Abstract
Background
Refractive amblyopia is a common cause of reduced visual acuity in childhood, but optimal treatment is not well defined. This review examined the treatment effect from spectacles and conventional occlusion.
Objectives
Evaluation of the evidence of the effectiveness of spectacles, occlusion or both in the treatment of unilateral and bilateral refractive amblyopia.
Search methods
We searched CENTRAL (which contains the Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group Trials Register) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 1), MEDLINE (January 1950 to January 2012), EMBASE (January 1980 to January 2012), Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature Database (LILACS) (January 1982 to January 2012), the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) (www.controlled‐trials.com), ClinicalTrials.gov (www.clinicaltrials.gov) and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (www.who.int/ictrp/search/en). There were no date or language restrictions in the electronic searches for trials. We last searched the electronic databases on 24 January 2012. We manually searched relevant conference proceedings.
Selection criteria
Randomised controlled trials of treatment for unilateral and bilateral refractive amblyopia by spectacles, with or without occlusion, were eligible. We included studies with participants of any age.
Data collection and analysis
Two authors independently assessed abstracts identified by the searches. We obtained full‐text copies and contacted study authors where necessary. Eleven trials were eligible for inclusion. We extracted data from eight. Insufficient data were present for the remaining three trials so data extraction was not possible. We identified no trials as containing participants with bilateral amblyopia. We performed no meta‐analysis as there were insufficient trials for each outcome.
Main results
For all studies mean acuity (standard deviation (SD)) in the amblyopic eye post‐treatment was reported. All included trials reported treatment for unilateral refractive amblyopia.
One study randomised participants to spectacles only compared to no treatment, spectacles plus occlusion compared to no treatment and spectacles plus occlusion versus spectacles only. For spectacles only versus no treatment, mean (SD) visual acuity was: spectacles group 0.31 (0.17); no treatment group 0.42 (0.19) and mean difference (MD) between groups was ‐0.11 (borderline statistical significance: 95% confidence interval (CI) ‐0.22 to 0.00). For spectacles plus occlusion versus no treatment, mean (SD) visual acuity was: full treatment 0.22 (0.13); no treatment 0.42 (0.19). Mean difference (MD) between the groups ‐0.20 (statistically significant: 95% CI ‐0.30 to ‐0.10). For spectacles plus occlusion versus spectacles only, MD was ‐0.09 (borderline statistical significance 95% CI ‐0.18 to 0.00). For two other trials that also looked at this comparison MD was ‐0.15 (not statistically significant 95% CI ‐0.32 to 0.02) for one trial and MD 0.01 (not statistically significant 95% CI ‐0.08 to 0.10) for the second trial.
Three trials reviewed occlusion regimes.One trial looked at two hours versus six hours for moderate amblyopia: MD 0.01 (not statistically significant: 95% CI ‐0.06 to 0.08); a second trial 2003b reviewed six hours versus full‐time for severe amblyopia: MD 0.03 (not statistically significant: 95% CI ‐0.08 to 0.14) and a third trial looked at six hours versus full‐time occlusion: MD ‐0.12 (not statistically significant: 95% CI ‐0.27 to 0.03). One trial looked at occlusion supplemented with near or distance activities: MD‐0.03 (not statistically significant 95% CI ‐0.09 to 0.03). One trial looked at partial occlusion and glasses versus glasses only: MD ‐0.01 (not statistically significant: 95% CI ‐0.05 to 0.03).
Authors' conclusions
In some cases of unilateral refractive amblyopia it appears that there is a treatment benefit from refractive correction alone. Where amblyopia persists there is evidence that adding occlusion further improves vision. Despite advances in the understanding of the treatment of amblyopia it is currently still not possible to tailor individual treatment plans for amblyopia. The nature of any dose/response effect from occlusion still needs to be clarified. Partial occlusion appears to have the same treatment effect as glasses alone when started simultaneously for the treatment of unilateral refractive amblyopia. Treatment regimes for bilateral and unilateral refractive amblyopia need to be investigated further.
Keywords: Adolescent; Child; Child, Preschool; Humans; Amblyopia; Amblyopia/pathology; Amblyopia/therapy; Bandages; Combined Modality Therapy; Combined Modality Therapy/methods; Eyeglasses; Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic; Refractive Errors; Refractive Errors/therapy; Visual Acuity
Plain language summary
Treatment for lazy eye caused by a need for glasses
Amblyopia (lazy eye) is a term describing reduced vision in one or both eyes. Amblyopia can sometimes be caused by a need for glasses. The need for glasses may be greater in one eye causing amblyopia only in the worse eye. This happens because the brain receives a weaker image from the eye with the greater need for glasses and prefers to use the eye with a clearer image. Sometimes there may be a strong need for glasses in both eyes causing amblyopia in both eyes. This is because the brain receives a blurred image from both eyes.
Children who have amblyopia due to a need for glasses in one eye only are often asked to wear a patch over the good eye, in addition to wearing their spectacles, to improve their vision. This review found that for some children with this type of amblyopia a period of glasses wear alone can restore normal vision. For those children for whom glasses wear alone does not improve vision there is evidence that wearing a patch can further improve vision. At present it is not possible to tell at the start of treatment which children will respond to glasses alone and which ones will need a patch as well. The amount of patching needed for an individual child cannot yet be predicted. This is because the effects of factors such as age are not fully understood. These findings are based on the results of eleven high‐quality trials.
Children who have amblyopia in both eyes because of a need for glasses in both eyes are currently advised to wear their glasses as much of the time as possible in order to improve their vision. No trials looking at treatment for children who had reduced vision in both eyes were found.
Background
Introduction
Amblyopia (lazy eye) can be defined as subnormal visual acuity, which is present with no demonstrable abnormality of the visual pathway and is not immediately resolved by wearing spectacles. Amblyopia occurs when the visual system is still developing and is vulnerable to poor‐quality visual stimulation. Although it can affect both eyes it is invariably unilateral. During this time of development, formerly referred to as the critical period, amblyopia is usually a reversible condition.
Amblyopia is commonly classified according to the aetiology (cause):
strabismic (caused by squint);
stimulus deprivation (e.g. caused by cataract or ptosis); and
refractive (caused by optical or refractive error).
It is not uncommon for these types to co‐exist.
This review deals with unilateral and bilateral amblyopia associated with refractive error. Interventions for the other types are being evaluated in a series of Cochrane reviews. See: Table 1 for a list of published Cochrane reviews on amblyopia.
1. Published Cochrane reviews on amblyopia.
| Title | Published | Author(s) |
| Interventions for stimulus deprivation amblyopia | 2006, Issue 3 | Antonio‐Santos A, Vedula SS, Hatt SR, Powell C |
| Interventions for strabismic amblyopia | 2011, Issue 8 | Taylor K, Elliott S |
| Conventional occlusion versus pharmacological penalisation for amblyopia | 2009, Issue 4 | Li T, Shotton K |
Refractive error
Refractive error is a mismatch in the length of the eye and its optical components. This may take the form of hypermetropia (long‐sight), myopia (short‐sight) or astigmatism (irregularly curved cornea). Hypermetropia occurs when the focal point of the eye's optical components is behind the retina and myopia occurs when the focal point is in front. Astigmatism prevents a sharp image from being formed at any point along the visual axis. In all cases, when refractive error is uncorrected, a blurred image falls on the retina (Elkington 1999).
Aetiology of refractive amblyopia
Refractive amblyopia can be subdivided into three different types (Ansons 2001):
ametropic amblyopia: a bilateral condition that occurs when there is a high degree of refractive error, and therefore blur, in both eyes;
meridional amblyopia: develops due to large amounts of astigmatism and may be either unilateral or bilateral;
anisometropic amblyopia: characterised by a difference in the refractive error between the two eyes (whether caused by hypermetropia, myopia or astigmatism), giving an unfocused image in one eye.
There is a lack of evidence regarding the magnitude of refractive error likely to lead to the development of amblyopia (Ansons 2001; PEDIG 2003a; PEDIG 2003b). To be as inclusive as possible we used broad definitions of refractive error. For people with anisometropia and unilateral amblyopia we used a difference of 0.50 dioptres or greater of spherical (DS) or cylindrical (DC) error. For people with bilateral refractive amblyopia, we included any degree of refractive error.
Epidemiology
Refractive error and refractive amblyopia
A major review of the literature by Snowden 1997 found estimates of the prevalence of refractive error in general of between 1.3% and 5.6%. This variation is probably due to differences in the populations studied and various definitions used. The incidence of amblyopia in general is thought to be between 2% and 2.5% (von Noorden 1996).
Microtropia
Many patients with unilateral refractive amblyopia also have a small‐angle squint known as microtropia. It has been suggested that the presence of a microtropia may limit the optimum acuity that can be achieved by amblyopia therapy to approximately one line less than the better eye (Mein 1991) because the amblyopic eye fixates eccentrically.
Presentation and diagnosis
A diagnosis of refractive amblyopia is made by carrying out a refraction (test for determining the required spectacle prescription to correct the optical error) and rechecking visual acuity wearing optimal correction using a vision test appropriate to the age of the child. Reduced acuity due to refractive error alone improves immediately once the correction (usually spectacles) is in place. Persistent acuity deficit despite best correction of refractive error and in the absence of any other possible cause of poor vision indicates the presence of amblyopia.
Treatment options
The aim of treatment is to restore the visual acuity of the amblyopic eye(s) to a normal level.
1. Refractive correction
Improvement in amblyopia due to spectacle wear, or alternatively contact lens wear, alone has long been suspected and was documented for all types of amblyopia by Stewart 2004 who termed it 'refractive adaptation.' It has since also been described as 'optical treatment' of amblyopia (PEDIG 2006b). A period of spectacle wear prior to any occlusion treatment is now widely accepted in the treatment of unilateral refractive amblyopia and is the only treatment available for bilateral refractive amblyopia.
2. Occlusion therapy
In cases of unilateral refractive amblyopia, if amblyopia ceases to improve with refractive correction alone, any residual deficit may be treated with occlusion. In occlusion therapy, the vision of the better seeing eye is temporarily compromised in order to encourage the use of the amblyopic eye. This can be achieved in various ways. The most common being:
conventional occlusion: total deprivation of form vision and light (e.g. adhesive patching);
partial occlusion: deprivation of form vision only (e.g. Bangerter foils (thin opaque filters of varying density used to cover the spectacles lens));
optical penalisation: deprivation of form vision by using lenses to blur the visual acuity of the non‐amblyopic eye;
pharmacological: deprivation of form vision by blurring the vision in the good eye with drops or ointment such as atropine sulphate.
3. Adjuncts to occlusion
To enhance outcomes from occlusion therapy other interventions have been added to occlusion therapy, for example the following.
