Abstract
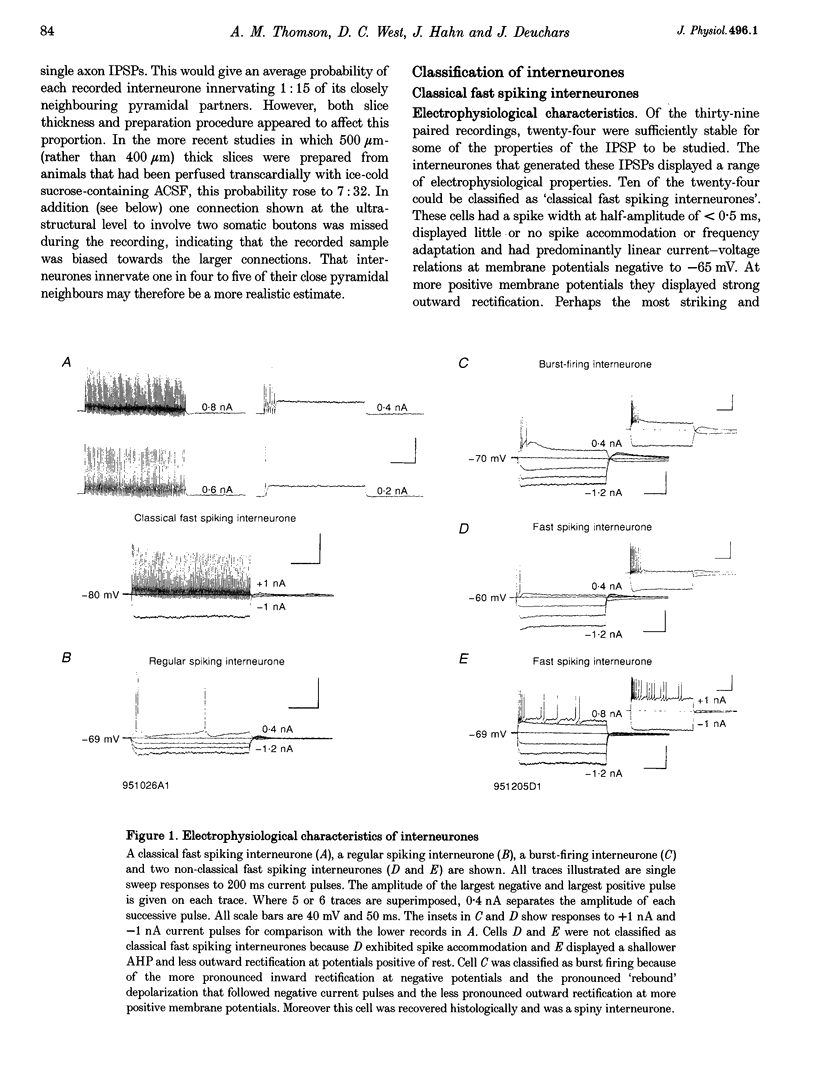
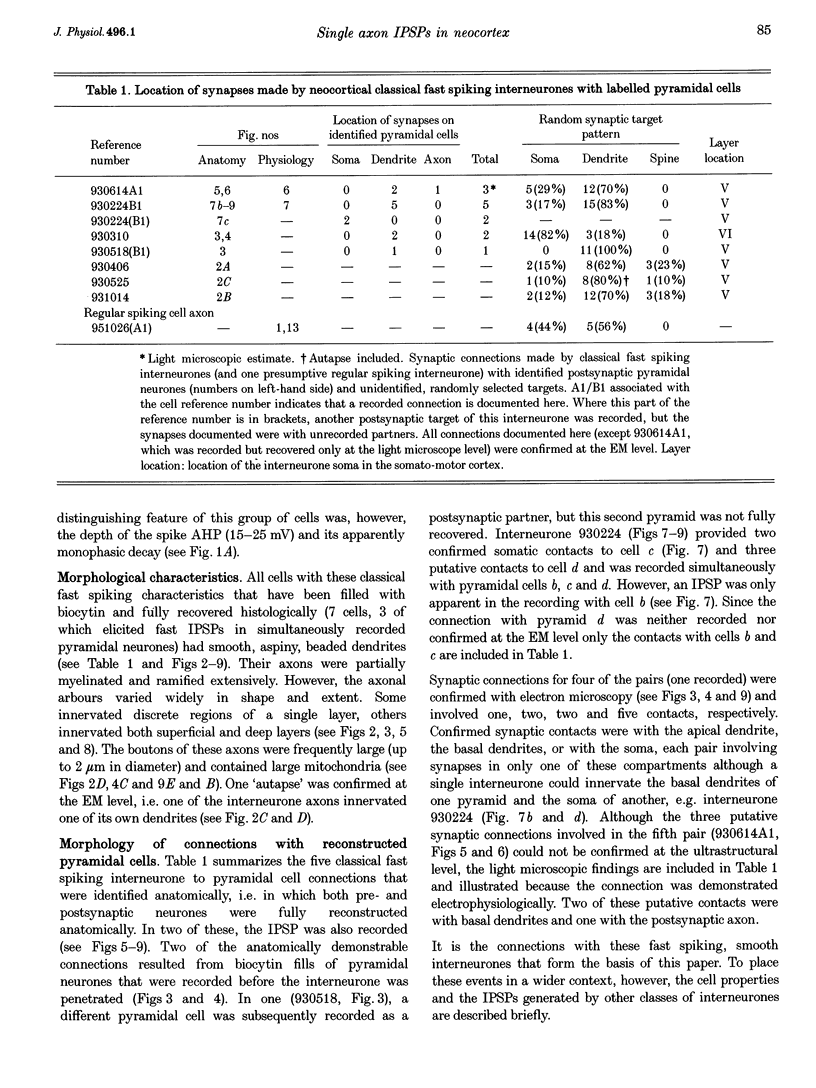
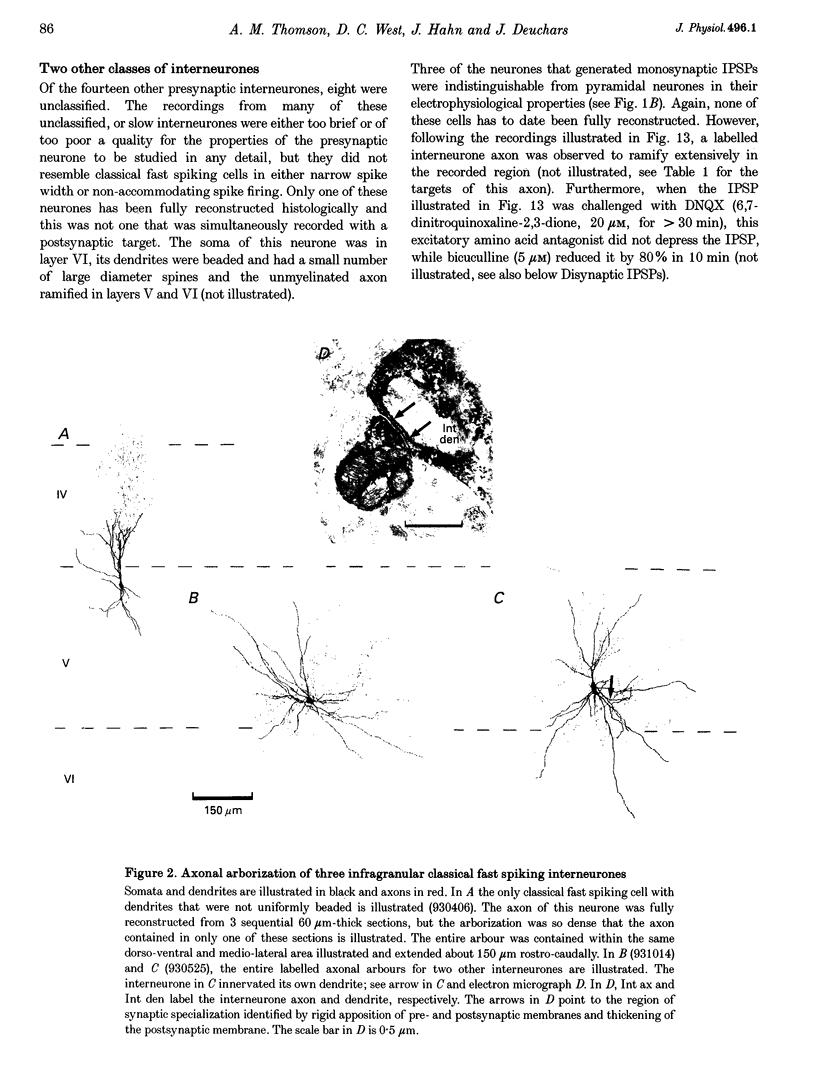
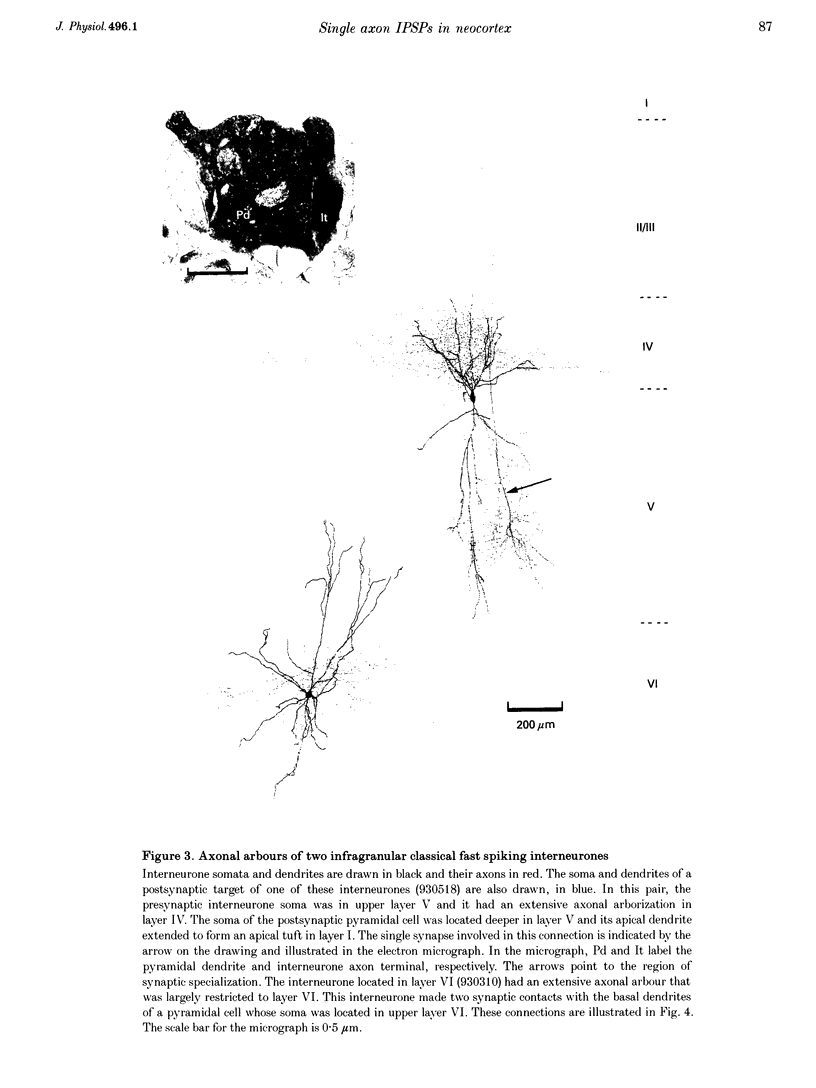
1. Using dual intracellular recordings in slices of adult rat neocortex, twenty-four IPSPs activated by single presynaptic interneurones were studied in simultaneously recorded pyramidal cells. Fast spiking interneurones inhibited one in four or five of their close pyramidal neighbours. No reciprocal connections were observed. After recordings neurones were filled with biocytin. 2. Interneurones that elicited IPSPs were classified as classical fast spiking (n = 10), as non-classical fast spiking (n = 3, including one burst-firing interneurone), as unclassified, or slow interneurones (n = 8), or as regular spiking interneurones (n = 3), i.e. interneurones whose electrophysiological characteristics were indistinguishable from those of pyramidal cells. 3. All of the seven classical fast spiking cells anatomically fully recovered had aspiny, beaded dendrites. Their partially myelinated axons ramified extensively, varying widely in shape and extent, but randomly selected labelled axon terminals typically innervated somata and large calibre dendrites on electron microscopic examination. One 'autapse' was demonstrated. One presumptive regular spiking interneurone axon made four somatic and five dendritic connections with unlabelled targets. 4. Full anatomical reconstructions of labelled classical fast spiking interneurones and their postsynaptic pyramids (n = 5) demonstrated one to five boutons per connection. The two recorded IPSPs that were fully reconstructed morphologically (3 and 5 terminals) were, however, amongst the smallest recorded (< 0.4 mV). Some connections may therefore involve larger numbers of contacts. 