Abstract
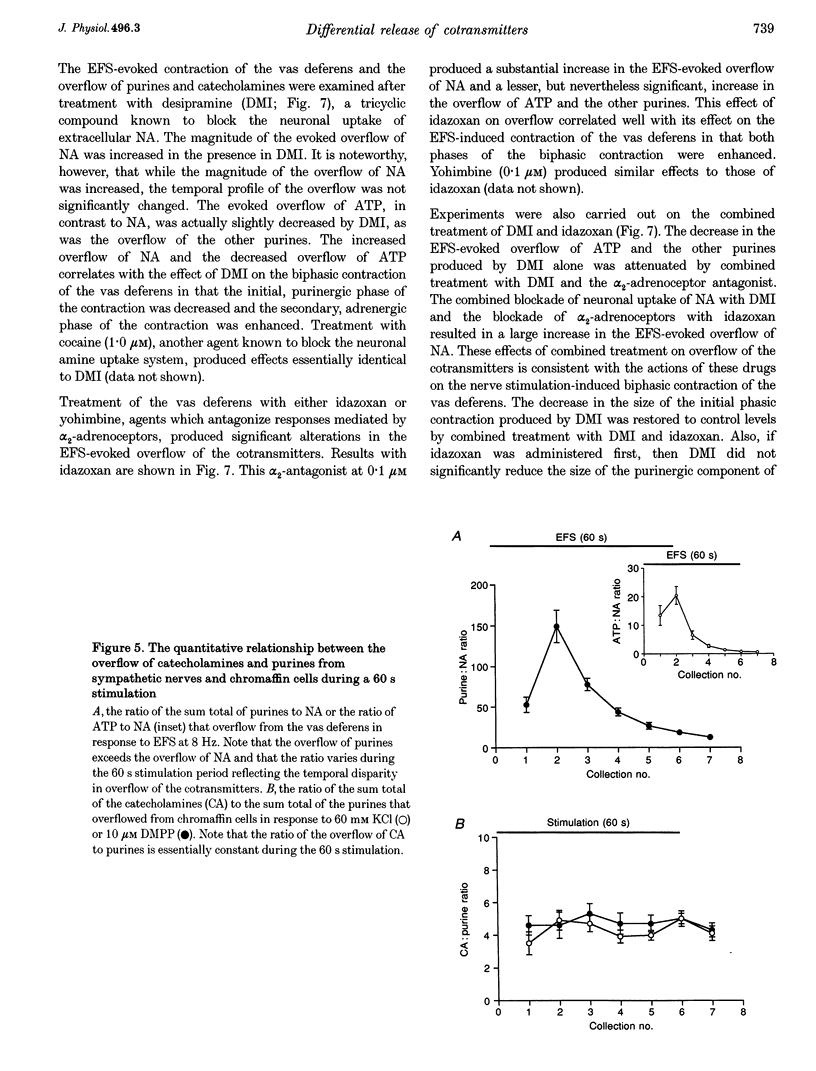
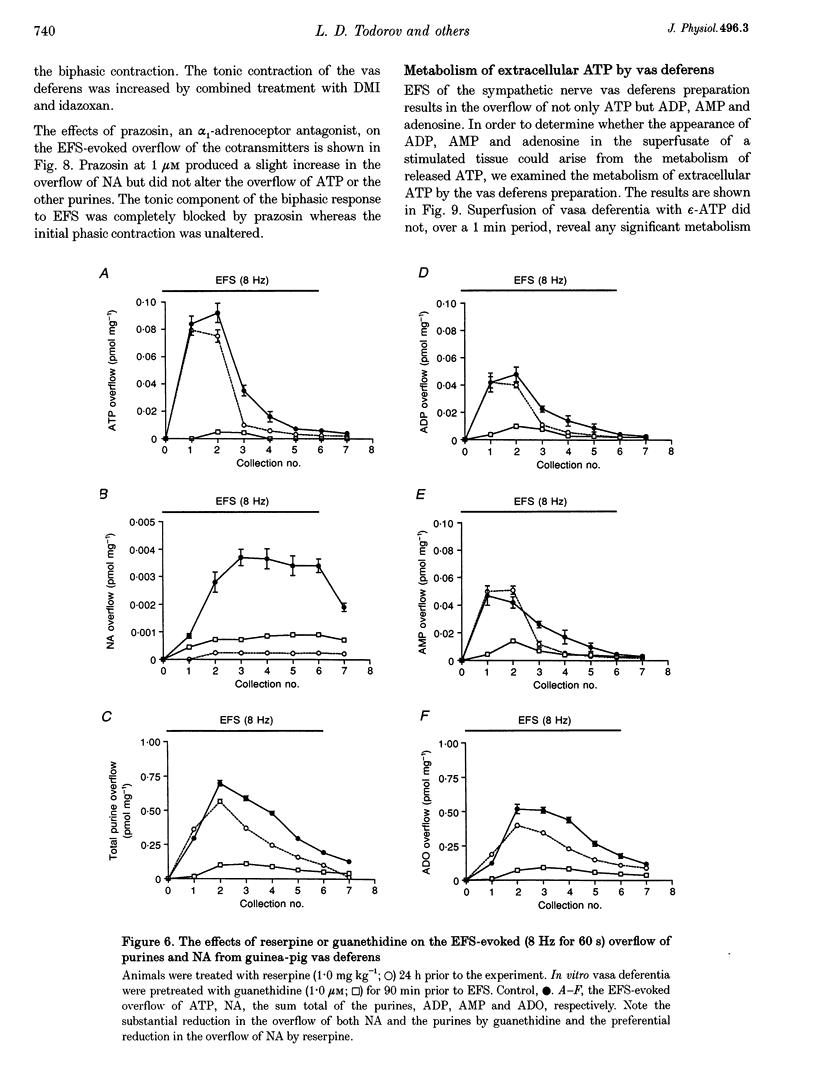
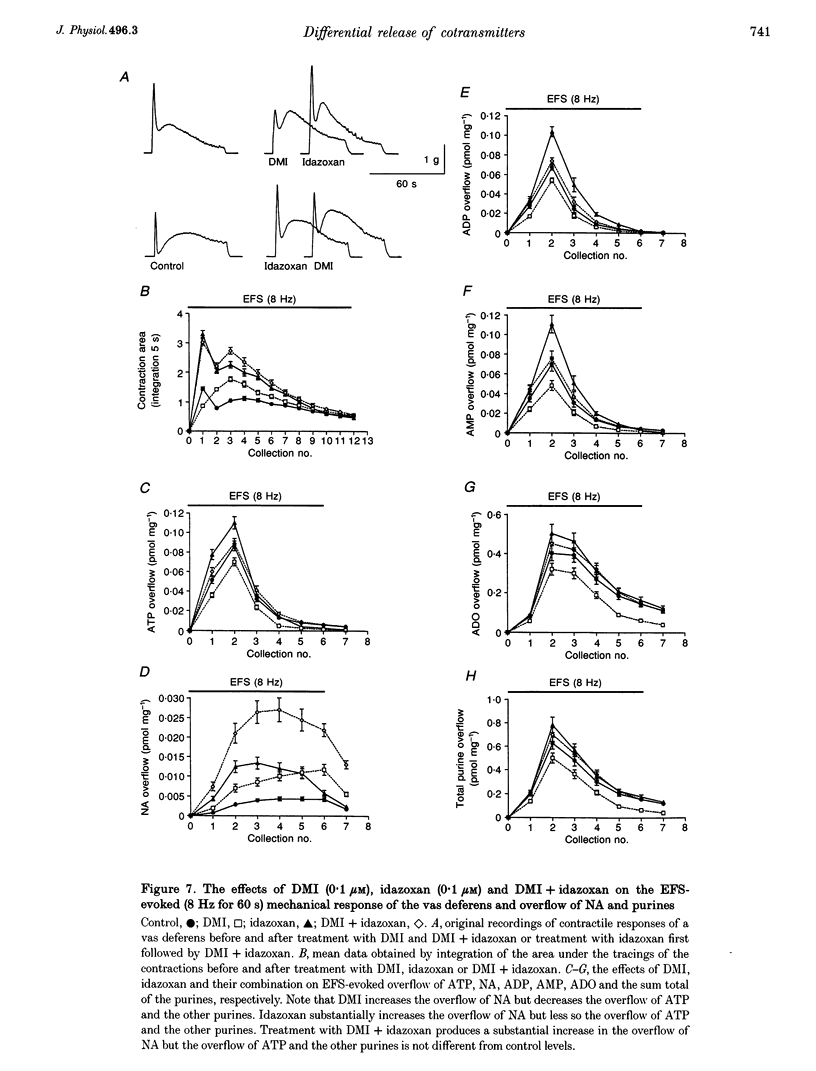
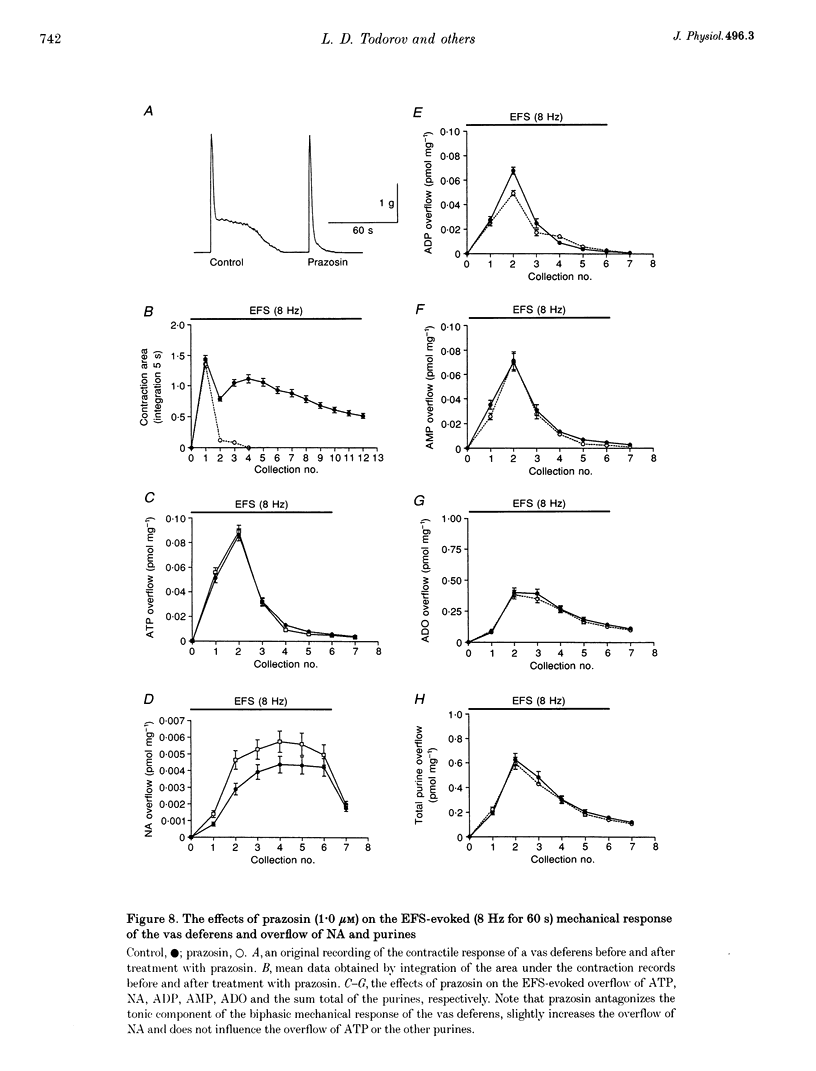
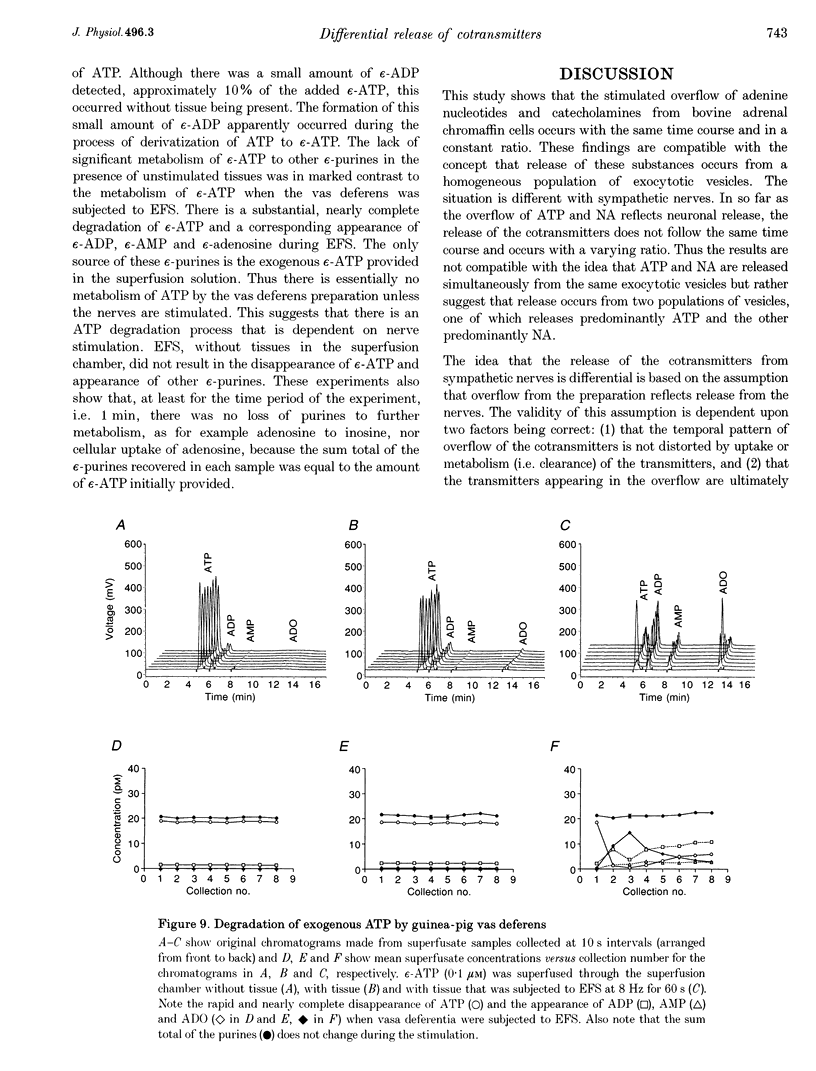
1. Experiments were carried out to quantify the stimulation-evoked overflow of catecholamines and purines (ATP, ADP, AMP and adenosine) from an in vitro sympathetic nerve-smooth muscle preparation of the guinea-pig vas deferens and from isolated bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. The superfused preparations were stimulated for 60 s with electrical field stimulation (EFS; vas deferens), dimethylphenylpiperazinium (chromaffin cells) or KCl (both preparations). 