Abstract
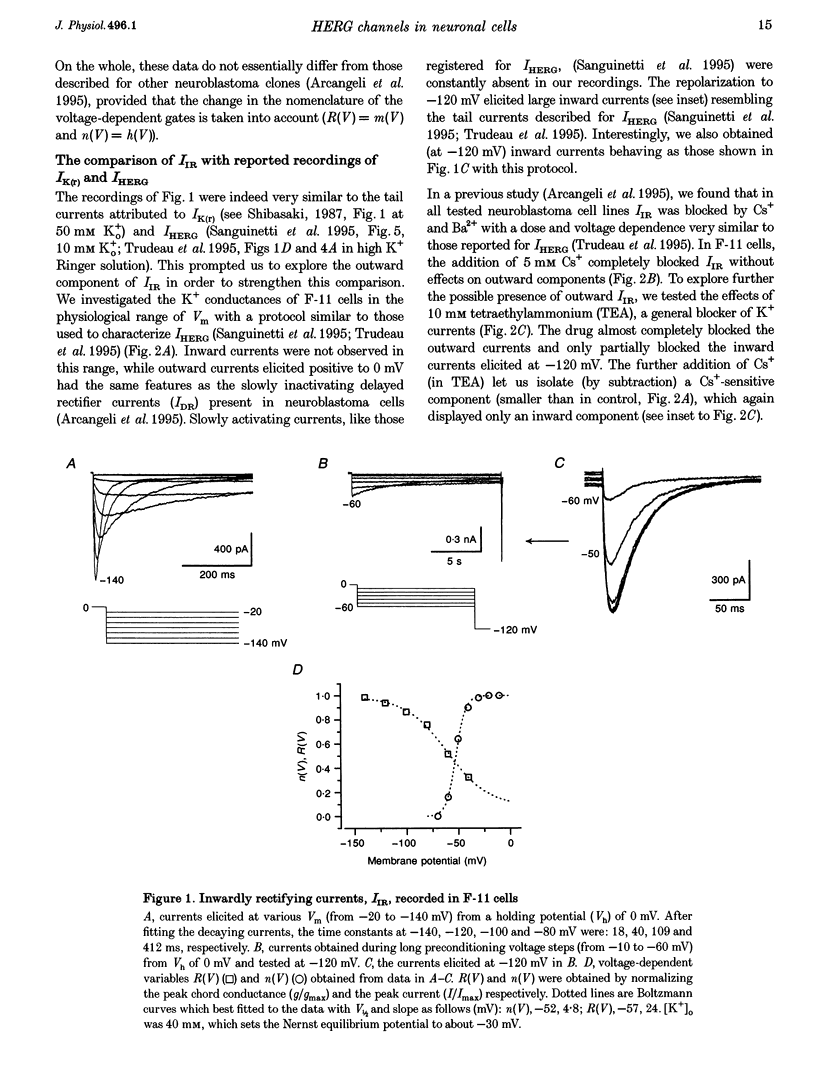
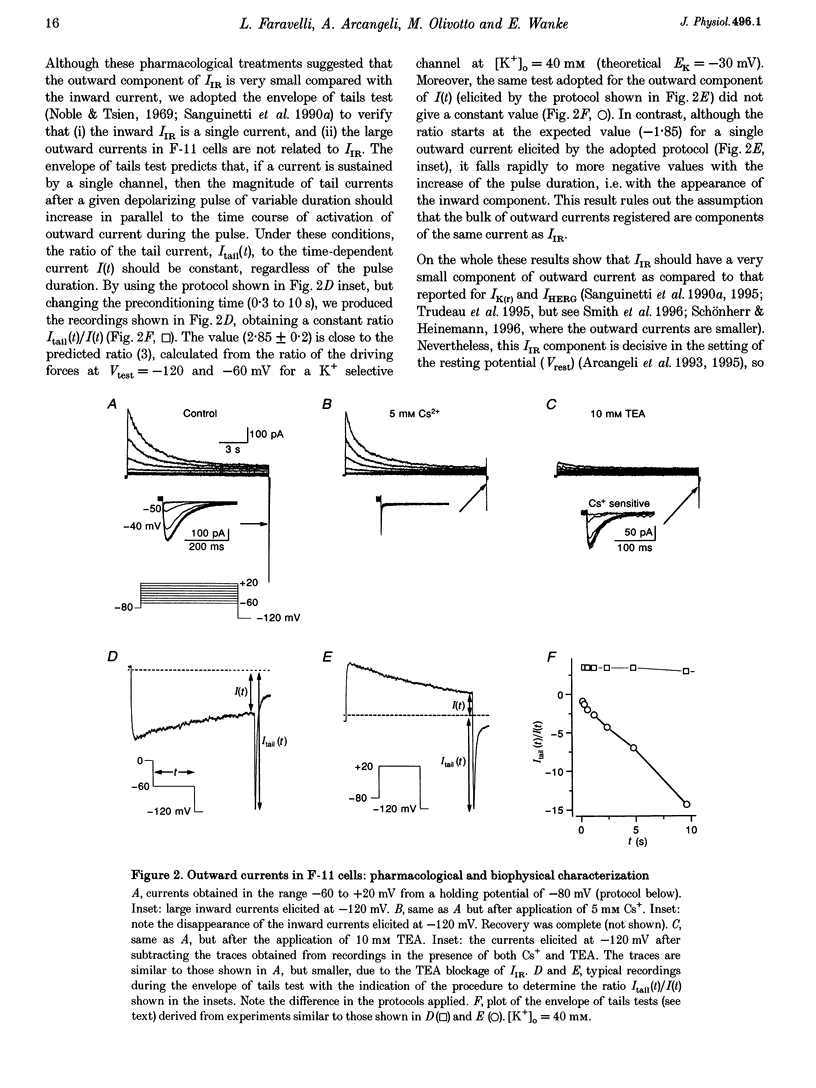
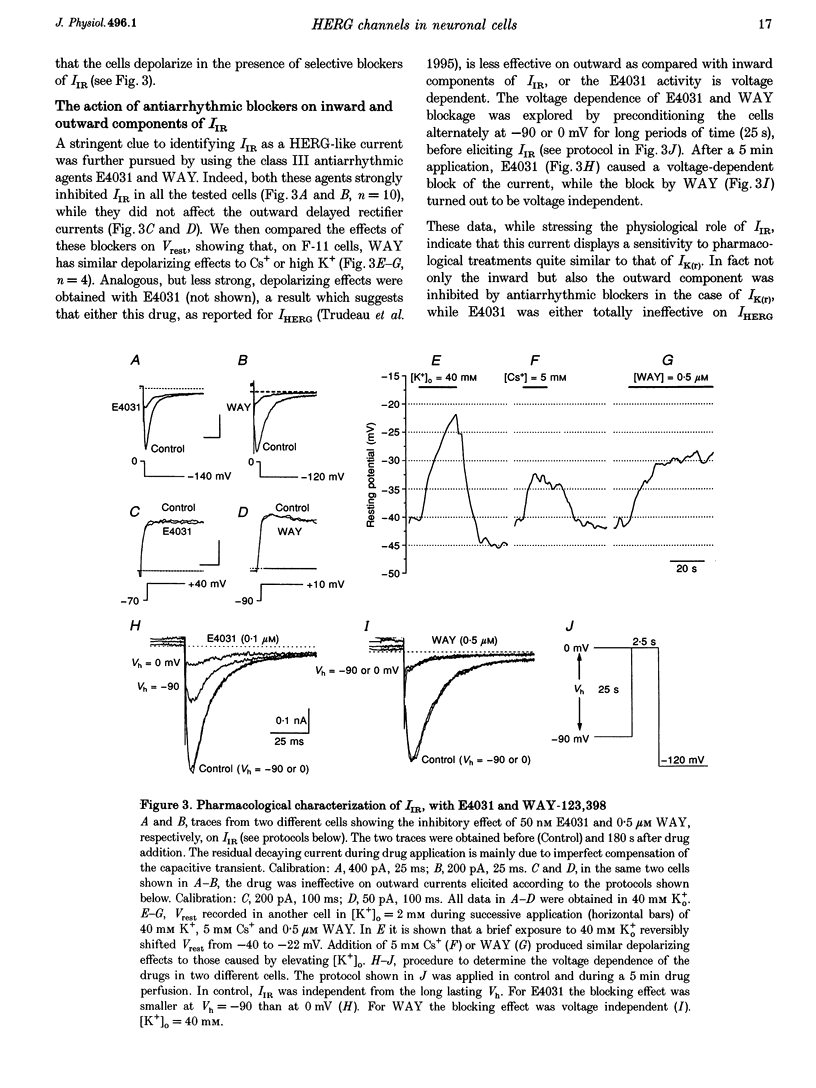
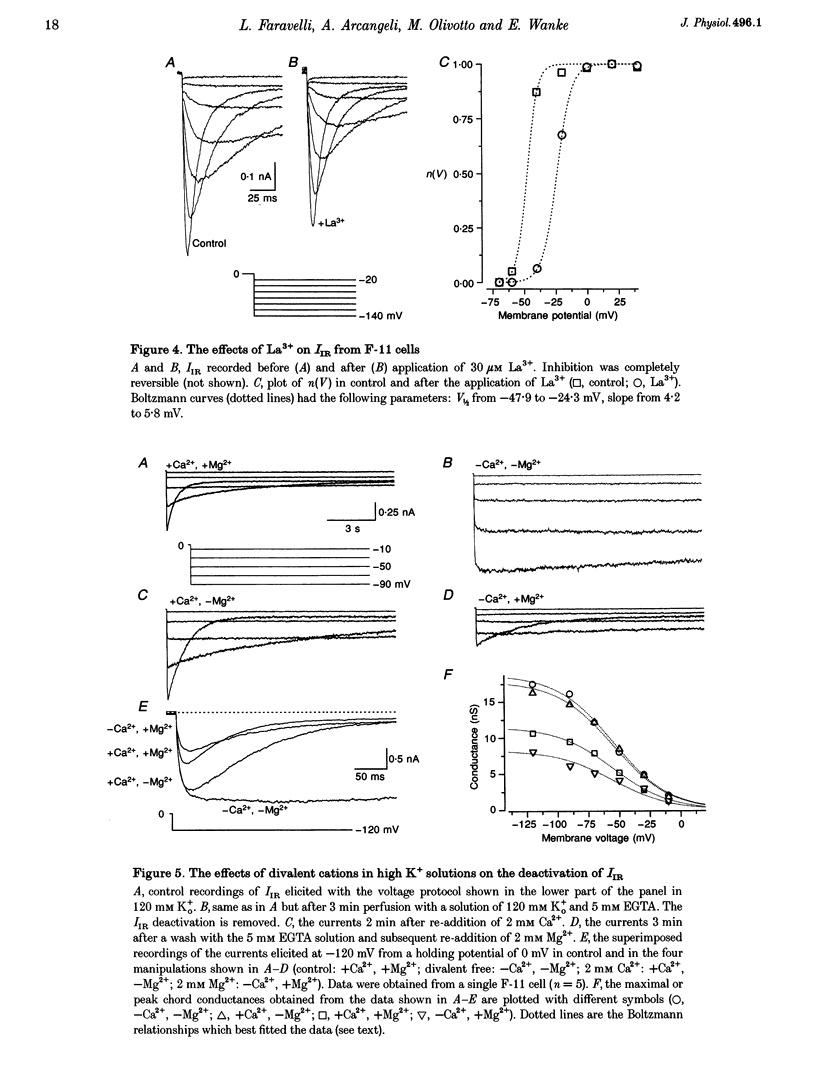
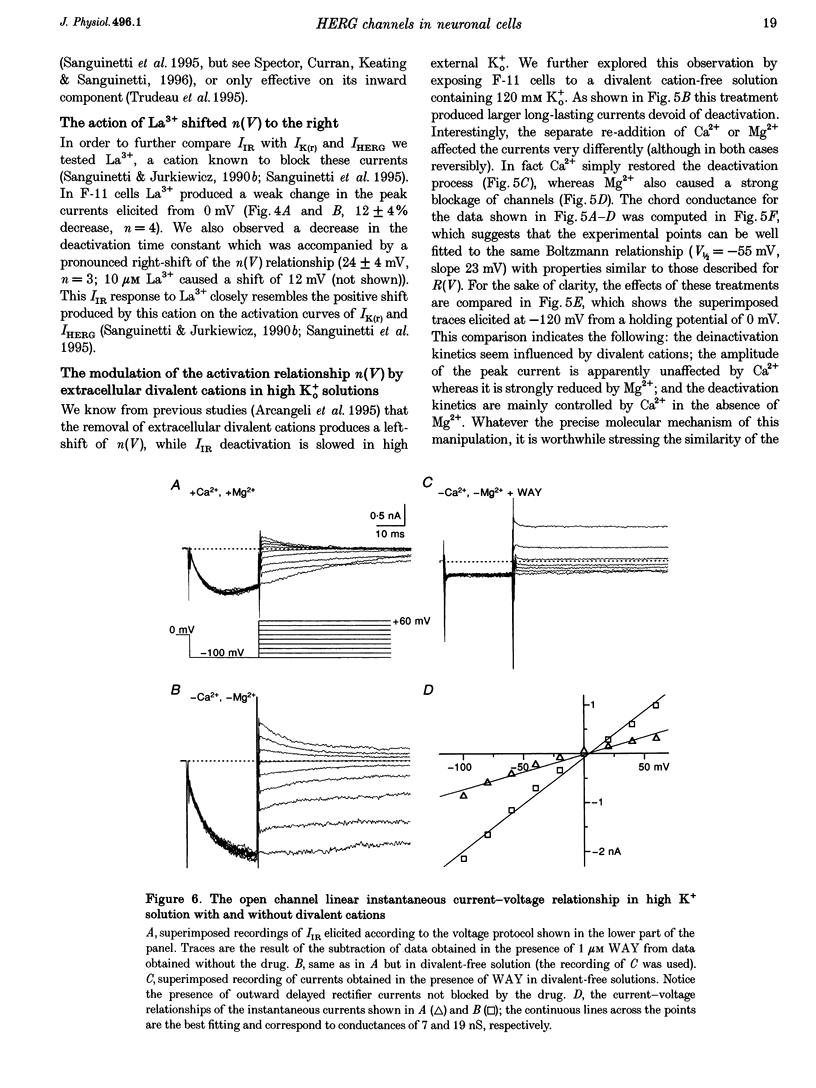
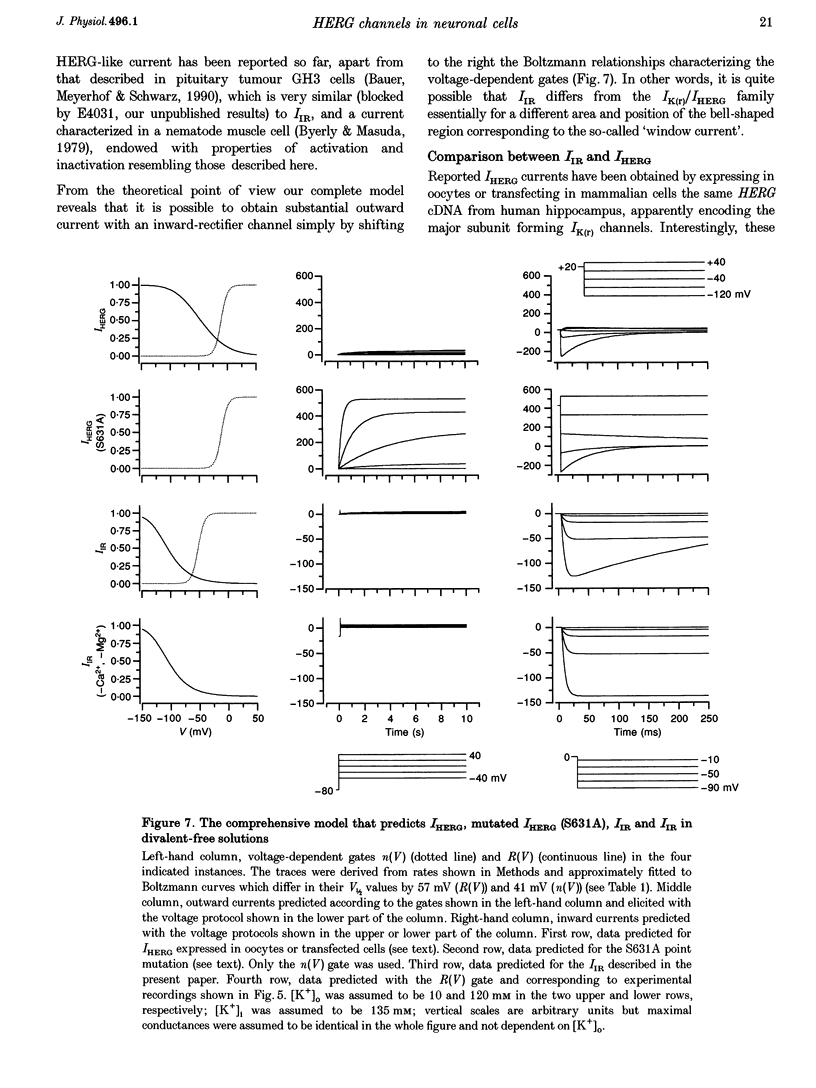
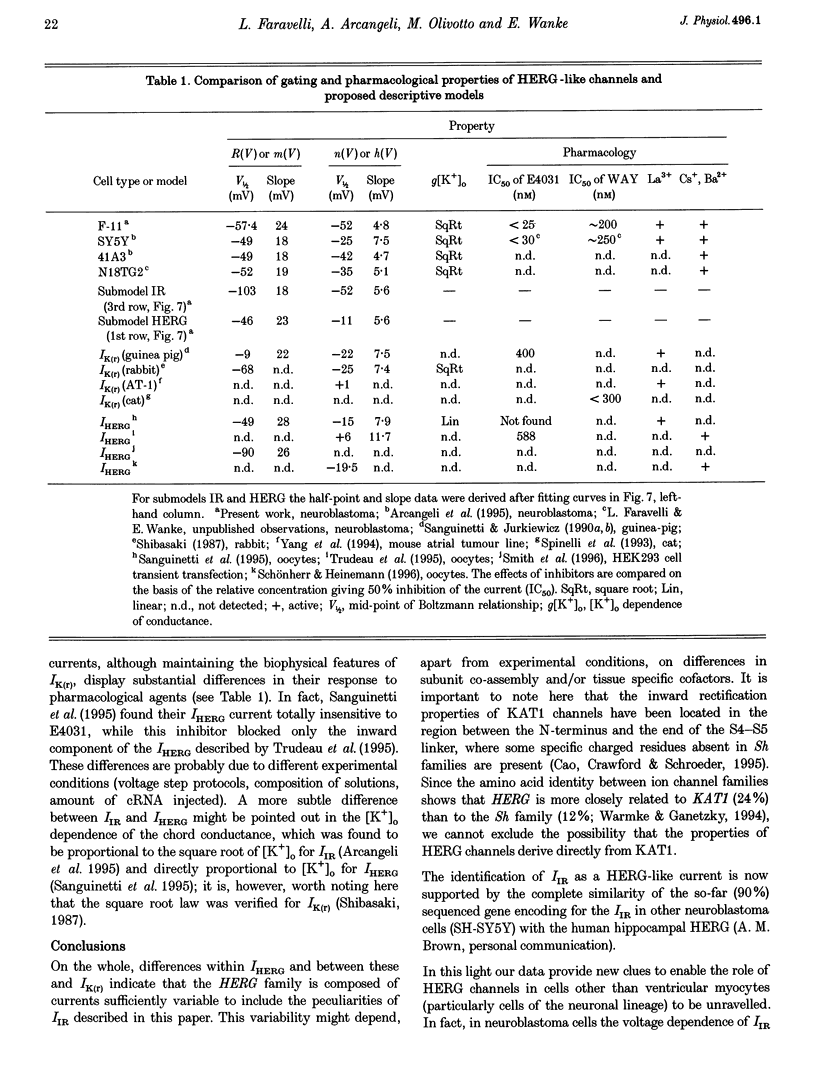
1. The relationships between the K+ inward rectifier current present in neuroblastoma cells (IIR) and the current encoded by the human ether-á-go-go-related gene (HERG), IHERG, and the rapidly activating repolarizing cardiac current IK(r), were investigated in a rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) x mouse neuroblastoma hybrid cell line (F-11) using pharmacological and biophysical treatments. 2. IIR shared the pharmacological features described for IK(r), including the sensitivity to the antiarrhythmic drugs E4301 and WAY-123,398, whilst responding to Cs+, Ba2+ and La3+ in a similar way to IHERG. 3. The voltage-dependent gating properties of IIR were similar to those of IK(r) and IHERG, although IIR outward currents were negligible in comparison. 