5. Single axon IPSPs were between 0.2 and 3.5 mV in average amplitude at -55 to -60 mV. Extrapolated reversal potentials were between -70 and -82 mV. IPSP time course correlated with the type of presynaptic interneurone, but not with IPSP latency, amplitude, reversal potential, or sensitivity to current injected at the soma. 6. Classical fast spiking interneurones elicited the fastest IPSPs (width at half-amplitude 14.72 +/- 3.83 ms, n = 10) and unclassified, or slow interneurones the slowest (56.29 +/- 23.44 ms, n = 8). Regular spiking interneurone IPSPs had intermediate half-widths (27.3 +/- 3.68 ms, n = 3). 7. Increasingly brief presynaptic interspike intervals increased the peak amplitude of, but not the area under, the summed IPSP. Only at interspike intervals between 10 and 20 ms did IPSP integrals exhibit paired pulse facilitation. Paired pulse depression was apparent at < 10 and 20-60 ms. During longer spike trains, summing IPSPs decayed to a plateau potential that was relatively independent of firing rate (100-250 Hz). Thereafter, the voltage response could increase again. 8. Summed IPSPs elicited by two to fifteen presynaptic spike trains decayed as, or more rapidly than, single-spike IPSPs. Summed IPSPs elicited by > 20 spikes (> 150 Hz), however, resulted in an additional, more slowly decaying component (latency > 50 ms, duration > 200 ms). The possible involvement of GABAB receptors in this component is discussed. 9. It is suggested that three broad classes of interneurones may activate GABAA receptors on relatively proximal portions of neocortical pyramidal neurones. The different time courses of the IPSPs elicited by the three classes may reflect different types of postsynaptic receptor rather than dendritic location. An additional class, burst firing, spiny interneurones appear to activate GABAA receptors on more distal sites.
