Abstract
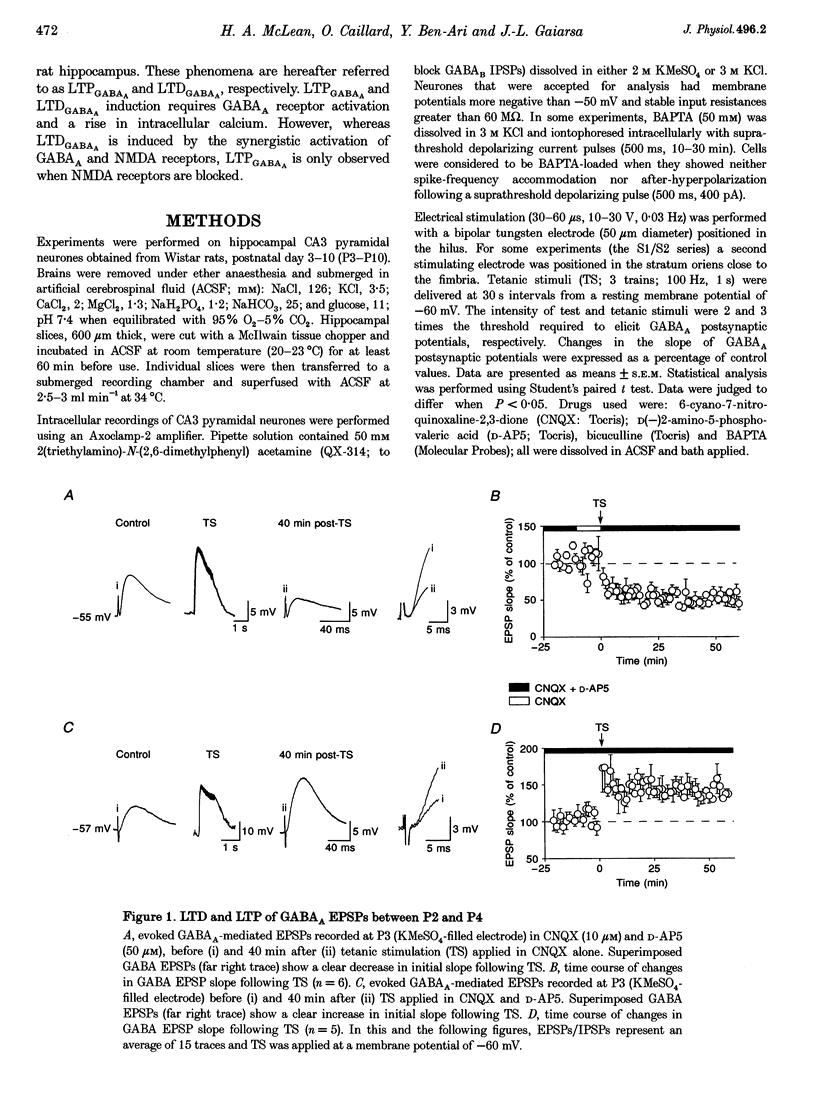
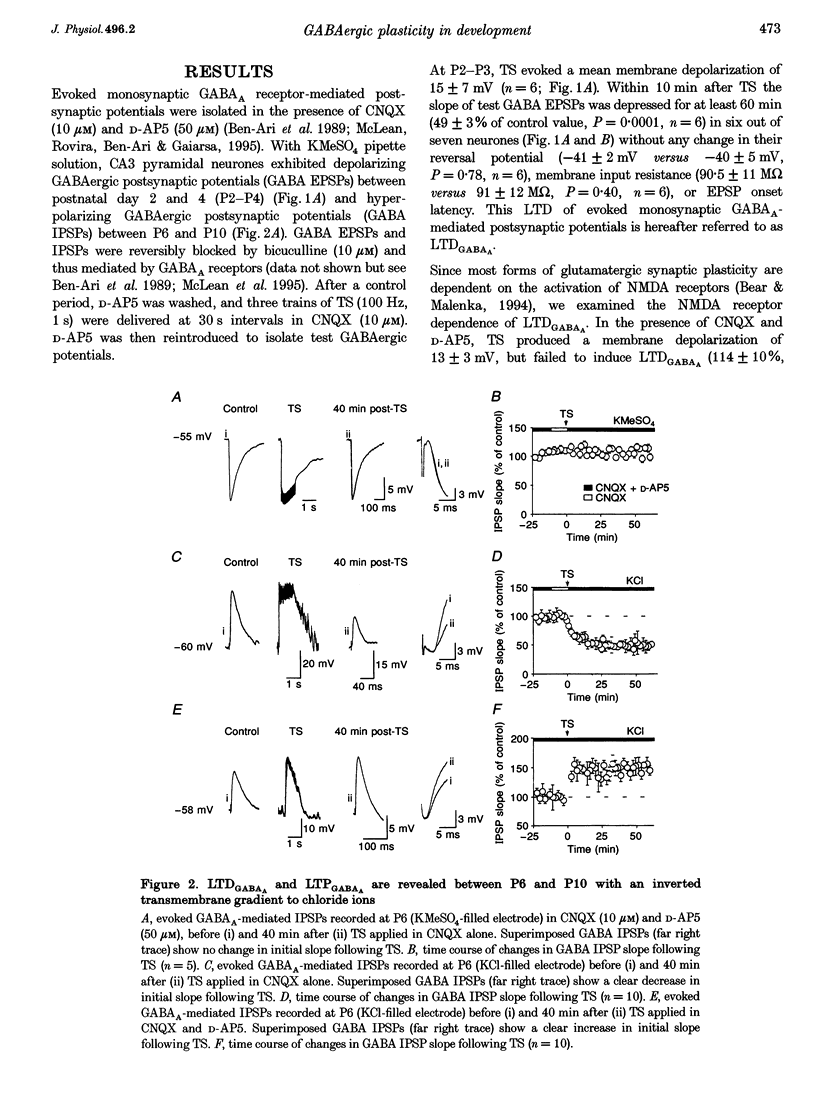
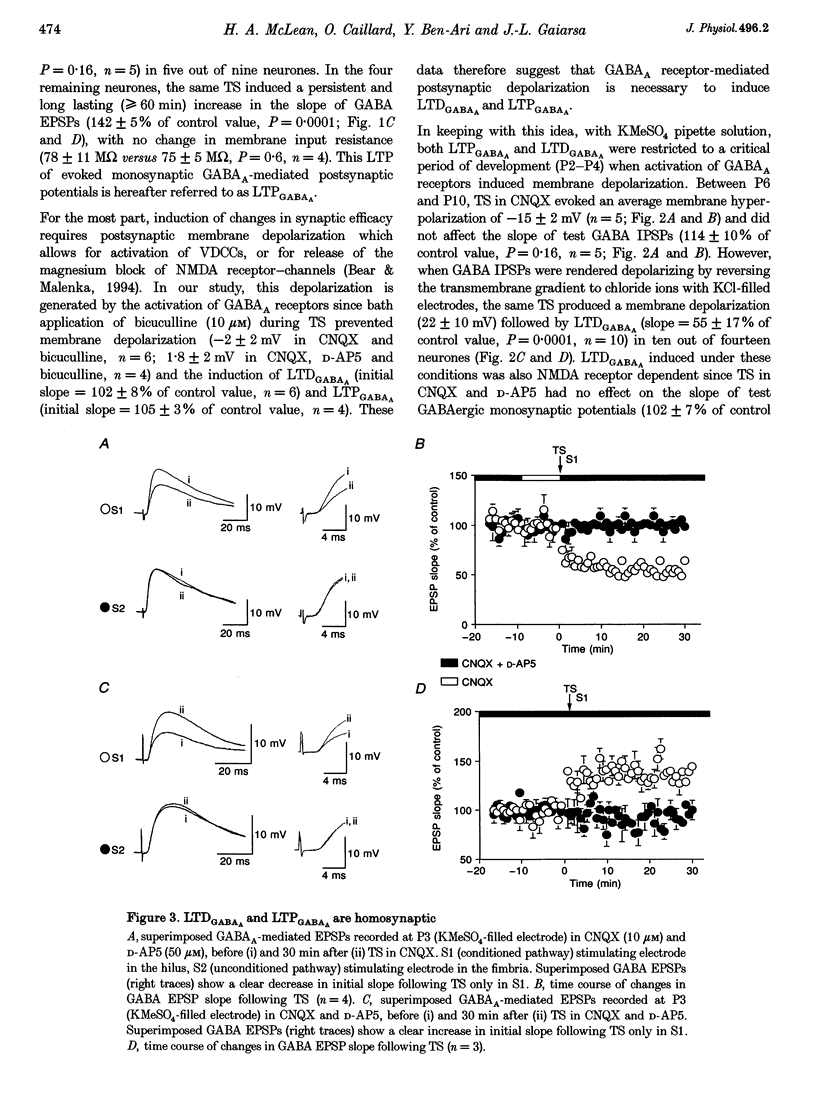
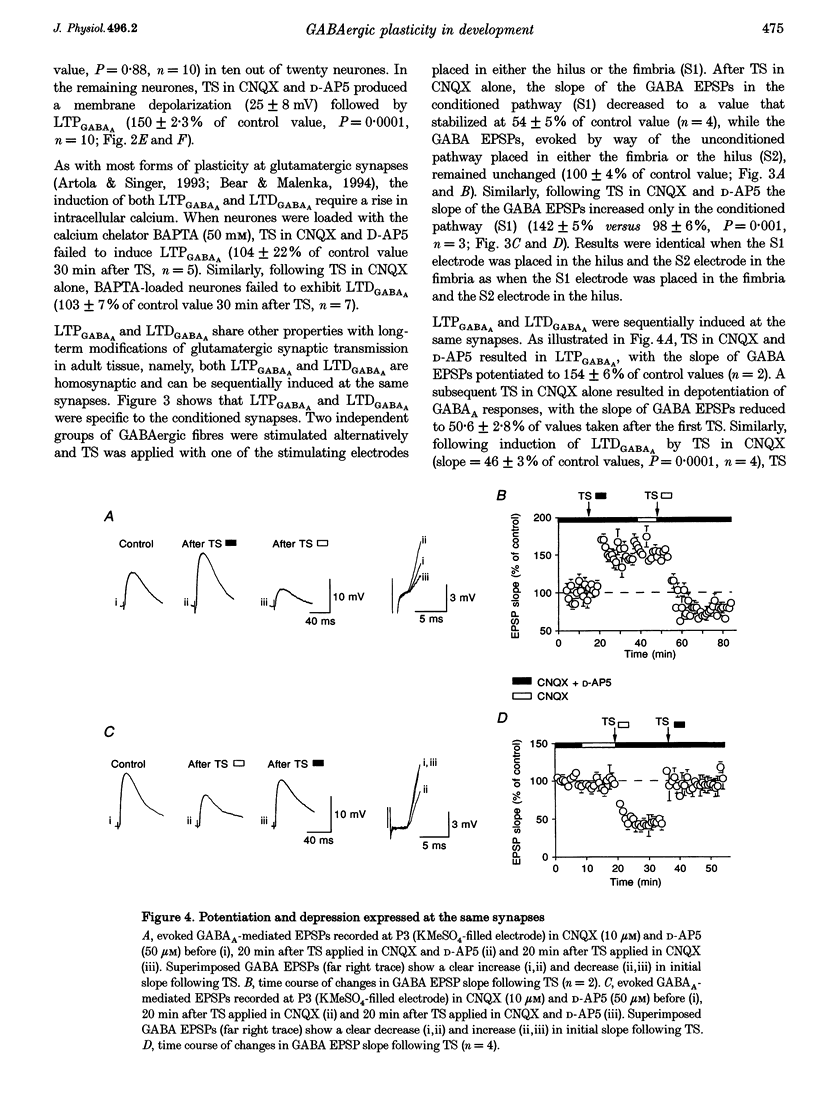
1. Activity-dependent plasticity of GABAergic synaptic transmission was investigated in neonatal rat hippocampal slices obtained between postnatal day (P) 2-10 using intracellular recording techniques. In all experiments, AMPA receptors were blocked by continual application of CNQX (10 microM). 2. Between P2 and P4, tetanic stimulation (TS) evoked NMDA receptor-dependent long-term depression of monosynaptic GABAA EPSPS (LTDGABAA). In contrast, when NMDA receptors were blocked by D-AP5 (50 microM), the same TS evoke long-term potentiation of GABAA EPSPS (LTPGABAA). 3. Between P6 and P10, TS failed to produce either LTP or LTD or hyperpolarizing monosynaptic GABAA IPSPS under the same recording conditions. However, when GABAergic potentials were rendered depolarizing (KCl-filled electrode) Ts induced either LTPGABAA or LTDGABAA in the presence or absence of D-AP5, respectively. 4. Both LTPGABAA and LTDGABAA were specific to the conditioned pathway and could be sequentially expressed at the same synapses. Potentiation of GABAergic synaptic efficacy was induced more easily following previous induction of LTDGABAA than in naive slices. 5. In conclusion, early in development, bidirectional synaptic plasticity is expressed by GABAA receptors and the activation (or not) of NMDA receptors determines the induction of either LTPGABAA or LTDGABAA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aniksztejn L., Ben-Ari Y. Novel form of long-term potentiation produced by a K+ channel blocker in the hippocampus. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):67–69. doi: 10.1038/349067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artola A., Singer W. Long-term depression of excitatory synaptic transmission and its relationship to long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Nov;16(11):480–487. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90081-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear M. F., Malenka R. C. Synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Cherubini E., Corradetti R., Gaiarsa J. L. Giant synaptic potentials in immature rat CA3 hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:303–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakov V. Y., Siegelbaum S. A. Postsynaptic induction and presynaptic expression of hippocampal long-term depression. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1148–1152. doi: 10.1126/science.7909958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek S. M., Bear M. F. Bidirectional long-term modification of synaptic effectiveness in the adult and immature hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):2910–2918. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02910.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand G. M., Kovalchuk Y., Konnerth A. Long-term potentiation and functional synapse induction in developing hippocampus. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):71–75. doi: 10.1038/381071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M. L., Novotny E. A., Lange G. D., Barker J. L. Embryonic and early postnatal hippocampal cells respond to nanomolar concentrations of muscimol. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 May 1;53(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90005-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. M., Teyler T. J. Developmental onset of long-term potentiation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:27–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Rexhausen U., Dreessen J., Konnerth A. Synaptic excitation produces a long-lasting rebound potentiation of inhibitory synaptic signals in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):601–604. doi: 10.1038/356601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y. Age-dependent long-term potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission in rat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 1):6488–6499. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06488.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Iwakiri M. Long-term modification of inhibitory synaptic transmission in developing visual cortex. Neuroreport. 1993 Jul;4(7):907–910. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199307000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinekugel X., Tseeb V., Ben-Ari Y., Bregestovski P. Synaptic GABAA activation induces Ca2+ rise in pyramidal cells and interneurons from rat neonatal hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 1;487(Pt 2):319–329. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Llano I. Modulation of inhibitory synapses in the mammalian brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Jun;5(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean H. A., Rovira C., Ben-Ari Y., Gaiarsa J. L. NMDA-dependent GABAA-mediated polysynaptic potentials in the neonatal rat hippocampal CA3 region. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Jul 1;7(7):1442–1448. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Postsynaptic spike firing reduces synaptic GABAA responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4122–4132. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer A., Simon G., Kovacs G., Rai R. Synaptic disinhibition during maintenance of long-term potentiation in the CA1 hippocampal subfield. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3058–3062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer A., Slater N. T., ten Bruggencate G. Activation of NMDA receptors blocks GABAergic inhibition in an in vitro model of epilepsy. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):698–701. doi: 10.1038/326698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Stelzer A. Shared calcium signaling pathways in the induction of long-term potentiation and synaptic disinhibition in CA1 pyramidal cell dendrites. J Neurophysiol. 1996 Apr;75(4):1687–1702. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.75.4.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


