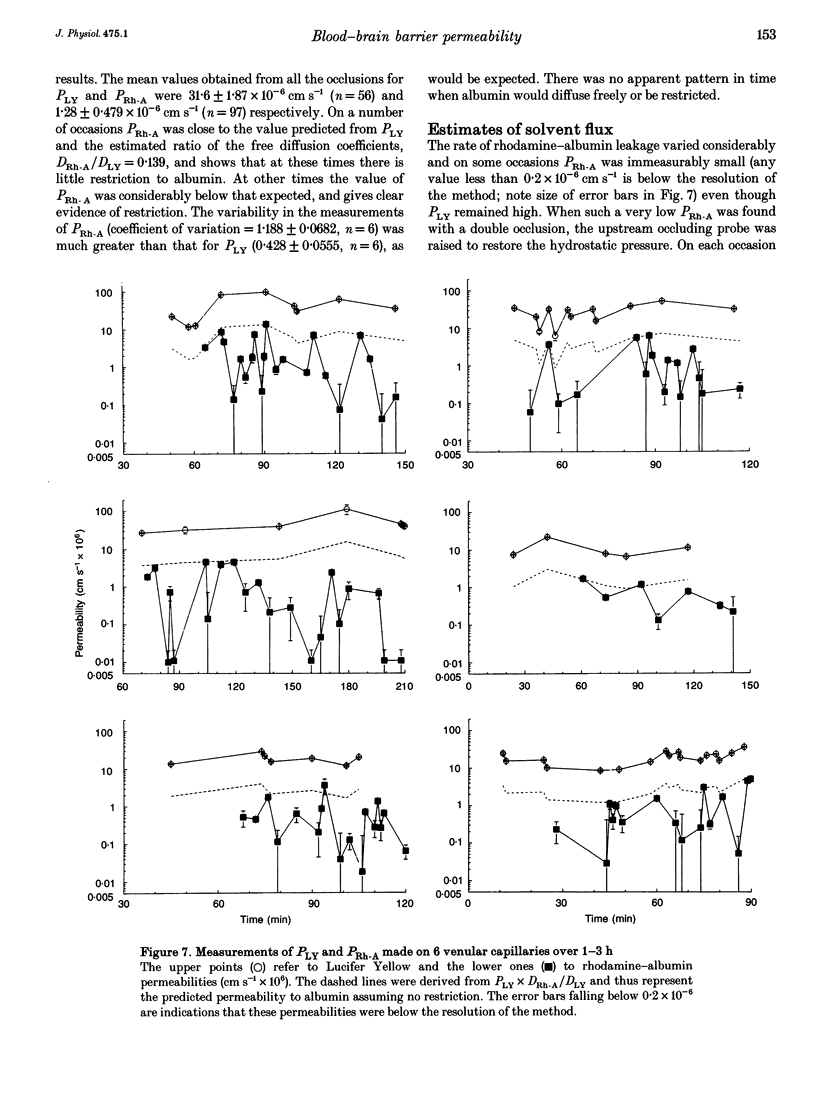
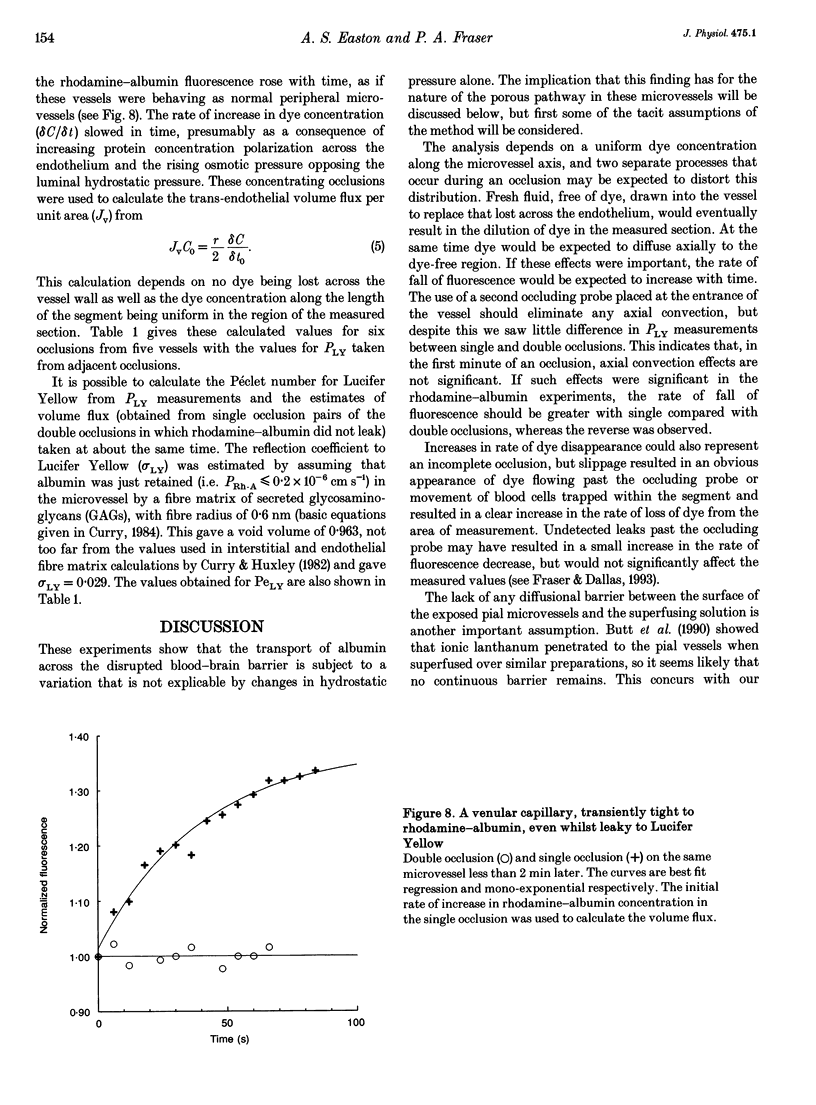
1. The possibility of restricted diffusion of macromolecules in single cerebral venular capillaries that have become leaky due to inflammation was investigated by comparing the permeabilities to Lucifer Yellow (457 Da; PLY) and rhodamine-labelled albumin (69 kDa; PRh-A). 2. The dyes were trapped between two micro-occlusion probes and the permeabilities were measured from the rates of decrease in dye fluorescence at low intraluminal hydrostatic pressure. 3. Removal of one probe had little effect on PLY but did reduce PRh-A, consistent with the influence of convection on diffusion through 22 nm wide transendothelial slits 1 micron deep. 4. Direct comparisons were made over time between PLY and PRh-A in six vessels while hydrostatic pressure effects were controlled. In all vessels PRh-A:PLY varied from being similar to the ratio of the free diffusion coefficients to virtually zero even though PLY remained high. The question of the source of this variable restriction to albumin is discussed in terms of the secretion and sloughing of glycosaminoglycans and the possible role of transient formation of transendothelial gaps.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYROM F. B. The pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy and its relation to the malignant phase of hypertension; experimental evidence from the hypertensive rat. Lancet. 1954 Jul 31;267(6831):201–211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)91821-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt A. M., Jones H. C., Abbott N. J. Electrical resistance across the blood-brain barrier in anaesthetized rats: a developmental study. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:47–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMEDSON C. J., HARTELIUS H., HOLMBERG G. The influence of carbon dioxide inhalation on the cerebral vascular permeability to trypan blue (the blood-brain barrier). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;42(2):137–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENTE C. D., HOLST E. A. Pathological changes in neurons, neuroglia, and blood-brain barrier induced by x-irradiation of heads of monkeys. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Jan;71(1):66–79. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02320370068005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough G., Michel C. C., Phillips M. E. Inflammatory changes in permeability and ultrastructure of single vessels in the frog mesenteric microcirculation. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:99–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough G., Michel C. C. Quantitative comparisons of hydraulic permeability and endothelial intercellular cleft dimensions in single frog capillaries. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:563–576. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E. A hydrodynamic description of the osmotic reflection coefficient with application to the pore theory of transcapillary exchange. Microvasc Res. 1974 Sep;8(2):236–252. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(74)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E., Joyner W. L., Rutledge J. C. Graded modulation of frog microvessel permeability to albumin using ionophore A23187. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):H587–H598. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.2.H587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E., Michel C. C. A fiber matrix model of capillary permeability. Microvasc Res. 1980 Jul;20(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. R., Huxley V. H. Comparison of the capillary membrane properties determining fluid exchange in single capillaries and whole organs. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1982;1(4):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., West K. A. Experimental cerebral heat lesions produced by trephine craniotomy in rabbits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1972;80(1):134–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. E., Caldwell R. B. The retinal microvasculature of spontaneously diabetic BB rats: structure and luminal surface properties. Microvasc Res. 1990 Jan;39(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(90)90056-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. A., Dallas A. D., Davies S. Measurement of filtration coefficient in single cerebral microvessels of the frog. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. A., Dallas A. D. Permeability of disrupted cerebral microvessels in the frog. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:619–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O., Asano T., Koide T., Takakura K. Ischemic brain edema following occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in the rat. I: The time courses of the brain water, sodium and potassium contents and blood-brain barrier permeability to 125I-albumin. Stroke. 1985 Jan-Feb;16(1):101–109. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B., Li C. L., Olsson Y., Klatzo I. The effect of acute arterial hypertension on the blood-brain barrier to protein tracers. Acta Neuropathol. 1970;16(2):117–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00687666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa T., Cahn R., Juhler M., Goping G., Campbell G., Klatzo I. Role of extracellular proteins in the dynamics of vasogenic brain edema. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;66(1):3–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00698288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa T., Ting P., Martinez H., Klatzo I. The biphasic opening of the blood-brain barrier to proteins following temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;68(2):122–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00688633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick J. R. Flow through interstitium and other fibrous matrices. Q J Exp Physiol. 1987 Oct;72(4):409–437. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1987.sp003085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossinsky A. S., Pluta R., Song M. J., Badmajew V., Moretz R. C., Wisniewski H. M. Mechanisms of inflammatory cell attachment in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: a scanning and high-voltage electron microscopic study of the injured mouse blood-brain barrier. Microvasc Res. 1991 May;41(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(91)90030-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal C. R., Michel C. C. Transcellular openings through microvascular walls in acutely inflamed frog mesentery. Exp Physiol. 1992 Nov;77(6):917–920. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I. Effect of concentrated solutions on blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jul;219(1):270–274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.1.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Rapoport S. I. Size selectivity of blood-brain barrier permeability at various times after osmotic opening. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):R459–R466. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.3.R459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidley J. W., Wissig S. L. Basement membrane of central nervous system capillaries lacks ruthenium red-staining sites. Microvasc Res. 1986 Nov;32(3):300–314. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(86)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smaje L. H., Fraser P. A., Clough G. The distensibility of single capillaries and venules in the cat mesentery. Microvasc Res. 1980 Nov;20(3):358–370. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Graham D. I., McCulloch J., Teasdale G. M. Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: 1. Description of technique and early neuropathological consequences following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):53–60. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


