Abstract
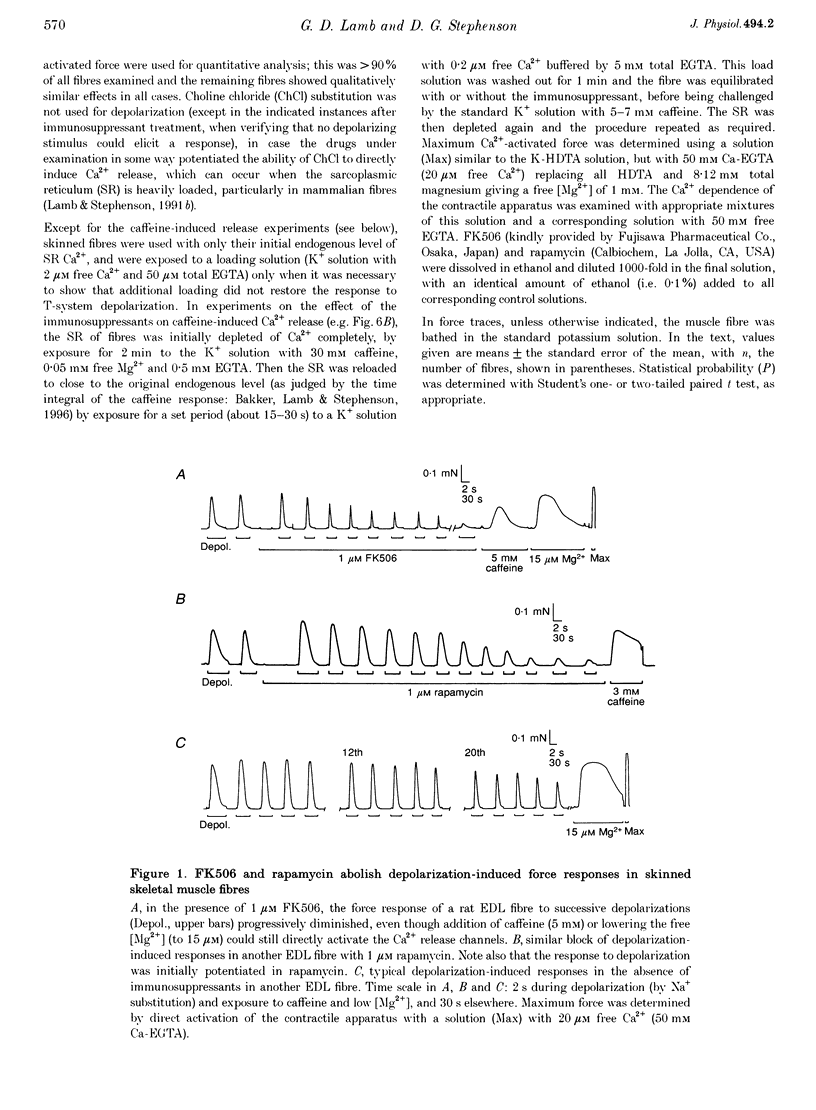
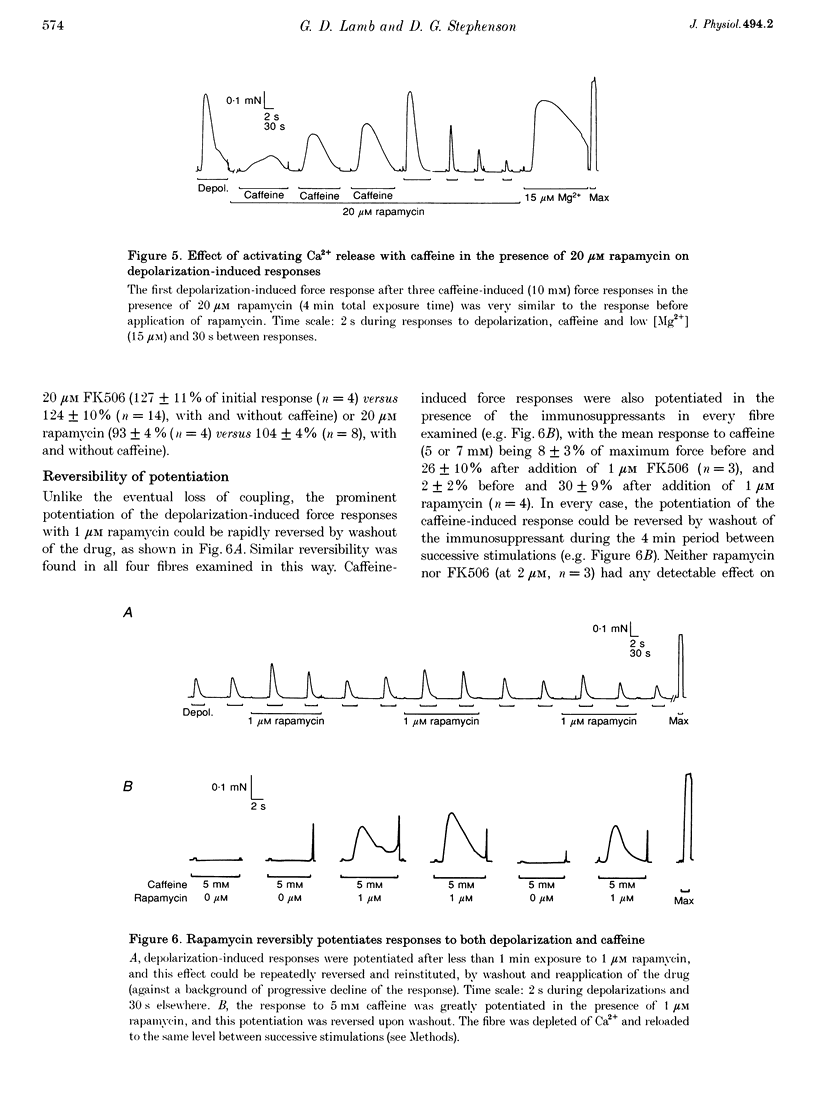
1. The effects of the immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin were examined in mechanically skinned skeletal muscle fibres of rat in order to determine whether the FK506-binding protein plays a role in the coupling between the voltage sensors and the Ca2+ release channels. 2. Both FK506 (1 microM) and rapamycin (1 microM) rapidly and reversibly potentiated Ca2+ release evoked by either depolarization of the transverse tubular system or caffeine application, suggesting a direct effect of the agents on the Ca2+ release channels. 3. In addition, repeated depolarizations in the presence of either FK506 (1 microM) or rapamycin (1 microM) caused irreversible loss of depolarization-induced Ca2+ release, without preventing direct activation of the Ca2+ release channels by caffeine or low [Mg2+]. If a fibre was exposed to either immunosuppressant for a similar period (10 min) without stimulation, or if the voltage sensors were kept inactivated, there was little if any loss of coupling. 