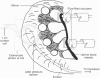
Abstract
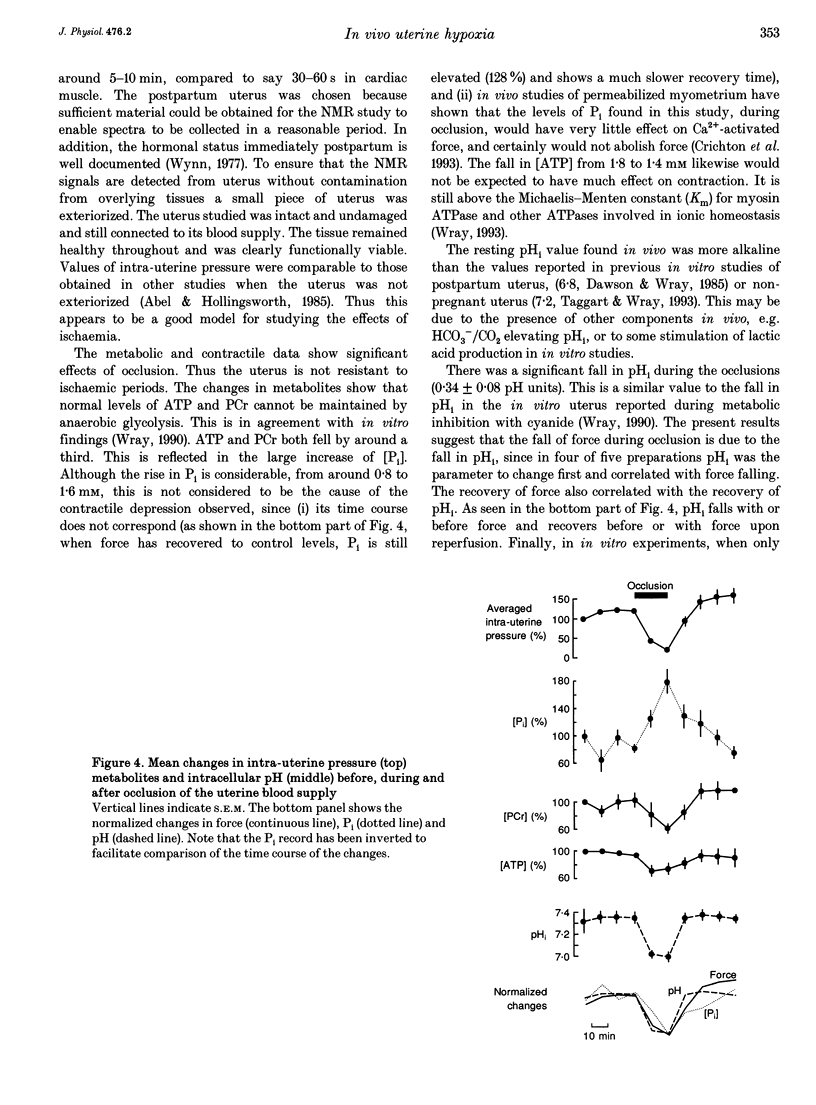
There are no data concerning the functional or metabolic effects of hypoxia in vivo in smooth muscle. We have therefore used 31P-NMR spectroscopy and intra-uterine pressure measurements to examine simultaneously, in vivo, the effect of ischaemia on uterine metabolites, intracellular pH (pHi) and force. A 1-2 cm portion of uterus from day 1 postpartum anaesthetized rats was exteriorized and an NMR surface coil placed on it. A balloon catheter in the uterine lumen recorded intra-uterine pressure changes from the same area. Reversible occluders were placed around the uterine artery. Occlusion produced a decrease and then abolition of contractions, within 10 min. In four of five animals contraction was abolished within 2 min. Upon reperfusion force was rapidly restored (1 min), in all preparations. The mean level of force was significantly above control (pre-occlusion) 20-30 min after reperfusion. The NMR data showed a significant fall in [ATP] (28%) and [phosphocreatine] (34%) during occlusion. Inorganic phosphate doubled in concentration during this period. Metabolites recovered slowly upon reperfusion, taking 20-30 min to return to pre-occlusion levels. The mean pHi fell from 7.32 to 7.00 upon occlusion and was rapidly reversed upon reperfusion. The changes in pHi closely correlated with the changes in uterine force. Decreases of pHi of a similar magnitude in vitro have previously been shown to abolish contractions; thus it is suggested that during ischaemia in vivo the depression of contraction is caused by the large fall in pHi.
