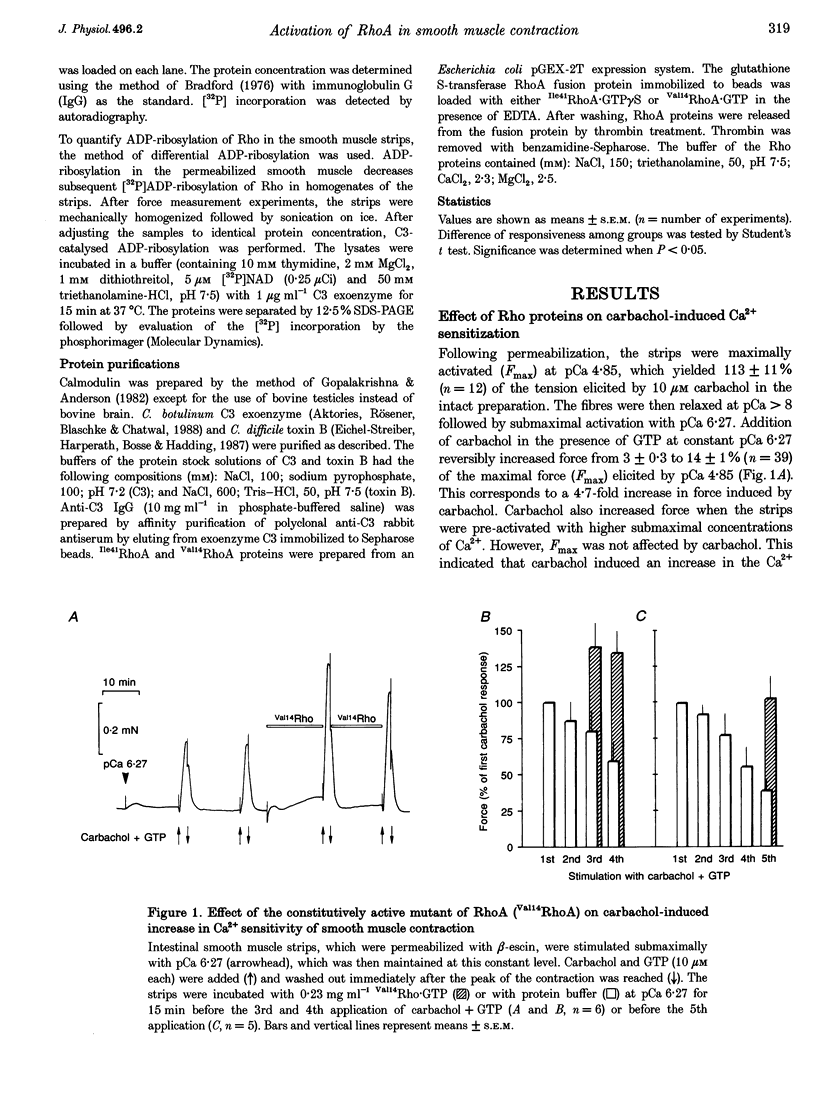
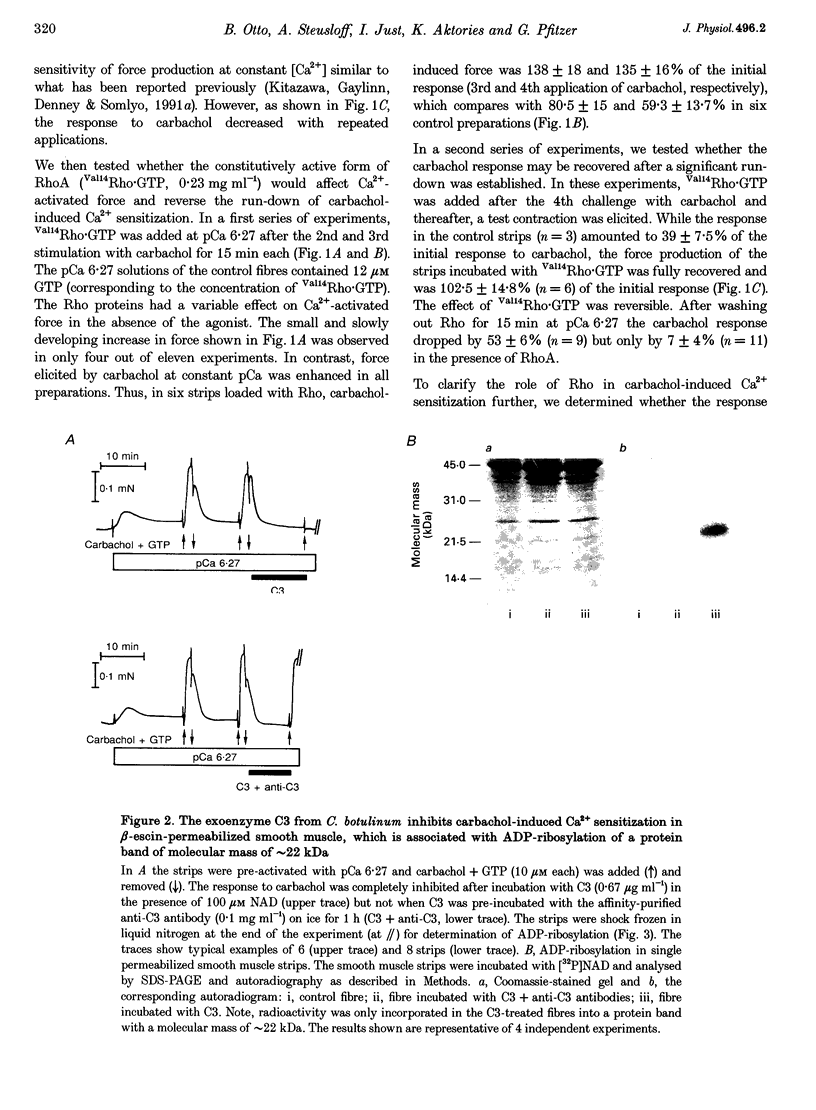
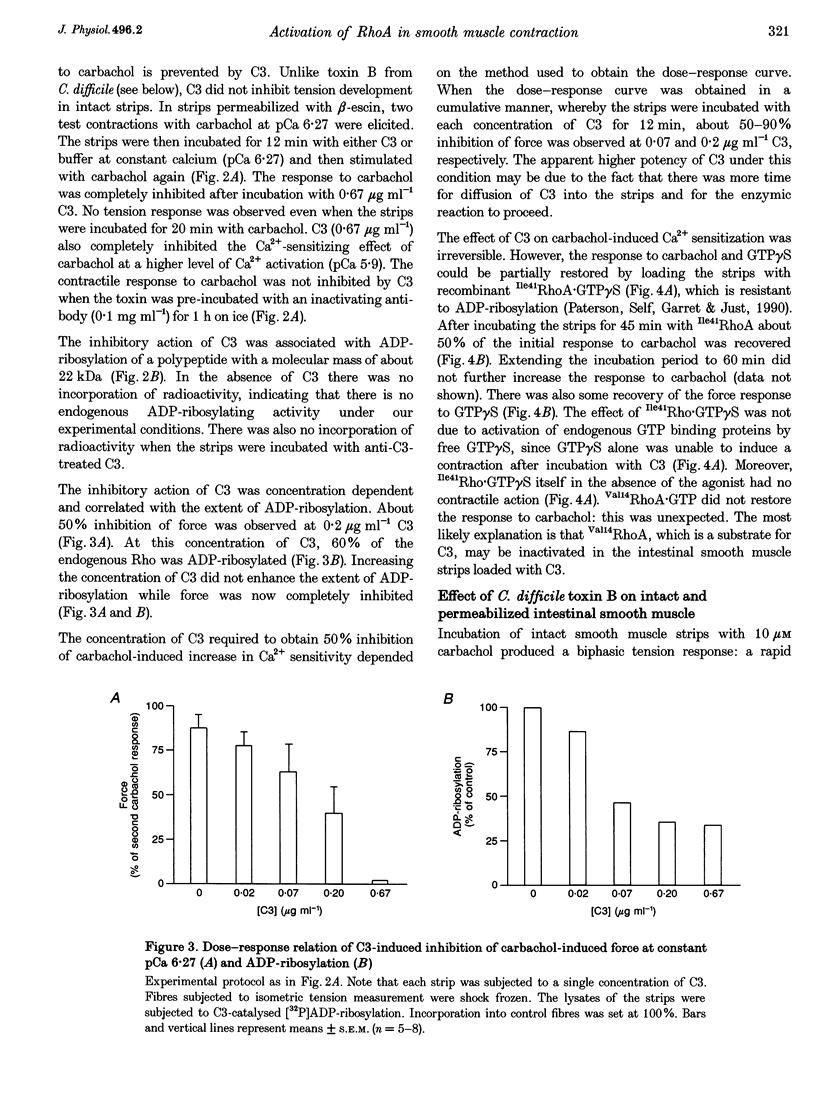
Abstract
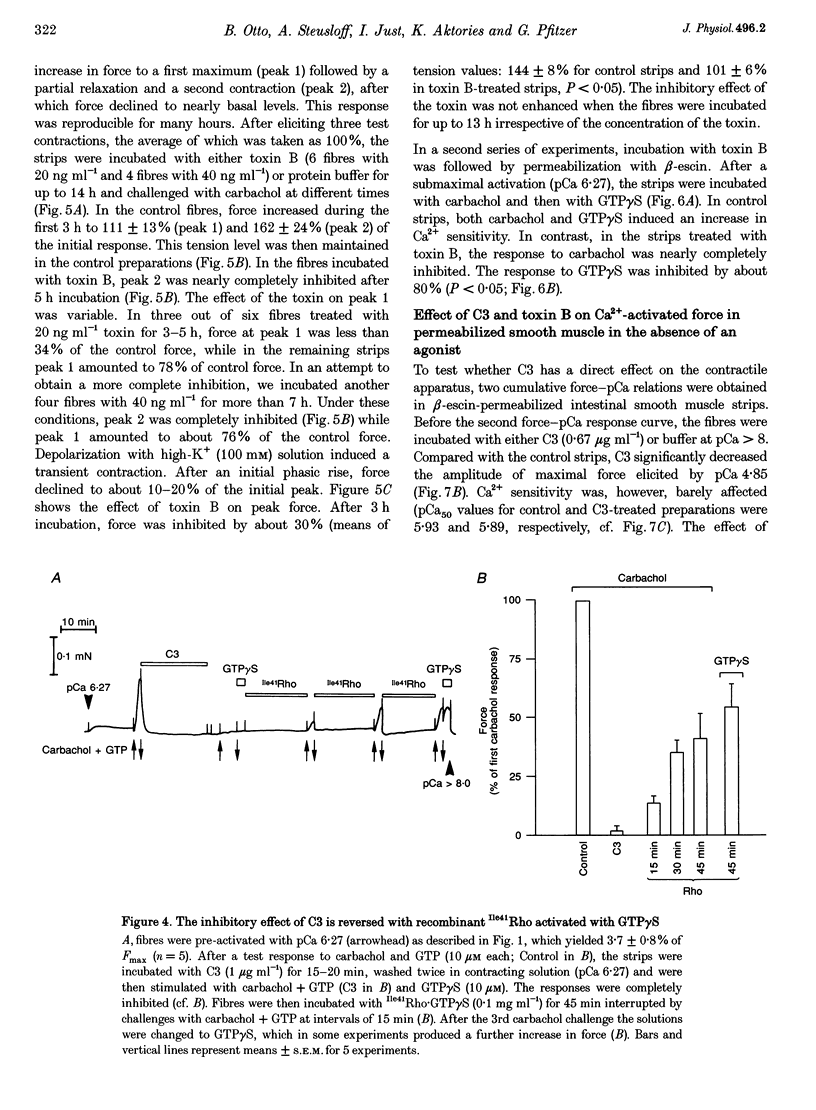
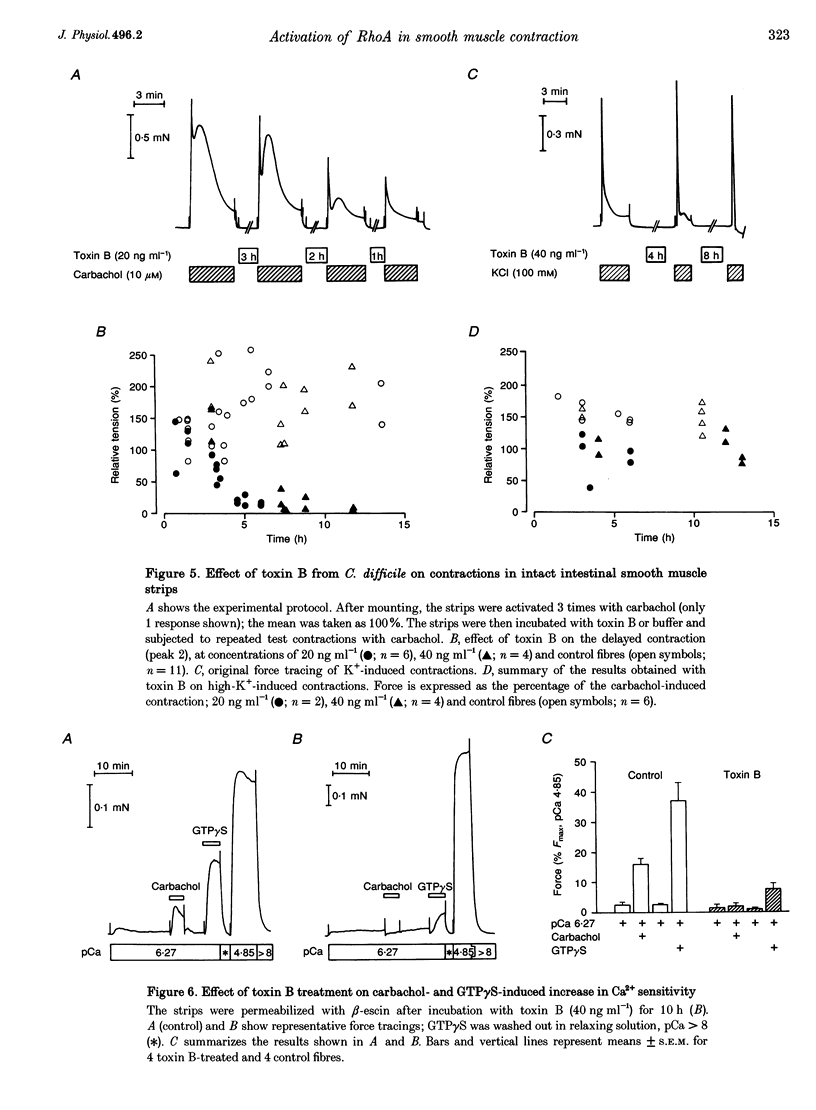
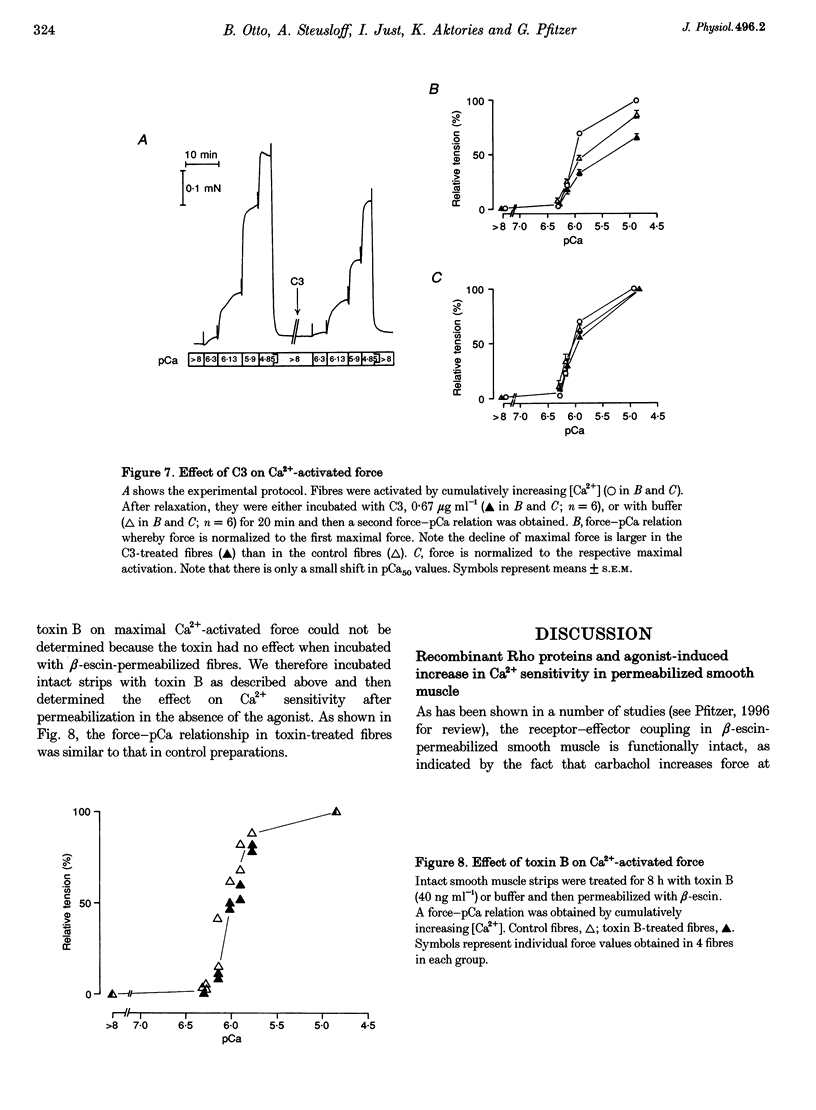
1. The aim of this study was to determine whether the low molecular mass GTPase RhoA or related proteins are involved in carbachol- and high-K(+)-induced contractions in intact intestinal smooth muscle as well as the carbachol-induced increase in Ca2+ sensitivity of the myofilaments in permeabilized preparations. 2. The carbachol-induced increase in the Ca2+ sensitivity of force production in beta-escin-permeabilized intestinal smooth muscle was enhanced in preparations that were loaded with the constitutively active mutant of RhoA, Val14RhoA, and was inhibited by exoenzyme C3 from Clostridium botulinum, which ADP-ribosylates and inactivates small GTPases of the Rho family. The effect of C3 on Ca2+ sensitivity in the absence of the agonist was negligible, while the maximal Ca(2+)-activated force was inhibited by about 20%. 3. Inhibition of carbachol-induced force was associated with an increase in ADP-ribosylation of a protein band with a molecular mass of approximately 22 kDa, corresponding to Rho, and was partially reversed in the presence of Ile41RhoA, which is not a substrate for C3. Val14RhoA did not restore carbachol-induced Ca2+ sensitization in C3-treated smooth muscle. 4. In intact intestinal smooth muscle, toxin B from Clostridium difficile, which monoglucosylates members of the Rho family, inhibited high-K(+)-induced contractions and the initial phasic response to carbachol by about 30%. The delayed contractile response to carbachol was completely inhibited. 5. In smooth muscle preparations that were permeabilized with beta-escin after treatment with toxin B, carbachol-and GTP gamma S-induced Ca2+ sensitization was significantly inhibited. 