Abstract
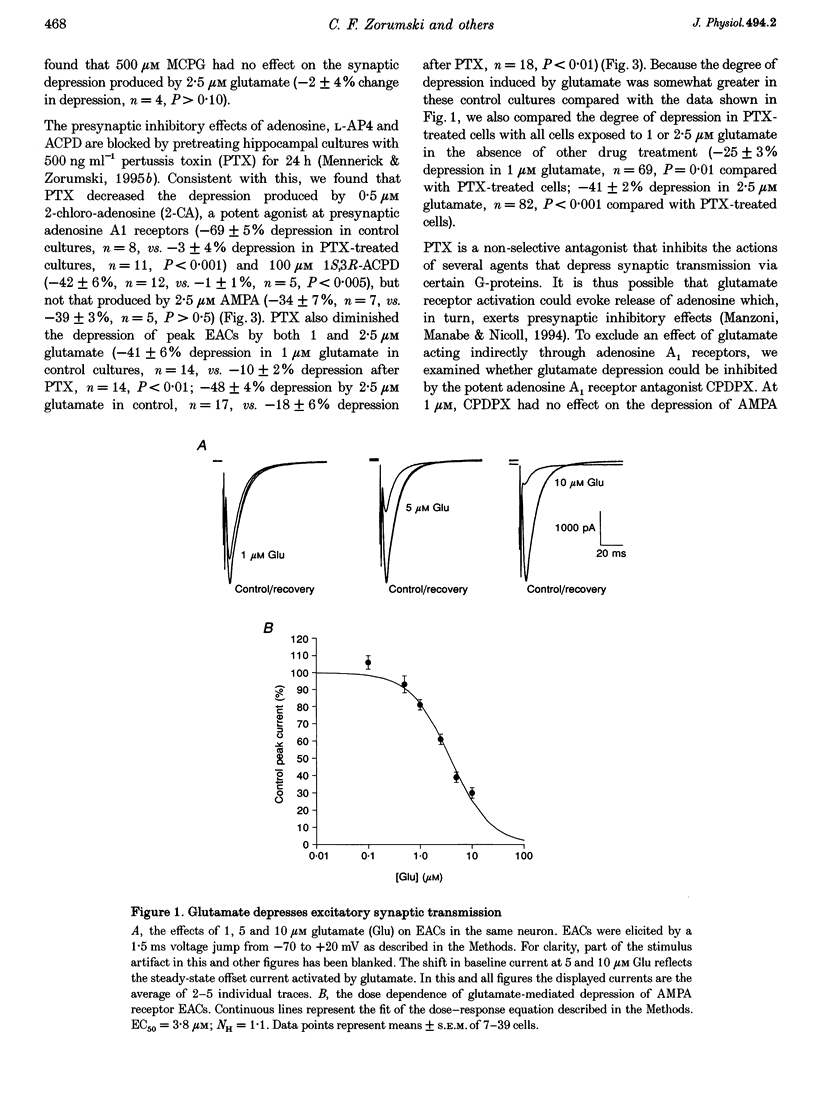
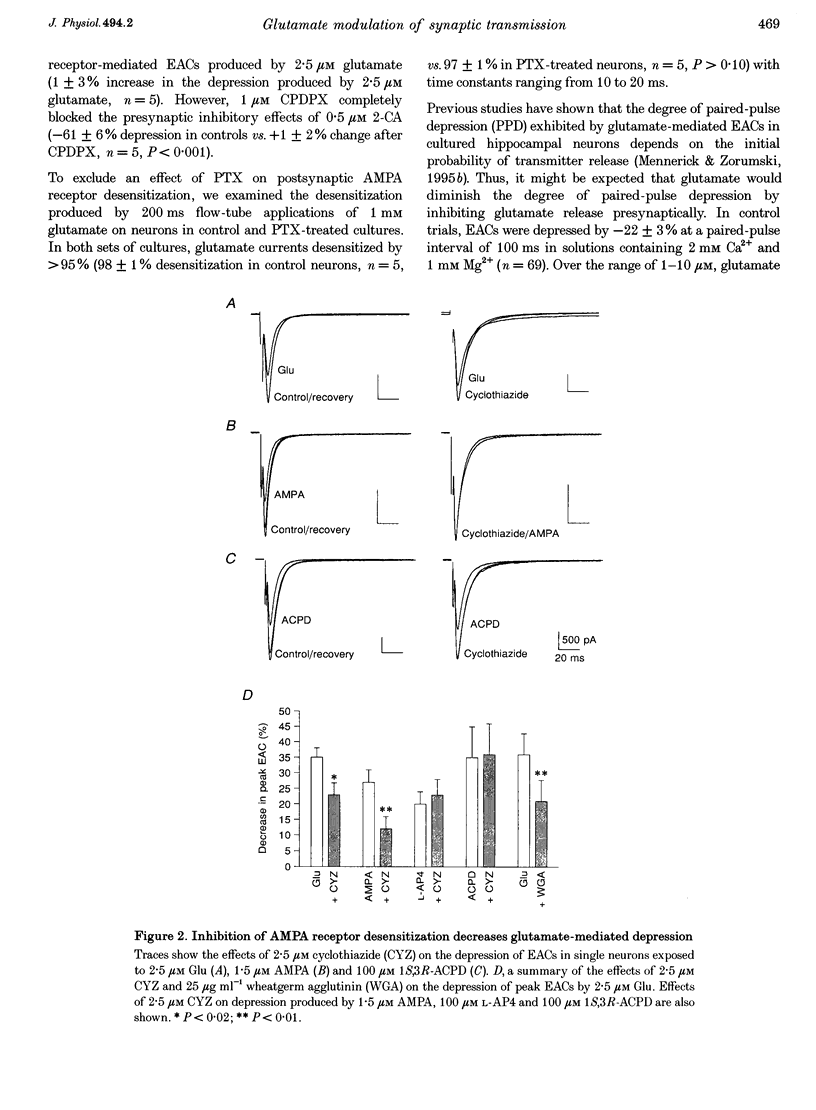
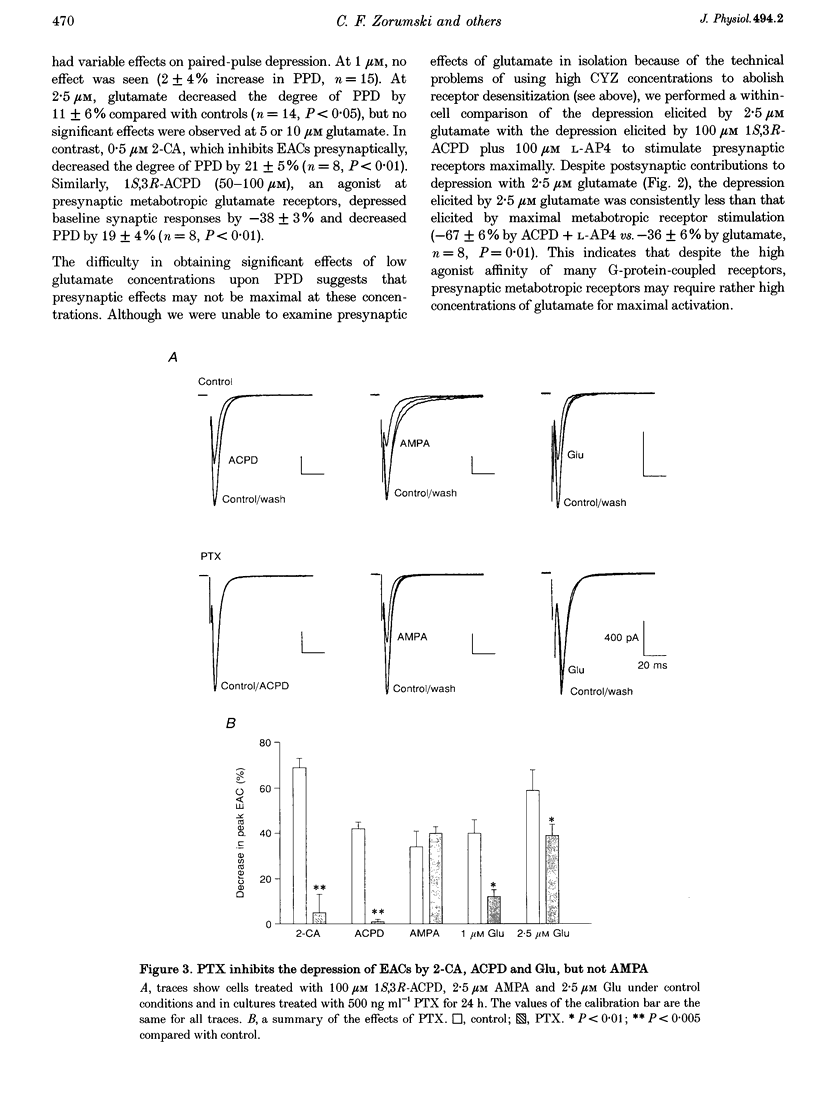
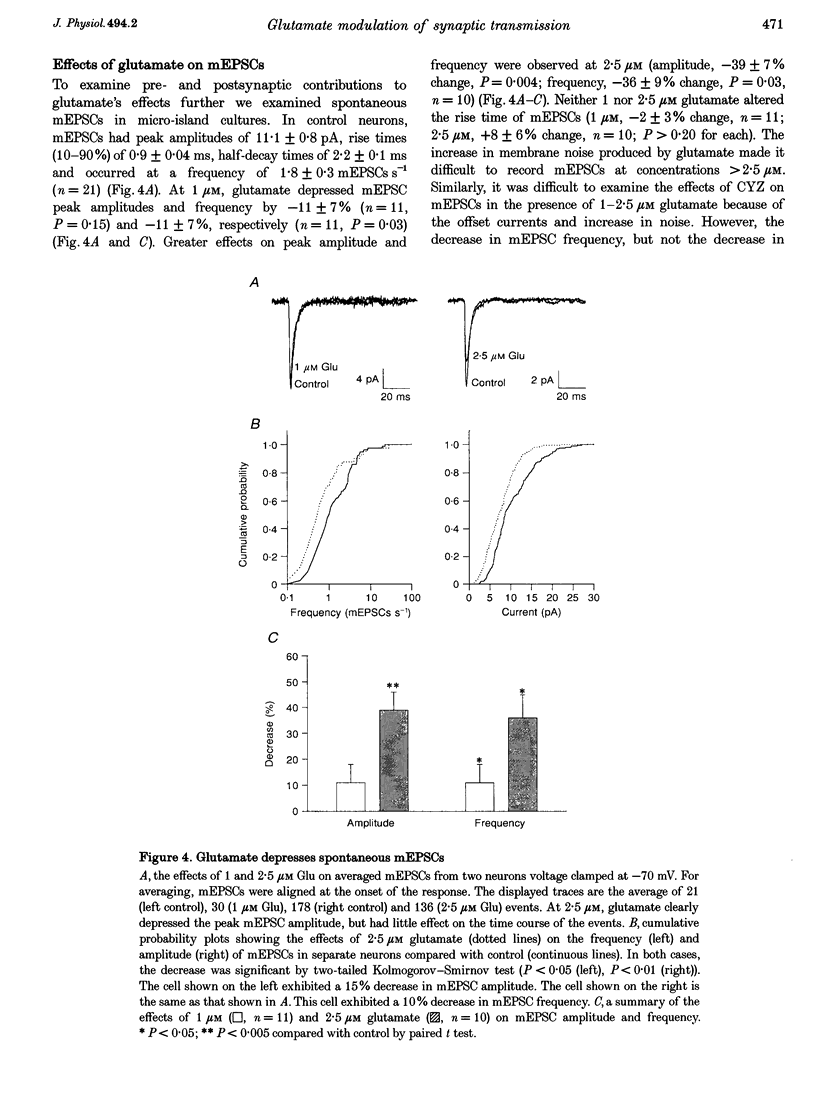
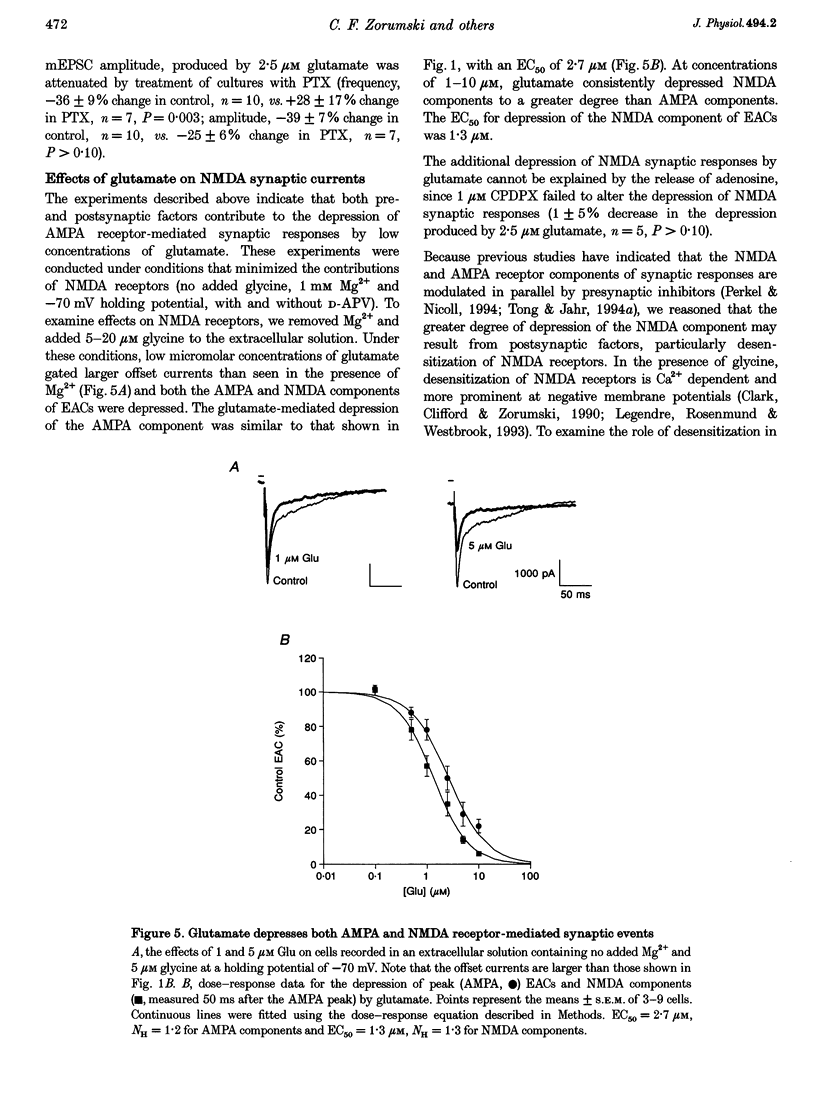
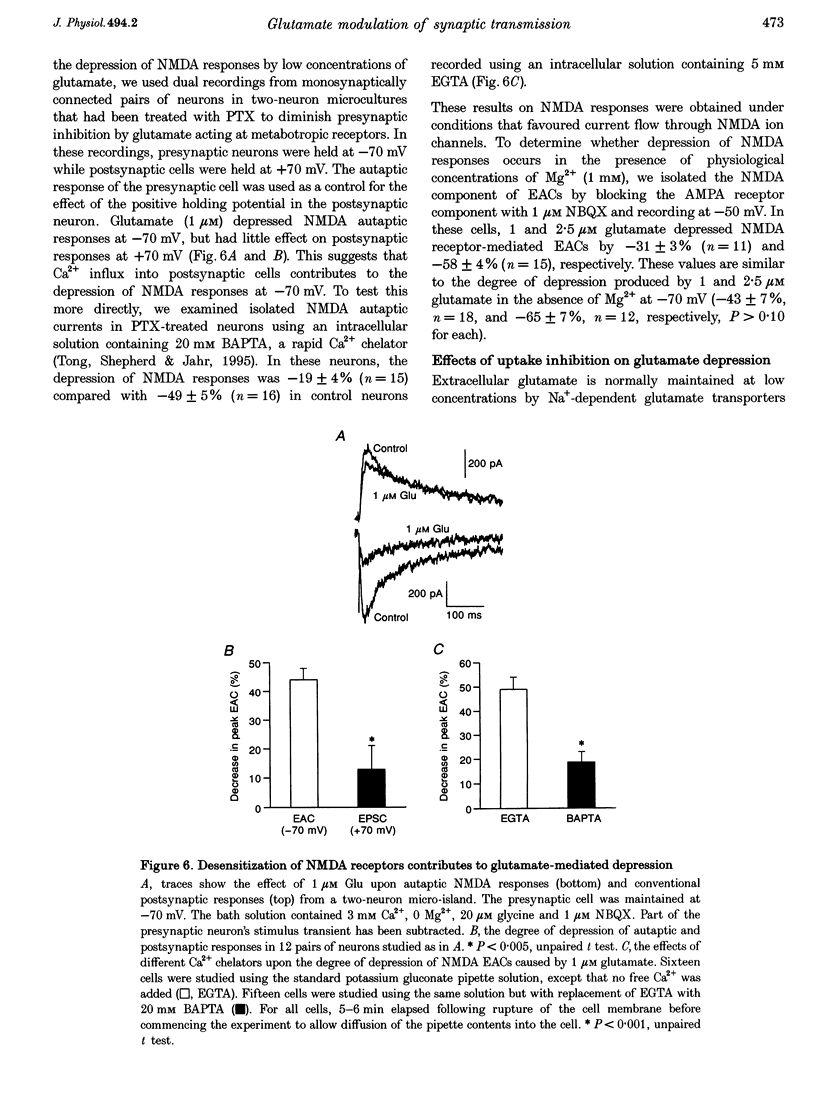
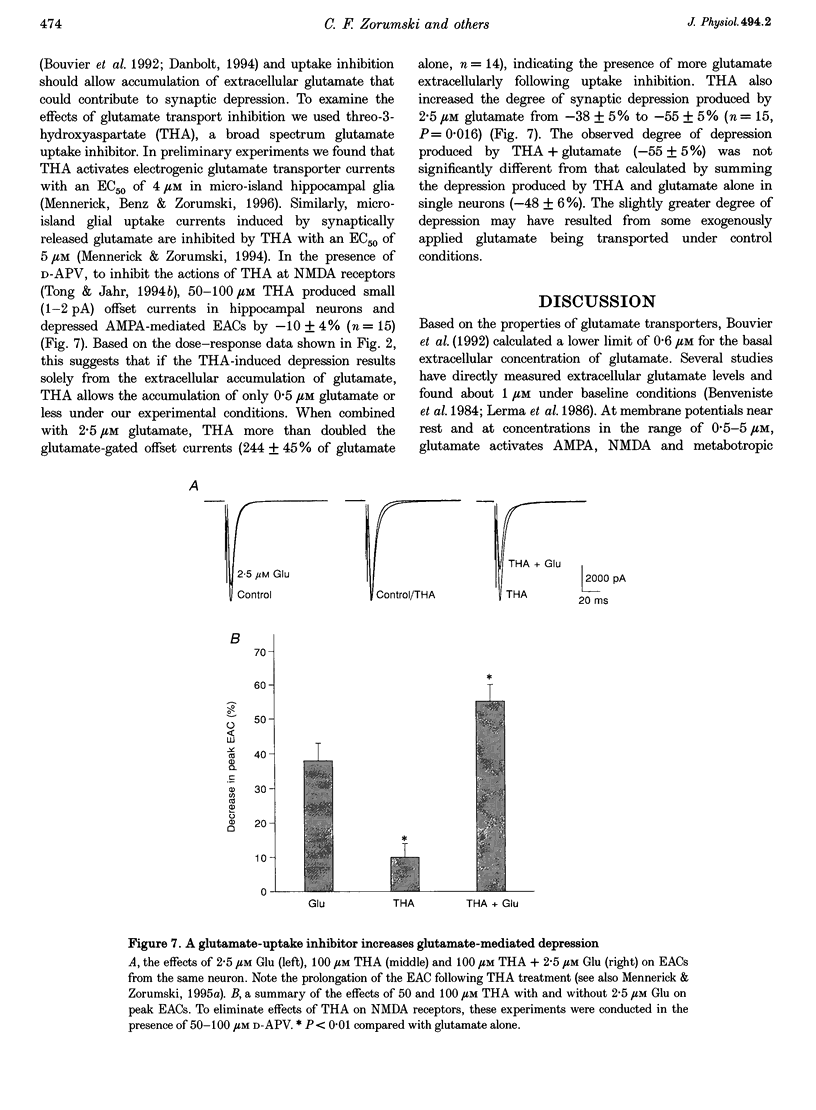
1. The effects of low micromolar concentrations of glutamate on fast excitatory synaptic responses were studied in microcultures of postnatal rat hippocampal neurons using whole-cell patch clamp recordings. 2. Glutamate depressed the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor component of excitatory autaptic currents (EACs) with an EC50 of 3.8 microM. 3. Both pre- and postsynaptic effects contributed to the depression of AMPA receptor-mediated EACs. Cyclothiazide and wheatgerm agglutinin, agents which inhibit AMPA receptor desensitization, partially reversed the depression produced by glutamate, as did pertussis toxin, an agent that blocks presynaptic inhibition mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors. 4. In neurons in which both the AMPA and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor components of EACs were examined, low concentrations of glutamate depressed the NMDA component of EACs to a greater extent. The EC50 for inhibiting the NMDA component was 1.3 microM. 