4. In high K+ extracellular solutions devoid of divalent cations, IIR deactivation kinetics were removed resulting in long-lasting currents apparently activated in hyperpolarization, with a marked (2.7-fold) increase in conductance, as recorded from the instantaneous linear current-voltage relationship at -120 mV. Re-addition of Ca2+ restored the original closure of the channel whereas re-addition of Mg2+ reduced the peak current. 5. The IIR described here, the heart IK(r) and the IHERG could be successfully predicted by a unique kinetic model where the voltage dependencies of the activation/inactivation gates were properly voltage shifted. On the whole, IIR seems to be the first example of a HERG-type current constitutively expressed and operating in mammalian cells of the neuronal lineage.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcangeli A., Becchetti A., Mannini A., Mugnai G., De Filippi P., Tarone G., Del Bene M. R., Barletta E., Wanke E., Olivotto M. Integrin-mediated neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells depends on the activation of potassium channels. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1131–1143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcangeli A., Bianchi L., Becchetti A., Faravelli L., Coronnello M., Mini E., Olivotto M., Wanke E. A novel inward-rectifying K+ current with a cell-cycle dependence governs the resting potential of mammalian neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1995 Dec 1;489(Pt 2):455–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp021065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. K., Meyerhof W., Schwarz J. R. An inward-rectifying K+ current in clonal rat pituitary cells and its modulation by thyrotrophin-releasing hormone. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:169–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland L. M., Dingledine R. Multiple components of both transient and sustained barium currents in a rat dorsal root ganglion cell line. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:223–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Masuda M. O. Voltage-clamp analysis of the potassium current that produces a negative-going action potential in Ascaris muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:263–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Crawford N. M., Schroeder J. I. Amino terminus and the first four membrane-spanning segments of the Arabidopsis K+ channel KAT1 confer inward-rectification