2. Samples of superfusate were taken at 10 s intervals during the 60 s stimulation period for analysis of purines by HPLC-fluorescence detection and catecholamines by HPLC-electrochemical detection. 3. The evoked overflow of catecholamines and purines from chromaffin cells occurred with the same time course and in a constant ratio of approximately 4:1 (catecholamine to purine). These findings are compatible with the release of catecholamines and purines from a homogeneous population of exocytotic vesicles in the chromaffin cells. 4. The evoked overflow of purines and noradrenaline (NA) from the vas deferens preparation differed from the pattern of overflow from chromaffin cells and there was also some temporal disparity in the overflow of the two cotransmitters. The evoked overflow of ATP exceeded that of NA. In addition, the overflow of NA was tonic while the overflow of ATP and the other purines was phasic. 5. The EFS-evoked overflow of NA and the purines from the guniea-pig vas deferens preparation was examined after treatment with the neuronal amine-uptake inhibitors desipramine and cocaine, the alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonist methoxamine, the alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin, the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists idazoxan and yohimbine, the noradrenaline-depleting drug reserpine and the adrenergic neuron-blocking agent guanethidine. The results of these studies, together with an analysis of the metabolic degradation of extracellular ATP, indicated that the temporal disparity in the overflow of NA and ATP is unlikely to be due to differences in the clearance of the cotransmitters or to the release of purines from non-neuronal sites. These results indicate that evoked overflow of the cotransmitters accurately reflects release from nerves. This pattern of release from nerves suggests that the two cotransmitters are released from two separate populations of exocytotic vesicles. 6. Superfusion of the vas deferens with exogenous epsilon-ATP, a fluorescent derivative of ATP, revealed that there was essentially no metabolism of the nucleotide over 60 s unless the tissue was subjected to EFS. Upon EFS, there was a rapid and nearly complete degradation of ATP with a corresponding increase in ADP, AMP and adenosine. This indicates the presence of a nerve stimulation-dependent metabolism of ATP.