5. Calcium-dependent desensitization of postsynaptic NMDA receptors contributed to the depression of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses. Both depolarization of postsynaptic neurons to +70 mV to decrease Ca2+ influx via NMDA channels and inclusion of high concentrations of a calcium chelator in recording pipettes decreased the depression of NMDA receptor-mediated EACs. 6. Threo-3-hydroxy-aspartate (THA), an inhibitor of glutamate transport, depressed EACs by about 10% and increased the degree of depression produced by 2.5 microM glutamate, suggesting that glutamate transport in microcultures helps to control ambient glutamate levels. 7. Because the normal extracellular concentration of glutamate is about 1 microM, these results suggest that the ambient glutamate level is an important determinant of synaptic efficacy. Relatively small changes in extracellular glutamate can alter fast excitatory synaptic transmission by both presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros-Ingerson J., Lynch G. Channel gating kinetics and synaptic efficacy: a hypothesis for expression of long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7903–7907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste H., Drejer J., Schousboe A., Diemer N. H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1369–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Szatkowski M., Amato A., Attwell D. The glial cell glutamate uptake carrier countertransports pH-changing anions. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):471–474. doi: 10.1038/360471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. M., Mehl E., Cameron P. L., Maycox P. R., Baumert M., Lottspeich F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptic vesicles immunoisolated from rat cerebral cortex contain high levels of glutamate. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):715–720. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. D., Clifford D. B., Zorumski C. F. The effect of agonist concentration, membrane voltage and calcium on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor desensitization. Neuroscience. 1990;39(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coan E. J., Irving A. J., Collingridge G. L. Low-frequency activation of the NMDA receptor system can prevent the induction of LTP. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Jonas P., Sakmann B. Action of brief pulses of glutamate on AMPA/kainate receptors in patches from different neurones of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:261–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danbolt N. C. The high affinity uptake system for excitatory amino acids in the brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;44(4):377–396. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. S., Jahr C. E. Asynchronous release of synaptic vesicles determines the time course of the AMPA receptor-mediated EPSC. Neuron. 1995 Nov;15(5):1097–1107. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Clements J. D. Presynaptic glutamate receptors depress excitatory monosynaptic transmission between mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Y., Colino A., Selig D. K., Malenka R. C. The influence of prior synaptic activity on the induction of long-term potentiation. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):730–733. doi: 10.1126/science.1346729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Major G., Sakmann B. Quantal components of unitary EPSCs at the mossy fibre synapse on CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:615–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legendre P., Rosenmund C., Westbrook G. L. Inactivation of NMDA channels in cultured hippocampal neurons by intracellular calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):674–684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00674.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Herranz A. S., Herreras O., Abraira V., Martín del Río R. In vivo determination of extracellular concentration of amino acids in the rat hippocampus. A method based on brain dialysis and computerized analysis. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 1;384(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F., Stevens C. F. Both open and closed NMDA receptor channels desensitize. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):2153–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-02153.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Robinson M. B., Dichter M. A. The glutamate uptake inhibitor L-trans-pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylate depresses excitatory synaptic transmission via a presynaptic mechanism in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 1):6754–6762. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06754.