Abstract
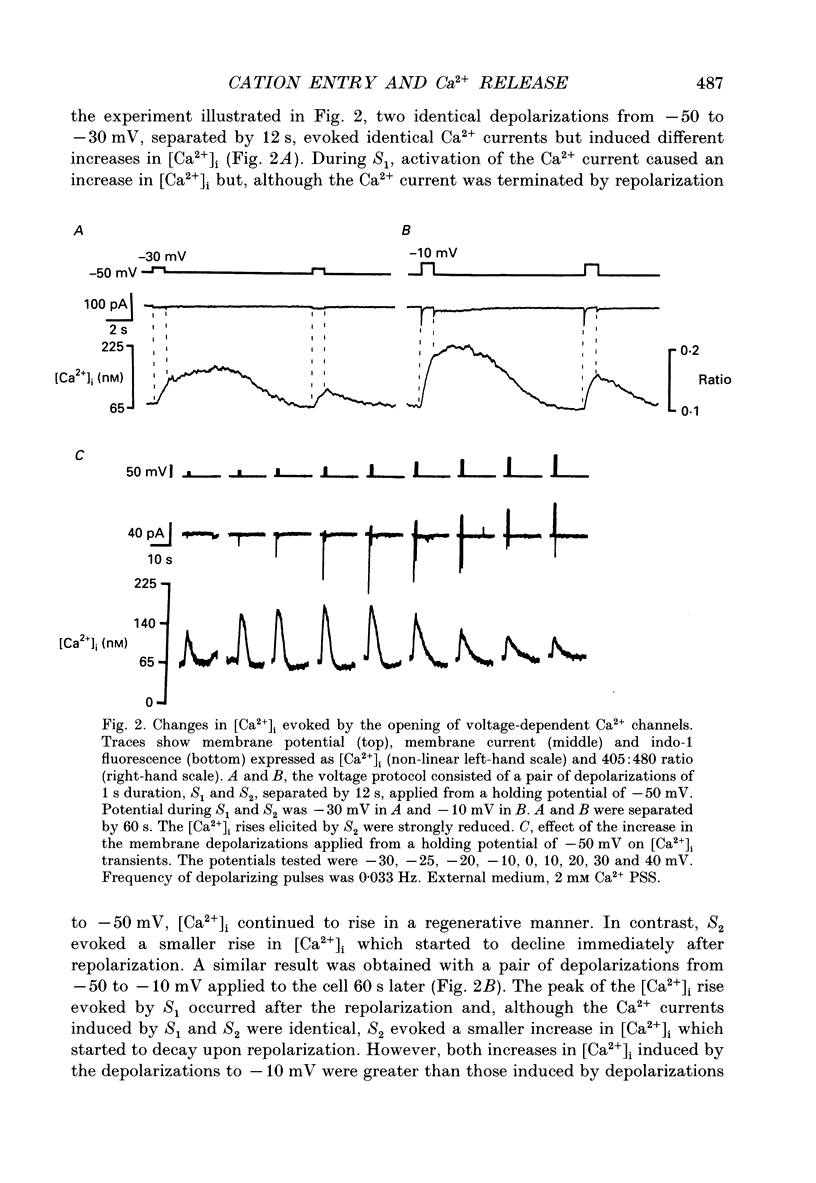
1. Changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) induced by membrane depolarizations were investigated using indo-1 microspectrofluorimetry in single patch-clamped smooth muscle cells of rat portal vein at room temperature (20-21 degrees C) and in the presence of 2 mM Ca2+. 2. During a 1 s depolarization from -50 to -30 mV [Ca2+]i rose, but, although the Ca2+ current was terminated by repolarization to -50 mV, [Ca2+]i continued to increase in a regenerative manner. The delay between the end of the voltage step and the peak of the [Ca2+]i rise was reduced by increasing the depolarization. 3. When a second identical depolarization was rapidly applied (8-13s) after the first one, it induced an identical Ca2+ current but a smaller increase in [Ca2+]i which started to decay upon repolarization. 4. A low concentration of caffeine (0.05 mM), applied to cells showing a small depolarization-induced [Ca2+]i transient which reached a peak at the end of the voltage step, produced an increase in amplitude and in duration of the [Ca2+]i rise without changing the amplitude of the depolarization-induced Ca2+ current. 5. The depolarization-induced [Ca2+]i rise was shortened and reduced in amplitude after noradrenaline- (NA 10 microM) or caffeine- (5 mM) induced release of Ca2+ store and when the patch pipette solution contained ryanodine (100 microM). Under these conditions, the depolarization-induced [Ca2+]i transient was maximal at the end of the voltage step and declined immediately when the membrane was repolarized at -50 mV. 6. Experiments were done by replacing extracellular Ca2+ by Sr2+. Depolarization-induced Sr2+ entry through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels could evoke an increase in indo-1 fluorescence which occurred after the termination of the voltage step. This delayed component of fluorescence increase displayed properties similar to those of the regenerative [Ca2+]i rise recorded in the Ca(2+)-containing solution. 7. The inefficiency of the second of two successive depolarizations to produce the delayed component of [Ca2+]i rise was not due to the emptiness of the intracellular Ca2+ store since, under these conditions, caffeine was still able to induce a Ca2+ release. 8. It is concluded that depolarization-evoked Ca2+ or Sr2+ entry through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels induced the release of Ca2+ from an intracellular store, which could occur in a regenerative manner, independent of the termination of the triggering current.