CAM (Cambridge) vision stimulator: apparatus designed to treat amblyopia by intense visual stimulation with rotating black and white gratings for short periods of time (Banks 1978). We believe that this apparatus is no longer commercially available.
Red filter treatment: a red filter is placed in front of the amblyopic eye during occlusion treatment in order to encourage use of the central fixation area of the eye (the fovea) (von Noorden 1996).
Pleoptics: in dense amblyopia, the central part of the retina (the fovea) may not be used for fixation. In order to disrupt this 'eccentric' fixation pleoptic treatment is used with apparatus such as the Euthyscope or the Projectoscope (Ansons 2001).
We are not aware of these interventions being used in current clinical practice, but to be inclusive any trials using these interventions which met the inclusion criteria were eligible to be included in the review.
The possibility of benefit from close work with occlusion was explored in a pilot randomised trial (PEDIG 2005a). A formal randomised controlled trial (RCT) has since been carried out and has been included within this review (PEDIG 2008).
Factors affecting outcome
Factors thought to affect treatment outcomes include:
compliance: it is recognised that compliance plays a significant role in the successful outcome of occlusion therapy (Newsham 2000; Simons 1999);
age at commencement of treatment (Hardman Lea 1989);
density of the amblyopia, the severity of the visual acuity deficit at presentation (Cleary 2000).
Rationale for a systematic review
Although the impact of living with untreated amblyopia has yet to be thoroughly evaluated, treatment for refractive amblyopia is common. The aim of treatment is to restore normal visual acuity and maximise binocular interaction. For over 200 years, the mainstay of therapy has been to prescribe any necessary spectacles and then, in unilateral amblyopia, to penalise vision in the sound eye.
The evidence for the role of spectacles in the treatment of refractive amblyopia and the impact of adding occlusion has not been systematically reviewed and summarised. Practice patterns, including prescribed occlusion regime and time allowed for optical treatment therefore vary widely (Mazow 2000; Tan 2003).
There was a need to examine and summa rise the literature in order to establish the respective treatment effects of refractive correction alone and occlusion therapy and to attempt to identify an optimum treatment protocol.
Objectives
The primary objective for this review was to establish the effects of refractive correction and occlusion therapy for the treatment of refractive amblyopia. In particular this review aimed to:
examine the treatment effect from refractive correction alone;
examine the impact of occlusion therapy (all types);
establish a) dose/response effect and b) the optimum duration of occlusion treatment;
analyse the role of adjuncts to occlusion, for example, close work.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
This review included RCTs for the treatment of unilateral and bilateral refractive amblyopia by spectacles or contact lenses with or without occlusion therapy.
Types of participants
We included trials with participants of any age, diagnosed with unilateral or bilateral refractive amblyopia. The criteria for diagnosis were:
reduced vision caused by refractive correction that does not immediately or fully correct to normal vision with refractive correction;
any amount or type of refractive error;
a difference in refractive correction between the two eyes of 0.50 DS/DC error or greater for unilateral refractive amblyopia;
initial corrected visual acuity in the amblyopic eye of worse than 6/9.5 (Snellen) or 0.200 (LogMAR) or equivalent measured on an age‐appropriate test;
in cases of unilateral refractive amblyopia, corrected visual acuity in the non‐amblyopic eye of 6/9.5 (Snellen) or 0.200 (LogMAR) or better measured on an age‐appropriate test.
Participants with co‐existing pathology that might reduce visual acuity (e.g. cataract) were not eligible. All participants had undergone cycloplegic refraction and had corrected visual acuity assessed using a test appropriate for age.
Since microtropia is commonly associated with unilateral refractive amblyopia we did not exclude participants with this type of manifest strabismus but planned to report the effect of associated microtropia on final visual acuity in a subgroup analysis. We are currently in correspondence with authors of included trials and hope to be able to present more data regarding microtropia in a future update of the review.
It has come to our attention that some trials may include participants who have had previous treatment. Where possible we will explore the effect of this in a subgroup analysis or if applicable describe by a narrative summary of the treatment outcomes.
It is likely that some period of refractive adaptation will be included in the trials prior to additional therapies being started. In cases where no refractive adaptation has been included, we will analyse the results from these trials separately from those that have included a period of refractive adaptation.
Types of interventions
Trials of the following interventions were eligible for inclusion.
Refractive correction by means of spectacles or contact lenses only (referred to below as 'refractive correction' for simplicity)
Conventional occlusion
Partial occlusion
Optical penalisation
CAM vision stimulator
Red filter occlusion
Pleoptics
We examined the following comparisons.
Refractive correction only to no treatment.
Refractive correction plus conventional total occlusion (any regime) to no treatment.
Refractive correction plus conventional total occlusion (any regime) to refractive correction only.
Conventional full‐time total occlusion plus refractive correction versus conventional part‐time total occlusion plus refractive correction.
Conventional part‐time total occlusion plus refractive correction versus conventional part‐time total occlusion plus refractive correction (e.g. two hours compared to six hours).
Partial occlusion (any regime) plus refractive correction to no treatment.
Partial occlusion (any regime) plus refractive correction to refractive correction only.
Partial full‐time occlusion plus refractive correction to partial part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction.
Partial part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction to partial part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction (e.g. two hours compared to six hours).
Refractive correction plus optical penalisation to no treatment.
Refractive correction plus optical penalisation to spectacles or contact lenses only.
Optical penalisation to refractive correction plus conventional occlusion (full‐time).
Optical penalisation to refractive correction plus conventional occlusion (part‐time).
CAM vision stimulator plus full treatment (occlusion therapy and refractive correction) to conventional occlusion (any duration) plus refractive correction.
Red filter treatment plus full treatment (occlusion therapy and refractive correction) to conventional occlusion (any duration) plus refractive correction.
Pleoptics prior to occlusion therapy to full treatment (conventional occlusion and refractive correction).
Near versus non‐near activities whilst undergoing conventional occlusion therapy (any regime) plus refractive correction.
Perceptual learning plus refractive correction to conventional occlusion (any regime) plus refractive correction.
For the purpose of this review we defined part‐time occlusion as six hours or less per day and defined full‐time occlusion as greater than six hours daily.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
The primary outcome for this review was the mean best corrected visual acuity of the amblyopic eye(s) on an age‐specific test at 12 months after commencement of refractive correction for bilateral amblyopia and 12 months from cessation of occlusion treatment for unilateral amblyopia. We chose 12 months to ensure that any benefit from treatment had been maintained.
Trials reporting visual acuity outcomes either by number of lines/letters change in acuity or the proportion of the vision deficit corrected were also eligible for inclusion.
Secondary outcomes
Since it was anticipated that many studies would not be able to provide data at 12 months post cessation of treatment, we included trials with shorter or longer periods of follow‐up. Outcomes are reported and potential for vision to improve with further treatment or to regress are commented on.
Adverse effects
Where included studies commented on adverse effects from either refractive correction (e.g. contact lens wear) or occlusion therapy, a narrative summary of their findings has been included in the 'Results' section.
Quality of life measures
We found no studies relating to the impact of living with untreated amblyopia. We will report any evidence found in the future in updates of the review.
Economic data
We found no economic data assessing the cost‐effectiveness of treating amblyopia either in studies designed to look specifically at cost or as part of the included trials. We will include any such data identified at a later date in updates.
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) 2012, Issue 1, part of The Cochrane Library. www.thecochranelibrary.com (accessed 22 January 2012), MEDLINE (January 1950 to January 2012), EMBASE (January 1980 to January 2012), Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature Database (LILACS) (January 1982 to January 2012), the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) (www.controlled‐trials.com), ClinicalTrials.gov (www.clinicaltrials.gov) and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (www.who.int/ictrp/search/en). There were no date or language restrictions in the electronic searches for trials. We last searched the electronic databases on 24 January 2012.
See: Appendices for details of search strategies for CENTRAL (Appendix 1), MEDLINE (Appendix 2), EMBASE (Appendix 3), LILACS (Appendix 4), mRCT (Appendix 5), ClinicalTrials.gov (Appendix 6) and the ICTRP(Appendix 7).
Searching other resources
We handsearched the following conference proceedings:
European Strabismus Association (ESA) (2001 to 2005);
American Association of Paediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) (2002 to 2005);
Royal College of Ophthalmologists (RCO) (2001 to 2005).
To date it has not been possible to search for unpublished data. Handsearching the proceedings of the International Strabismus Association (ISA) has not yet been carried out. We are in the process of handsearching the British Orthoptic Journal and the American Orthoptic Journal. We will report any trials found in updates of the review. We have as yet made no attempt to identify unpublished trials.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors undertook independent assessment of abstracts to ascertain which studies met the inclusion criteria for the review. We labelled abstracts included, unclear or excluded. We obtained full copies of all included and unclear studies and two review authors then worked independently to determine which studies met the inclusion criteria. Again, we labelled the studies as included, unclear or excluded. We resolved disagreements by discussion.
Data extraction and management
Two authors working independently extracted data from included trials using a data collection form. Where possible, we collected data directly from the published paper but in some cases extra data were provided by trial co‐ordinators (PEDIG 2003a; PEDIG 2003b; PEDIG 2005b; PEDIG 2006a; PEDIG 2008; Stewart 2007a). Although both of the CAM trials met the inclusion criteria it was only possible to extract data from Tytla 1981. We contacted the authors of Nyman 1983 but unfortunately data were no longer available. We entered data into RevMan (Review Manager 2011); one author entered the data which a second author then checked for errors. Two authors independently extracted data from the trial by Agervi 2009 and collected additional data from the trial authors. Two authors independently extracted data from the trial by Chen 2008. Unfortunately insufficient data were available from the published paper and contact with the authors has not been possible.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Once studies had been identified as meeting the inclusion criteria we assessed them for methodological quality according to Chapter 8 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011).
We considered the following parameters: generation of the random sequence, masking of examiners, allocation concealment and completeness of follow‐up. In addition we considered whether there appeared to be any evidence of selective reporting of results or other sources of bias.
We graded each parameter of trial quality as low risk of bias, high risk of bias or unclear. Where any parameter was graded as unclear we contacted authors for clarification. Three studies were judged have unclear risk (Chen 2008; Nyman 1983; Tytla 1981). Contact with the authors was attempted but unfortunately no further information was able to be given.
Data synthesis
All of the trials included in the review reported the mean vision achieved by the intervention and control groups. We therefore calculated the mean difference in acuity between groups. This method of measuring outcome is not ideally suited to the type of outcome of interest in this review as it does not always reflect improvement (or indeed the lack of it) for individual patients and therefore can be misleading.