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni O. J., Manabe T., Nicoll R. A. Release of adenosine by activation of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2098–2101. doi: 10.1126/science.7916485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S., Benz A., Zorumski C. F. Components of glial responses to exogenous and synaptic glutamate in rat hippocampal microcultures. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan;16(1):55–64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-01-00055.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S., Zorumski C. F. Glial contributions to excitatory neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal cells. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):59–62. doi: 10.1038/368059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S., Zorumski C. F. Paired-pulse modulation of fast excitatory synaptic currents in microcultures of rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 1995 Oct 1;488(Pt 1):85–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S., Zorumski C. F. Postsynaptic modulation of NMDA synaptic currents in rat hippocampal microcultures by paired-pulse stimulation. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 15;490(Pt 2):405–417. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S., Zorumski C. F. Presynaptic influence on the time course of fast excitatory synaptic currents in cultured hippocampal cells. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):3178–3192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-03178.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2385–2399. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkel D. J., Nicoll R. A. Evidence for all-or-none regulation of neurotransmitter release: implications for long-term potentiation. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:481–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Feltz A., Westbrook G. L. Calcium-dependent inactivation of synaptic NMDA receptors in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jan;73(1):427–430. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.1.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah P., Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A. Tonic activation of NMDA receptors by ambient glutamate enhances excitability of neurons. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):815–818. doi: 10.1126/science.2573153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W., Dieudonné S., MacDonald J. F., Ascher P. Activation and desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in nucleated outside-out patches from mouse neurones. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:643–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. M., Furshpan E. J. Epileptiform activity in microcultures containing small numbers of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Nov;64(5):1390–1399. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.5.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thio L. L., Clark G. D., Clifford D. B., Zorumski C. F. Wheat germ agglutinin enhances EPSCs in cultured postnatal rat hippocampal neurons by blocking ionotropic quisqualate receptor desensitization. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Dec;68(6):1930–1938. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.6.1930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong G., Jahr C. E. Block of glutamate transporters potentiates postsynaptic excitation. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1195–1203. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong G., Jahr C. E. Multivesicular release from excitatory synapses of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong G., Shepherd D., Jahr C. E. Synaptic desensitization of NMDA receptors by calcineurin. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1510–1512. doi: 10.1126/science.7878472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Fischbach G. D. Glutamate receptor desensitization and its role in synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklicky L., Jr, Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by drugs that reduce desensitization at AMPA/kainate receptors. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):971–984. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90342-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. A., Tang C. M. Benzothiadiazides inhibit rapid glutamate receptor desensitization and enhance glutamatergic synaptic currents. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3904–3915. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]