Abstract
1. Single acetylcholine receptor (AChR) channel openings, detected by the whole-cell patch clamp technique, were used to monitor quantal and non-quantal ACh release at synapses in 1- and 2-day-old co-cultures of Xenopus embryonic motoneurons and muscle cells. motoneuron growth cones in ways that presumably reflect muscle-nerve inductive influences and the development of neurotransmitter release mechanisms. 2. Miniature endplate currents (MEPCs) occurred at a mean frequency of approximately 0.6 s-1 with a skewed distribution and mean amplitude of about twenty channel openings. In addition, occasional brief episodes of rapid deviations in the baseline were observed in some cells, with mean amplitudes of 4-8 pA and durations of a few hundred milliseconds. However, these episodes did not closely resemble summated openings of AChR channels. Moreover, where tested, these episodes were not blocked by curare; and comparable episodes were seen in an uninnervated myocyte. Thus they appear not to reflect ACh release from the nerve terminal. 3. Single-channel openings that might have been responses to non-quantal release of ACh were observed at rates of 0.9-12.3 min-1 (mean 3.0 min-1), only 1-5 times the rate of spontaneous AChR channel openings in uninnervated myocytes (mean 1.4 min-1). 4. We conclude that there is no significant non-quantal ACh leak from the presynaptic contacts in these immature synapses under these culture conditions. This is in disagreement with other, less direct, experimental reports, but consistent with findings in mature frog motor nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF

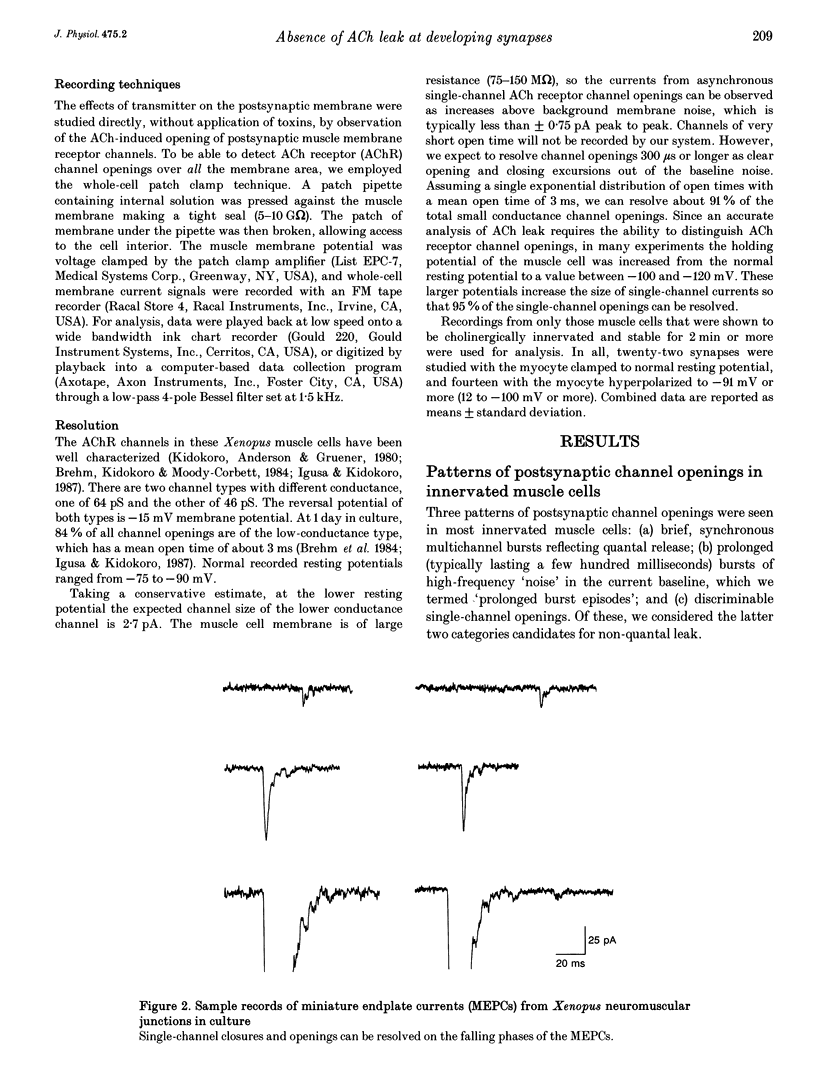
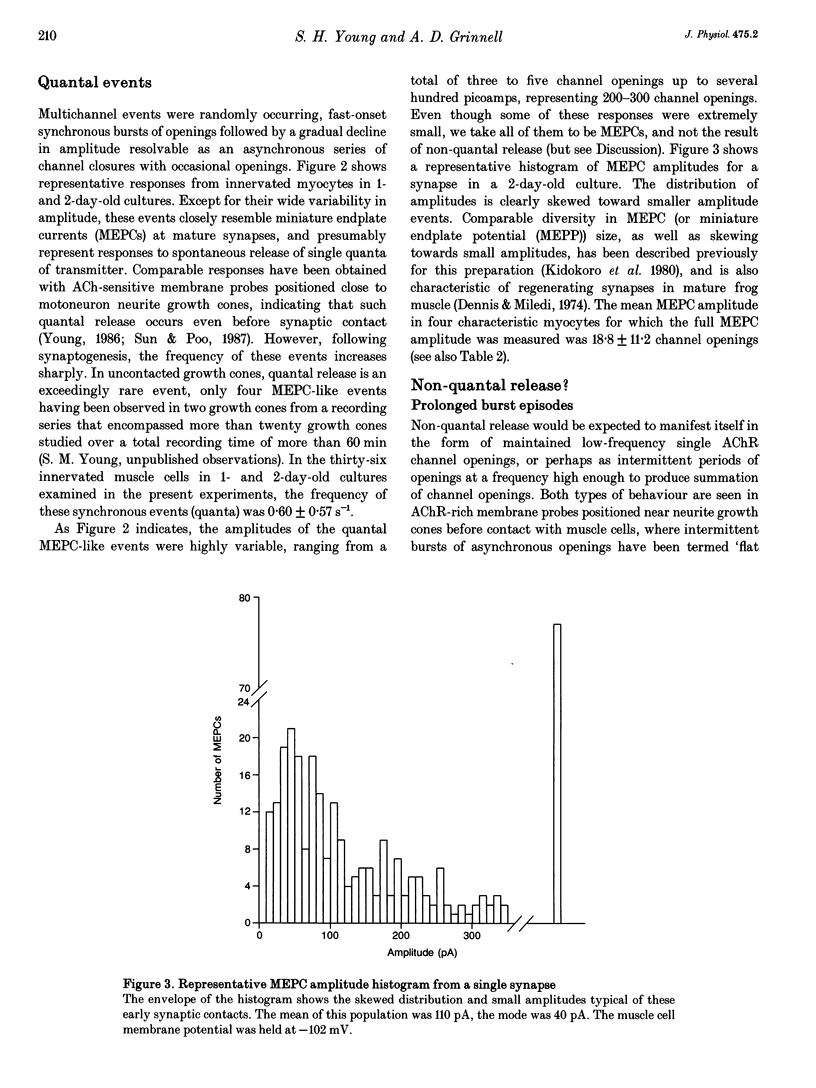

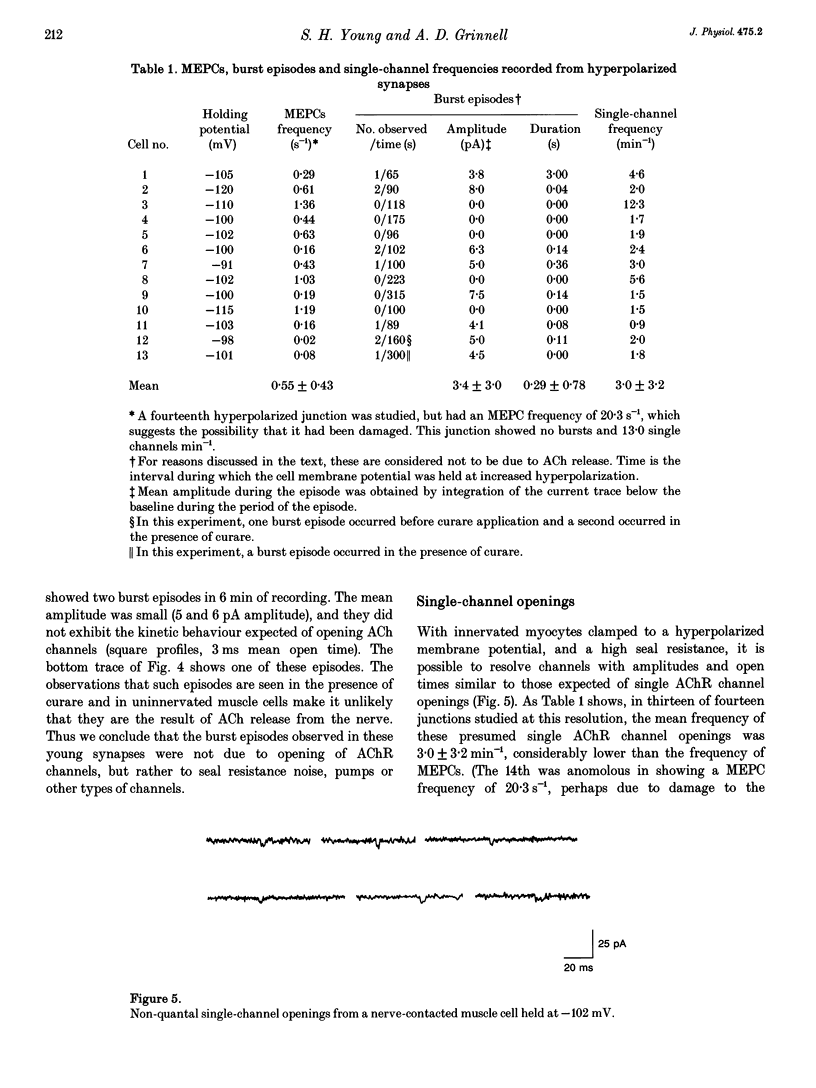




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brehm P., Kidokoro Y., Moody-Corbett F. Acetylcholine receptor channel properties during development of Xenopus muscle cells in culture. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:203–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow I., Poo M. M. Release of acetylcholine from embryonic neurons upon contact with muscle cell. J Neurosci. 1985 Apr;5(4):1076–1082. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-04-01076.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Miledi R. Characteristics of transmitter release at regenerating frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):571–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding R. Comparison of morphology and physiology of synapses formed at ectopic and original endplate sites in frog muscle. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 16;253(1-2):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90673-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolezal V., Vyskocil F., Tucek S. Decrease of the spontaneous non-quantal release of acetylcholine from the phrenic nerve in botulinum-poisoned rat diaphragm. