Abstract
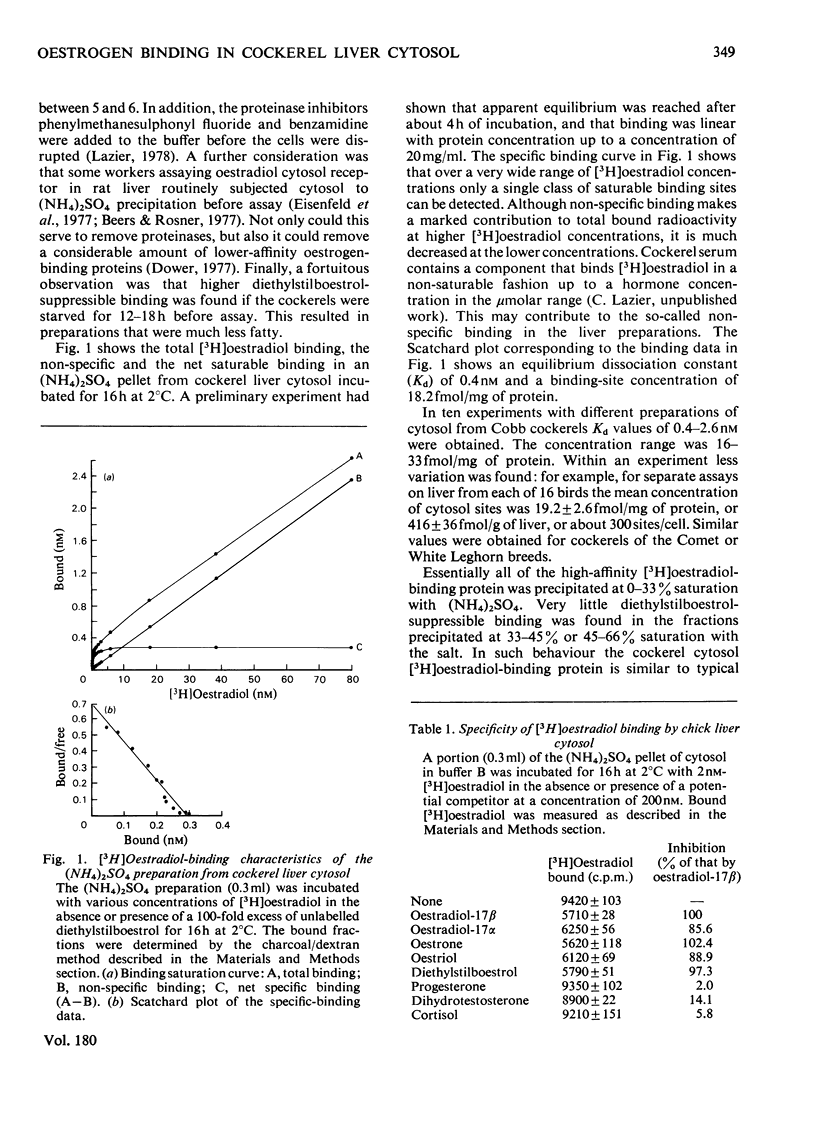
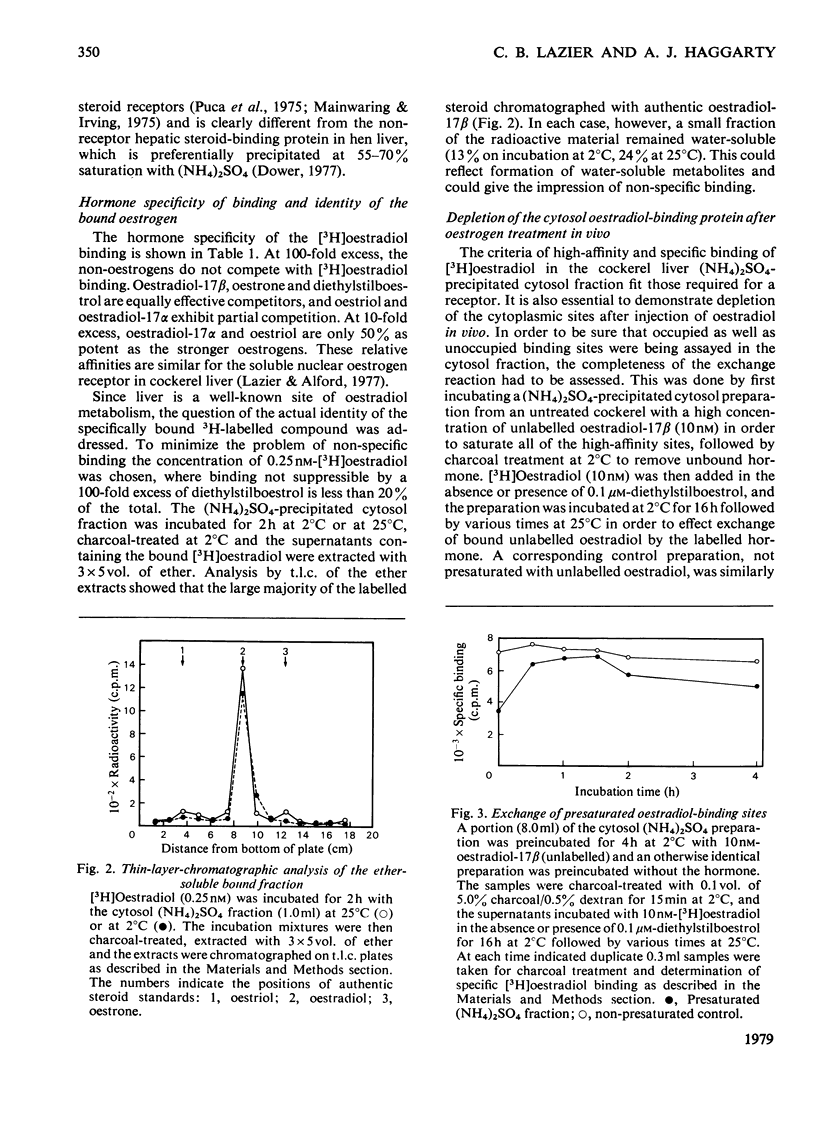
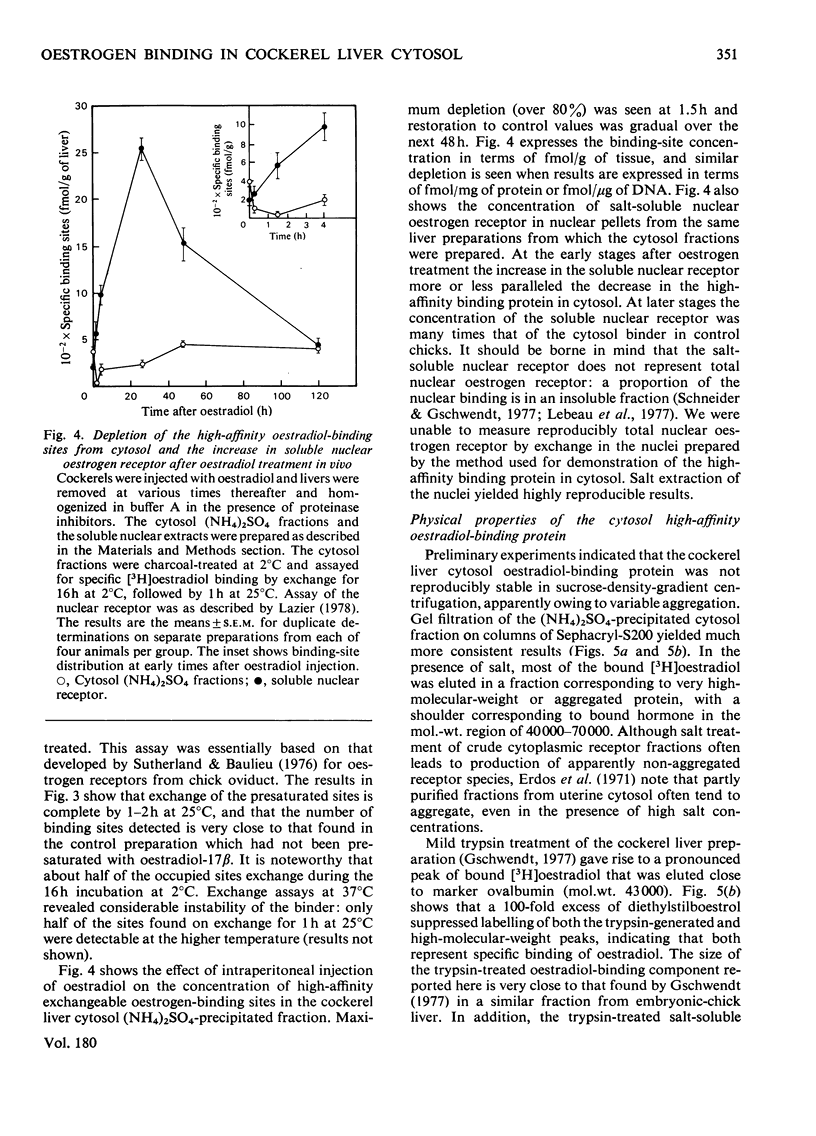
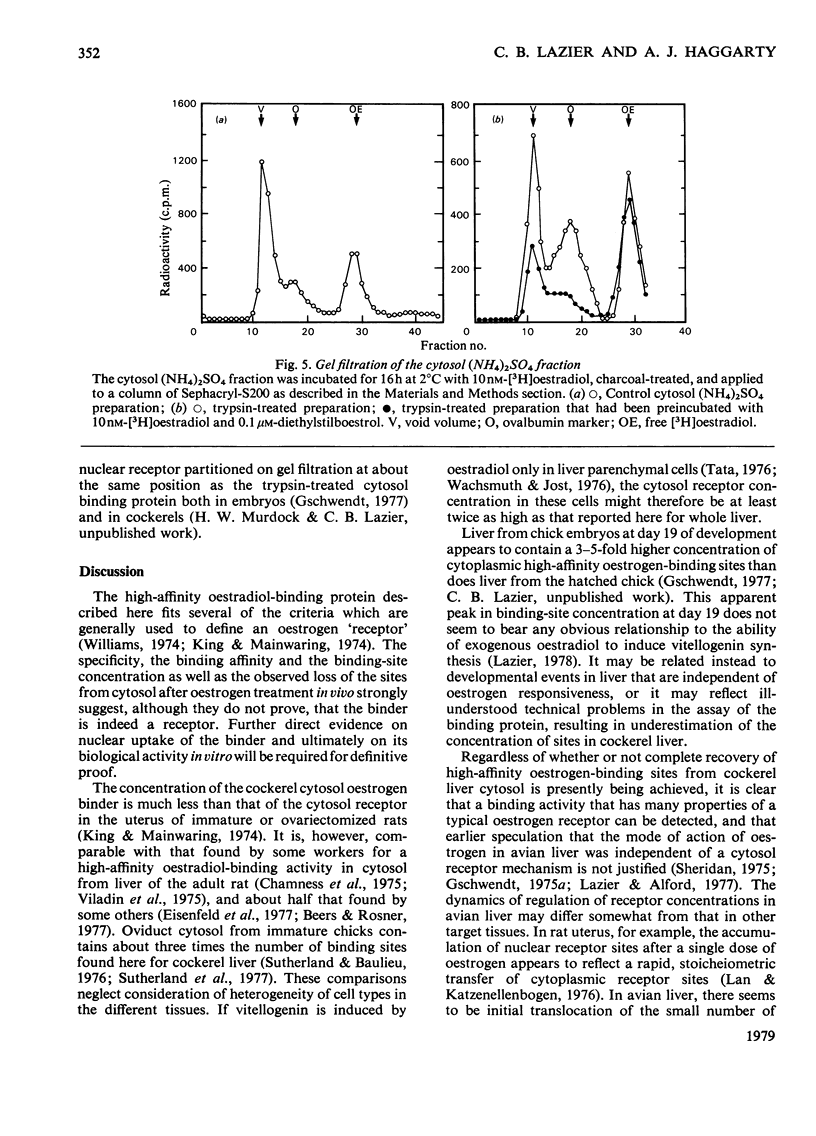
In contrast with several earlier reports, cytosol from cockerel liver contains a significant concentration of a protein that binds oestradiol with high affinity. To demonstrate the activity, certain alterations in the conventional method of preparation of cytosol must be made. Homogenization in sucrose-containing buffer at pH 8.4 in the presence of proteinase inhibitors and rapid fractionation of the cytosol with (NH4)2SO4 enables demonstration of a single class of oestradiol-binding sites with a Kd of about 1 nM and specificity only for oestrogens. The concentration is about 300 sites per cell in liver from 2-week-old cockerels. Oestradiol treatment in vivo decreases the number of exchangeable cytosol oestradiol-binding sites by about 80% for 1--4h, after which time it is gradually restored. Gel filtration of the cytosol preparation in the presence of high salt concentrations reveals that most of the oestradiol-binding activity is in high-molecular-weight aggregates, but a mild trypsin treatment generates a specific binding protein with an approximate mol.wt. of 40 000. This protein may be an oestrogen receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker H. J., Shapiro D. J. Rapid accumulation of vitellogenin messenger RNA during secondary estrogen stimulation of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4521–4524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers P. C., Rosner W. The binding of estrogens in the liver of the rat: demonstration and endocrine influences. J Steroid Biochem. 1977 Apr;8(4):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(77)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns A. T., Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Udell D. S., Mullinix K. P., Goldberger R. F. Primary induction of vitellogenin mRNA in the rooster by 17beta-estradiol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1815–1819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamness G. C., Costlow M. E., McGuire W. L. Estrogen receptor in rat liver and its dependence on prolactin. Steroids. 