Abstract
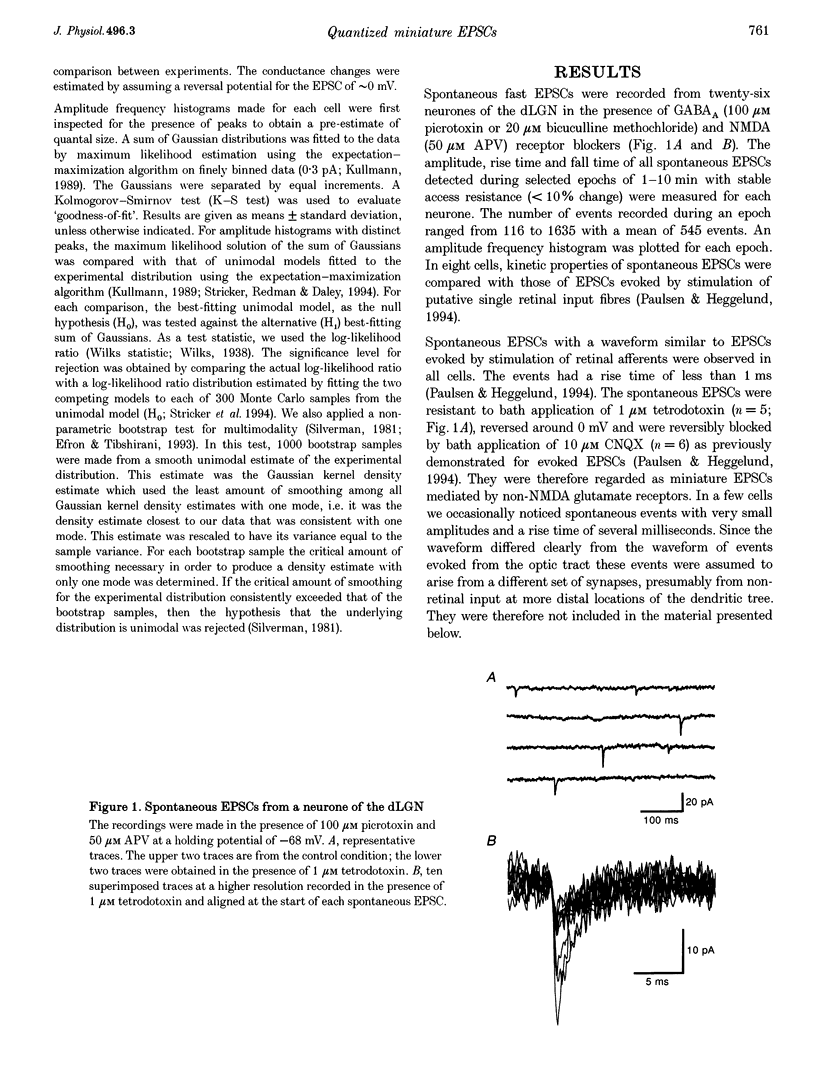
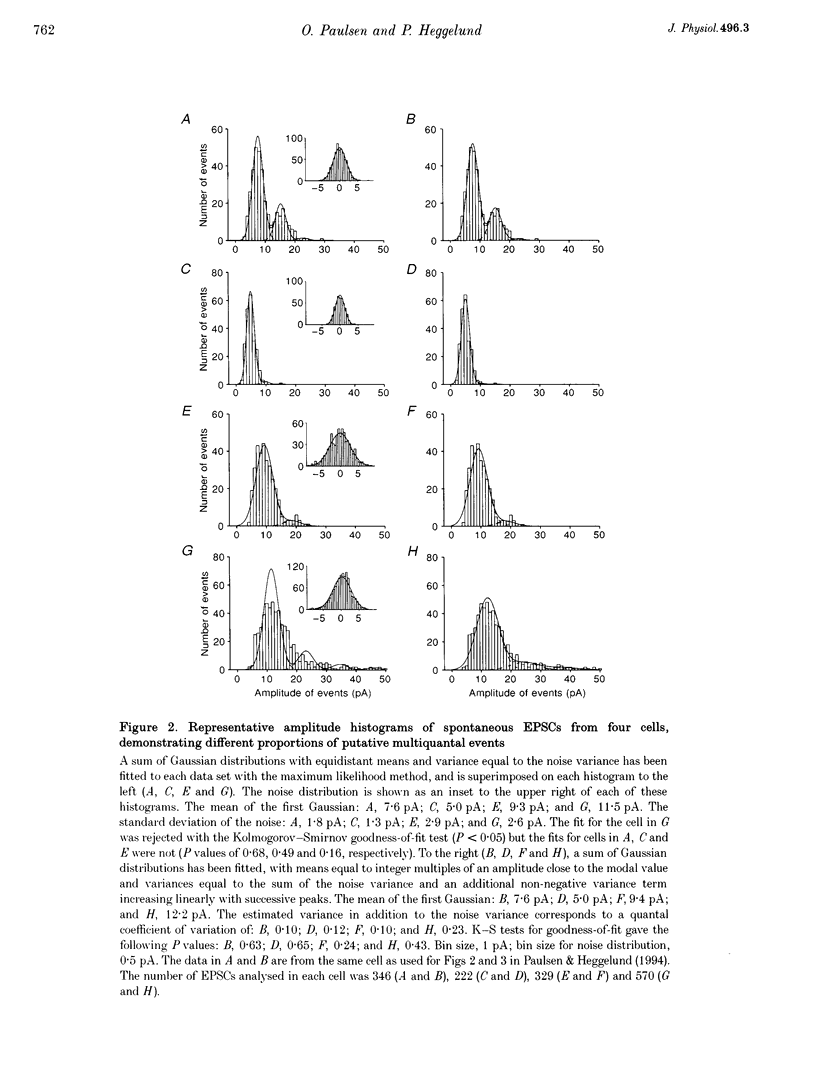
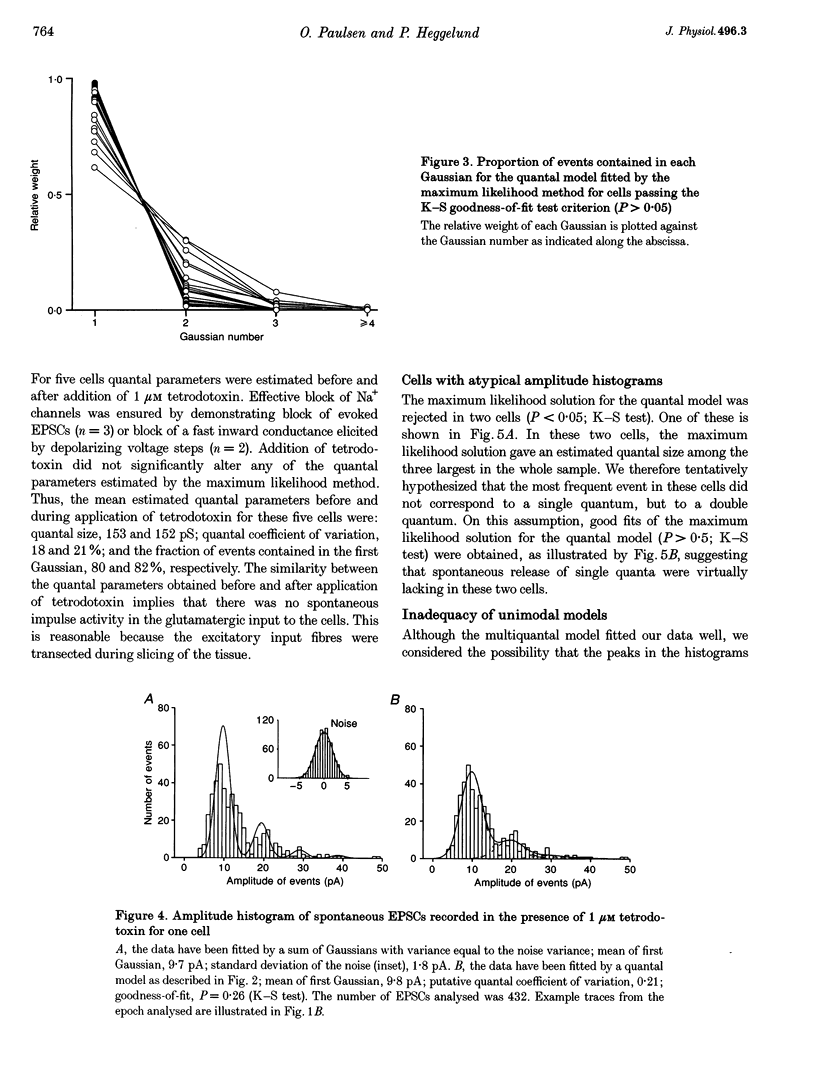
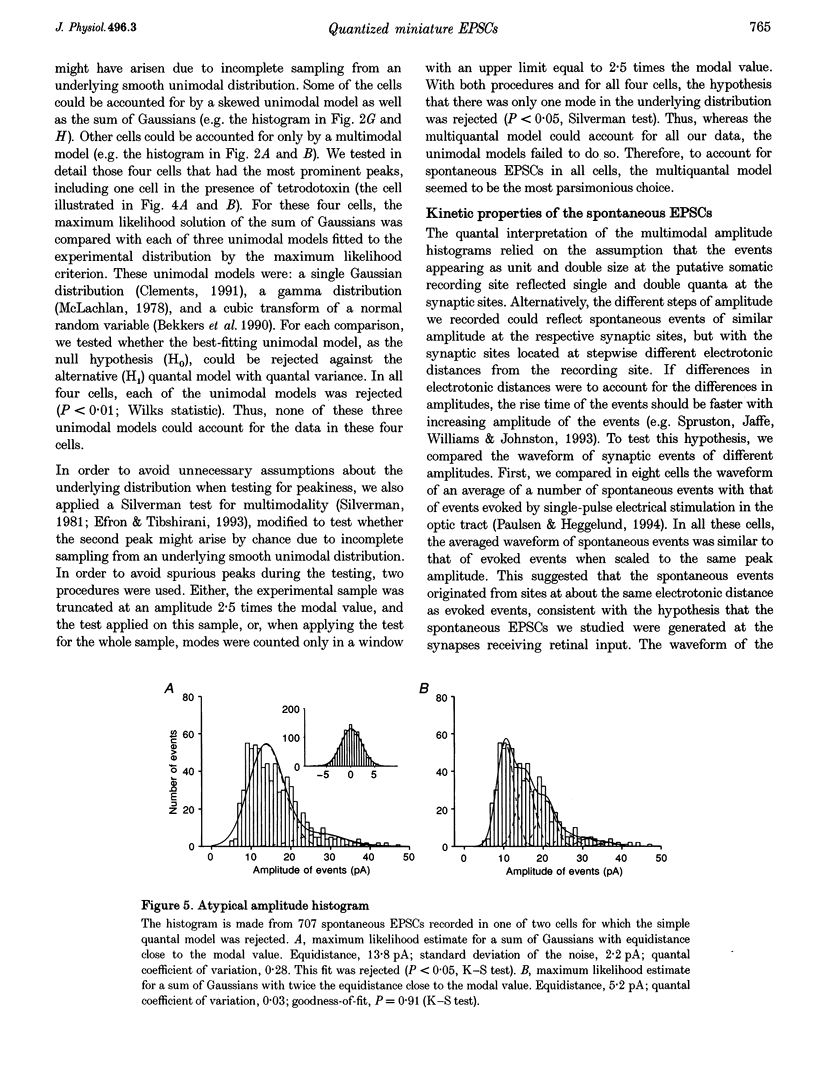
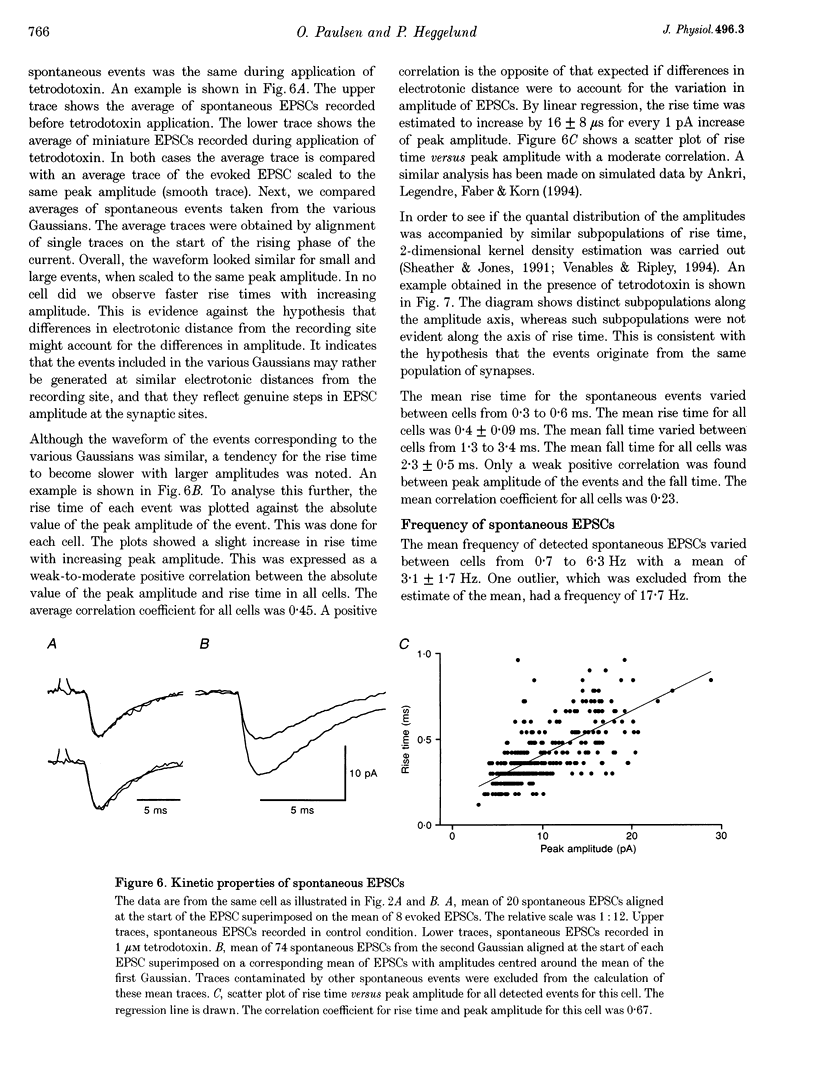
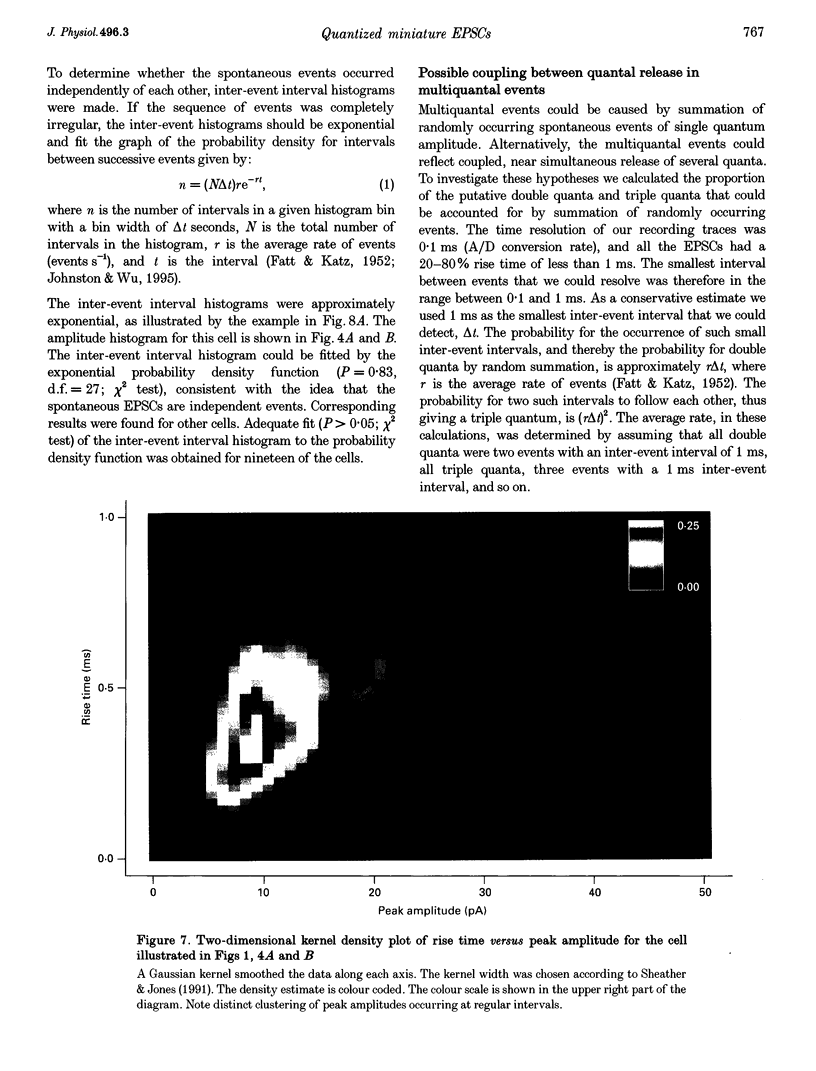
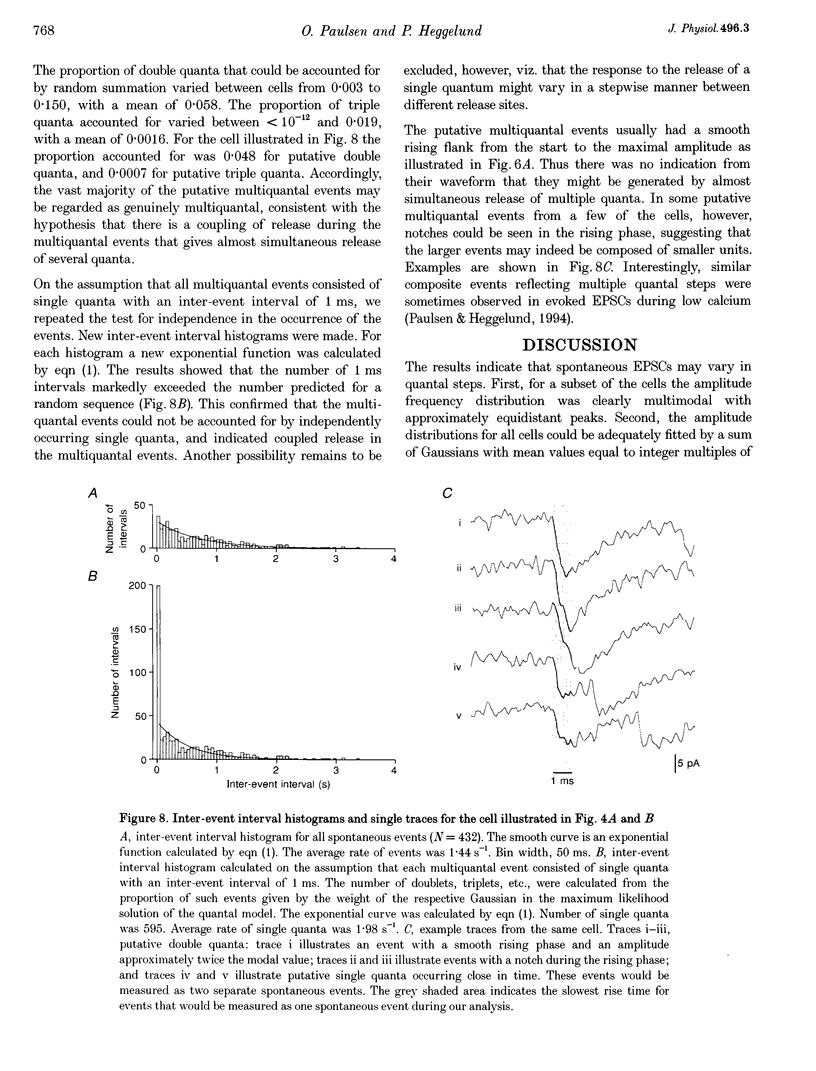
1. Spontaneous non-NMDA glutamate receptor-mediated EPSCs were recorded with the whole-cell patch-clamp technique from twenty-six neurones in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in thalamic slices from guinea-pig. 2. Amplitude distributions of the EPSCs were skewed towards larger values. The skewness could be accounted for by multiquantal properties. The multiquantal properties were most clearly demonstrated in four cells that had prominent peaks in the amplitude distribution, and peak separation approximately corresponding to the modal value. The amplitude distribution for all cells could be adequately fitted by a quantal model consisting of a sum of Gaussians with means equal to integer multiples of a quantal unit. The variance of each Gaussian was equal to the sum of the noise variance of the recordings and an additional non-negative variance which increased linearly with the number of the Gaussian in the series. The estimated mean quantal size was 152 +/- 37 pS. The estimated mean quantal coefficient of variation was 15%. Addition of tetrodotoxin did not significantly change any of the quantal parameters (n = 5). 3. The waveform of the EPSCs was similar for small and large events, and similar to that of events evoked by stimulation of retinal input fibres. There was a positive correlation between peak amplitude and rise time. This is the opposite of that expected if differences in electrotonic distances were to explain differences in amplitude. 