4. The loss of coupling was faster at higher drug concentrations, with 20 microM rapamycin causing 50% inhibition in 7-8 min without stimulation; this was further accelerated by repeated depolarizations in the presence of the drug, but was not noticeably altered by direct activation of the release channels by repeated exposure to caffeine. The irreversible loss of coupling indicates that the FK506-binding protein may play a vital role in enabling the voltage sensors to activate the Ca2+ release channels.
Full text
PDF
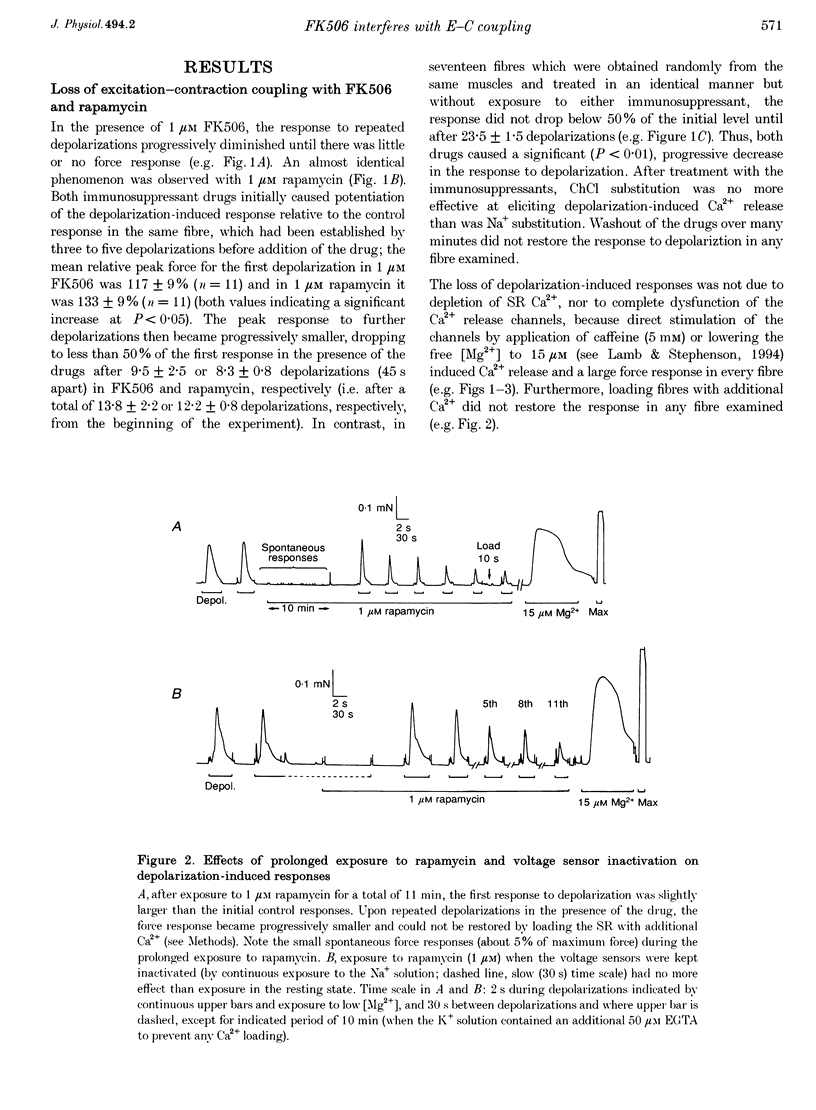
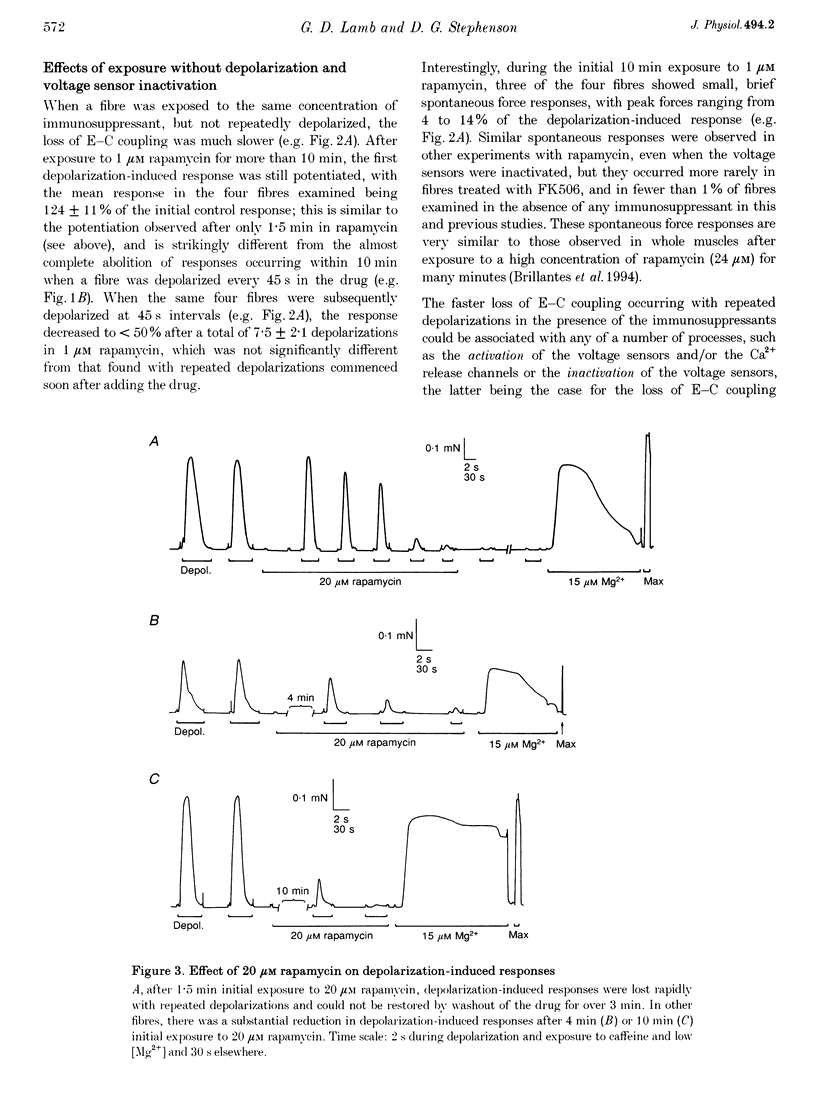
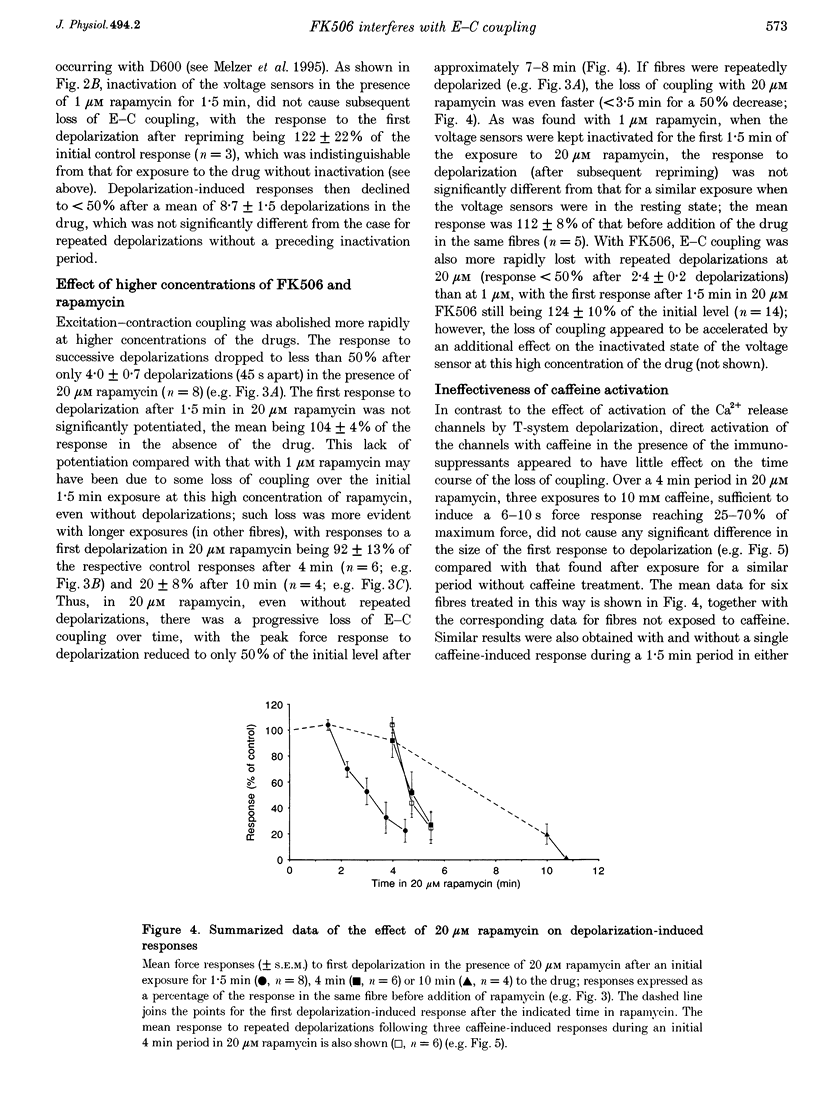


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahern G. P., Junankar P. R., Dulhunty A. F. Single channel activity of the ryanodine receptor calcium release channel is modulated by FK-506. FEBS Lett. 1994 Oct 3;352(3):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brillantes A. B., Ondrias K., Scott A., Kobrinsky E., Ondriasová E., Moschella M. C., Jayaraman T., Landers M., Ehrlich B. E., Marks A. R. Stabilization of calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function by FK506-binding protein. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Effect of Mg2+ on the control of Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle fibres of the toad. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:507–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Effects of intracellular pH and [Mg2+] on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 15;478(Pt 2):331–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad in the presence of GTP gamma S. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:65–84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack M. M., Molinski T. F., Buck E. D., Pessah I. N. Novel modulators of skeletal muscle FKBP12/calcium channel complex from Ianthella basta. Role of FKBP12 in channel gating. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):23236–23249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrleitner M., Timerman A. P., Wiederrecht G., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506 binding protein: effect of FKBP-12 on single channel activity of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Cell Calcium. 1994 Feb;15(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(94)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Herrmann-Frank A., Lüttgau H. C. The role of Ca2+ ions in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 8;1241(1):59–116. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)00014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Wiederrecht G., Marcy A., Fleischer S. Characterization of an exchange reaction between soluble FKBP-12 and the FKBP.ryanodine receptor complex. Modulation by FKBP mutants deficient in peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2451–2459. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