Full text
PDF









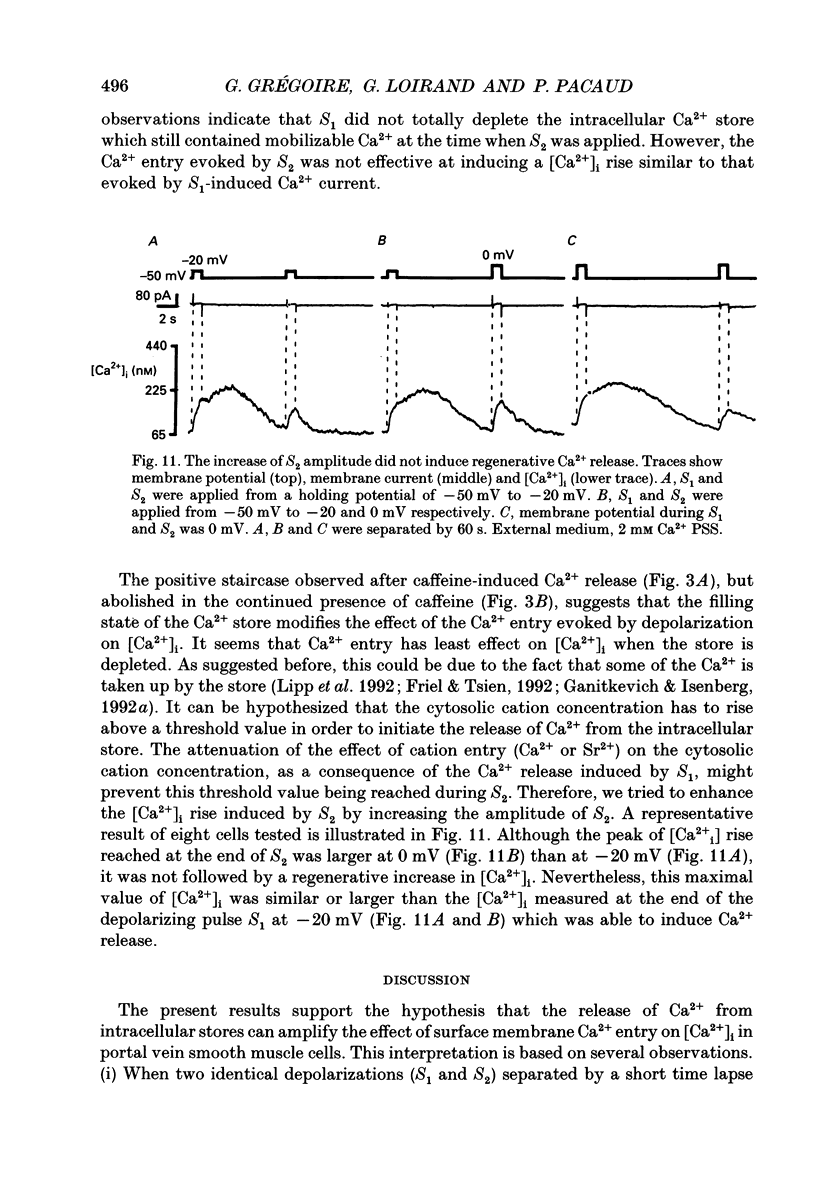




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
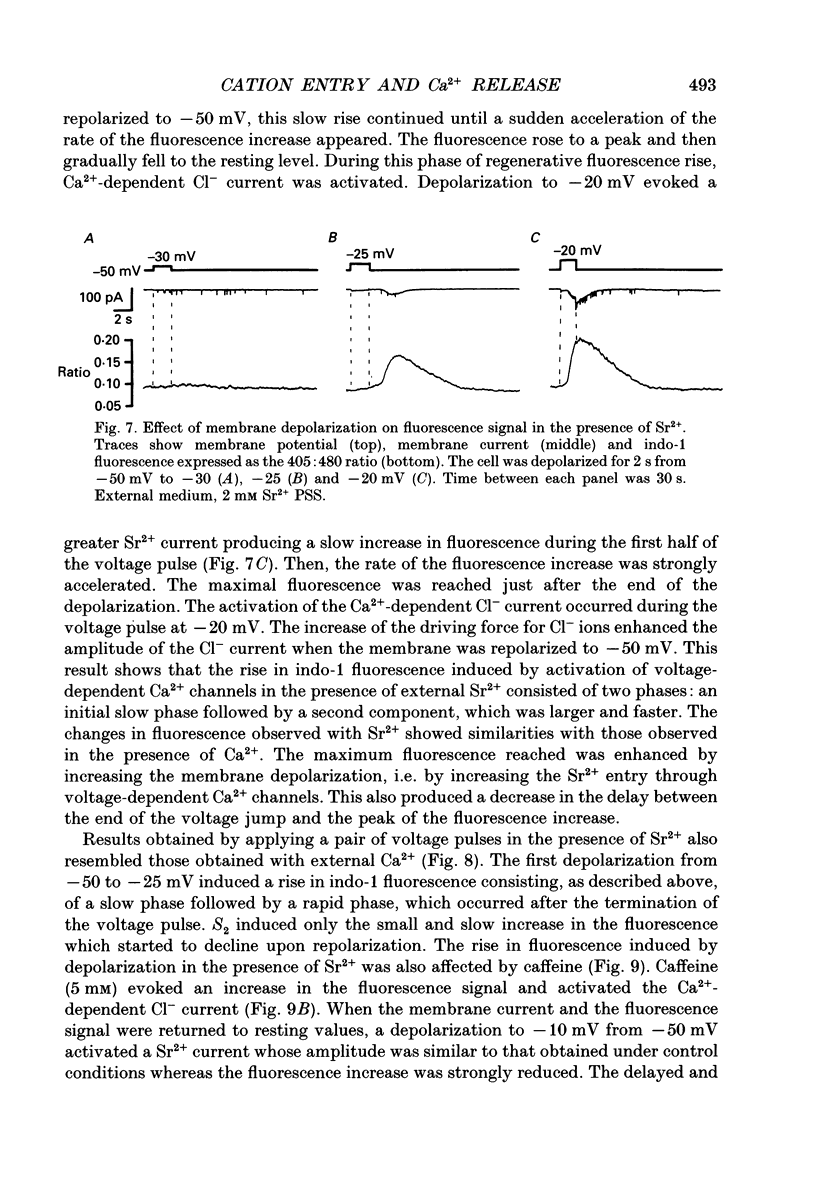
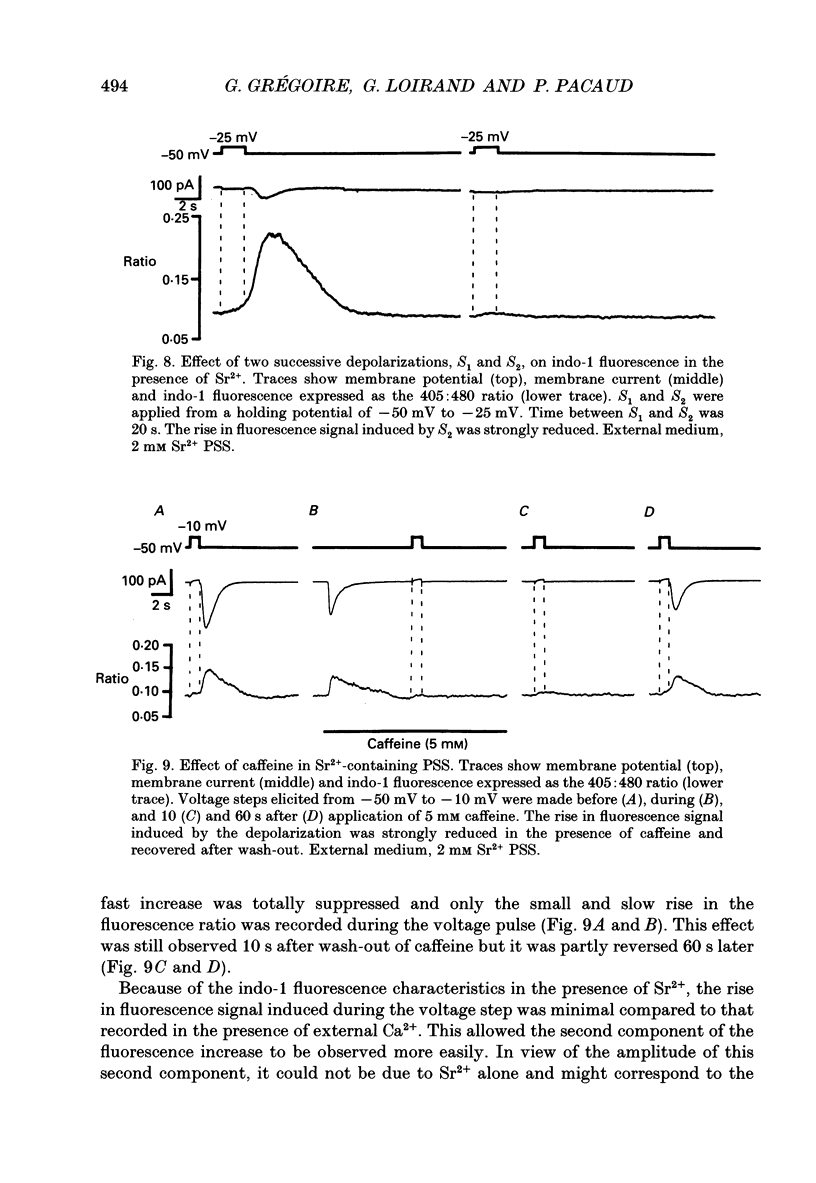
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Pacaud P., Loirand G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Pharmacological block of Ca(2+)-activated Cl- current in rat vascular smooth muscle cells in short-term primary culture. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Dec;419(6):553–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00370294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Mechanism of release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Agonist-induced [Ca2+]i waves and Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in mammalian vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):H576–H586. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.2.H576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Cleemann L., Morad M. Epinephrine enhances Ca2+ current-regulated Ca2+ release and Ca2+ reuptake in rat ventricular myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):2009–2013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Tsien R. W. A caffeine- and ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ store in bullfrog sympathetic neurones modulates effects of Ca2+ entry on [Ca2+]i. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori T., Jencks W. P. The kinetics for the phosphoryl transfer steps of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase are the same with strontium and with calcium bound to the transport sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18466–18474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Isenberg G. Caffeine-induced release and reuptake of Ca2+ by Ca2+ stores in myocytes from guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:99–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V. Y., Isenberg G. Contribution of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release to the [Ca2+]i transients in myocytes from guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:119–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist J. S., Belcastro A. N., Katz S. Intraluminal Ca2+ dependence of Ca2+ and ryanodine-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20850–20856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann-Frank A., Darling E., Meissner G. Functional characterization of the Ca(2+)-gated Ca2+ release channel of vascular smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00550873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. D., Hering S., Bolton T. B. The action of caffeine on inward barium current through voltage-dependent calcium channels in single rabbit ear artery cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):462–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00370755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Calcium-induced calcium release mechanism in guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Aug;94(2):363–383. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F. The path of calcium in cytosolic calcium oscillations: a unifying hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9883–9887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Effects of caffeine on calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:599–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Inositol trisphosphate releases stored calcium to block voltage-dependent calcium channels in single smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jun;418(5):437–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00497770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Pott L., Callewaert G., Carmeliet E. Calcium transients caused by calcium entry are influenced by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in guinea-pig atrial myocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:321–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Imaging of cytosolic Ca2+ transients arising from Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ channels in sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loirand G., Pacaud P., Baron A., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Large conductance calcium-activated non-selective cation channel in smooth muscle cells isolated from rat portal vein. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:461–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P. The initiation of calcium release following muscarinic stimulation in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:665–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiaen L., De Smedt H., Droogmans G., Casteels R. Ca2+ release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is a steady-state phenomenon controlled by luminal Ca2+ in permeabilized cells. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):599–602. doi: 10.1038/357599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. E., Nelson K. E. Intra- and extraluminal sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane regulatory sites for Ca2(+)-induced Ca2+ release. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):292–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Baron A., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Ca2+ channel activation and membrane depolarization mediated by Cl- channels in response to noradrenaline in vascular myocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):1000–1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Grégoire G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Noradrenaline-activated heparin-sensitive Ca2+ entry after depletion of intracellular Ca2+ store in portal vein smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3866–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Noradrenaline activates a calcium-activated chloride conductance and increases the voltage-dependent calcium current in cultured single cells of rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):139–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Simon B. J. Inactivation of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:727–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Williams A. J. Divalent cation conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):479–493. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