Where the data were available to dichotomise outcomes into restoration of normal vision (0.200 or better) and residual acuity loss (worse than 0.200) we planned to calculate the risk difference (RD) in order to be able to present the number needed to treat to benefit (NNT). No trials published data to allow us to do this but we are in correspondence with trial authors and if possible this will be included in an update of the review.
We identified no trials that only reported the proportion of acuity deficit corrected or number of lines/letters change. If this is reported in trials included in updates of the review we will contact the authors to request data that will allow us to dichotomise the outcomes.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
The electronic searches retrieved 259 references from CENTRAL, 730 references from MEDLINE, 890 references from EMBASE and 293 references from LILACS. After de‐duplication the search identified a total of 1584 references. After independent review of the titles and abstracts by two review authors we retrieved 18 full‐text articles.
An update search done in January 2012 identified 465 new reports of trials. The Trials Search Co‐ordinator scanned the search results and removed 430 references which were not relevant to the scope of the review. We reviewed the remaining 35 references and obtained full‐text copies of five studies but all were excluded from the review (Agervi 2010; Chen 2010; Huang 2009; PEDIG 2010; Wu 2010). The search identified two trials which are awaiting further assessment as currently results are not available (ISRCTN55960730; ISRCTN98018344). We found no new trial meeting the criteria of the review to be eligible for inclusion.
Included studies
Eleven trials met the inclusion criteria and have been included in the review. See the 'Characteristics of included studies' table.
Agervi 2009: this trial included 80 participants with an age range of 4.0 years to 5.4 years diagnosed with untreated unilateral refractive amblyopia. Uncorrected visual acuity of the amblyopic eye ranged from 0.300 to 1.300 LogMAR assessed using a Lea Symbols vision chart. Anisometropia was defined as intraocular spherical refractive error difference of 1.0 DS or more. Refractive correction alone was compared to refractive correction plus Bangerter filters (partial occlusion). Glasses were prescribed on the first visit for full‐time wear although participants were instructed not to wear the glasses until the day of baseline examination. All treatments began simultaneously without a period for refractive adaptation. Participants randomised into the Bangerter filter treatment group were prescribed a filter of density 0.3 which was attached to the back of the glasses of the non‐amblyopic eye and worn full‐time. The Bangerter filter was removed when vision in the amblyopic eye was equal to that of the non‐amblyopic eye.
Thirty‐three participants for each treatment group were included for the final analysis. Mean visual acuity of the amblyopic eye for the spectacles only group changed from 0.4 (range 0.3 to 0.9) to 0.1 (range ‐0.1 to 0.2). Amblyopia resolved in an average of 3.9 months (± 3.2 months) in 31 (94%) participants of the glasses only group. Thirty‐one participants (94%) also achieved resolution of amblyopia in the Bangerter filter treatment group. Amblyopia resolved within 2.2 months (± 1.9 months). No reoccurrence of amblyopia was reported in the trial.
Chen 2008: this trial included 61 participants of varying age groups; younger children (three to seven years of age), older children (eight to 18 years of age) and adult patients (older than 18 years of age). All participants were diagnosed with unilateral refractive amblyopia ranging from 0.1 to 0.9 as assessed on an age‐appropriate LogMAR based test. Full‐time glasses wear was specified for three months prior to treatment commencing. Anisometropia was defined as > 1 DS. Participants were randomised to receive either conventional patching therapy as per the Paediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) studies (PEDIG 2003a; PEDIG 2003b) or perceptual learning. Perceptual learning participants underwent a training session three times per week with an average of 30 minutes per session. The average number of training sessions was 48 (29.5 hours). Participants with mild or moderate amblyopia (0.100 to 0.600) were prescribed two hours daily occlusion and those with severe amblyopia (0.700 to 1.300) were prescribed six hours daily occlusion. The mean treatment duration for participants receiving occlusion was 37.3 weeks (522.2 hours).
The mean visual acuity of the amblyopic eye improved by 0.34 LogMAR (95% CI 0.22 to 0.47 LogMAR) with occlusion and 0.25 LogMAR (95% CI 0.16 to 0.35) with perceptual learning. Resolution of amblyopia was achieved in 10 out 26 patients (38%) in the perceptual learning group and 17 of 27 patients (63%) in the occlusion group. Resolution of amblyopia was defined as 0.100 LogMAR in this trial.
We contacted the authors to try to obtain data on the participants who met the criteria of this review for both improvement in visual acuity and for those in which amblyopia was resolved. Unfortunately we have received no reply. This means there are insufficient data reported in the paper to include this trial in the review and we have therefore performed no 'Risk of bias' assessment.
Clarke 2003: this trial included 177 participants aged between three and five years recruited from eight centres in the UK, who had been identified in a preschool vision screening programme in England. Of the 177 participants in the study, 173 had significant refractive error in one or both eyes, 127 of which were considered by the authors to be anisometropic. Six participants were thought to have microtropia. No participants were diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia. Data were analysed in two groups by start visual acuity: mild (0.200 (6/9) to 0.300 (6/12)) and moderate (worse than 0.300 (6/12)). We extracted data for participants meeting the review definition of amblyopia (n = 119). We contacted the authors but data are no longer available to allow separate analysis of patients with unilateral refractive error meeting the review definition of anisometropia. No data were available to allow subgroup analysis of participants with microtropia.
At entry into the study, participants were randomised into one of three groups: no treatment (n = 59), spectacles only (n = 59) or full treatment (spectacles and occlusion) (n = 59) and then refracted. There was an initial six‐week spectacles only (refractive adaptation) phase for the patients in the full treatment group.
The primary outcome measure was best corrected visual acuity on a crowded LogMAR test at 12 months, reported as mean acuity for each group. Participants in the full treatment group were started on occlusion after six weeks of spectacles wear if visual acuity was still reduced. Regimes of occlusion were not standardised. Participants in the spectacles only group received spectacles only for 52 weeks and participants in the no treatment group received no active treatment for 52 weeks. There was then a further six months of follow‐up during which time all groups were eligible for full treatment as indicated.
Nyman 1983: this trial compared adding CAM stimulation by black and white gratings to occlusion therapy alone. Fifty participants aged between four and 6½ years with all types of amblyopia were recruited at paediatric care centres in Stockholm. Amblyopia was defined as a difference in distance visual acuity of more than two lines between the two eyes, provided the vision in the worse seeing eye was not better than 6/12 after eight weeks of full‐time spectacles wear. A Snellen E chart with decimal steps was used to assess vision. Spectacles were prescribed and worn for eight weeks, after which participants were randomly assigned to receive CAM vision therapy or occlusion alone. Participants in the occlusion group were prescribed either partial (Bangerter filters) or total occlusion.
Treatment with CAM therapy lasted approximately seven minutes and the number of treatments given varied from five to 10.
It was not possible either to separate the data for those participants diagnosed with unilateral refractive amblyopia or to extract the data needed from the published paper. We contacted the authors but unfortunately the data were no longer available. Since no relevant data were available it was not possible to assess this study for risk of bias.
Paediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group
The Paediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) is a collaboration of clinical sites based in the USA. The group has carried out a series of studies of treatment for amblyopia, four of which meet the inclusion criteria for this review. All the PEDIG studies use an electronic visual acuity tester with a standardised testing protocol and report outcomes as mean visual acuity. In addition to any prescribed occlusion, participants in all the included PEDIG studies were required to carry out an hour of close work. In the PEDIG studies, vision at baseline is classified into either moderate amblyopia (0.300 to 0.600 LogMAR) or severe amblyopia (0.700 to 1.300 LogMAR). None of the PEDIG studies had data that allowed us to assess the effect of microtropia on the reported outcomes.
PEDIG 2003a: this trial examined the impact of prescribing two hours daily conventional occlusion compared to prescribing six hours daily conventional occlusion for 189 children under seven years of age with moderate amblyopia. We contacted the authors and they provided data for the 62/189 who had unilateral refractive amblyopia; 34 in the two‐hour group and 28 in the six‐hour group. No trial participant was diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia. The main outcome measure was visual acuity in the amblyopic eye after four months of treatment.
Participants wore spectacles full‐time for four weeks prior to beginning occlusion therapy. Compliance with treatment was assessed by means of a parental diary.
PEDIG 2003b: all 175 participants in this study had severe amblyopia and were under seven years of age. The trial lasted for four months. The main outcome measure for this trial was vision in the amblyopic eye after four months of treatment.
Participants underwent cycloplegic refraction and were instructed to wear spectacles for four weeks prior to starting occlusion. Participants were randomised to receive either six hours daily occlusion (n = 29) or full‐time daily occlusion (n = 28).
All types of amblyopia were included. The authors were contacted and provided data for the participants diagnosed with unilateral refractive amblyopia (n = 57). No participants were diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia.
PEDIG 2005b: this trial included 507 participants aged seven to 17 years with all types of amblyopia ranging from 0.300 to 1.300 LogMAR some of whom had had previous treatment for amblyopia.
Those who had not received previous treatment were provided with spectacles and instructed not to wear them prior to the baseline assessment. Participants were randomised into either an optical correction group who only received spectacles or a treatment group who were prescribed two to six hours of occlusion. Participants under the age of 13 years in the treatment group also had atropine sulphate and were therefore excluded from this review. We contacted the authors and they provided data for those participants (n = 103) who met the inclusion criteria for the review. No participants with bilateral refractive amblyopia were enrolled in the trial.
Visual acuity was assessed every six weeks for 24 weeks; the primary outcome measure was vision at the visit where maximum acuity was recorded.
PEDIG 2006a: this trial was designed to assess whether a treatment effect could be identified from adding occlusion to spectacles in the treatment of moderate and severe amblyopia rather than to elicit the maximum potential benefit from occlusion. All participants were under seven years of age. Eighty‐two of 180 people met the inclusion criteria for this review (additional data provided by authors). No participants were diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia.
Participants who required refractive correction entered a spectacle run‐in phase prior to treatment; optimal refractive correction was prescribed and worn full‐time until vision in the amblyopic eye stabilised. They were then randomised to two hours of daily occlusion with spectacles or to a spectacles only treatment group.
The main outcome measure was best corrected vision in the amblyopic eye after five weeks of treatment.
PEDIG 2008: this trial included 425 children aged between three and seven years diagnosed with strabismic, anisometropic or mixed amblyopia ranging from 0.300 to 1.300 LogMAR. Glasses were prescribed for a minimum of 16 weeks before the participants were randomised to received either two hours daily occlusion with near activities or two hours daily occlusion with distance activities.
Visual acuity was assessed at two, five, eight and 17 weeks. The main outcome visit was at eight weeks, meaning some participants may have further improvement to their vision.
No participants were diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia as defined in this review and the trial organiser provided data on the 215 patients diagnosed with unilateral refractive amblyopia.