property of plant-animal chimeric channels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17697–17701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. E., Splawski I., Timothy K. W., Vincent G. M., Green E. D., Keating M. T. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Aldrich R. W. Conversion of a delayed rectifier K+ channel to a voltage-gated inward rectifier K+ channel by three amino acid substitutions. Neuron. 1996 Apr;16(4):853–858. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platika D., Boulos M. H., Baizer L., Fishman M. C. Neuronal traits of clonal cell lines derived by fusion of dorsal root ganglia neurons with neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jiang C., Curran M. E., Keating M. T. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jurkiewicz N. K. Lanthanum blocks a specific component of IK and screens membrane surface change in cardiac cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):H1881–H1889. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.6.H1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jurkiewicz N. K. Two components of cardiac delayed rectifier K+ current. Differential sensitivity to block by class III antiarrhythmic agents. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jul;96(1):195–215. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtman D. P., Schroeder J. I., Lucas W. J., Anderson J. A., Gaber R. F. Expression of an inward-rectifying potassium channel by the Arabidopsis KAT1 cDNA. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1654–1658. doi: 10.1126/science.8966547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönherr R., Heinemann S. H. Molecular determinants for activation and inactivation of HERG, a human inward rectifier potassium channel. J Physiol. 1996 Jun 15;493(Pt 3):635–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki T. Conductance and kinetics of delayed rectifier potassium channels in nodal cells of the rabbit heart. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:227–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Baukrowitz T., Yellen G. The inward rectification mechanism of the HERG cardiac potassium channel. Nature. 1996 Feb 29;379(6568):833–836. doi: 10.1038/379833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector P. S., Curran M. E., Keating M. T., Sanguinetti M. C. Class III antiarrhythmic drugs block HERG, a human cardiac delayed rectifier K+ channel. Open-channel block by methanesulfonanilides. Circ Res. 1996 Mar;78(3):499–503. doi: 10.1161/01.res.78.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli W., Moubarak I. F., Parsons R. W., Colatsky T. J. Cellular electrophysiology of WAY-123,398, a new class III antiarrhythmic agent: specificity of IK block and lack of reverse use dependence in cat ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 1993 Sep;27(9):1580–1591. doi: 10.1093/cvr/27.9.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudeau M. C., Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B., Robertson G. A. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.7604285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B. A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3438–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T., Wathen M. S., Felipe A., Tamkun M. M., Snyders D. J., Roden D. M. K+ currents and K+ channel mRNA in cultured atrial cardiac myocytes (AT-1 cells). Circ Res. 1994 Nov;75(5):870–878. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.5.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


