Abstract
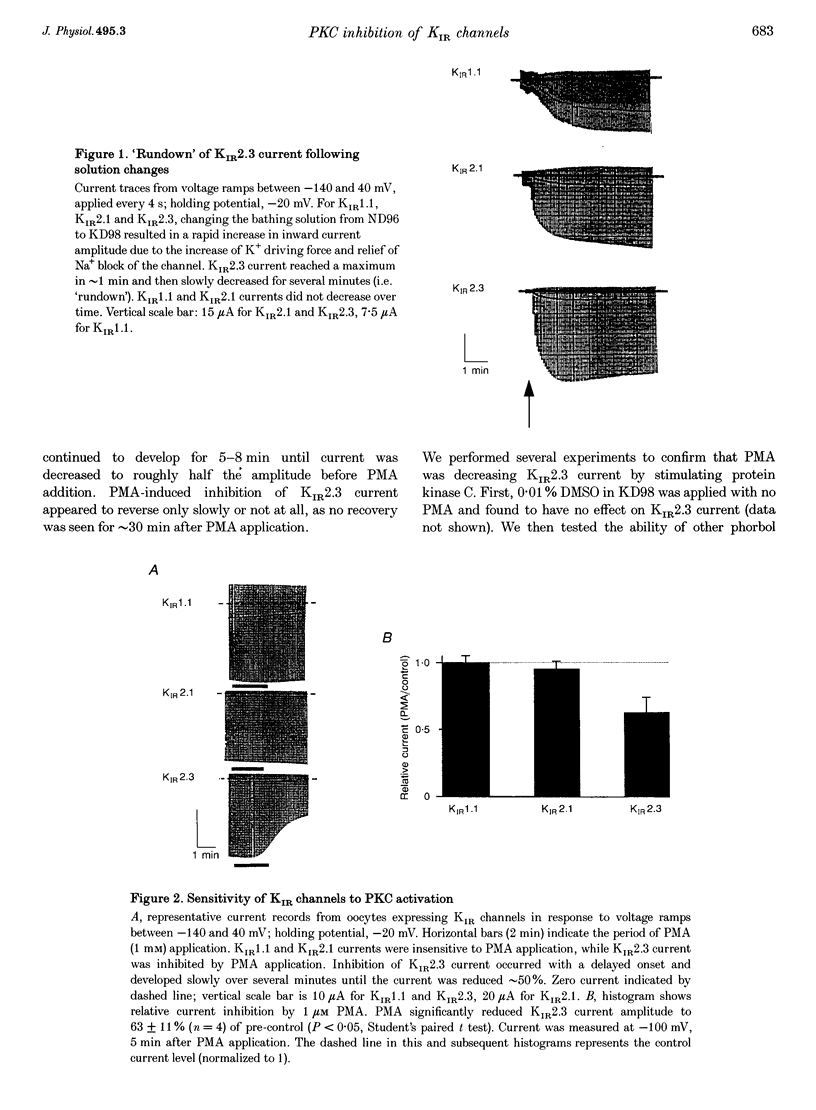
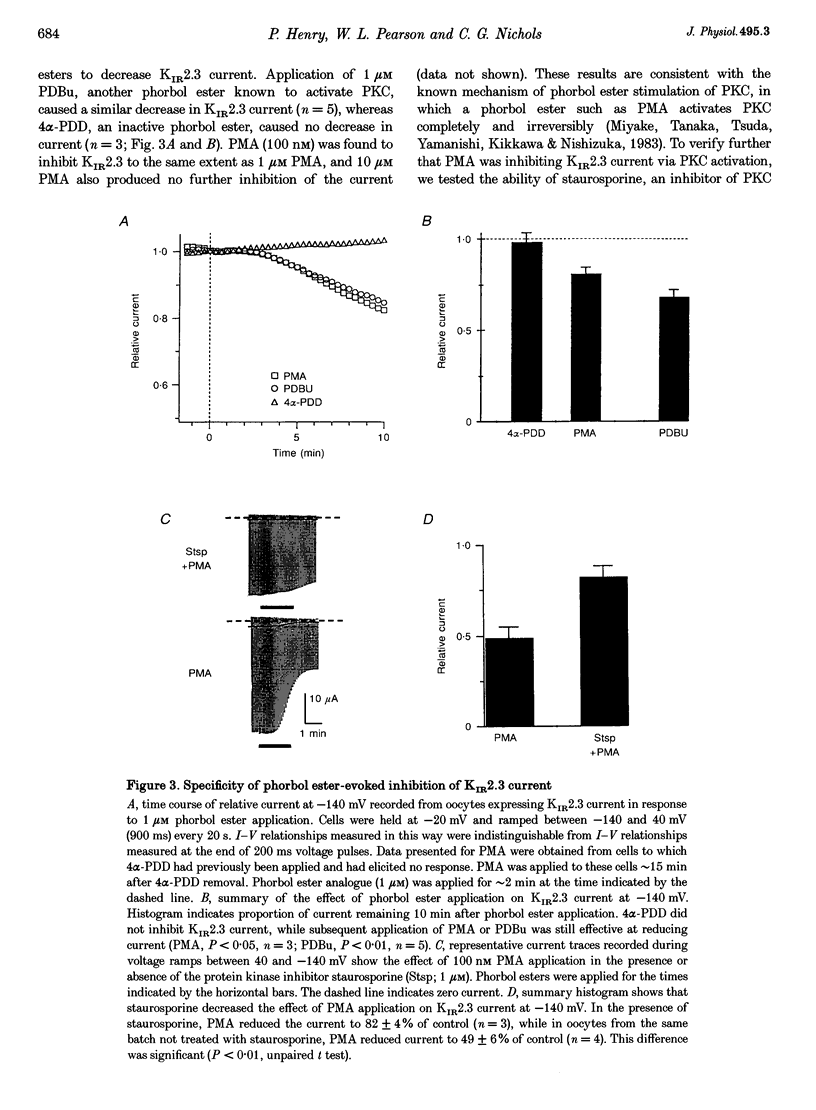
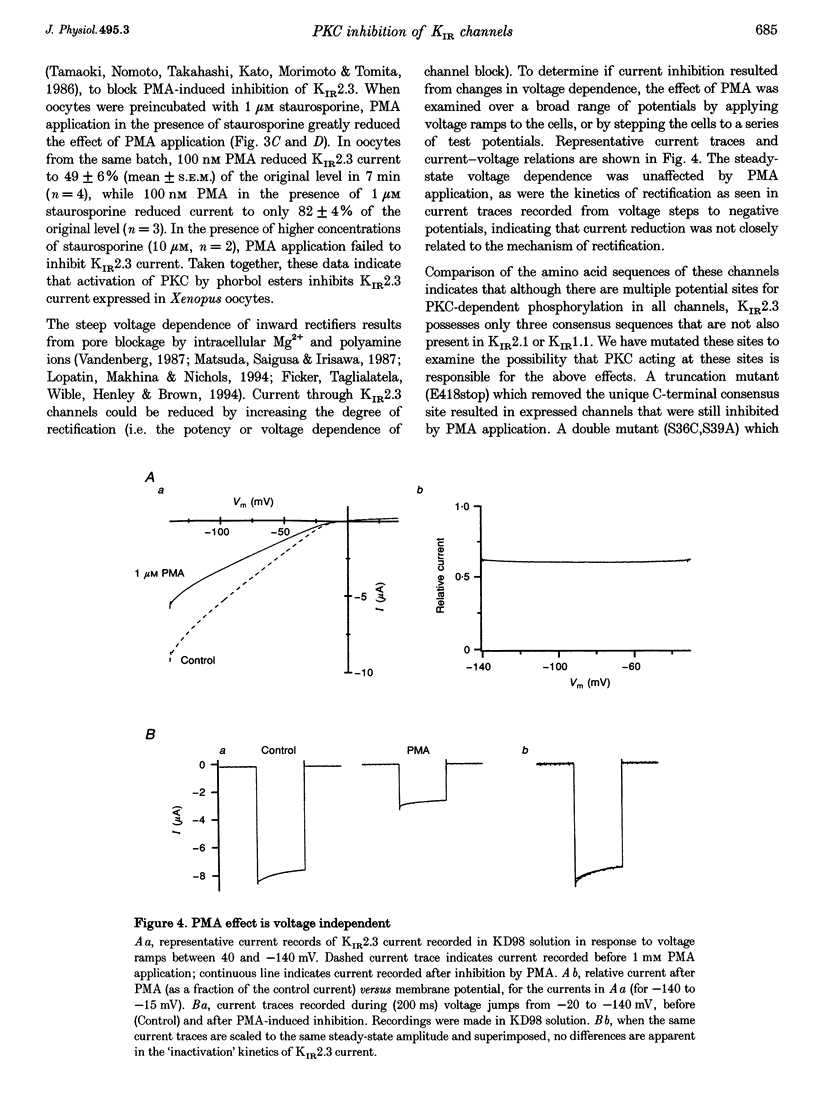
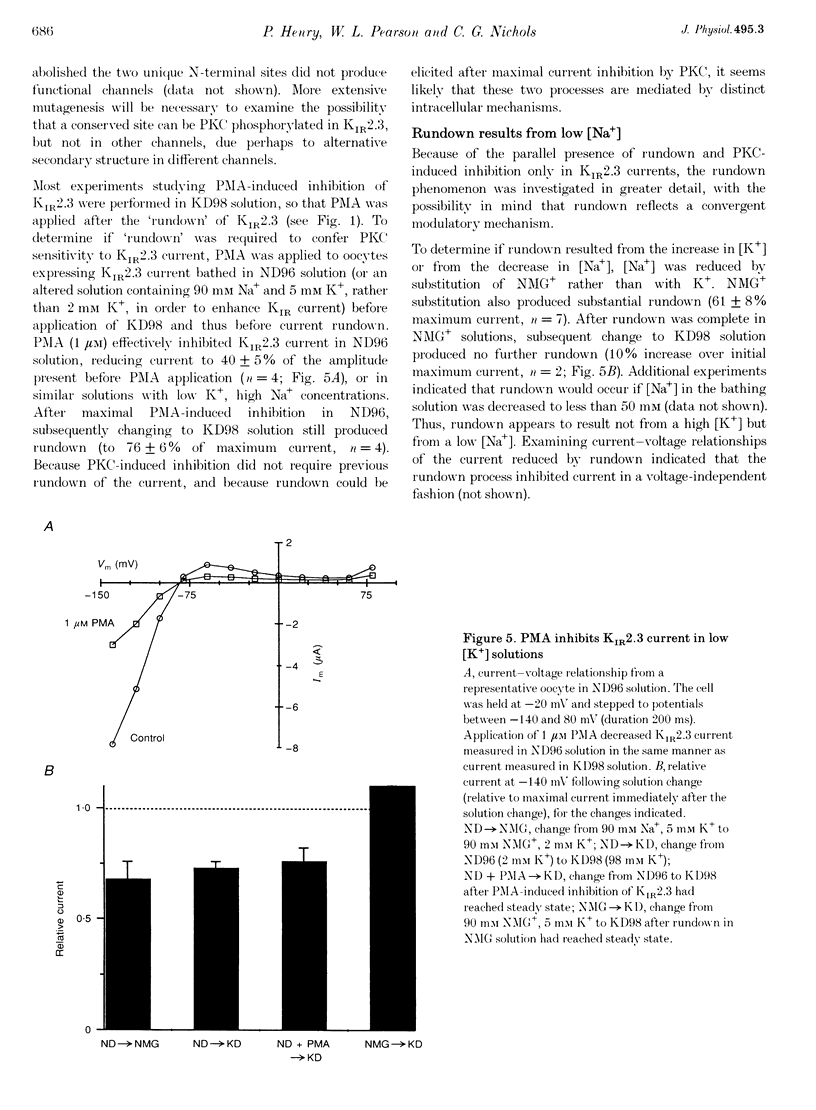
1. The effect of protein kinase activators on cloned inward rectifier channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes was examined using a two-electrode voltage clamp. PKA activators caused no change in KIR1.1, KIR2.1, or KIR2.3 current. The PKC activators phorbol 12-myristate 14-acetate (PMA) and phorbol 12, 13-dibutyrate (PDBu) inhibited KIR2.3 currents, but not KIR2.1 or KIR1.1 current. This inhibition was blocked by staurosporine. An inactive phorbol ester, 4 alpha-phorbol 12, 13-didecanoate (4 alpha-PDD), had no effect on KIR2.3. 2. Upon changing solution from 2 to 98 microM K+, KIR2.3 but not KIR1.1 or KIR2.1 currents typically 'ran down' over 5 min to 60-80% of maximum amplitude. Rundown occurred even if PMA was applied before changing to high [K+] solution, indicating that rundown was independent of PKC activity. Rundown was evoked by substituting NMG+ for Na+, showing that it results from low [Na+] and not from high [K+]. 3. These results suggest that KIR2.3, but not KIR1.1 or KIR2.1, is subject to regulation, both by PKC activation and as a consequence of low [Na+]o. The difference in secondary regulation may account for specific responses to PKC stimulation of tissues expressing otherwise nearly identical KIR channels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong S., Downey J. M., Ganote C. E. Preconditioning of isolated rabbit cardiomyocytes: induction by metabolic stress and blockade by the adenosine antagonist SPT and calphostin C, a protein kinase C inhibitor. Cardiovasc Res. 1994 Jan;28(1):72–77. doi: 10.1093/cvr/28.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billman G. E. Role of ATP sensitive potassium channel in extracellular potassium accumulation and cardiac arrhythmias during myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res. 1994 Jun;28(6):762–769. doi: 10.1093/cvr/28.6.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt B. C., Kroll B., Frömter E. Proton transport mechanism in the cell membrane of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Jan;420(1):78–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00378644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud A., Boyer J., Ozon R. Calcium sequestering activities of reticulum vesicles from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Dec;155(2):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupnik C. A., Davidson N., Lester H. A. The inward rectifier potassium channel family. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Jun;5(3):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Glowatzki E., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. Kir2.1 inward rectifier K+ channels are regulated independently by protein kinases and ATP hydrolysis. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1413–1420. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficker E., Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Henley C. M., Brown A. M. Spermine and spermidine as gating molecules for inward rectifier K+ channels. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1068–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7973666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin A. N., Makhina E. N., Nichols C. G. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):366–369. doi: 10.1038/372366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhina E. N., Kelly A. J., Lopatin A. N., Mercer R. W., Nichols C. G. Cloning and expression of a novel human brain inward rectifier potassium channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20468–20474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Saigusa A., Irisawa H. Ohmic conductance through the inwardly rectifying K channel and blocking by internal Mg2+. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):156–159. doi: 10.1038/325156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake R., Tanaka Y., Tsuda T., Yamanishi J., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Membrane phospholipid turnover in signal transduction; protein kinase C and mechanism of action of tumor promoters. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1983;14:167–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périer F., Radeke C. M., Vandenberg C. A. Primary structure and characterization of a small-conductance inwardly rectifying potassium channel from human hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6240–6244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speechly-Dick M. E., Mocanu M. M., Yellon D. M. Protein kinase C. Its role in ischemic preconditioning in the rat. Circ Res. 1994 Sep;75(3):586–590. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabcharani J. A., Boucher A., Eng J. W., Hanrahan J. W. Regulation of an inwardly rectifying K channel in the T84 epithelial cell line by calcium, nucleotides and kinases. J Membr Biol. 1994 Nov;142(2):255–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00234947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Stanfield P. R., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Protein kinase C-mediated inhibition of an inward rectifier potassium channel by substance P in nucleus basalis neurons. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):999–1008. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A. Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T., Wang H. L. Protein kinase C mediates neurotensin inhibition of inwardly rectifying potassium currents in rat substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Jan 23;184(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)11185-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