Stewart 2007a: this trial examined the dose/response of occlusion for amblyopia by measuring the actual dose of occlusion received by the patient. The primary outcome measures were concordance with occlusion and change in visual acuity, proportion of acuity deficit corrected and final visual acuity on a LogMAR letter recognition test.
The visual acuity inclusion criterion for this trial was "significant intraocular difference of 0.100 log units". Ninety‐seven participants, aged between three and eight years at entry, were included in the study. Of these, 34 were classified as anisometropic. We contacted the authors and they provided data for the 24/34 (71%) of these who met the review definition of amblyopia. Data were not available to allow us to comment on the numbers with microtropia. No participants with bilateral refractive amblyopia were included in this trial.
Participants wore optimal refractive correction for 18 weeks and were then randomised to being prescribed either six or 12 hours occlusion daily.
Tytla 1981: this study included 15 participants with all levels and types of amblyopia aged between five and 12 years. Corrected starting visual acuity ranged from 6/18 to 6/60 Snellen in the amblyopic eye. Participants were randomised to receive CAM vision stimulation or stimulation with homogeneous grey discs. The trial lasted for four weeks, with vision being assessed before, during and after each weekly session. Three participants met the review inclusion criteria, however, data were only available for two of them. It was not possible to utilise these data in any of the comparisons and therefore we did not assess this trial for quality and the 'Risk of bias' table for it is empty.
Excluded studies
We excluded three studies as on closer examination they did not match our inclusion criteria (Keith 1980; Mehdorn 1981; Schor 1985). We excluded a further study as the participants had strabismic and mixed amblyopia (Awan 2005). For three studies, it was unclear from the abstracts whether the papers were eligible: for two (Hayashi 1969; Johnson 1969) we were not able to obtain full copies and therefore excluded them. The third abstract (Pasmanik 1993) was obtained but on translation was found not to meet the inclusion criteria. Updated searches from January 2012 revealed a further five studies which we excluded from the review (Agervi 2010; Chen 2010; Huang 2009; PEDIG 2010; Wu 2010). See the 'Characteristics of excluded studies' table for further details.
Risk of bias in included studies
See: Risk of bias in included studies for more information as well as Figure 1 and Figure 2.
1.
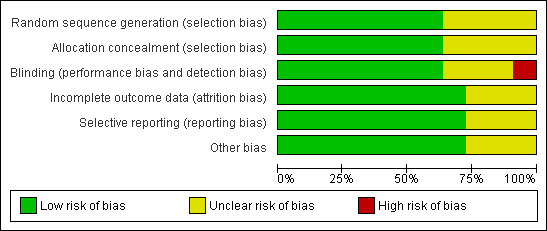
'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.
2.
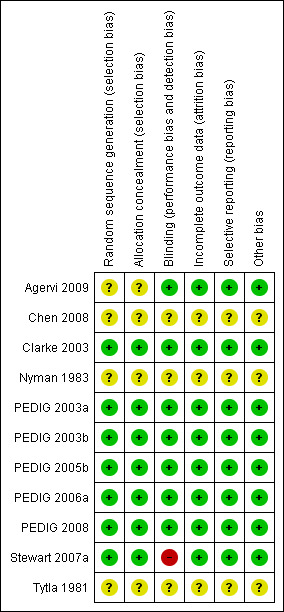
'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.
Allocation
Seven of the included eleven studies showed no evidence of selection bias.
Blinding
In all of the included trials sequence generation and allocation concealment were conducted by methods recognised to produce comparable groups and prevent bias at recruitment. All but one (Stewart 2007a) of the included studies was masked, minimising the risk of performance bias. For three studies (Chen 2008, Nyman 1983, Tytla 1981) performance and detection bias were judged to be unclear. Attempted contact with the authors could not resolve this.
Incomplete outcome data
Attrition rates in the included studies were low and were similar in control and intervention groups (Agervi 2009, Clarke 2003, PEDIG 2003a, PEDIG 2003b, PEDIG 2005b, PEDIG 2006a, PEDIG 2008). Attrition bias was unclear in the remaining three studies (Chen 2008, Nyman 1983, Tytla 1981)
Selective reporting
No evidence of selective reporting was apparent for eight of the included studies (Agervi 2009, Clarke 2003, PEDIG 2003a, PEDIG 2003b, PEDIG 2005b, PEDIG 2006a, PEDIG 2008, Stewart 2007a). It was unclear for the remaining three (Chen 2008, Nyman 1983, Tytla 1981).
Other potential sources of bias
No steps have been taken to investigate the possibility of publication bias.
Effects of interventions
We extracted data from eight trials for seven comparisons. We extracted data from two other trials (Chen 2008; Tytla 1981) but did not use the data in any comparisons. Where more than one trial provided data for a comparison there was significant heterogeneity, therefore a narrative summary of the results is provided. For each study the results are presented in terms of the mean difference (MD) in final visual acuity measured using LogMAR notation.
No study contained data for our primary outcome measure: visual acuity at 12 months post cessation of treatment. Main outcome measures were reported at various time points and not necessarily at the end of treatment. This may mean that for some participants there were further changes in vision after the trial ended. Reported outcomes therefore do not necessarily reflect optimum treatment effect but a comparison of treatment effectiveness at a given point in time. It is also possible that for some participants vision regressed after treatment stopped. No trials had data available to allow subgroup analysis by starting visual acuity or by whether or not there was a co‐existing microtropia.
It is important to note that all of the extracted data represent participants who met the review inclusion criteria and not the entire study data set. The included trials were not powered to detect an effect with the sub‐sample of data we extracted. All participants included in the analysis were diagnosed with unilateral refractive amblyopia. No trials have been found as yet comparing treatment outcomes for bilateral amblyopia.
Spectacles only compared to no treatment
We extracted data for those participants with starting vision of 0.400 LogMAR or worse. At 12 months from treatment commencement the mean visual acuity in the spectacles only group (n = 20) was 0.31 (0.17 standard deviation (SD) compared to 0.42 (0.19 SD) in the no treatment group (n = 22) giving a mean difference (MD) of ‐0.11 (95% confidence interval (CI) ‐0.22 to 0.00), which although not statistically significant is suggestive of some evidence of a difference (Clarke 2003; Analysis 1.1).
1.1. Analysis.
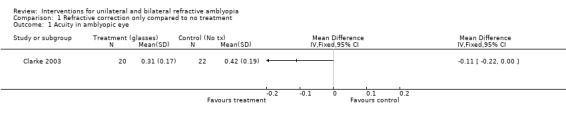
Comparison 1 Refractive correction only compared to no treatment, Outcome 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye.
Spectacles plus conventional occlusion compared to no treatment
We extracted data for participants with starting acuity of 0.400 LogMAR or worse. At 12 months from the commencement of the study the mean vision for the full treatment group (n = 21) was 0.22 (0.13 SD) and in the no treatment group (n = 22) it was 0.42 (0.19 SD). The MD was therefore ‐0.20 (95% CI ‐0.30 to ‐0.10), which is statistically significant (Clarke 2003; Analysis 2.1).
2.1. Analysis.
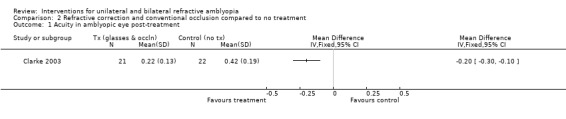
Comparison 2 Refractive correction and conventional occlusion compared to no treatment, Outcome 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment.
Spectacles plus conventional occlusion compared to spectacles only
See Analysis 3.1.
3.1. Analysis.
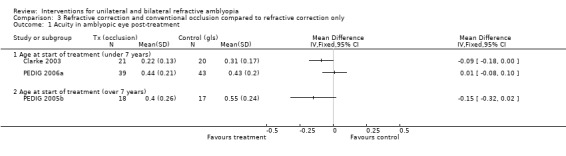
Comparison 3 Refractive correction and conventional occlusion compared to refractive correction only, Outcome 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment.
Participants seven years and under
Two hours occlusion with spectacles compared to spectacles only
The start visual acuity was 0.300 to 1.300 LogMAR. The primary outcome measure was recorded after five weeks of treatment. Mean visual acuity at that point was very similar in both groups: 0.43 (0.20 SD) in the spectacles group (n = 43) and 0.44 (0.21 SD) in the full treatment group (n = 39). The MD was calculated as 0.01 (95% CI ‐0.08 to 0.10), which is not statistically significant (PEDIG 2006a).
Occlusion (any regime) with spectacles compared to spectacles only
The primary outcome measure was recorded at 12 months of treatment (i.e. the end of the trial). At that point the spectacles group (n = 20) had a mean visual acuity of 0.31 (0.17 SD) compared to 0.22 (0.13 SD) in the full treatment group (n = 21): MD ‐0.09 (95% CI ‐0.18 to 0.00), which suggests some evidence of a difference (Clarke 2003).
Participants over seven years of age
Part‐time occlusion (various regimes) with spectacles compared to spectacles only
We extracted data for participants over 13 years old at the start of treatment. The primary outcome measure was best visual acuity measured at any time point during the 24 weeks of the study. In the spectacles only group (n = 17) the mean visual acuity at the maximum improvement visit was 0.55 (0.24 SD) and in the full treatment group (n = 18) the mean visual acuity was 0.40 (0.26). This gave a MD of ‐0.15 (95% CI ‐0.32 to 0.02), which is not statistically significant.
A significantly greater proportion of participants who had not had previous treatment were classified as responders to treatment; 47% in the full treatment group compared to 20% in the spectacles only group (PEDIG 2005b).
Conventional full‐time occlusion plus spectacles compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus spectacles
See Analysis 4.1.
4.1. Analysis.
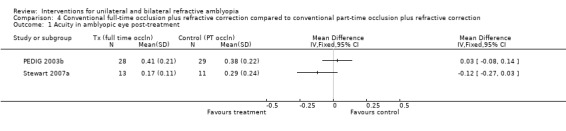
Comparison 4 Conventional full‐time occlusion plus refractive correction compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction, Outcome 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment.
Six hours of occlusion compared to full‐time occlusion for severe amblyopia
The study lasted four months. At that time the mean visual acuity for the six‐hour group (n=29) was 0.38 (0.22 SD) and 0.41 (0.21 SD) for the full‐time group (n=28). The MD was 0.03 (95% CI ‐0.08 to 0.14), which is not statistically significant (PEDIG 2003b).