Full text
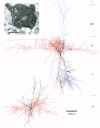
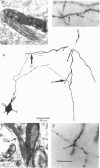
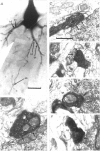
PDF


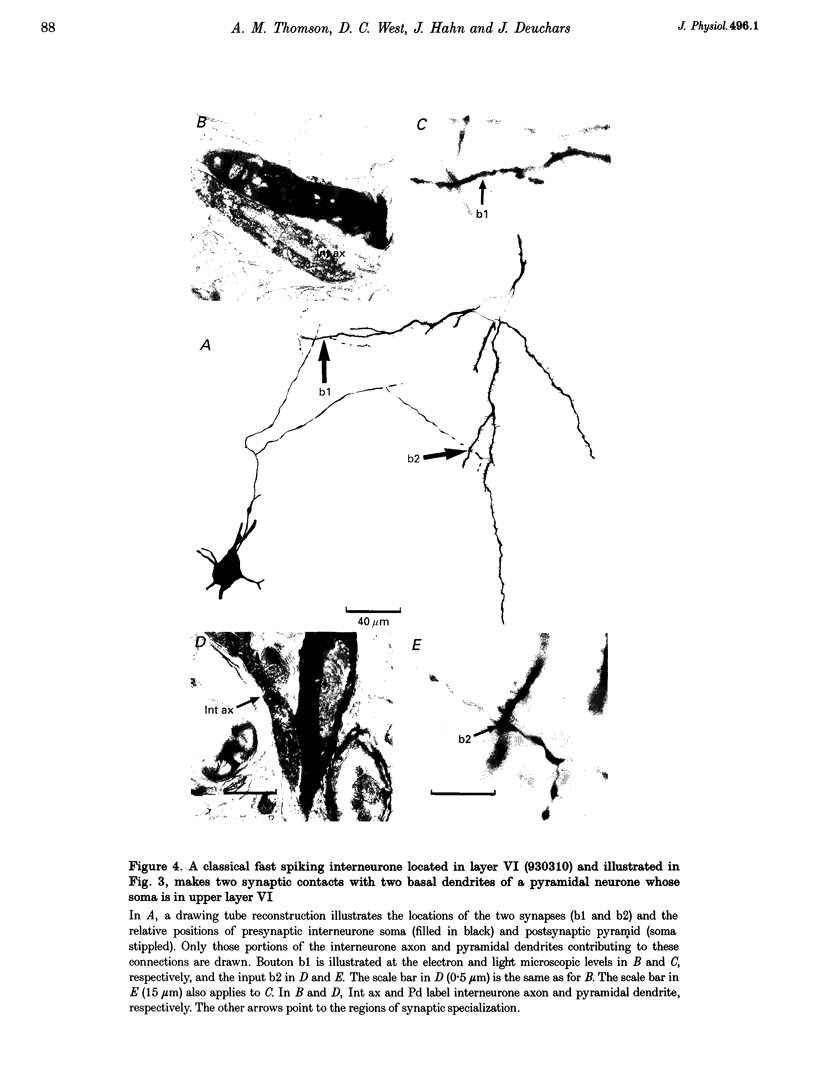
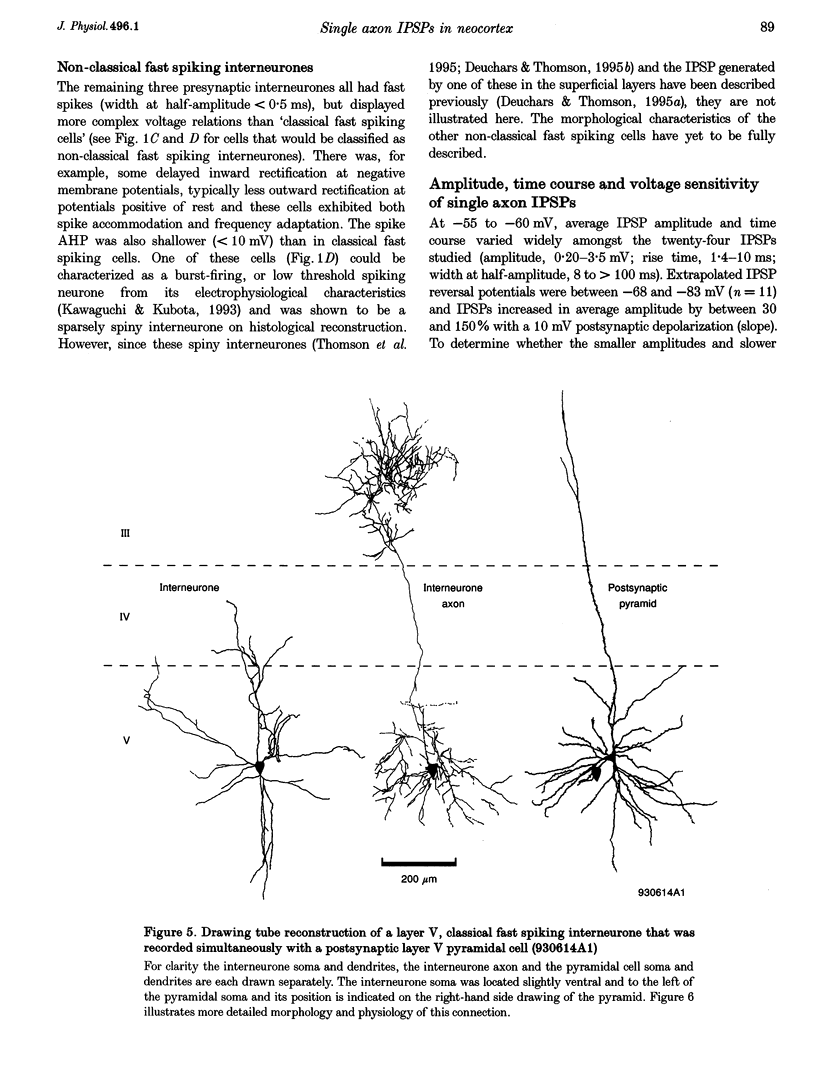
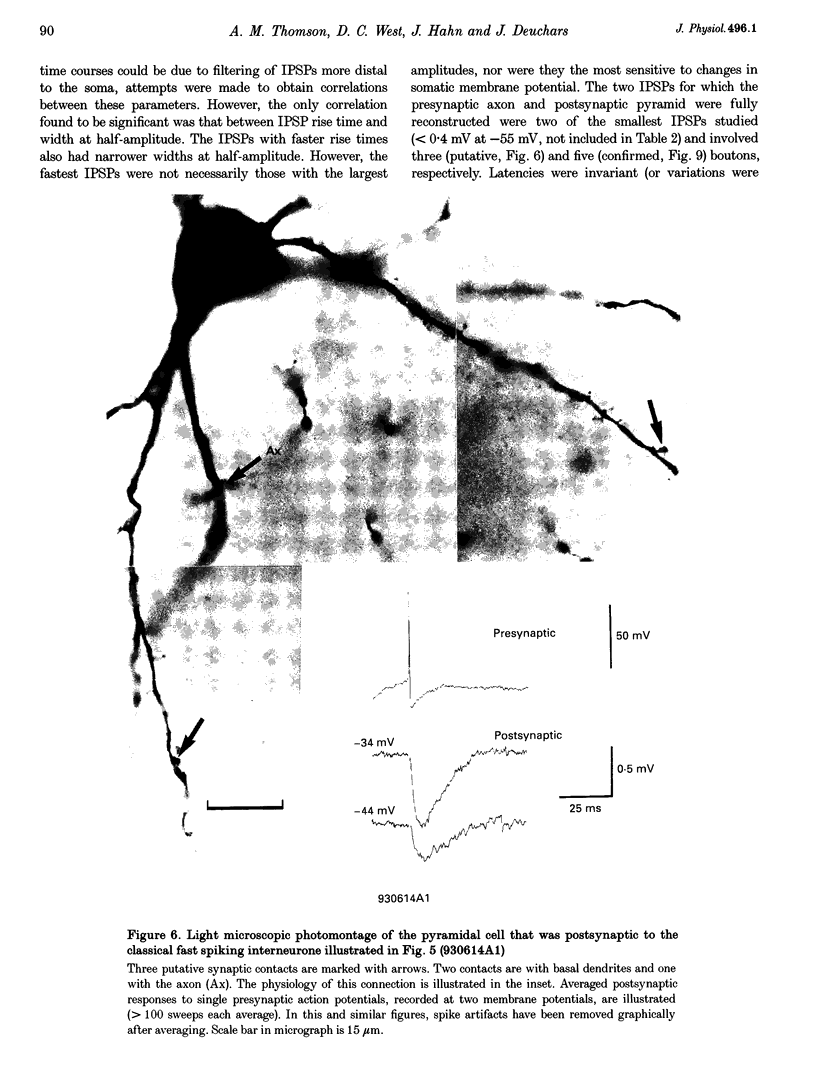
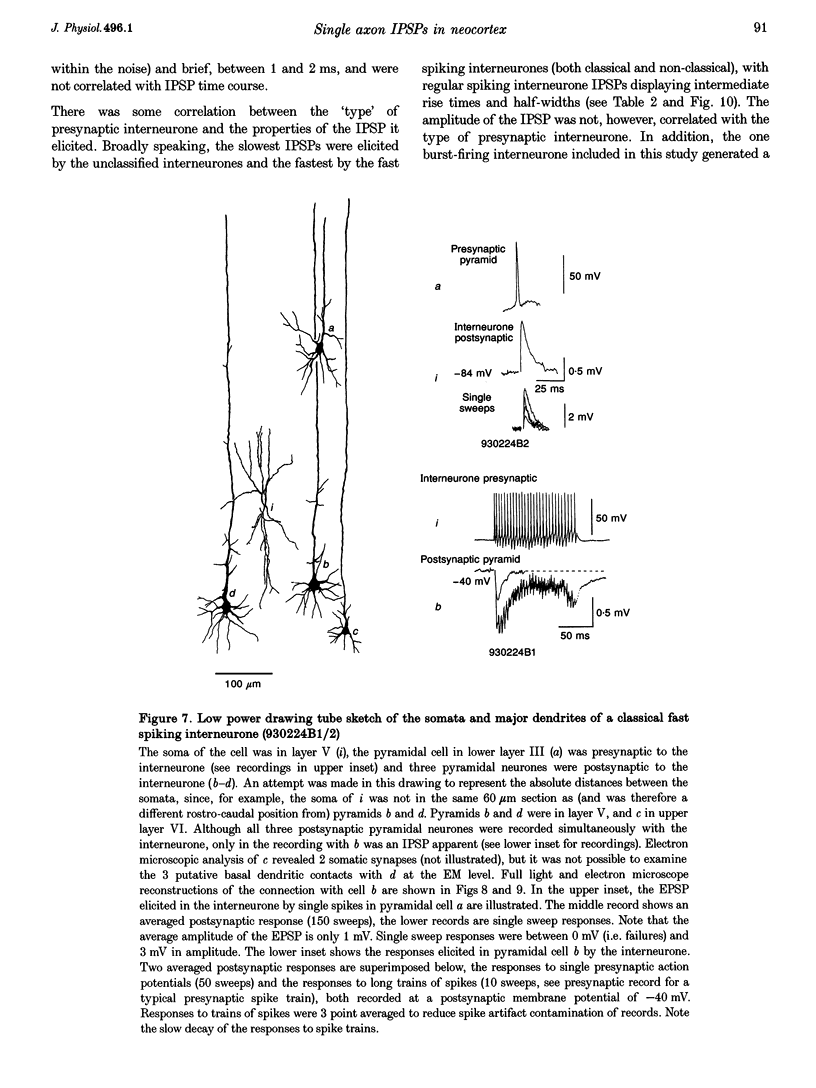
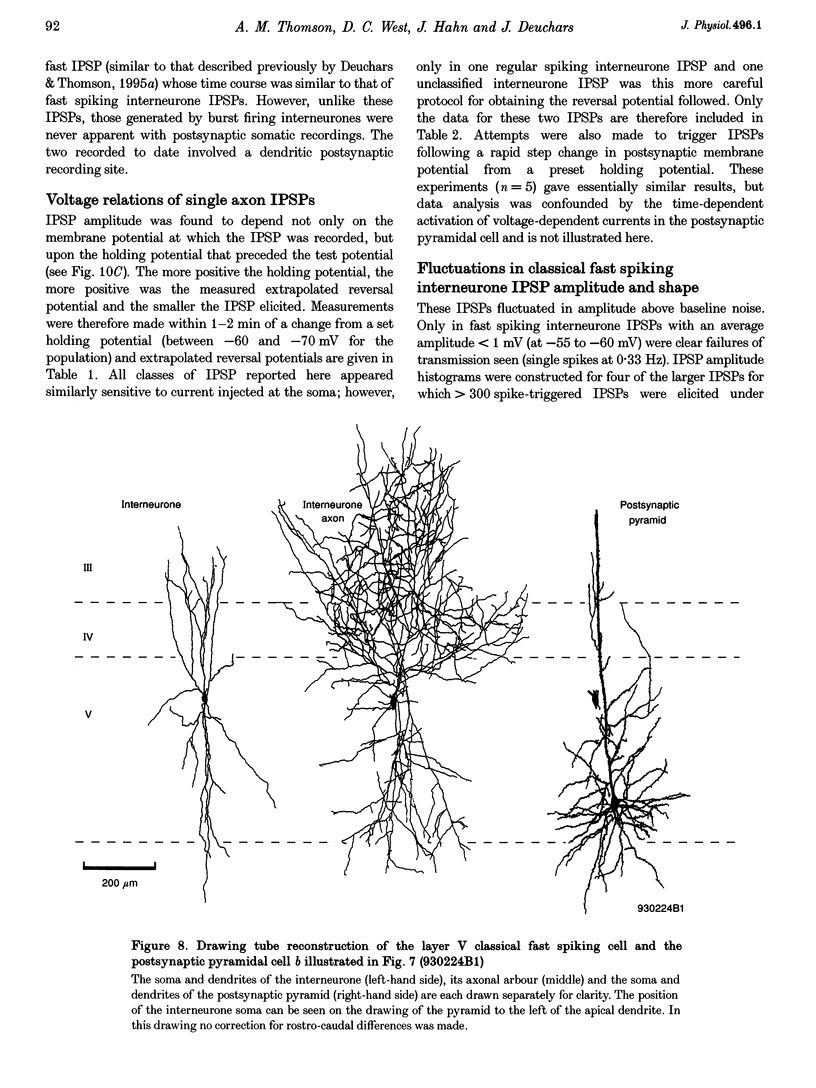
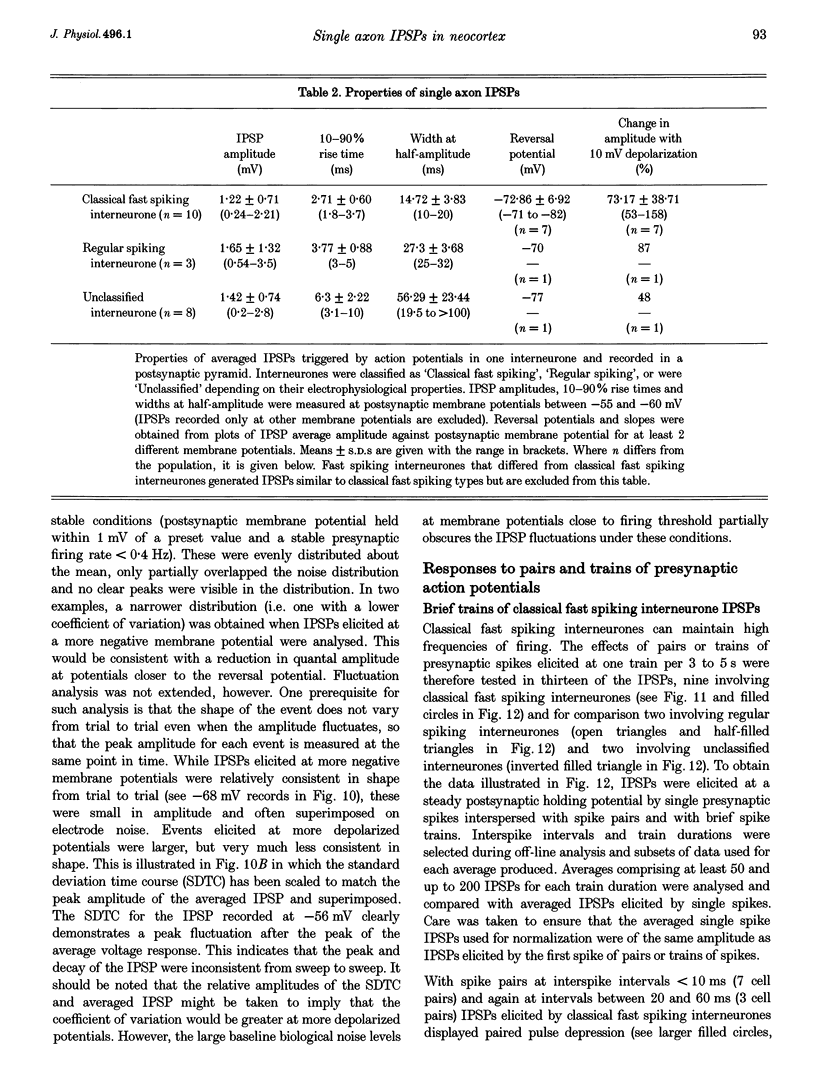
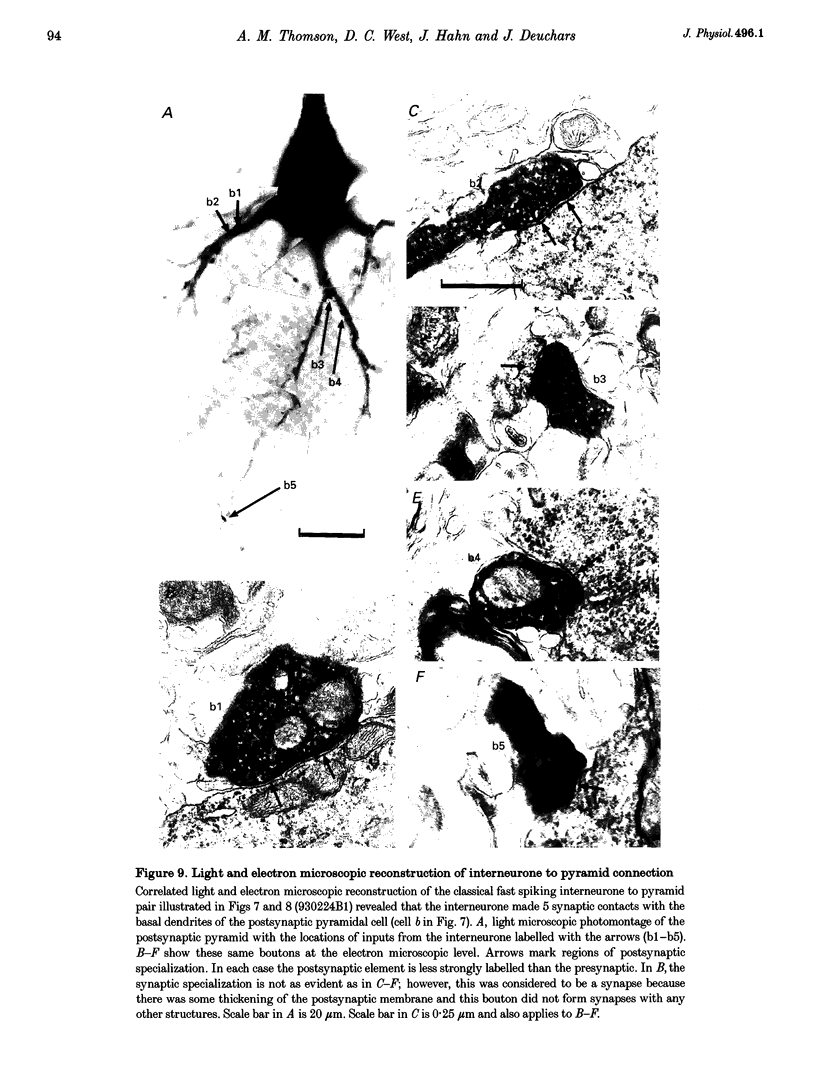
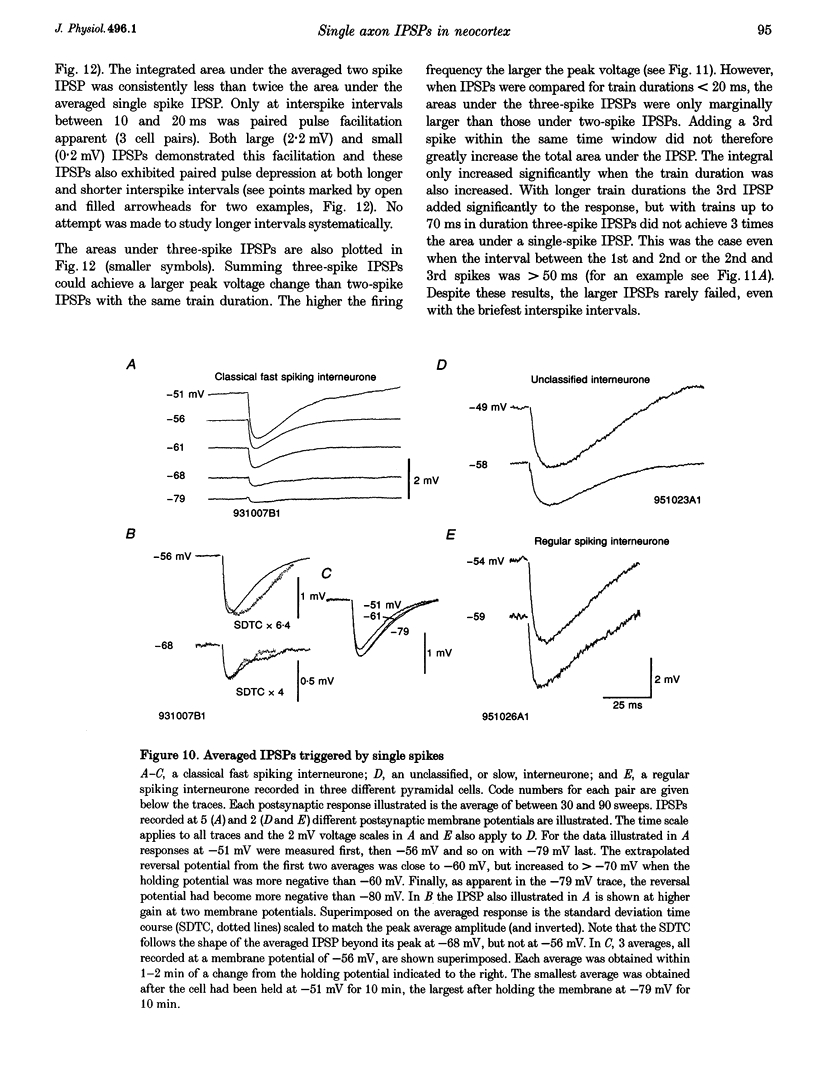
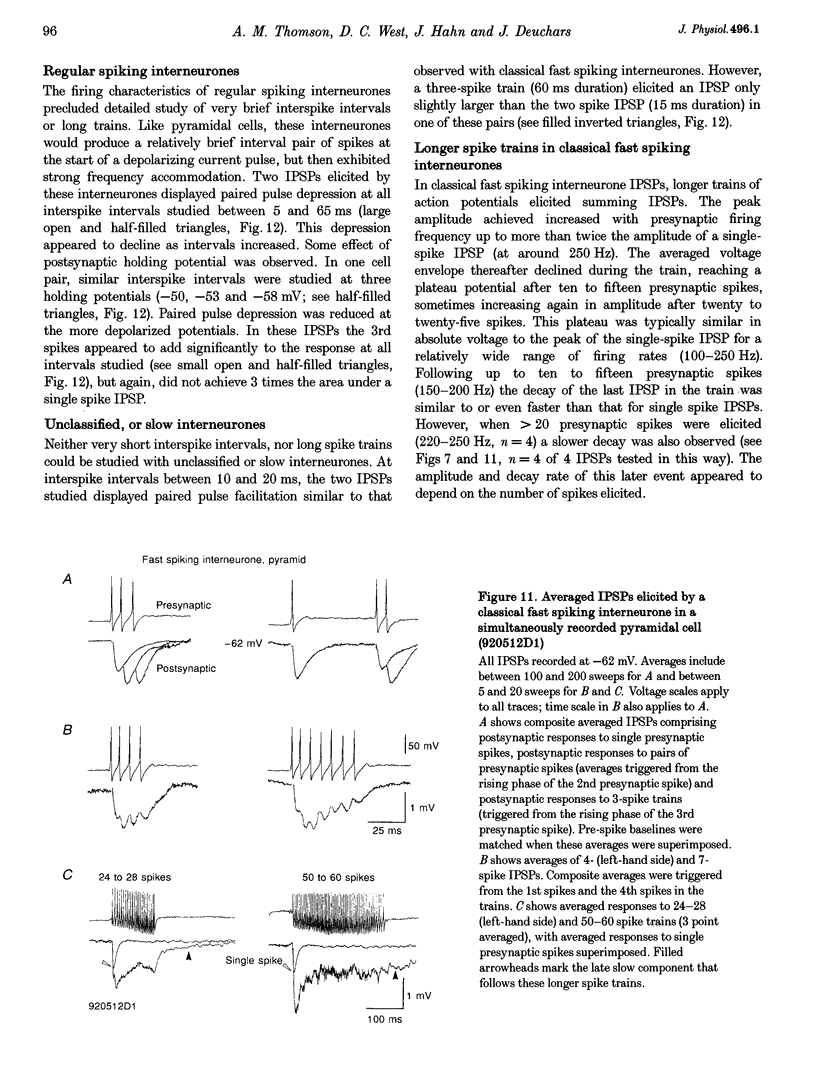
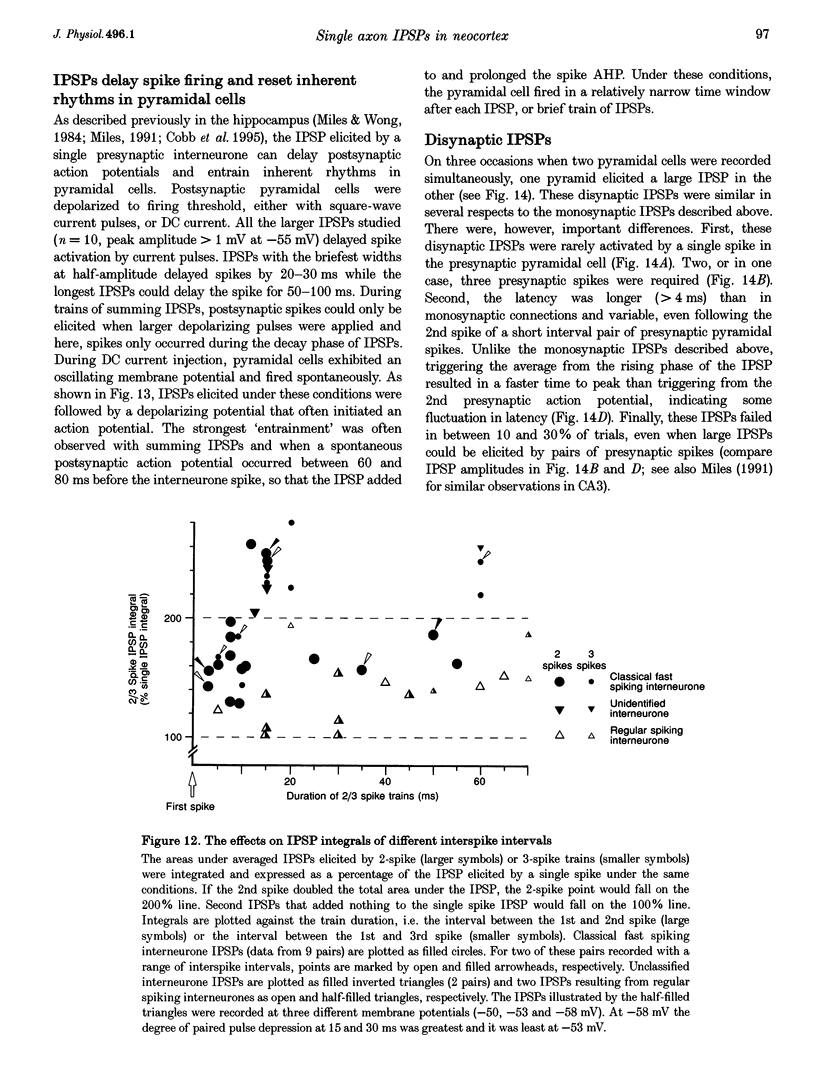
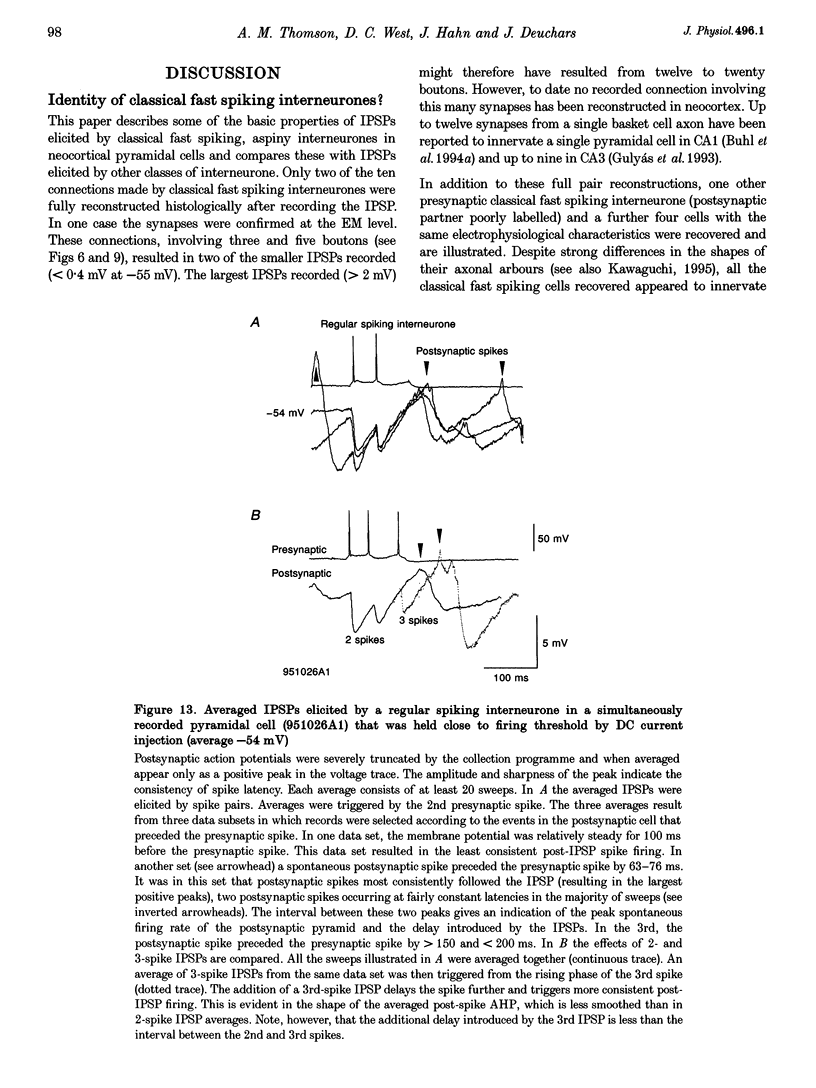
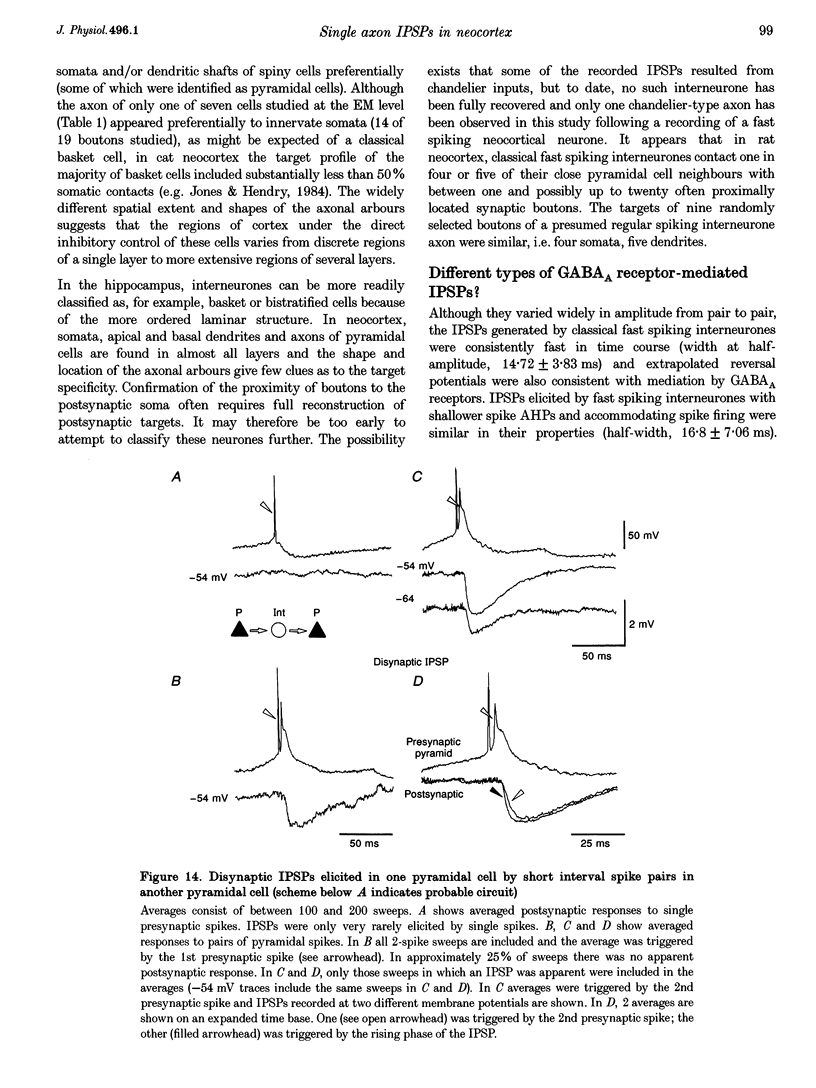



Images in this article
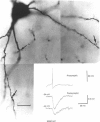
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benardo L. S. Separate activation of fast and slow inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat neocortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 15;476(2):203–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Cobb S. R., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Properties of unitary IPSPs evoked by anatomically identified basket cells in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Sep 1;7(9):1989–2004. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):823–828. doi: 10.1038/368823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Han Z. S., Lörinczi Z., Stezhka V. V., Karnup S. V., Somogyi P. Physiological properties of anatomically identified axo-axonic cells in the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Apr;71(4):1289–1307. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.4.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Szilágyi T., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Physiological properties of anatomically identified basket and bistratified cells in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus in vitro. Hippocampus. 1996;6(3):294–305. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:3<294::AID-HIPO7>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. R., Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Paulsen O., Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):75–78. doi: 10.1038/378075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condé F., Lund J. S., Jacobowitz D. M., Baimbridge K. G., Lewis D. A. Local circuit neurons immunoreactive for calretinin, calbindin D-28k or parvalbumin in monkey prefrontal cortex: distribution and morphology. J Comp Neurol. 1994 Mar 1;341(1):95–116. doi: 10.1002/cne.903410109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors B. W., Malenka R. C., Silva L. R. Two inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and GABAA and GABAB receptor-mediated responses in neocortex of rat and cat. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:443–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Haby M., Jassik-Gerschenfeld D., Leresche N., Pirchio M. Cl- - and K+-dependent inhibitory postsynaptic potentials evoked by interneurones of the rat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Jones E. G. Synapses of double bouquet cells in monkey cerebral cortex visualized by calbindin immunoreactivity. Brain Res. 1989 Nov 27;503(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91702-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Río M. R., DeFelipe J. A study of SMI 32-stained pyramidal cells, parvalbumin-immunoreactive chandelier cells, and presumptive thalamocortical axons in the human temporal neocortex. J Comp Neurol. 1994 Apr 15;342(3):389–408. doi: 10.1002/cne.903420307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuchars J., Thomson A. M. Innervation of burst firing spiny interneurons by pyramidal cells in deep layers of rat somatomotor cortex: paired intracellular recordings with biocytin filling. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):739–755. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00288-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuchars J., Thomson A. M. Single axon fast inhibitory postsynaptic potentials elicited by a sparsely spiny interneuron in rat neocortex. Neuroscience. 1995 Apr;65(4):935–942. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00020-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuchars J., West D. C., Thomson A. M. Relationships between morphology and physiology of pyramid-pyramid single axon connections in rat neocortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1994 Aug 1;478(Pt 3):423–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Miles R., Hájos N., Freund T. F. Precision and variability in postsynaptic target selection of inhibitory cells in the hippocampal CA3 region. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Dec 1;5(12):1729–1751. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Tóth K., Dános P., Freund T. F. Subpopulations of GABAergic neurons containing parvalbumin, calbindin D28k, and cholecystokinin in the rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Oct 15;312(3):371–378. doi: 10.1002/cne.903120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Z. S., Buhl E. H., Lörinczi Z., Somogyi P. A high degree of spatial selectivity in the axonal and dendritic domains of physiologically identified local-circuit neurons in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 May 1;5(5):395–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y., Kaneko T., Ohishi H., Endo K., Araki T. Spatiotemporally differential inhibition of pyramidal cells in the cat motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Jan;71(1):280–293. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.1.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Hama K. Physiological heterogeneity of nonpyramidal cells in rat hippocampal CA1 region. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(3):494–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00250594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Kubota Y. Correlation of physiological subgroupings of nonpyramidal cells with parvalbumin- and calbindinD28k-immunoreactive neurons in layer V of rat frontal cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Jul;70(1):387–396. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.1.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y. Physiological subgroups of nonpyramidal cells with specific morphological characteristics in layer II/III of rat frontal cortex. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2638–2655. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02638.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisvárday Z. F., Beaulieu C., Eysel U. T. Network of GABAergic large basket cells in cat visual cortex (area 18): implication for lateral disinhibition. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 15;327(3):398–415. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. I. Intracellular response characteristics, synaptic responses, and morphology. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1400–1410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01400.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. G., Somogyi P., Tepper J. M., Buzsáki G. Axonal and dendritic arborization of an intracellularly labeled chandelier cell in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1992;90(3):519–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00230934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Korpi E. R., Seeburg P. H. GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity: neurophysiological implications. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Mar;34(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00158-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R. Tetanic stimuli induce a short-term enhancement of recurrent inhibition in the CA3 region of guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:669–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R. Variation in strength of inhibitory synapses in the CA3 region of guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:659–676. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Unitary inhibitory synaptic potentials in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otis T. S., Mody I. Differential activation of GABAA and GABAB receptors by spontaneously released transmitter. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jan;67(1):227–235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulack D. D., Lacaille J. C. Hyperpolarizing synaptic potentials evoked in CA1 pyramidal cells by glutamate stimulation of interneurons from the oriens/alveus border of rat hippocampal slices. II. Sensitivity to GABA antagonists. Hippocampus. 1993 Jul;3(3):345–358. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450030309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Structure and pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):181–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sik A., Penttonen M., Ylinen A., Buzsáki G. Hippocampal CA1 interneurons: an in vivo intracellular labeling study. J Neurosci. 1995 Oct;15(10):6651–6665. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06651.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P. A specific 'axo-axonal' interneuron in the visual cortex of the rat. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90808-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita S., Johnson S. W., North R. A. Synaptic inputs to GABAA and GABAB receptors originate from discrete afferent neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jan 6;134(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90518-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Gähwiler B. H. Effects of the GABA uptake inhibitor tiagabine on inhibitory synaptic potentials in rat hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jun;67(6):1698–1701. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.6.1698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Deuchars J. Temporal and spatial properties of local circuits in neocortex. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Mar;17(3):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Deuchars J., West D. C. Large, deep layer pyramid-pyramid single axon EPSPs in slices of rat motor cortex display paired pulse and frequency-dependent depression, mediated presynaptically and self-facilitation, mediated postsynaptically. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Dec;70(6):2354–2369. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.6.2354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Deuchars J., West D. C. Single axon excitatory postsynaptic potentials in neocortical interneurons exhibit pronounced paired pulse facilitation. Neuroscience. 1993 May;54(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90257-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., West D. C., Deuchars J. Properties of single axon excitatory postsynaptic potentials elicited in spiny interneurons by action potentials in pyramidal neurons in slices of rat neocortex. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00287-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S., Lacaille J. C. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potentials evoked by electrical stimulation and by glutamate stimulation of interneurons in stratum lacunosum-moleculare in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in vitro. Synapse. 1992 Jul;11(3):249–258. doi: 10.1002/syn.890110309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]