1975 Sep;26(3):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., O'Malley B. W. Mechanism of action of the sex steroid hormones (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 10;294(24):1322–1328. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606102942405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. H., Peck E. J., Jr, Anderson J. N. Oestrogen receptors and antagonism of steroid hormone action. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):446–448. doi: 10.1038/251446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Mullinix K. P., Binastein M., Goldberg R. F. Primary activation of the vitellogenin gene in the rooster. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8310–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenfeld A. J., Aten R. F., Haselbacher G. K., Halpern K. Specific macromolecular binding of estradiol in the mammalian liver supernatant. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 15;26(10):919–922. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Gannon F. Current models of steroid hormone action: a critique. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:425–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M. A cytoplasmic oestrogen-binding component in chicken liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Feb;356(2):157–165. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W. A cytoplasmic high affinity estrogen-binding protein in the embryonic chicken liver. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):461–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W. Specific binding of estradiol to the liver chromatin of estrogenized roosters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):84–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M. The effect of antiestrogens on egg yolk protein synthesis and estrogen-binding to chromatin in the rooster liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 13;399(2):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Mohla S., Gorell T. A., De Sombre E. R. The role of estrophilin in estrogen action. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:89–127. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joss U., Bassand C., Dierks-Ventling C. Rapid appearance of estrogen receptor in chick liver nuclei: partial inhibition by cycloheximide. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80525-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Temporal relationships between hormone receptor binding and biological responses in the uterus: studies with short- and long-acting derivatives of estriol. Endocrinology. 1976 Jan;98(1):220–227. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-1-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B., Alford W. S. Interaction of the anti-oestrogen, nafoxidine hydrochloride, with the soluble nuclear oestradiol-binding protein in chick liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):659–667. doi: 10.1042/bj1640659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B. Ontogeny of the vitellogenic response to oestradiol and of the soluble nuclear oestrogen receptor in embryonic-chick liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):143–152. doi: 10.1042/bj1740143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. (3H)-estradiol binding by chick liver nuclear extracts: mechanism of increase in binding following estradiol injection. Steroids. 1975 Sep;26(3):281–298. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainwaring W. I., Irving R. Methods for the purification of androgen receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1975;36:366–374. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)36035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Nuclear estrogen receptor of chick liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):236–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Female steroid hormones and target cell nuclei. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):610–620. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puca G. A., Nola E., Sica V., Bresciani F. Purification of estrogen receptors. I. Methods Enzymol. 1975;36:331–349. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)36033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W., Gschwendt M. Kinetics of the appearance of nuclear estrogen binding sites in chicken liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Dec;358(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. J. Is there an alternative to the cytoplasmic receptor model for the mechanism of action of steroids? Life Sci. 1975 Aug 15;17(4):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. L., Baulieu E. E. Quantitative estimates of cytoplasmic and nuclear oestrogen receptors in chick oviduct. Effect of oestrogen on receptor concentration and subcellular distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Tamoxifen is a potent "pure" anti-oestrogen in chick oviduct. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):434–435. doi: 10.1038/267434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. The expression of the vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viladiu P., Delgado C., Pensky J., Pearson O. H. Estrogen binding protein of rat liver. Endocr Res Commun. 1975;2(3):273–280. doi: 10.3109/07435807509053854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth E. D., Jost J. P. Localization of vitellogenin and serum albumin in hepatic parenchymal cells of normal and estradiol-treated immature chickens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L. The estrogen receptor: a minireview. Life Sci. 1974 Aug 15;15(4):583–597. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90500-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