Six hours of occlusion compared to 12 hours occlusion in all levels of amblyopia
The study duration was nine weeks. Mean visual acuity for the six‐hour group (n = 11) was 0.29 (0.24 SD) and for the 12‐hour group (n = 13) was 0.17 (0.11 SD). The MD was ‐0.12 (95% CI ‐0.27 to 0.03), which is not statistically significant. However, mean dose actually received was not statistically significantly different either: 4.2 hours and 6.2 hours respectively (P = 0.06) (Stewart 2007a).
Conventional part‐time occlusion plus spectacles compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus spectacles
See Analysis 5.1.
5.1. Analysis.
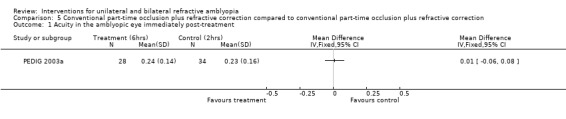
Comparison 5 Conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction, Outcome 1 Acuity in the amblyopic eye immediately post‐treatment.
Two hours of occlusion compared to six hours of occlusion for moderate amblyopia
At the end of four months of treatment the mean visual acuity in the two‐hour group (n = 34) was 0.23 (0.16 SD) and 0.24 (0.14 SD) in the six‐hour group (n = 28). The MD was 0.01 (95% CI ‐0.06 to 0.08), which is not statistically significant (PEDIG 2003a).
Conventional part‐time occlusion whilst undertaking near activities to conventional part‐time occlusion plus distance activities
See Analysis 6.1.
6.1. Analysis.
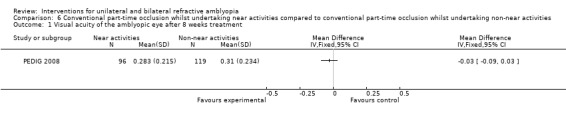
Comparison 6 Conventional part‐time occlusion whilst undertaking near activities compared to conventional part‐time occlusion whilst undertaking non‐near activities, Outcome 1 Visual acuity of the amblyopic eye after 8 weeks treatment.
We extracted data for the 215 participants with unilateral refractive amblyopia as defined within this review. Two hours daily occlusion with full‐time glasses wear was carried out by all participants. For 96 participants, near activities were performed whilst wearing occlusion and mean visual acuity after eight weeks of treatment was 0.283 (0.215 SD). Distance activities were performed by 119 participants with a mean visual acuity after eight weeks of 0.314 (0.234 SD). The mean difference was ‐0.03 (95% CI ‐0.09 to 0.03), which is not statically significant (PEDIG 2008).
Partial occlusion plus refractive correction to refractive correction alone
See Analysis 7.1.
7.1. Analysis.
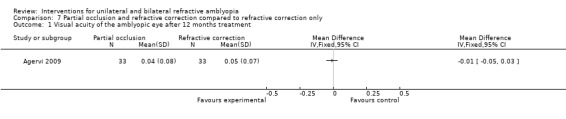
Comparison 7 Partial occlusion and refractive correction compared to refractive correction only, Outcome 1 Visual acuity of the amblyopic eye after 12 months treatment.
Data were provided by the trial authors for the remaining 66 patients to allow for data analysis. Full‐time glasses wear was supplemented with full‐time partial occlusion for half of the trial participants. All participants included within the trial were eligible for inclusion within this review. For 33 participants with refractive correction alone, best corrected visual acuity after one year was 0.050 (± 0.07 SD). For the remaining 33 participants who supplemented glasses wear with full‐time partial occlusion, best corrected visual acuity after one year was 0.04 (± 0.08 SD). The mean difference was ‐0.01 (95% CI ‐0.05 to 0.03), which is not statistically significant (Agervi 2009).
Cambridge (CAM) vision stimulator
It was not possible to extract the necessary data from Nyman 1983 and we have been advised by the authors that these data are no longer available.
Tytla 1981 had three participants who met our inclusion criteria; two in the intervention group and one in the control. None had any change in visual acuity. See: Table 2.
2. Data extraction for Tytla 1981.
| STUDY ID | PRE‐TREATMENT VISION | POST‐TREATMENT VISION |
| Treatment group | ||
| CD | 6/36 | 6/36 |
| CH | Data missing | Data missing |
| Control group | ||
| JW | 6/60 | 6/60 |
Perceptual learning plus refractive correction compared to conventional occlusion plus refractive correction
It was not possible to extract the necessary data from Chen 2008 for participants meeting the pre‐defined inclusion criteria for this review. Contact with the authors has not been possible and so no data have been included in this review.
Adverse effects
Mild
Reduction in vision of the occluded eye
Occlusion therapy carries the risk of adversely affecting the vision in the better/occluded eye. None of the four included studies (PEDIG 2003a;PEDIG 2003b;PEDIG 2006a; PEDIG 2008) which reported change in vision in the sound eye over the course of the study found a statistically significant difference between the control and intervention groups.
Psychological distress
The PEDIG collaboration uses the Amblyopia Treatment Index (PEDIG 2001) to assess adverse effects from treatment. The scale includes questions about the psycho‐social effects of occlusion. PEDIG 2003b reported a median score on this scale of 3.00 (P = 0.10); this was the same for both treatment groups (six‐hour and full‐time occlusion). PEDIG 2003a, however, reported more social stigma in the six‐hour occlusion group than in the two‐hour group. The median scores were 3.00 and 2.67 (P = 0.01) respectively out of a possible 15.
Skin irritation
No studies reported any cases of minor or severe skin irritation.
Severe
No reports of severe adverse effects (reverse amblyopia, psychological distress requiring treatment or occlusion‐induced squint resulting in intractable diplopia) were found in any of the included studies.
Discussion
Evidence for the effectiveness of treatment for unilateral refractive amblyopia has grown substantially over recent years, however treatment for bilateral refractive amblyopia has not been subjected to the same intensity. For unilateral amblyopia the respective roles of treatment by refractive correction and treatment by conventional occlusion have become more clearly defined, and some progress has been made towards clarifying the effect of differing amounts of occlusion. Comparing outcomes from treatment for the various studies included in this review was difficult due to variation in treatment protocols, outcome reporting and post‐treatment follow‐up. However, data from the high‐quality randomised controlled trials (RCTs) included in this review inform some of the fundamental questions regarding the treatment of unilateral refractive amblyopia.
The natural history of untreated unilateral and bilateral refractive amblyopia
There are few studies documenting the natural history of unilateral refractive amblyopia. The best available data are contained within the study by Clarke 2003 who randomised patients to a 'no treatment' control group for 12 months. After 12 months, although vision in the control group had not deteriorated, mean acuity was statistically significantly poorer in the control group when compared to the full treatment (spectacles and occlusion) group. When treated at the end of the 12 months, 44% of the entire control group (at a mean age of five years) required spectacles alone, 44% went on to need occlusion and the remainder required no treatment at all. The improvement in the children who needed no treatment may indicate that amblyopia resolved spontaneously over the 12 months but the improvement is more likely to be explained by increased maturity and therefore improved ability to co‐operate with testing. It is also possible that the visual deficit was not in fact amblyopia but purely an uncorrected refractive error that resolved spontaneously over the 12 months. Taken together these data suggest that for the majority of patients (88%), intervention (spectacles +/‐ occlusion) is required to resolve unilateral refractive amblyopia but, equally as important, some children may spontaneously improve, which was not previously believed to be the case.
The best available evidence for the natural history of bilateral refractive amblyopia comes from case reports from patients who have failed to comply with treatment. Simons 1999 showed via a case series of 18 patients a very poor response in terms of improvement to visual acuity where spectacle treatment had not been tolerated over a period of one year. However, it should be noted that only one patient in this series was diagnosed with bilateral refractive amblyopia.
Optimum treatment protocol for unilateral refractive amblyopia
Refractive adaptation/optical treatment of amblyopia
Included studies utilised a variety of approaches to refractive or optical treatment so it is possible that, in some cases, occlusion was started before maximum benefit from optical treatment alone had been achieved. The lack of standardisation of this phase of treatment means we are unable to draw firm conclusions from our data regarding the optimum duration of spectacles wear prior to occlusion therapy. However, a period of spectacle wear alone is now well recognised as the initial stage in the treatment of refractive amblyopia (PEDIG 2006b; Stewart 2004). A pragmatic approach, adopted in more recent Paediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) studies, is to monitor acuity until there is no significant improvement for at least two consecutive visits.
The impact of occlusion on visual outcomes
One of the objectives of the review was to identify the impact of adding occlusion therapy to spectacles in the management of unilateral refractive amblyopia. Isolating and comparing the treatment effect from occlusion across the included studies was complicated by the varying periods allowed for optical treatment and other differences such as including an hour of close work. The role of close work whilst undertaking occlusion has also be examined as part of this review. PEDIG 2008 found no statistical difference in adding close work to occlusion.
Data regarding the treatment effect of spectacles alone versus spectacles plus total occlusion needs to be interpreted in the light of some important considerations. The data from two of the three studies included for this comparison (PEDIG 2005b; PEDIG 2006a) were extracted from a larger study population including other types of amblyopia. Using extracted data, with fewer participants, resulted in reduced statistical power and therefore a reduced likelihood of finding a difference even if there was one. The study by Clarke 2003 found a trend towards a significant treatment effect from adding occlusion therapy to glasses wear. Further work is needed to clarify the magnitude of the added treatment benefit from occlusion.
The role of partial occlusion was examined in one trial. Agervi 2009 randomised participants to receive glasses alone versus glasses and Bangerter filter treatment. However, both treatments were started simultaneously without any allowance for refractive adaptation. No statistical significance was found in terms of final mean vision achieved between the two treatment groups, but in the intervention group time to resolution of the amblyopia was almost twice as fast: 2.2 months compared to 3.9 months. The outcomes from this study could indicate that all occlusion adds is speed; maybe other studies just have not been giving optical treatment enough time.
Occlusion dose/response
PEDIG 2003a and PEDIG 2003b did not find a difference between prescribing two versus six hours or between prescribing six hours versus full‐time occlusion. This could be taken as evidence that no dose/response relationship exits in occlusion therapy. The investigators, however, postulate that one explanation for this might be the fact that actual amounts of occlusion achieved were different to that prescribed. Another proposed explanation is that the rate of response to treatment is limited at an anatomical level and that there is therefore a maximum rate of recovery.
Recent trials have added to the evidence for a dose/response relationship in the treatment of amblyopia. Stewart 2007a randomised children to receive either six hours or 12 hours of occlusion per day and found very similar visual outcomes between the two groups. Data from the occlusion dose monitor, however, confirmed that the amount of occlusion actually achieved was also similar in both groups: 4.2 hours in the six‐hour group compared to 6.2 in the 12‐hour group.
Taking into account the dose actually received the study data suggest that dose rates of between three and six hours per day are associated with optimum improvement. The effect of age, density of amblyopia and other factors on the rate of improvement and final outcome are not yet fully understood. The authors recommend that in the interim “achieving an initial dose rate of three to four hours/day should be a clinical priority”.