6. These findings are consistent with a role for Rho or Rho-like proteins in agonist-induced increase in Ca2+ sensitivity of force production in intact and permeabilized intestinal smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam L. P., Franklin M. T., Raff G. J., Hathaway D. R. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in porcine carotid arteries. Circ Res. 1995 Feb;76(2):183–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Mohr C., Koch G. Clostridium botulinum C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;175:115–131. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76966-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Rösener S., Blaschke U., Chhatwal G. S. Botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3. Purification of the enzyme and characterization of the ADP-ribosylation reaction in platelet membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):445–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Traynor-Kaplan A., Bokoch G. M., Schwartz M. A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. M., Walsh M. P., Morgan K. G. Contraction of single vascular smooth muscle cells by phenylephrine at constant [Ca2+]i. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 2):H754–H762. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.3.H754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Salvo J., Pfitzer G., Semenchuk L. A. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation, cellular Ca2+, and Ca2+ sensitivity for contraction of smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;72(11):1434–1439. doi: 10.1139/y94-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Salvo J., Steusloff A., Semenchuk L., Satoh S., Kolquist K., Pfitzer G. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors suppress agonist-induced contraction in smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 15;190(3):968–974. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin I., Thelestam M. Internalization of Clostridium difficile cytotoxin into cultured human lung fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz G., Aktories K. ADP-ribosylation of Rho proteins by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 is influenced by phosphorylation of Rho-associated factors. Biochem J. 1994 May 15;300(Pt 1):133–139. doi: 10.1042/bj3000133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita A., Takeuchi T., Nakajima H., Nishio H., Hata F. Involvement of heterotrimeric GTP-binding protein and rho protein, but not protein kinase C, in agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization of skinned muscle of guinea pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):555–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Itoh T., Kubota Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of guanosine nucleotides on skinned smooth muscle tissue of the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:535–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. J., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Yakubovich M. Clostridium difficile toxin B activates calcium influx required for actin disassembly during cytotoxicity. Am J Physiol. 1995 Mar;268(3 Pt 1):G487–G495. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.3.G487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong M. C., Iizuka K., Nixon G., Browne J. P., Hall A., Eccleston J. F., Sugai M., Kobayashi S., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Role of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins--ras-family or trimeric proteins or both--in Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site on calmodulin: application for purification of calmodulin by phenyl-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Somlyo A. P. Free-calcium and force transients during depolarization and pharmacomechanical coupling in guinea-pig smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki M., Komori S., Unno T., Syuto B., Ohashi H. Possible involvement of a small G-protein sensitive to exoenzyme C3 of Clostridium botulinum in the regulation of myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in beta-escin skinned smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;67(1):1–7. doi: 10.1254/jjp.67.