Full text
PDF


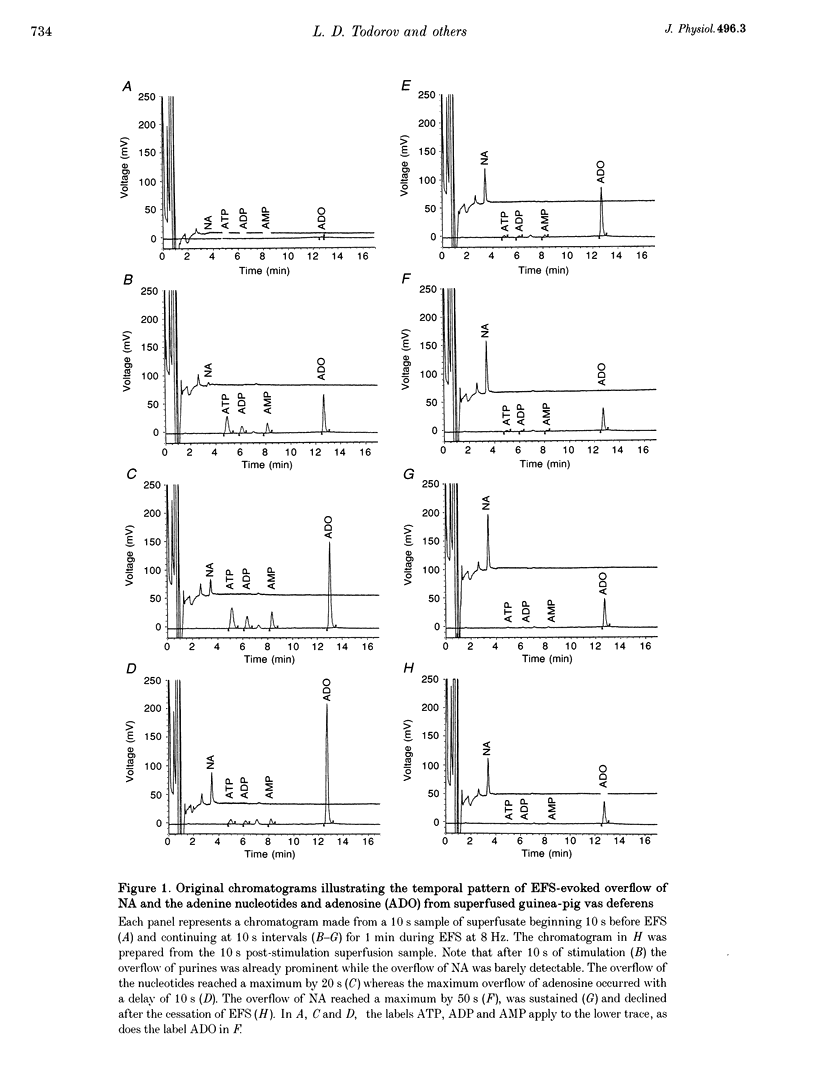

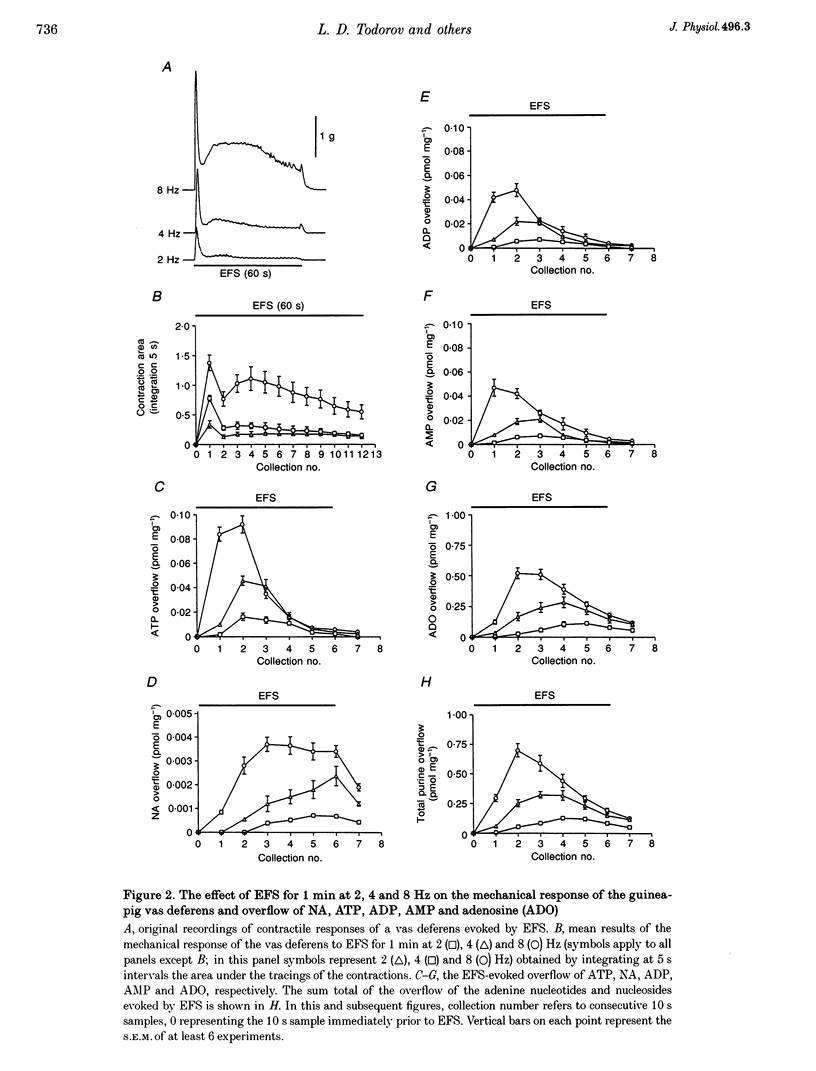
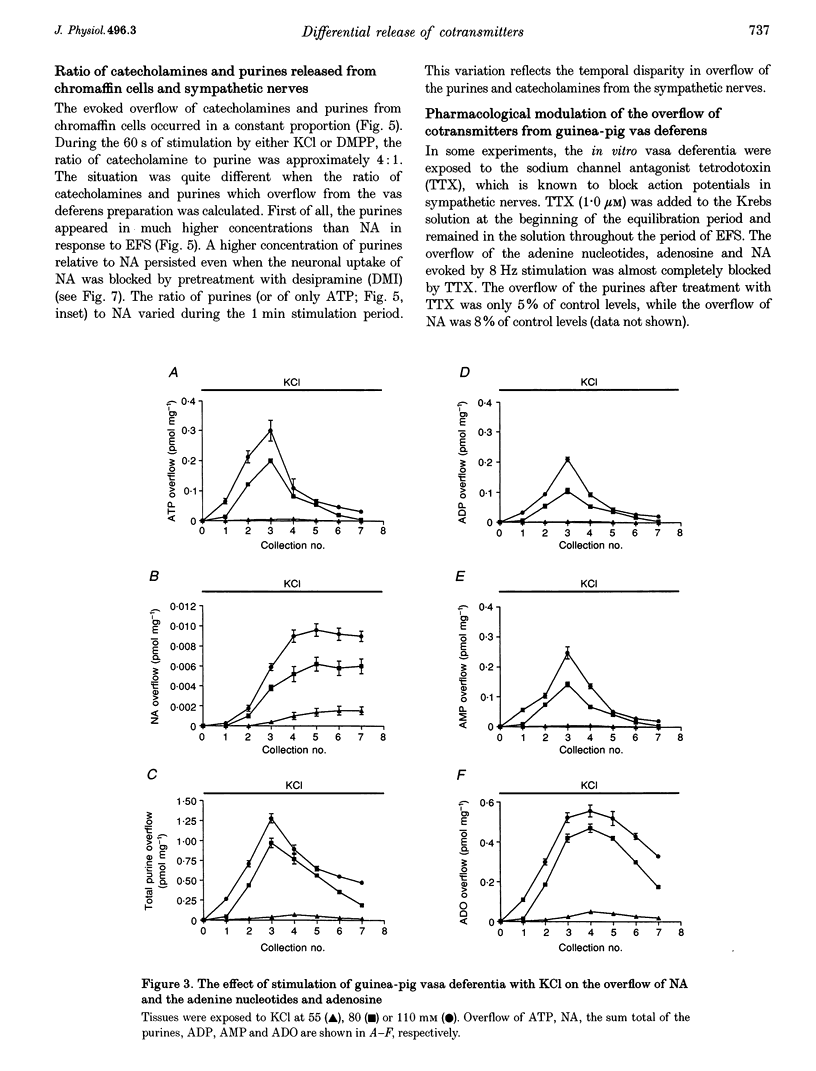
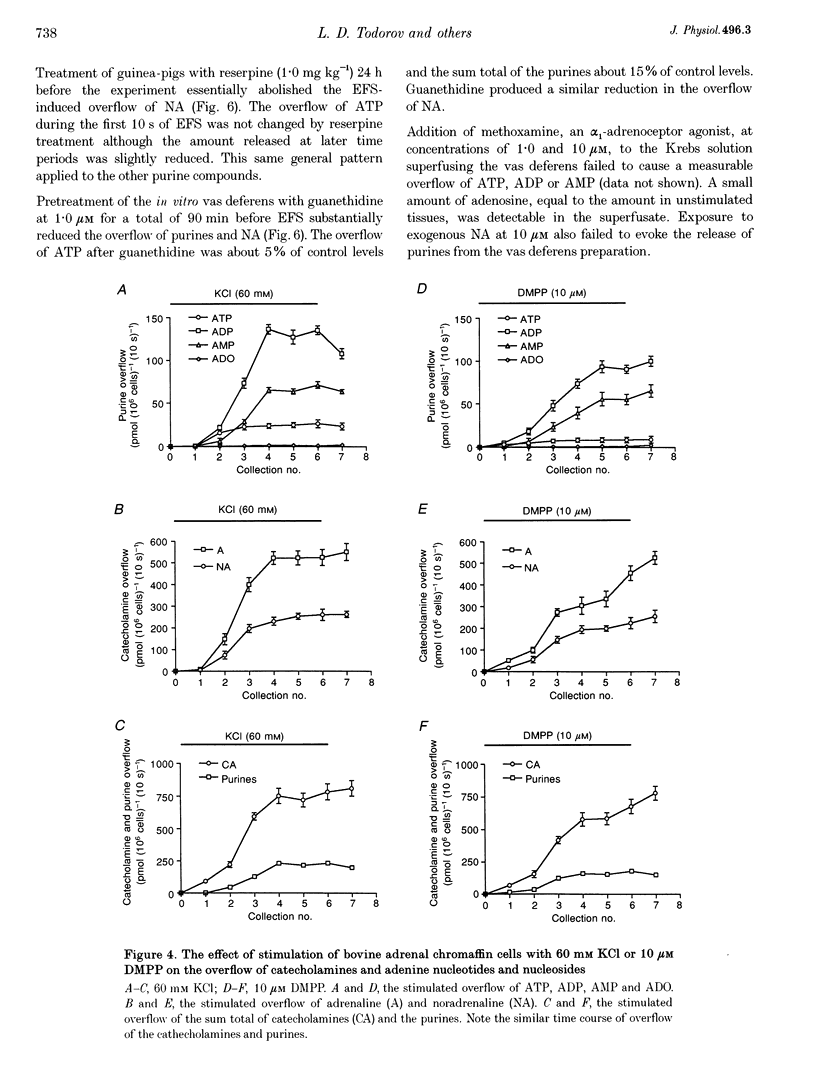





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao J. X., Gonon F., Stjärne L. Kinetics of ATP- and noradrenaline-mediated sympathetic neuromuscular transmission in rat tail artery. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Dec;149(4):503–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen B., von Kügelgen I., Starke K. P1-purinoceptor-mediated modulation of neural noradrenaline and ATP release in guinea-pig vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;350(1):42–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00180009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. L., Burnstock G. Angiotensin neuromodulation of adrenergic and purinergic co-transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1157–1164. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. L., Burnstock G. Modulation by prostaglandin E2 of ATP and noradrenaline co-transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Auton Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;10(6):363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1990.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P., Colby J., Westfall D. P. Contribution by purines to the neurogenic response of the vas deferens of the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90600-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth K. M., Pollock D. Clonidine and morphine increase [3H]-noradrenaline overflow in mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Iwayama T. The arrangement and identification of axons innervating the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J Anat. 1972 Nov;113(Pt 2):179–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Morris J. L., Gibbins I. L., Costa M. Chemical coding of neurons and plurichemical transmission. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:289–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B. Transmission to the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens: The effect of pretreatment with guanethidine. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;50(1):63–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves J., Bültmann R., Driessen B. Opposite modulation of cotransmitter release in guinea-pig vas deferens: increase of noradrenaline and decrease of ATP release by activation of prejunctional beta-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;353(2):184–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00168756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuragi T., Tokunaga T., Usune S., Furukawa T. A possible coupling of postjunctional ATP release and transmitters' receptor stimulation in smooth muscles. Life Sci. 1990;46(18):1301–1307. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90363-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoyi M. A., Westfall D. P., Buxton I. L., Akhtar-Khavari F., Rezaei E., Salaices M., Sanchez-Garcia P. Norepinephrine and potassium induced calcium translocation in rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):917–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick K., Burnstock G. Sympathetic nerve-mediated release of ATP from the guinea-pig vas deferens is unaffected by reserpine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt B., Head R. J., Westfall D. P. High-pressure liquid chromatographic-fluorometric detection of adenosine and adenine nucleotides: application to endogenous content and electrically induced release of adenyl purines in guinea pig vas deferens. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msghina M., Mermet C., Gonon F., Stjärne L. Electrophysiological and electrochemical analysis of the secretion of ATP and noradrenaline from the sympathetic nerves in rat tail artery: effects of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists and noradrenaline reuptake blockers. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;346(2):173–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00165299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweinsberg P. D., Loo T. L. Simultaneous analysis of ATP, ADP, AMP, and other purines in human erythrocytes by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jan 11;181(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedaa K. O., Bjur R. A., Shinozuka K., Westfall D. P. Nerve and drug-induced release of adenine nucleosides and nucleotides from rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1060–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka K., Hashimoto M., Masumura S., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P., Hattori K. In vitro studies of release of adenine nucleotides and adenosine from rat vascular endothelium in response to alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1203–1208. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. ATP as a co-transmitter in rat tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperlágh B., Vizi E. S. Is the neuronal ATP release from guinea-pig vas deferens subject to alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated modulation? Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90485-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov L. D., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Temporal dissociation of the release of the sympathetic co-transmitters ATP and noradrenaline. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994 Nov;21(11):931–932. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1994.tb02469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachte G. J. Angiotensin effects on vas deferens adrenergic and purinergic neurotransmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 9;146(2-3):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachte G. J., Binder S. B., Peach M. J. Indirect evidence for separate vesicular neuronal origins of norepinephrine and ATP in the rabbit vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Bennett W. F., Boehme R., Hankins L., Gilmer-Waymire K., Haycock J. W. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: high-yield purification and viability in suspension culture. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Apr;7(4):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall D. P., Stitzel R. E., Rowe J. N. The postjunctional effects and neural release of purine compounds in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul 1;50(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S., Cheek D. J., Westfall D. P., Buxton I. L. Purinergic axis in cardiac blood vessels. Agonist-mediated release of ATP from cardiac endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1994 Mar;74(3):401–407. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Corelease of noradrenaline and ATP by brief pulse trains in guinea-pig vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00241085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Release of noradrenaline and ATP by electrical stimulation and nicotine in guinea-pig vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;344(4):419–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00172581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