Concordance with occlusion
In order for any treatment to succeed it has to be acceptable to the patient and, in the case of amblyopia, also to the parents or other principal caregivers. Attempts to describe and quantify psycho‐social effects of treatment are increasing, for example the use of the Amblyopia Treatment Index in the PEDIG studies. Three studies included in this review attempted to measure concordance (PEDIG 2003a; PEDIG 2003b; Stewart 2007a) and all reported considerable variation in compliance: prescribing higher doses of occlusion was associated with more variation in compliance. A recent RCT (Loudon 2006) was designed to investigate predictors of non‐concordance with occlusion therapy. Results from the study showed that education aimed primarily at the child significantly improved compliance and reduced the number of children who would not wear the occlusion at all. The authors identified low vision at the start of treatment to be the most significant clinical predictor of poor concordance. In addition the study findings suggest that poor understanding of the treatment and its purpose due to language and cultural/educational barriers are associated with reduced concordance. The inter‐play between these factors and the psycho‐social aspects of occlusion therapy warrant further investigation.
When to treat?
PEDIG 2005b demonstrated some response to occlusion therapy in children who were 13 to 17 years of age. However, all of these older participants demonstrated a residual visual deficit. In the study by Clarke 2003 treatment was delayed for 12 months in the control group, giving a mean age of five years (as opposed to four years) at commencement of treatment. There was no evidence of harm from delaying treatment commencement until approximately five years of age. As a small proportion of patients in the Clarke 2003 study showed spontaneous improvement over the 12 months without treatment, it could be argued that such a delay may mean some patients avoid unnecessary treatment. It should be noted though that evidence from the trial conducted by Stewart 2007a suggests that younger children with amblyopia (under four years of age) require lower doses of occlusion. Additional, comparable studies are needed to confirm or refute these findings.
Adjuncts to occlusion therapy
Although at the time there was much interest in and hope for the Cambridge (CAM) vision stimulator the treatment has fallen out of general use. The two included trials (Nyman 1983; Tytla 1981) did not detect any benefit from adding CAM stimulation to occlusion therapy.
The role of other adjuncts such as prescribed periods of close work remain controversial.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
The results reported in this review need to be considered in the light of some limitations. We extracted data for participants with unilateral refractive amblyopia from trials powered for a larger sample, e.g. including other types of amblyopia or 0.200 or better entry acuity. Using smaller numbers in our analyses may explain why some comparisons failed to reach statistical significance. Only one of the included trials (Stewart 2007a) had a design that specifically addressed one of the objectives of the review: the dose/response from conventional occlusion. Eliciting the impact of adding occlusion alone may have been confounded by the addition of a period of close work in the PEDIG studies and the lack of a standard approach to allow vision to stabilise in spectacles across the included studies. In addition some of the included trials had been designed to investigate whether a treatment effect could be elicited rather than to establish maximum benefit from treatment and therefore reported outcomes included data on participants who were still undergoing occlusion. It may be that in these studies optimum acuity had not yet been achieved. It is also important to note that none of the studies included a post‐treatment follow‐up period, precluding assessment of sustainability of treatment effects.
The primary outcome measure for all the included trials was mean visual acuity and it is possible that this may have masked both failure to improve and magnitude of improvement. In updates of the review we are therefore hoping to be able to present the number needed to treat to benefit (NNT).
Optimum treatment protocol for bilateral refractive amblyopia
Bilateral refractive amblyopia, by its very nature, is caused by a high degree of bilateral refractive error. The aim of treatment is restoration of visual acuity in one or both eyes. Current treatment revolves around correction of the refractive error by either glasses or contact lenses and time. A gradual improvement in vision over time is expected. Wallace 2007 identified 113 participants with previously untreated bilateral refractive amblyopia. Mean binocular acuity improved 3.9 lines over a one‐year period. The cumulative probability of binocular acuity of 0.100 or better after one year of glasses wear was 74%. No randomised trials comparing differing treatment options for bilateral refractive amblyopia where available for analysis.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
For some patients with unilateral refractive amblyopia, refractive correction alone may resolve the visual deficit. At present it is not possible to determine at the start of treatment which children will fall into this category.
A pragmatic approach to treatment may be to allow time for improvement in vision with refractive correction alone and then prescribe occlusion for any persistent amblyopia. This approach should minimise occlusion treatment.
Concordance with prescribed dose of occlusion varies in an unpredictable fashion and it appears that higher doses are associated with greater variation in concordance.
Current evidence suggests that the majority of children with amblyopia will benefit from three to six hours of occlusion per day. Children under the age of four may require less occlusion but the effect of age on the dose/response relationship is not yet fully understood.
Current evidence does not suggest any benefit can be gained by the addition of close work with prescribed occlusion.
Implications for research.
While the high‐quality studies included in this review enable a more evidence‐based approach to amblyopia treatment, there is still a significant need for further research. Specific areas that require further study are:
identification of factors associated with successful treatment by optical correction alone;
determining the degree of anisometropia likely to cause amblyopia;
determining the magnitude of visual gain from occlusion therapy;
clarification of the effect of:
age at treatment commencement;
duration of acuity deficit;
type and degree of refractive error;
magnitude of visual loss.
Regarding the overall outcome of therapy and the dose/response relationship the following issues require clarification:
investigating effectiveness of adjuncts to occlusion therapy such as optical penalisation;
sustainability of treatment effect and rate of recurrence of amblyopia after cessation of treatment including factors associated with/preventing recurrence;
establishing overall impact of treatment:
effect on psycho‐social and emotional well‐being of the child;
non‐concordance with therapy ‐ causes, effects, measures to reduce;
cost‐effectiveness of treatment;
consequences of not treating.
Investigating the role of other modes of occlusion/optical penalisation.
Difficulties in planning and conducting trials in this area include:
the need for an agreed definition of amblyopia, including reference to published normative data on commonly used children's vision tests;
measurement of compliance with prescribed treatment in the absence of a commercially viable occlusion dose monitor;
the need for multicentre co‐operation in order to recruit sufficient numbers;
logistical and funding constraints on obtaining long‐term follow‐up data.
We are aware that high‐quality trials addressing some of these questions are underway and any that meet the inclusion criteria will be reported in updates of the review.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 15 May 2012 | Amended | The plain language summary title and some of the text has been amended for clarity. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 1, 2005 Review first published: Issue 4, 2008
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 March 2012 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | Issue 4 2012: The scope of the review has been broadened to include bilateral refractive amblyopia. Lead/contact author's surname has changed. |
| 1 March 2012 | New search has been performed | Issue 4 2012: Updated searches yielded three new trials that were included in the review. |
| 15 May 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. |
Acknowledgements
We thank Catey Bunce, Suzanne Brodney‐Folse, Swaroop Vedula and Cathy Williams for their peer review comments. We also thank Sue Elliott, Anupa Shah and Richard Wormald for their guidance on the review. The Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group created and ran the electronic searches. We would also like to acknowledge the previous work of Gerasimos Voros (GV) on the review.
Richard Wormald (Co‐ordinating Editor for CEVG) acknowledges financial support for his CEVG research sessions from the Department of Health through the award made by the National Institute for Health Research to Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology for a Specialist Biomedical Research Centre for Ophthalmology. The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the Department of Health.
Appendices
Appendix 1. CENTRAL search strategy
#1 MeSH descriptor Amblyopia #2 MeSH descriptor Refractive Errors #3 MeSH descriptor Anisometropia #4 amblyop* #5 anisometropi* #6 refract* #7 meridional #8 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7) #9 MeSH descriptor Contact Lenses #10 MeSH descriptor Eyeglasses #11 (optic* or vision* or visual*) near/5 (occlus* or penalis* or stimulat*) #12 (eyeglass* or glass* or spectacle*) near/5 (occlus* or penalis* or stimulat*) #13 (lens* or contact?lens* or filter*) near/5 (occlus* or penalis* or stimulat*) #14 MeSH descriptor Orthoptics #15 pleoptic* #16 (#9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15) #17 (#8 AND #16)
Appendix 2. MEDLINE search strategy
1 randomised controlled trial.pt. 2 (randomised or randomised).ab,ti. 3 placebo.ab,ti. 4 dt.fs. 5 randomly.ab,ti. 6 trial.ab,ti. 7 groups.ab,ti. 8 or/1‐7 9 exp animals/ 10 exp humans/ 11 9 not (9 and 10) 12 8 not 11 13 exp amblyopia/ 14 exp refractive errors/ 15 exp anisometropia/ 16 amblyo$.tw. 17 anisometrop$.tw. 18 refract$.tw. 19 meridional.tw. 20 or/13‐19 21 exp contact lenses/ 22 exp eyeglasses/ 23 ((optic$ or vision$ or visual$) adj5 (occlus$ or penalis$ or stimulat$)).tw. 24 ((eyeglass$ or glass$ or spectacle$) adj5 (occlus$ or penalis$ or stimulat$)).tw. 25 ((lens$ or contact?lens$ or filter$) adj5 (occlus$ or penalis$ or stimulat$)).tw. 26 exp orthoptics/ 27 pleoptic$.tw. 28 or/21‐27 29 20 and 28 30 12 and 29
The search filter for trials at the beginning of the MEDLINE strategy is from the published paper by Glanville et al (Glanville 2006).
