Abstract
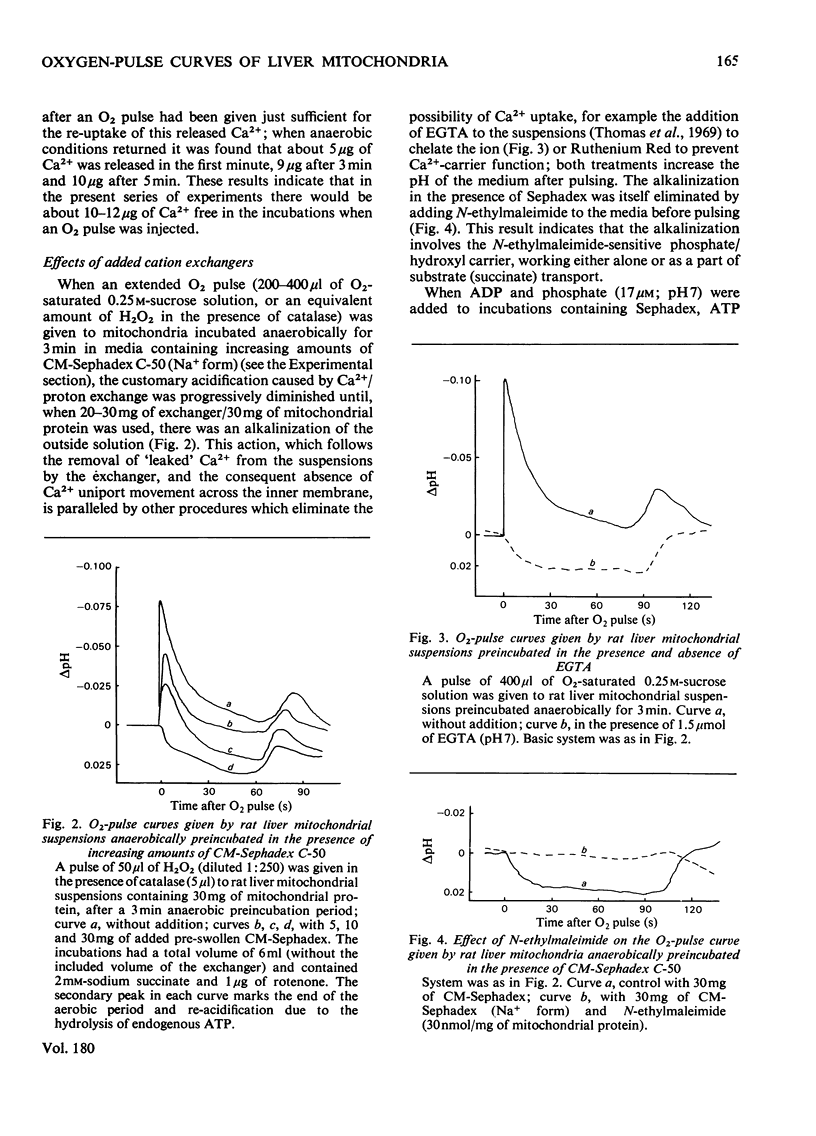
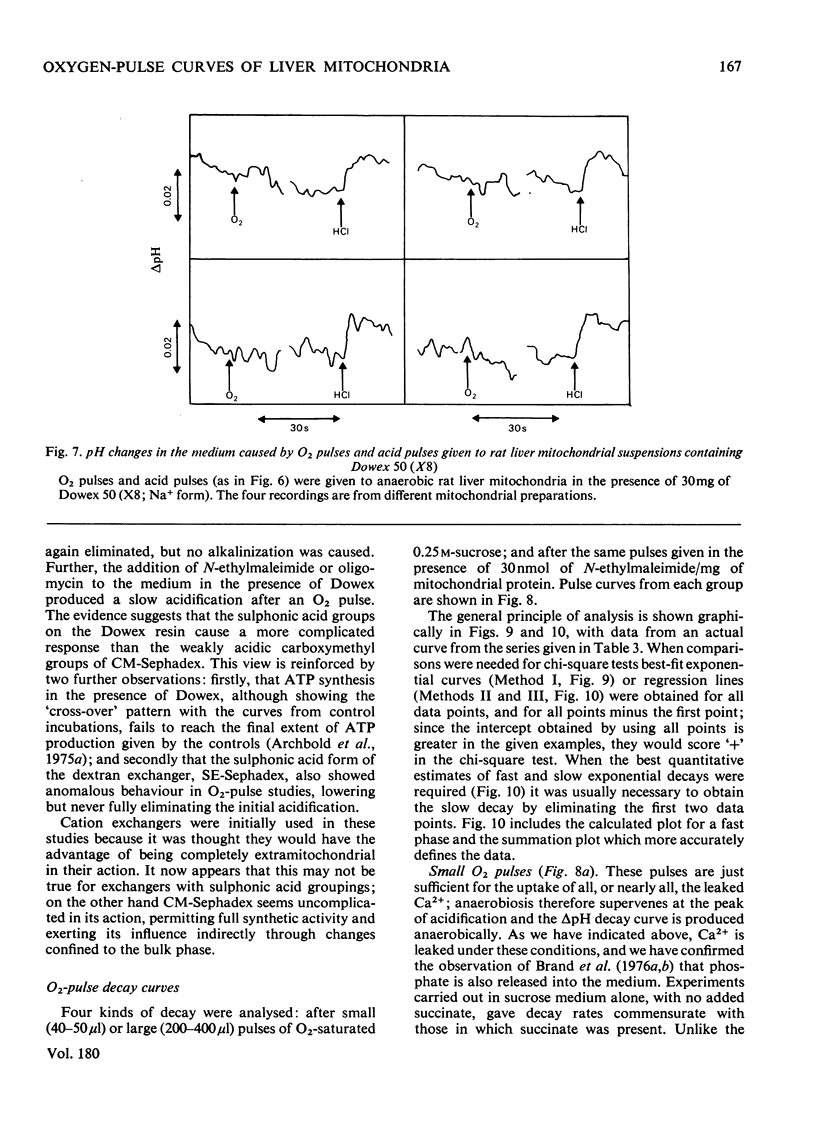
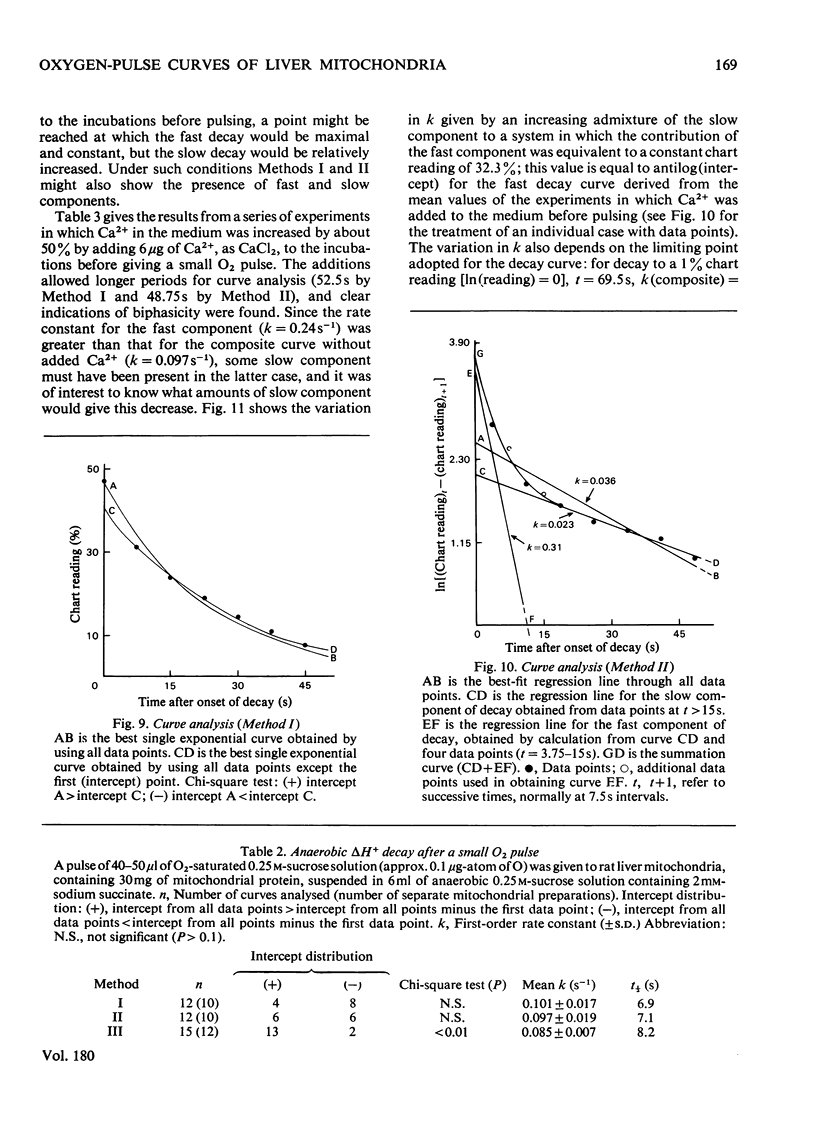
1. The inference, implicit in the chemiosmotic hypothesis, that protons move into the bulk phase during ATP synthesis was investigated. 2. Incubation of rat liver mitochondria in the presence of the cation exchanger CM-Sephadex C-50 caused alkalinization in the medium, though total ATP synthesis remained unchanged. The addition of N-ethylmaleimide prevented the alkalinization, but there was still no indication of protons passing into the medium. The expected proton movement [Mitchell & Moyle (1967) Biochem. J. 105, 1147--1162] was readily detected when as an equivalent acid pulse. 3. Analysis of delta H+ decay curves after O2 pulses (3 micrograms-atoms of O/g of protein) indicated the presence of fast and slow components of decay, with first-order rate constants (k) of 0.24s-1 and 0.032s-1. The fast decay was finite and was eliminated in the presence of N-ethylmaleimide. 4. These observations are interpreted as evidence for the development of unmasking of fixed charges on the outer surface of the mitochondrial inner membrane during energization and for the existence of proton-retentive electrical fields (rho-zones) on this surface. The charge concentration is calculated as about 1 charge/10nm2. 5. A cycle of changes in a single fixed-charge molecule is proposed which mediates both Ca2+ uptake and the first step in the utilization of the rho-zone protonmotive force, delta p rho.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiuchi T., Kamo N., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. Significance of surface potential in interaction of 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate with mitochondria: fluorescence intensity and zeta-potential. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archbold G. P., Farrington C. L., Malpress F. H. Proton movements and adenosine triphosphate synthesis in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(2):321–324. doi: 10.1042/bst0030321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archbold G. P., Farrington C. L., McKay A. M., Malpress F. H. Respiration rates and adenosine triphosphate synthesis in rat liver mitochondria: state 4-3-4 transition experiments. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(4):504–507. doi: 10.1042/bst0030504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archbold G. P., Farrington C. L., McKay A. M., Malpress F. H. The protonmotive force, the phosphate potential and respiratory control: the rho-zone interpretation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(1):91–94. doi: 10.1042/bst0040091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Chen C. H., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometry of H+ ejection during respiration-dependent accumulation of Ca2+ by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):968–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Lehninger A. L. H+/ATP ratio during ATP hydrolysis by mitochondria: modification of the chemiosmotic theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Re-evaluation of the H+/site ratio of mitochondrial electron transport with the oxygen pulse technique. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5670–5679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand M. D., Reynafarje B., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometric relationship between energy-dependent proton ejection and electron transport in mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):437–441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. Respiratory enzymes in oxidative phosphorylation. III. The steady state. J Biol Chem. 1955 Nov;217(1):409–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Lehninger A. L. A survey of the interaction of calcium ions with mitochondria from different tissues and species. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):681–690. doi: 10.1042/bj1220681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coster H. G. A quantitative analysis of the voltage-current relationships of fixed charge membranes and the associated property of "punch-through". Biophys J. 1965 Sep;5(5):669–686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(65)86745-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coster H. G. The double fixed charge membrane. Soluble-membrane ion partition effects and membrane potentials. Biopolymers. 1973 Feb;13(2):133–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuti T., Yokota M., Arakaki N., Hattori A., Tani I. Sidedness of inhibition of energy transduction in oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria by ethidium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 8;503(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamo N., Muratsugu M., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. Change in surface charge density and membrane potential of intact mitochondria during energization. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80979-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnally K. W., Tedeschi H., Maloff B. L. Use of dyes to estimate the electrical potential of the mitochondrial membrane. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3419–3428. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J., Hackenbrock C. E. Adenosine triphosphate: continuous measurement in mitochondrial suspension by firefly luciferase luminescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1262–1270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro A. Space Charge Regions in Fixed Charge Membranes and the Associated Property of Capacitance. Biophys J. 1962 Mar;2(2 Pt 