Full text
PDF
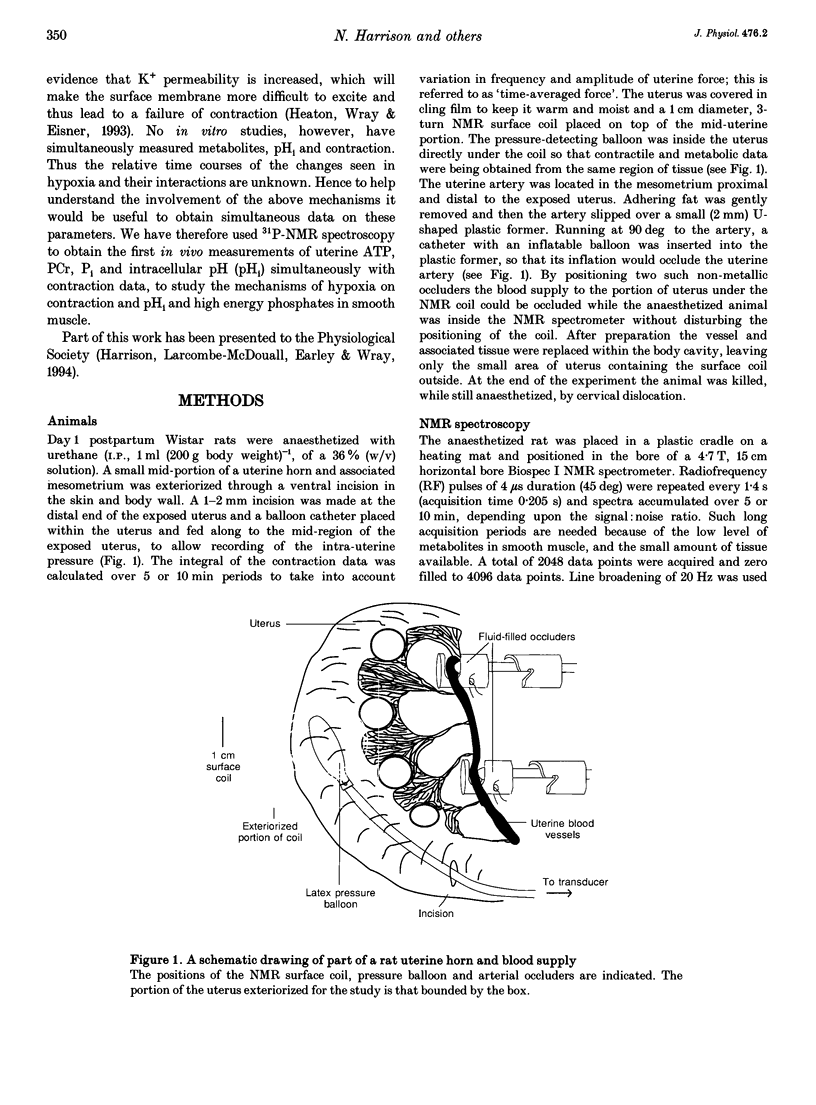
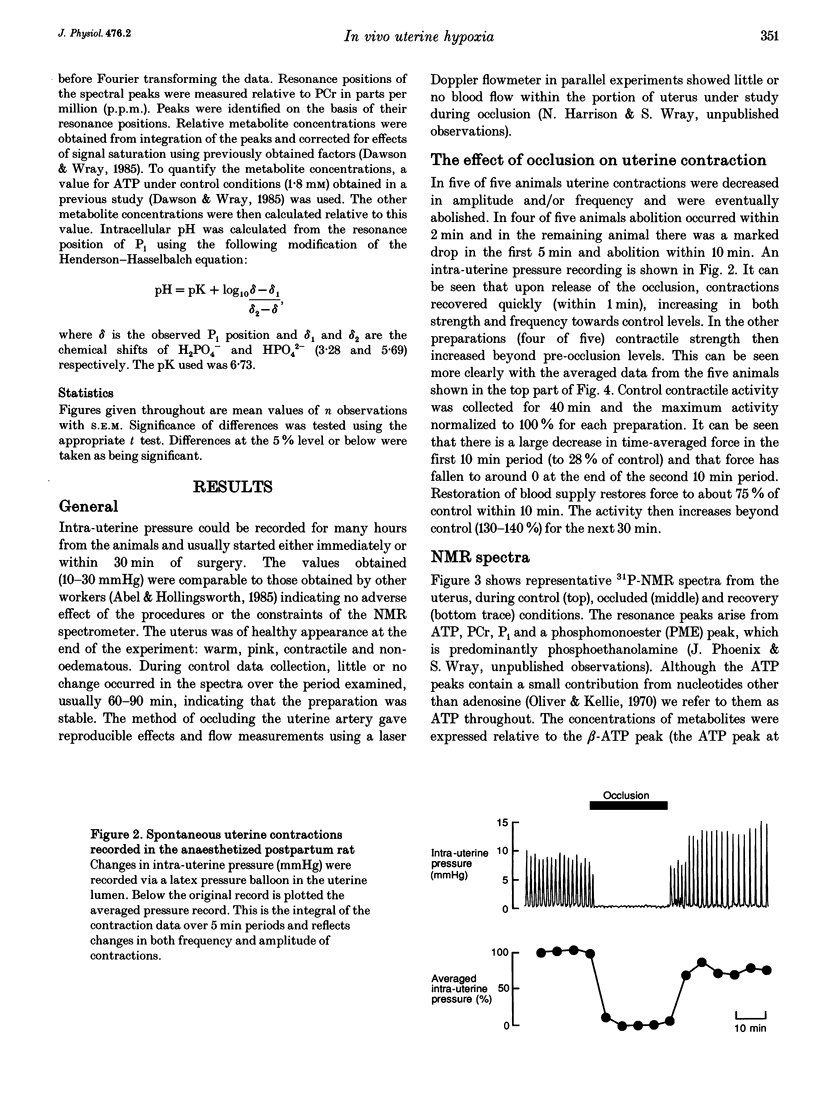
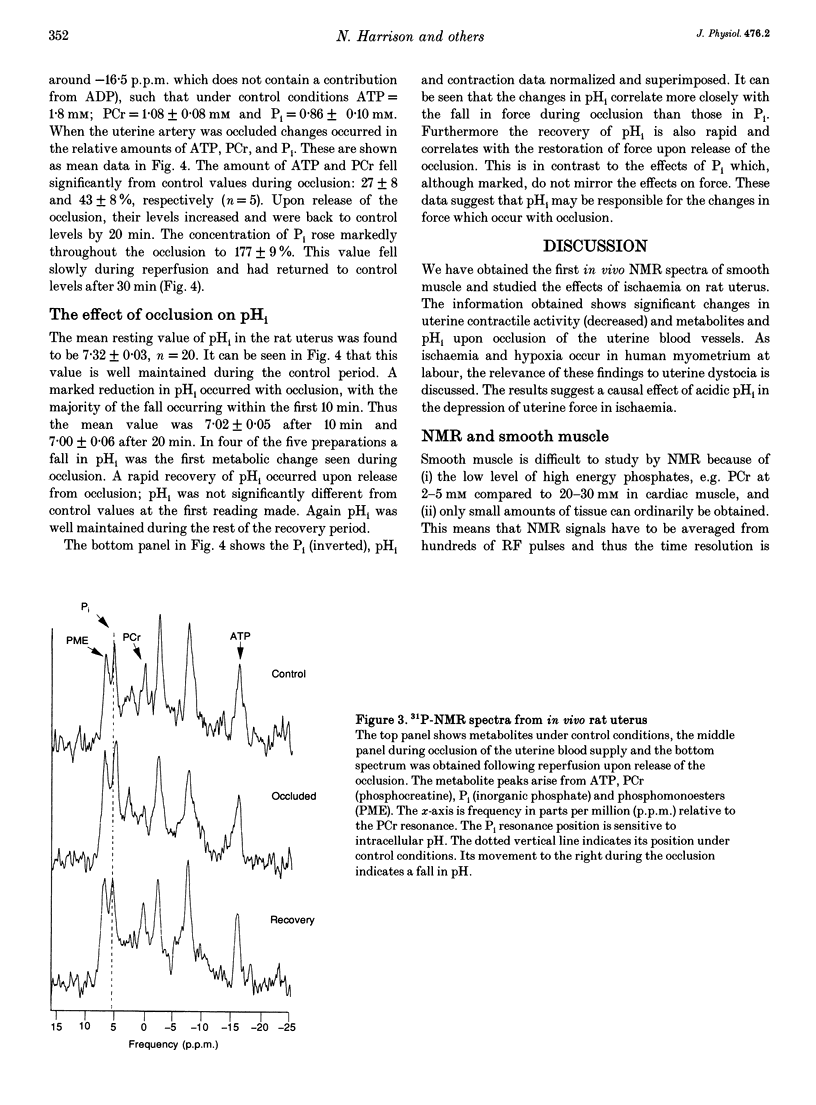

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel M. H., Hollingsworth M. The potencies and selectivities of four calcium antagonists as inhibitors of uterine contractions in the rat in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):263–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton C. A., Taggart M. J., Wray S., Smith G. L. Effects of pH and inorganic phosphate on force production in alpha-toxin-permeabilized isolated rat uterine smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:629–645. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Wray S. The effects of pregnancy and parturition on phosphorus metabolites in rat uterus studied by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiss F. C., Jr Effect of labor on uterine blood flow. Observations on gravid ewes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Dec 1;93(7):917–923. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(65)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton R. C., Wray S., Eisner D. A. Effects of metabolic inhibition and changes of intracellular pH on potassium permeability and contraction of rat uterus. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:43–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Kellie A. E. The effects of oestradiol on the acid-soluble nucleotides of rat uterus. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):187–191. doi: 10.1042/bj1190187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phoenix J., Wray S. Changes in frequency and force production of the human myometrium with alteration of pH and metabolism. J Reprod Fertil. 1993 Mar;97(2):507–512. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0970507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart M., Wray S. Simultaneous measurement of intracellular pH and contraction in uterine smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jun;423(5-6):527–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00374951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S., Duggins K., Iles R., Nyman L., Osman V. The effects of metabolic inhibition and acidification on force production in the rat uterus. Exp Physiol. 1992 Mar;77(2):307–319. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. The effects of metabolic inhibition on uterine metabolism and intracellular pH in the rat. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:411–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. Uterine contraction and physiological mechanisms of modulation. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C1–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]