Appendix 3. EMBASE search strategy
1 exp randomised controlled trial/ 2 exp randomisation/ 3 exp double blind procedure/ 4 exp single blind procedure/ 5 random$.tw. 6 or/1‐5 7 (animal or animal experiment).sh. 8 human.sh. 9 7 and 8 10 7 not 9 11 6 not 10 12 exp clinical trial/ 13 (clin$ adj3 trial$).tw. 14 ((singl$ or doubl$ or trebl$ or tripl$) adj3 (blind$ or mask$)).tw. 15 exp placebo/ 16 placebo$.tw. 17 random$.tw. 18 exp experimental design/ 19 exp crossover procedure/ 20 exp control group/ 21 exp latin square design/ 22 or/12‐21 23 22 not 10 24 23 not 11 25 exp comparative study/ 26 exp evaluation/ 27 exp prospective study/ 28 (control$ or prospectiv$ or volunteer$).tw. 29 or/25‐28 30 29 not 10 31 30 not (11 or 23) 32 11 or 24 or 31 33 exp amblyopia/ 34 exp refractive errors/ 35 exp anisometropia/ 36 amblyo$.tw. 37 anisometrop$.tw. 38 refract$.tw. 39 meridional.tw. 40 or/33‐39 41 exp contact lenses/ 42 exp spectacles/ 43 ((optic$ or vision$ or visual$) adj5 (occlus$ or penalis$ or stimulat$)).tw. 44 ((eyeglass$ or glass$ or spectacle$) adj5 (occlus$ or penalis$ or stimulat$)).tw. 45 exp orthoptics/ 46 pleoptic$.tw. 47 or/41‐46 48 40 and 47 49 32 and 48
Appendix 4. LILACS search strategy
amblyop$ or anisometrop$ or meridional or refractive and optic$ or vision$ or visual$ or glass$ or spectacle$ or lens$ or occlu$ or penalis$ or stimulat$
Appendix 5. metaRegister of Controlled Trials search strategy
unilateral amblyopia
Appendix 6. ClinicalTrials.gov search strategy
Unilateral Amblyopia
Appendix 7. ICTRP search strategy
Unilateral Amblyopia
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Refractive correction only compared to no treatment.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 2. Refractive correction and conventional occlusion compared to no treatment.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 3. Refractive correction and conventional occlusion compared to refractive correction only.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Age at start of treatment (under 7 years) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Age at start of treatment (over 7 years) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
Comparison 4. Conventional full‐time occlusion plus refractive correction compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Acuity in amblyopic eye post‐treatment | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 5. Conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction compared to conventional part‐time occlusion plus refractive correction.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Acuity in the amblyopic eye immediately post‐treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 6. Conventional part‐time occlusion whilst undertaking near activities compared to conventional part‐time occlusion whilst undertaking non‐near activities.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Visual acuity of the amblyopic eye after 8 weeks treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 7. Partial occlusion and refractive correction compared to refractive correction only.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Visual acuity of the amblyopic eye after 12 months treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Agervi 2009.
| Methods | Prospective randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | 80 participants age range 4 to 5.4 years diagnosed with untreated monocular anisometropic amblyopia. 40 participants randomised to each treatment group. Visual acuity range 0.300 to 1.300 | |
| Interventions | 1. Spectacles only 2. Spectacles in combination with Bangerter filter worn on the spectacle lens of the better seeing eye |
|
| Outcomes | Time course to the resolution of amblyopia. Main vision outcome documented after 1 year of treatment | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Method of randomisation not reported within write up of results |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not documented within trial write up |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | There are no reports of masking being breached |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Data are published accounting for all participants who entered the study including those no longer eligible after randomisation and those lost to follow‐up. All recruits were analysed by original treatment group. 33 participants from each group were available for analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other potential sources of bias were identified |
Chen 2008.
| Methods | Prospective randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | 30 participants recruited to perceptual learning group. Outcomes for 26 available 31 participants recruited to occlusion group. Outcomes for 27 available Visual acuity range 0.1 to 0.9 Age range 3 to > 18 years |
|
| Interventions | 1. Perceptual learning 2. Conventional occlusion ‐ regime issued dependant upon visual acuity of amblyopic eye |
|
| Outcomes | Visual acuity of the amblyopic eye at the end of treatment | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
Clarke 2003.
| Methods | Single masked randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: No treatment Group 2: Spectacles only Group 3: Full treatment (spectacles and occlusion) | |
| Outcomes | 1. Best corrected acuity after treatment 2. Vision outcomes recorded at 12 months | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated stratified by centre prior to recruitment |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Tickets stored in numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes. Centres telephoned the main centre after recruitment to obtain allocation |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Vision was assessed by an Orthoptist who was unaware of treatment allocation. If masking was breached subsequent vision tests were carried out by a deputy research Orthoptist who was unaware of the treatment group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | A table is published accounting for all participants who entered the study including those lost to follow‐up and those who rejected allocation. All recruits were analysed by original treatment group. There were 59 participants in each of 3 treatment groups at the outset |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other potential sources of bias were identified |
Nyman 1983.
| Methods | Random allocation to receive occlusion therapy or CAM therapy | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | 1. Occlusion 2. CAM therapy | |
| Outcomes | Improvement in the treated eye of at least 2 lines on the Snellen chart | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
PEDIG 2003a.
| Methods | Prospective multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: 2 hours occlusion Group 2: 6 hours occlusion | |
| Outcomes | 1. Best corrected acuity after treatment 2. Vision outcomes after 4 months 3. Adverse events ‐ reduction in visual acuity of non‐amblyopic eye not requiring treatment | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated using a permuted block design |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was achieved by accessing the main study website after recruitment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Vision testing was carried out by study personnel masked to the treatment group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Primary outcome data were collected on 97% of patients in the 2‐hour group and 95% in the 6‐hour group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The published protocol is available and outcomes were reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected |
PEDIG 2003b.
| Methods | Prospective multicentre randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: Full‐time occlusion Group 2: 6 hours (part‐time) occlusion | |
| Outcomes | 1. Best corrected acuity after treatment 2. Vision outcomes after 4 months 3. Adverse events ‐ reduction in visual acuity of non‐amblyopic eye not requiring treatment | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated using a permuted block design |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was achieved by accessing the main study website after recruitment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Vision testing was carried out by study personnel masked to the treatment group. The number of occasions this was breached is published: 6% in the 6‐hour group and 11% in the full‐time group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | The primary outcome measure was completed by 86% of participants in the 6‐hour group and 93% in the full‐time group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected or suspected |
PEDIG 2005b.
| Methods | Prospective randomised multicentre clinical trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: 2 to 6 hours daily patching with near activities Group 2: Optical correction only |
|
| Outcomes | 1. Best corrected vision at 24 weeks 2. Adverse events ‐ diplopia (double vision) due to treatment |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated using a permuted block design stratified by site, age and visual acuity |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Master randomisation list was access via the study website after recruitment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Masked examiners carried out the acuity testing |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 93% of participants in the full treatment group and 82% in the spectacles only group completed the primary outcome visit measure |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected or suspected |
PEDIG 2006a.
| Methods | Prospective randomised multicentre trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: 2 hours occlusion Group 2: Spectacles wear only | |
| Outcomes | 1. Best corrected VA in the amblyopic eye after 5 weeks | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated using a permuted block design |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation via study website after recruitment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Masked examiners carried vision testing. Percentage of occasions when the masking was breached is published; 5% in the patching group, 1% in the control group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Main outcome measure was completed by 98% of patients in the intervention group and 95% in the control group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected or suspected |
PEDIG 2008.
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial | |
| Participants | 425 children aged between 3 and 7 years of age with strabismic, anisometropic or mixed amblyopia (0.300 to 1.300) which persisted after glasses wear | |
| Interventions | 2 hours daily patching with near activities or 2 hours daily patching with distance activities | |
| Outcomes | Masked assessment of visual acuity at 8 weeks | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequence was computer‐generated using a permuted block design |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation via study website after recruitment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Examiner masked to treatment group in 97% of cases |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Main outcome visit was achieved in 95% of patients receiving distance activities and 92% of patient receiving near activities. Clear reasons are given in the paper as to why outcomes are not achieved in all cases |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected or suspected |
Stewart 2007a.
| Methods | Prospective unmasked randomised trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Group 1: 6 hours daily occlusion Group 2: 12 hours daily occlusion | |
| Outcomes | 1. Visual acuity in the amblyopic eye | |
| Notes | 1. Compliance measured by occlusion dose monitor | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | By random number generator in statistical package 'R' (www.r‐project.org) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Concealed typed allocation list |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Neither the patients nor the examiners were masked to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | A table is used to account for all participants recruited to the trial |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study protocol is published and outcomes are reported as pre‐specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other sources of bias were detected or suspected |
Tytla 1981.
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants |
|
|
| Interventions | Grey rotation discs (control) versus CAM | |
| Outcomes | 1. Change in acuity post‐treatment 2. Vision 1 month post‐treatment | |
| Notes | 1. Contrast sensitivity data collected 2. Linear vision only recorded for 13 participants | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information not clear in trial report |
CAM: Cambridge vision stimulator; VA: visual acuity
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Agervi 2010 | This trial included a regime of occlusion not covered by the review and was therefore excluded |
| Awan 2005 | Included participants with strabismic and mixed amblyopia. No participants with unilateral refractive amblyopia |
| Chen 2010 | This review compared different methods of refractive correction (contact lenses to glasses) |
| Hayashi 1969 | Unable to obtain full copy ‐ will be considered for inclusion in update if article can be found |
| Huang 2009 | Compared conventional occlusion to atropine therapy |
| Johnson 1969 | Unable to obtain full copy ‐ will be considered for inclusion in update if article can be found |
| Keith 1980 | Compared rotation gratings to homogeneous grey discs. No control group received occlusion therapy only and therefore does not meet study comparisons |
| Mehdorn 1981 | Compared rotation gratings to black and white pictures. No control group received occlusion therapy only and therefore study does not meet the reviews comparisons |
| Pasmanik 1993 | Once translated no longer met criteria |
| PEDIG 2010 | Compared partial occlusion to conventional occlusion. Not covered by the remit of this review |
| Schor 1985 | Compared rotation gratings to homogeneous grey discs. No control group received occlusion therapy only and therefore does not meet study comparisons |
| Wu 2010 | Compared telescopic magnification as a treatment for amblyopia. This is not a current intervention in this review |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
ISRCTN55960730.
| Methods | Double‐masked randomised controlled trial |
| Participants | Participants aged between 10 to 65 years. Visual acuity between 6/9 and 6/36 in the amblyopic eye and 6/6 or better in the good eye where the amblyopia is caused by anisometropia or strabismus |
| Interventions | Control group: placebo Intervention Group: modified CAM ‐ Mallett IPS |
| Outcomes | Improvement in visual acuity |
| Notes |
ISRCTN98018344.
| Methods | Randomised control trial |
| Participants | Unilateral amblyopia with visual acuity better than 6/36 but worse than 6/9 in the amblyopic eye and 6/6 or better in the non‐amblyopic eye. Amblyogenic factor: amblyopic eye is either strabismic or has at least 1D more hypermetropia or 2 D more astigmatism than the non‐amblyopic eye. Patients must be at least 10 years old |
| Interventions | Control group: computerised control treatment Intervention Group: computerised IPS |
| Outcomes | Unclear |
| Notes |
CAM: Cambridge vision stimulator IPS: Intermittent photic stimulator
Differences between protocol and review
Condition
The scope of the review has been broadened to include bilateral refractive amblyopia.
Interventions
The scope of the review has been broadened to include:
trials of spectacle correction without occlusion;
partial occlusion, e.g. Bangerter filters;
other adjuncts to occlusion, e.g. close work;
perceptual learning.
Comparisons
Part‐time occlusion has been redefined as six hours or less.
Provision to include trials comparing two or more regimes of part‐time occlusion.