1):179–198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86848-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat-liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):588–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1040588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Estimation of membrane potential and pH difference across the cristae membrane of rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):471–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Proton translocation coupled to ATP hydrolysis in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):530–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Respiration-driven proton translocation in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1147–1162. doi: 10.1042/bj1051147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Stoichiometry of proton translocation through the respiratory chain and adenosine triphosphatase systems of rat liver mitochondria. Nature. 1965 Oct 9;208(5006):147–151. doi: 10.1038/208147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell P. Electric charge stoicheiometry of calcium translocation in rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 1;73(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80964-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell P. The lanthanide-sensitive calcium phosphate porter of rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 15;77(2):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. The influence of respiration and ATP hydrolysis on the proton-electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria as determined by ion distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):305–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Guerrieri F., Simone S., Lorusso M., Larosa D. Mechanism of respiration-driven proton translocation in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):20–38. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Lofrumento N. E., Quagliariello E., Meijer A. J., Tager J. M. Coupling mechanisms in anionic substrate transport across the inner membrane of rat-liver mitochondria. J Bioenerg. 1971 Sep;1(3):287–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01516289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintanilha A. T., Packer L. Surface potential changes on energization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. A re-evaluation of energy-independent calcium-ion binding by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):555–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1420555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Manger J. R., Harris E. J. Cation uptake as the basis for production of proton pulses by mitochondria at the anaerobic-aerobic transition. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(3):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