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Jun 1;397(4):319–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00580268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Dolezal V., Tucek S., Zemková H., Vyskocil F. Is an acetylcholine transport system responsible for nonquantal release of acetylcholine at the rodent myoneural junction? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Miniature end-plate currents and potentials generated by quanta of acetylcholine in glycerol-treated toad sartorius fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell A. D., Gundersen C. B., Meriney S. D., Young S. H. Direct measurement of ACh release from exposed frog nerve terminals: constraints on interpretation of non-quantal release. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:225–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harish O. E., Poo M. M. Retrograde modulation at developing neuromuscular synapses: involvement of G protein and arachidonic acid cascade. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1201–1209. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90077-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igusa Y., Kidokoro Y. Two types of acetylcholine receptor channels in developing Xenopus muscle cells in culture: further kinetic analyses. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:271–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Does the motor nerve impulse evoke 'non-quantal' transmitter release? Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 May 7;212(1186):131–137. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Transmitter leakage from motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Feb 11;196(1122):59–72. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Anderson M. J., Gruener R. Changes in synaptic potential properties during acetylcholine receptor accumulation and neurospecific interactions in Xenopus nerve-muscle cell culture. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):464–483. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Gruener R. Distribution and density of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites on innervated and noninnervated Xenopus muscle cells in culture. Dev Biol. 1982 May;91(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meriney S. D., Young S. H., Grinnell A. D. Constraints on the interpretation of nonquantal acetylcholine release from frog neuromuscular junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F., Silver A. The spontaneous release of acetylcholine from the denervated hemidiaphragm of the rat. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):117–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolsky E. E., Voronin V. A., Vyskocil F. Kinetic differences in the effect of calcium on quantal and non-quantal acetylcholine release at the murine diaphragm. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Feb 25;123(2):192–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90928-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M. M., Poo W. J., Lam J. W. Lateral electrophoresis and diffusion of Concanavalin A receptors in the membrane of embryonic muscle cell. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):483–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. A., Poo M. M. Evoked release of acetylcholine from the growing embryonic neuron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2540–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. A., Poo M. M. Non-quantal release of acetylcholine at a developing neuromuscular synapse in culture. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):634–642. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00634.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Vyskocil F. Changes in total and quantal release of acetylcholine in the mouse diaphragm during activation and inhibition of membrane ATPase. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyskocil F., Illés P. Non-quantal release of transmitter at mouse neuromuscular junction and its dependence on the activity of Na+-K+ ATP-ase. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Sep 16;370(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00585542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyskocil F., Nikolsky E., Edwards C. An analysis of the mechanisms underlying the non-quantal release of acetylcholine at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Neuroscience. 1983 Jun;9(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Z. P., Poo M. M. Initial events in the formation of neuromuscular synapse: rapid induction of acetylcholine release from embryonic neuron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7069–7073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. H., Poo M. M. Spontaneous release of transmitter from growth cones of embryonic neurones. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):634–637. doi: 10.1038/305634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. H. Spontaneous release of transmitter from the growth cones of Xenopus neurons in vitro: the influence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. P., Van der Kloot W. Non-quantal acetylcholine release at mouse neuromuscular junction: effects of elevated quantal release and aconitine. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Sep 4;117(1-2):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90128-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemková H., Vyskocil F. Effect of Mg2+ on non-quantal acetylcholine release at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Sep 11;103(3):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