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Hengeveld T., Morii N., Narumiya S., Moolenaar W. H. Inhibition of lysophosphatidate- and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):801–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Fritz G., Aktories K., Giry M., Popoff M. R., Boquet P., Hegenbarth S., von Eichel-Streiber C. Clostridium difficile toxin B acts on the GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10706–10712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Mohr C., Schallehn G., Menard L., Didsbury J. R., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Aktories K. Purification and characterization of an ADP-ribosyltransferase produced by Clostridium limosum. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10274–10280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Selzer J., Wilm M., von Eichel-Streiber C., Mann M., Aktories K. Glucosylation of Rho proteins by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):500–503. doi: 10.1038/375500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil R. A., Lajoie C., Resnick M. S., Morgan K. G. Ca(2+)-independent isoforms of protein kinase C differentially translocate in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C714–C719. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Masuo M., Somlyo A. P. G protein-mediated inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9307–9310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Cytosolic heparin inhibits muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. Physiological role of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in pharmacomechanical coupling. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17997–18004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokubu N., Satoh M., Takayanagi I. Involvement of botulinum C3-sensitive GTP-binding proteins in alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating Ca(2+)-sensitization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun 23;290(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Nomura M., Kamm K. E., Mumby M. C., Stull J. T. GTP gamma S-dependent regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):C405–C410. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.2.C405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai N., Morii N., Fujisawa K., Nemoto Y., Narumiya S. ADP-ribosylation of rho p21 inhibits lysophosphatidic acid-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation in cultured Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24535–24538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Yasuda-Fukazawa C., Moriishi K., Kato T., Okuda T., Kurokawa K., Takuwa Y. Involvement of rho in GTP gamma S-induced enhancement of phosphorylation of 20 kDa myosin light chain in vascular smooth muscle cells: inhibition of phosphatase activity. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 3;367(3):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00573-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavalko F. M., Adam L. P., Wu M. F., Walker T. L., Gunst S. J. Phosphorylation of dense-plaque proteins talin and paxillin during tracheal smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1995 Mar;268(3 Pt 1):C563–C571. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.3.C563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin S., Morii N., Narumiya S., Rozengurt E. Botulinum C3 exoenzyme blocks the tyrosine phosphorylation of p125FAK and paxillin induced by bombesin and endothelin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 14;354(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembold C. M. Modulation of the [Ca2+] sensitivity of myosin phosphorylation in intact swine arterial smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:77–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Comoglio P. M., Hall A. Regulation of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor responses by Ras, Rac, and Rho in MDCK cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):1110–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Kreutz R., Wilm C., Ganten D., Pfitzer G. Augmented agonist-induced Ca(2+)-sensitization of coronary artery contraction in genetically hypertensive rats. Evidence for altered signal transduction in the coronary smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1994 Oct;94(4):1397–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI117475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Rensland H., Pfitzer G. Ras proteins increase Ca(2+)-responsiveness of smooth muscle contraction. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81395-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):231–236. doi: 10.1038/372231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steusloff A., Paul E., Semenchuk L. A., Di Salvo J., Pfitzer G. Modulation of Ca2+ sensitivity in smooth muscle by genistein and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Jul 10;320(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(95)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai M., Hashimoto K., Kikuchi A., Inoue S., Okumura H., Matsumoto K., Goto Y., Ohgai H., Moriishi K., Syuto B. Epidermal cell differentiation inhibitor ADP-ribosylates small GTP-binding proteins and induces hyperplasia of epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2600–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Sasaki T., Kato M., Yamochi W., Kuroda S., Nakamura T., Takeichi M., Takai Y. Involvement of Rho p21 small GTP-binding protein and its regulator in the HGF-induced cell motility. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Cooper J. A. Rho family members: activators of MAP kinase cascades. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):527–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eichel-Streiber C., Harperath U., Bosse D., Hadding U. Purification of two high molecular weight toxins of Clostridium difficile which are antigenically related. Microb Pathog. 1987 May;2(5):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]