4. The spontaneous EPSCs occurred randomly at an average frequency of 3.1 Hz. The events with amplitudes approximately equal to multiples of the quantal size were, in most cells, more numerous than could be accounted for by coincidence of randomly occurring events of quantal size. 5. The results indicate that spontaneous EPSCs can reflect more than a single quantum, and suggest that quantal events may be coupled due to action potential-independent near-synchronous multiquantal release of transmitter.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankri N., Legendre P., Faber D. S., Korn H. Automatic detection of spontaneous synaptic responses in central neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 1994 Apr;52(1):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(94)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Richerson G. B., Stevens C. F. Origin of variability in quantal size in cultured hippocampal neurons and hippocampal slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5359–5362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton M. G., Lo Turco J. J., Kriegstein A. R. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield S. A., Hamos J. E., Sherman S. M. Passive cable properties and morphological correlates of neurones in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:653–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein J. C. Spontaneous multiquantal release at synapses in guinea-pig hypogastric ganglia: evidence that release can occur in bursts. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:375–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. Quantal synaptic transmission? Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):396–396. doi: 10.1038/353396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Leresche N., Parnavelas J. G. Membrane properties of morphologically identified X and Y cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B. Quantal analysis of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices: a patch-clamp study. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:213–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Young W. S., Legendre P., Korn H. Intrinsic quantal variability due to stochastic properties of receptor-transmitter interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1494–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.1279813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamos J. E., Van Horn S. C., Raczkowski D., Sherman S. M. Synaptic circuits involving an individual retinogeniculate axon in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 May 8;259(2):165–192. doi: 10.1002/cne.902590202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J., Wong K. The components of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group Ia afferents. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:65–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Major G., Sakmann B. Quantal components of unitary EPSCs at the mossy fibre synapse on CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:615–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Bausela F., Charpier S., Faber D. S. Synaptic noise and multiquantal release at dendritic synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Sep;70(3):1249–1254. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.3.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Faber D. S. Transmission at a central inhibitory synapse. IV. Quantal structure of synaptic noise. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):198–222. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann D. M. Applications of the expectation-maximization algorithm to quantal analysis of postsynaptic potentials. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann D. M., Nicoll R. A. Long-term potentiation is associated with increases in quantal content and quantal amplitude. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):240–244. doi: 10.1038/357240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. Spontaneous release of transmitter substance in multiquantal units. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):595–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman A., Stratford K., Jack J. Quantal analysis of excitatory synaptic action and depression in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):344–347. doi: 10.1038/350344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D., Jones A., Malinow R. Direct measurement of quantal changes underlying long-term potentiation in CA1 hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1089–1097. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90068-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen O., Heggelund P. The quantal size at retinogeniculate synapses determined from spontaneous and evoked EPSCs in guinea-pig thalamic slices. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 1;480(Pt 3):505–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raastad Morten, Storm Johan F., Andersen Per. Putative Single Quantum and Single Fibre Excitatory Postsynaptic Currents Show Similar Amplitude Range and Variability in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Eur J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;4(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapisardi S. C., Miles T. P. Synaptology of retinal terminals in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Mar 10;223(4):515–534. doi: 10.1002/cne.902230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. Quantal analysis of synaptic potentials in neurons of the central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):165–198. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson J. A. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of the patterns of retinal input to neurons in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Aug 8;334(2):324–336. doi: 10.1002/cne.903340212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert N., Miles R., Korn H. Characteristics of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurones of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:707–722. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. A., Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Rapid-time-course miniature and evoked excitatory currents at cerebellar synapses in situ. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):163–166. doi: 10.1038/355163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruston N., Jaffe D. B., Williams S. H., Johnston D. Voltage- and space-clamp errors associated with the measurement of electrotonically remote synaptic events. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Aug;70(2):781–802. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.2.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P., Edwards F. A., Sakmann B. Fast and slow components of unitary EPSCs on stellate cells elicited by focal stimulation in slices of rat visual cortex. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker C., Redman S., Daley D. Statistical analysis of synaptic transmission: model discrimination and confidence limits. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):532–547. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80513-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich D., Lüscher H. R. Miniature excitatory synaptic currents corrected for dendritic cable properties reveal quantal size and variance. J Neurophysiol. 1993 May;69(5):1769–1773. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.5.1769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kloot W. The regulation of quantal size. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(2):93–130. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90019-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Friedlander M. J., Sherman S. M. Fine structural morphology of identified X- and Y-cells in the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jun 22;221(1225):411–436. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]