Data synthesis
For updates of the review we plan to obtain data to allow us to calculate the risk difference (RD) in order to report the number needed to treat to benefit (NNT). Additional subgroup analyses are planned to account for any participants who have had previous treatment for their amblyopia and/or who have a microtropia.
The changes to the review have been made in response to peer review feedback and in the light of experience in preparing the review. The changes are designed to keep the review current and representative of relevant work being carried out in the field. In addition 'Risk of bias' tables have been completed and 'Risk of bias' graphs are included.
Contributions of authors
Conceiving the review: KS Designing the review: KS Co‐ordinating the review: KS Undertaking manual searches: KS, CP, GV Screening search results: KS, CP, GV, CS Organising retrieval of papers: KS Screening retrieved papers against inclusion criteria: KS, CP, CS Appraising quality of papers: KS, CP, Extracting data from papers: KS, CP, CS Writing to authors of papers for additional information: CP Providing additional data about papers: KS,CP Data management for the review: KS, CP Entering data into RevMan: KS, CP Analysis of data: KS, CP, SH, CS Interpretation of data: KS, CP, SH, CS Writing the review: KS, CP, SH, CS
Update of review Issue 4, 2012: KS and CS screened search results and identified new studies for inclusion. All authors assisted in writing the text for the update.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Royal Victoria Infirmary, UK.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
None known.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Agervi 2009 {published data only}
- Agervi P, Kugelburg U, Kugelberg M, Simonsson G, Fornander M, Zetterstrom C. Treatment of anisometropic amblyopia with spectacles or in combination with translucent Bangerter filters. Ophthalmology 2009;116(8):1475‐80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chen 2008 {published data only}
- Chen PL, Chen JT, Fu JJ, Chien KH, Lu CD. A pilot study of anisometropic amblyopia improved in adults and children by perceptual learning: an alternative treatment to patching. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics 2008;28(5):422‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Clarke 2003 {published data only}
- Clarke MP, Wright CM, Hrisos S, Anderson JD, Henderson J, Richardson SR. Randomised controlled trial of treatment of unilateral visual impairment detected at preschool vision screening. BMJ 2003;327(7426):1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nyman 1983 {published data only}
- Nyman KG, Singh G, Rydberg A, Fornander M. Controlled study comparing CAM treatment with occlusion therapy. British Journal of Ophthalmology 1983;67(3):178‐80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2003a {published data only}
- Repka MX, Beck RW, Holmes JM, Birch EE, Chandler DL, Cotter SA, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomized trial of patching regimens for treatment of moderate amblyopia in children. Archives of Ophthalmology 2003;121(5):603‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2003b {published data only}
- Holmes JM, Kraker RT, Beck RW, Birch EE, Cotter SA, Everett DF, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomized trial of prescribed patching regimens for treatment of severe amblyopia in children. Ophthalmology 2003;110(11):2075‐87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2005b {published data only}
- Scheiman MM, Hertle RW, Beck RW, Edwards AR, Birch E, Cotter SA, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Randomized trial of treatment of amblyopia in children aged 7 to 17 years. Archives of Ophthalmology 2005;123(4):437‐47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2006a {published data only}
- Wallace DK, Edwards AR, Cotter SA, Beck RW, Arnold RW, Astle WF, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomized trial to evaluate 2 hours of daily patching for strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia in children. Ophthalmology 2006;113(6):904‐12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2008 {published and unpublished data}
- Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomised trial of near versus distance activities while patching for amblyopia in children aged 3 to less than 7 years. Ophthalmology 2008;115(11):2071‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stewart 2007a {published and unpublished data}
- Stewart CE, Stephens DA, Fielder AR, Moseley MJ. ROTAS Cooperative. Objectively monitored patching regimens for treatment of amblyopia: randomised trial. BMJ 2007;335(7622):707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tytla 1981 {published data only}
- Tytla ME, Labow‐Daily LS. Evaluation of the CAM treatment for amblyopia: a controlled study. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1981;20(3):400‐6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Agervi 2010 {published data only}
- Agervi P, Kugelberg U, Kugelberg M, Simonssson G, Formander M, Zetterstrom C. Randomised evaluation of spectacles plus alternate day occlusion to treat amblyopia. Ophthalmology 2010;117(2):381‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Awan 2005 {published data only}
- Awan M, Proudlock FA, Gottlob I. A randomized controlled trial of unilateral strabismic and mixed amblyopia using occlusion dose monitors to record compliance. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2005;46(4):1435‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chen 2010 {published data only}
- Chen W, Sun G, Zhang C. Wearing RGP to treat anisometropic amblyopia. Chinese International Journal of Ophthalmology 2010;10(10):2006‐7. [Google Scholar]
Hayashi 1969 {published data only}
- Hayashi H, Hanai Y, Nii M, Yoshihara M, Hiyoshi H. Application of contact lenses for the treatment of anisometropic hypermetropic amblyopia. Kaiin Dayori. Nippon Kontakuto Renzu Gakkai 1969;11(10):101‐27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Huang 2009 {published data only}
- Huang Y, Yang J, Zhang D, Shen P. Comparison between blinkers eyeshade occlusion and atropine therapy for the treatment of ametropic amblyopia. International Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;9(8):1615‐7. [Google Scholar]
Johnson 1969 {published data only}
- Johnson DJ. Treatment of amblyopia with drugs and contact lenses. Kaiin Dayori. Nippon Kontakuto Renzu Gakkai 1969;11(Supplement):33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Keith 1980 {published data only}
- Keith CG, Howell ER, Mitchell DE, Smith S. Clinical trial of the use of rotating grating patterns in the treatment of amblyopia. British Journal of Ophthalmology 1980;64(8):597‐606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mehdorn 1981 {published data only}
- Mehdorn E, Mattheus S, Schuppe A, Klein U, Kommerell G. Treatment for amblyopia with rotating gratings and subsequent occlusion: a controlled study. International Ophthalmology 1981;3(3):161‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pasmanik 1993 {published data only}
- Pasmanik ED, Nizovtseva TR. The combined treatment of amblyopia by the methods of acupuncture reflexotherapy and traditional pleoptics. Vestnik Oftalmologii 1993;109(4):6‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2010 {published data only}
- PEDIG writing committee. Full time Bangerter filters versus part time daily patching for moderate amblyopia. Ophthalmology 2010;117(5):998‐1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schor 1985 {published data only}
- Schor C, Wick B. Rotating grating treatment of amblyopia with and without eccentric fixation. Journal of American Optometric Association 1985;54(6):545‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wu 2010 {published data only}
- Wu J, Nazami F, Schofiled J, Mirabella G, Wong AM. Effectiveness of telescopic magnification in the treatment of amblyopia: a pilot study. Archives of Ophthalmology 2010;128(3):297‐303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
ISRCTN55960730 {published data only}
- ISRCTN55960730. Double‐masked randomised controlled trial of an amblyopia treatment. http://www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN55960730 (accessed 13 July 2011).
ISRCTN98018344 {published data only}
- ISRCTN98018344. IPS Amblyopia treatment, Phase 3: RCT of a computer program for treating amblyopia. http://www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN98018344 (accessed 13 July 2011).
Additional references
Ansons 2001
- Ansons A, Davis H. Diagnosis and Management of Ocular Disorders. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 2001. [Google Scholar]
Banks 1978
- Banks RV, Campbell FW, Hess RF, Watson PG. A new treatment for amblyopia. British Orthoptic Journal 1978;35:1‐12. [Google Scholar]
Cleary 2000
- Cleary M. Efficacy of occlusion for strabismus amblyopia: can an optimal duration be identified?. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2000;84(6):572‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elkington 1999
- Elkington AR, Frank HJ, Greaney MJ. Clinical Optics. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 1999. [Google Scholar]
Glanville 2006
- Glanville JM, Lefebvre C, Miles JN, Camosso‐Stefinovic J. How to identify randomized controlled trials in MEDLINE: ten years on. Journal of the Medical Library Association 2006;94(2):130‐6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hardman Lea 1989
- Hardman Lea SJ, Loades J, Rubinstein MP. The sensitive period for anisometropic amblyopia. Eye 1989;3(Pt 6):783‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Loudon 2006
- Loudon SE, Fronius M, Looman CW, Awan M, Simonsz B, ser Haas PJ, et al. Predictors and a remedy for noncompliance with amblyopia therapy in children measured with the occlusion dose monitor. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2006;47(10):4393‐400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mazow 2000
- Mazow MD, Chuang A, Vital MC, Prager T. Outcome study in amblyopia: treatment and practice variations. Journal of AAPOS 2000;4(1):1‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mein 1991
- Mein J, Trimble R. Diagnosis and Management of Ocular Motility Disorders. 2nd Edition. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 1991. [Google Scholar]
Newsham 2000
- Newsham D. Parental non‐concordance with occlusion therapy. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2000;84(9):957‐62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2001
- Cole SR, Beck RW, Moke PS, Celano MP, Drews CD, Repka MX, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. The Amblyopia Treatment Index. Journal of AAPOS 2001;5(4):250‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2005a
- Holmes JM, Edwards AR, Beck RW, Arnold RW, Johnson DA, Klimek DL, et al. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. A randomised pilot study of near activities versus non‐near activities during patching therapy for amblyopia. Journal of AAPOS 2005;9(2):129‐36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
PEDIG 2006b
- Cotter SA. Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Treatment of anisometropic amblyopia in children with refractive correction. Ophthalmology 2006;113(6):895‐903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2011 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Simons 1999
- Simons K, Preslan M. Natural history of amblyopia untreated owing to lack of compliance. British Journal of Ophthalmology 1999;83(5):582‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Snowden 1997
- Snowden SK, Stewart‐Brown SL. Preschool vision screening: results of a systematic review. NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination 1997; Vol. Report 9.
Stewart 2004
- Stewart CE, Moseley MJ, Stephens DA, Fielder AR. MOTAS cooperation. Treatment dose‐response in amblyopia therapy: the Monitored Occlusion Treatment of Amblyopia Study (MOTAS). Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2004;45(9):3048‐54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tan 2003
- Tan JH, Thompson JR, Gottlob I. Differences in the management of amblyopia between European countries. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2003;87(3):291‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
von Noorden 1996
- Noorden GK. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility: Theory and Management of Strabismus. 5th Edition. St Louis: Mosby, 1996. [Google Scholar]
Wallace 2007
- Wallace DK, Chandler DL, Beck RW, Arnold RW, Dacal DA, Birch EE, Paediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Treatment of bilateral refractive amblyopia in children 3 to <10 years old. American Journal of Ophthalmology 2007;144(4):487‐96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Shotton 2008
- Shotton K, Powell C, Hatt SR, Stewart C. Interventions for unilateral refractive amblyopia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005137.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


