Abstract
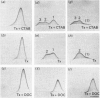
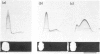
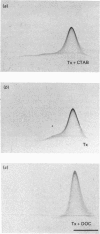
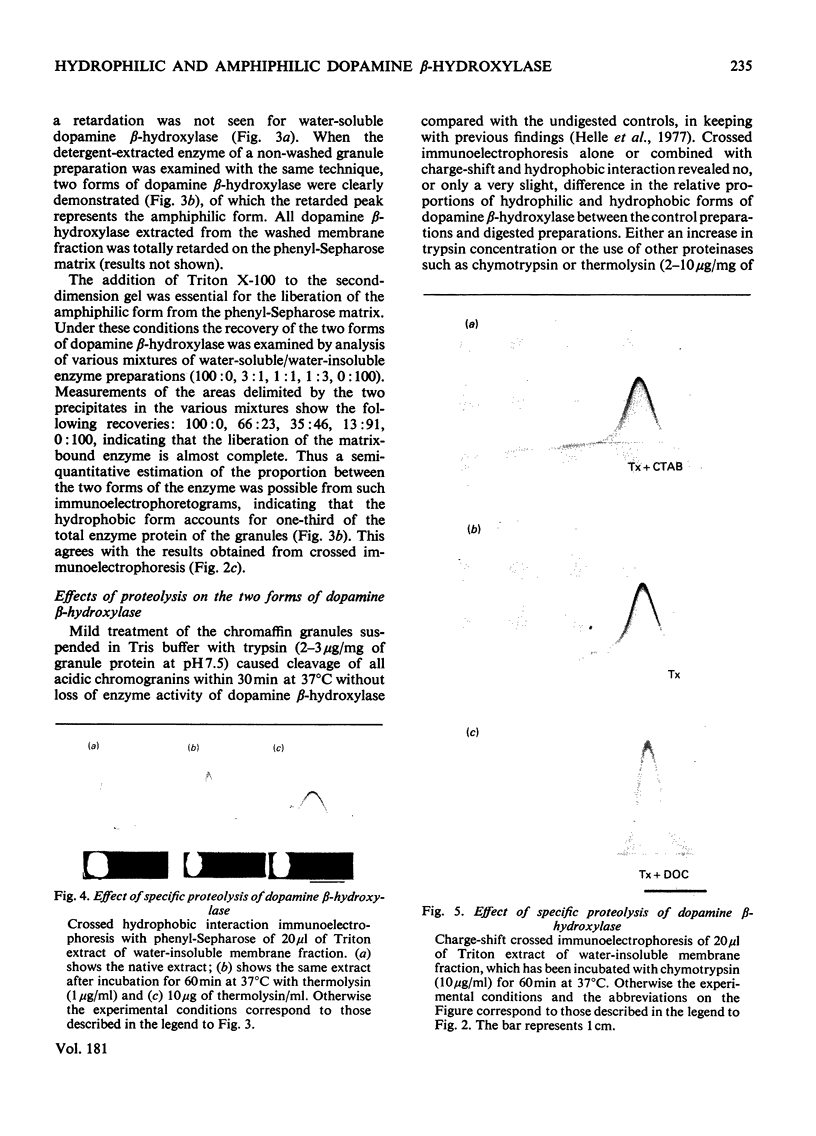
By means of a monospecific antibody, dopamine beta-hydroxylase was monitored immunoelectrophoretically in various extracts of chromaffin granules. Approximately one-third of the dopamine beta-hydroxylase present was located in the membrane fraction and could only be liberated with detergent. The dopamine beta-hydroxylases of the buffer and membrane fractions were antigenically identical, but differed in their amphiphilicity, as demonstrated by the change in precipitation patterns on removal of Triton X-100 from the gel, on charge-shift crossed immunoelectrophoresis and on crossed hydrophobic interaction immunoelectrophoresis with phenyl-Sepharose. Furthermore, immunoelectrophoretic analysis in the presence of Triton X-100 plus the cationic detergent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide indicates additional heterogeneity of the membrane-bound dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. By limited proteolysis with chymotrypsin and thermolysin the amphiphilic form could be convered into its hydrophilic counterpart.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aunis D., Allard D., Miras-Portugal M. T., Mandel P. Bovine adrenal medullary chromogranin A: studies on the structure and further evidence for identity with dopamine-beta-hydroxylase subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 26;393(2):284–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J. Detection of amphiphilic proteins and peptides in complex mixtures. Charge-shift crossed immunoelectrophoresis and two-dimensional charge-shift electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J., Bhakdi S. Demonstration of binding of triton X-100 to amphiphilic proteins in crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80949-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J. Crossed hydrophobic interaction immunoelectrophoresis: an analytical method for detection of amphiphilic proteins in crude mixtures and for prediction of the result of hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):331–348. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J. Immunochemical investigation of membrane proteins. A methodological survey with emphasis placed on immunoprecipitation in gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 9;472(2):135–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Charge shift electrophoresis: simple method for distinguishing between amphiphilic and hydrophilic proteins in detergent solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):529–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B. Biochemical studies of the chromaffin granule. 3. Redistribution of lipid phosphate, dopamine-beta-hydroxylase and chromogranin A after freezing and thawing of the isolated granule membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 22;318(2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B. Biochemical studies of the chromaffin granule. II. Properties of membrane-bound and water-soluble forms of chromogranin A and dopamine- -hydroxylase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):94–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B., Serck-Hanssen G., Bock E. Complexes of chromogranin A and dopamine beta-hydroxylase among the chromogranins of the bovine adrenal medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 26;533(2):396–407. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B., Serck-Hanssen G. The adrenal medulla: a model for studies of hormonal and neuronal storage and release mechanisms. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Feb 28;6(2):127–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01732006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogue-Angeletti R. A. Nonidentity of chromogranin A and dopamine beta-monooxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Dec;184(2):364–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Winkler H., Lochs H. Membrane proteins of chromaffin granules, dopamine -hydroxylase, a major constituent. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):187–195. doi: 10.1042/bj1290187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen O. S. Charge shift electrophoresis of synaptosomal membrane antigens. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S., FRIEDMAN S. DOPAMINE-BETA-HYDROXYLASE. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Jun;17:71–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Skotland T., Flatmark T. Purification and characterization of dopamine beta-hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström H., Norén O., Jeppesen L., Staun M., Svensson B., Christiansen L. Purification of different amphiphilic forms of a microvillus aminopeptidase from pig small intestine using immunoadsorbent chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):503–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Arqueros L., Connett R. J., Kirshner N. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. 3. Studies of dopamine beta-hydroxylase as a marker for catecholamine storage vesicle membranes in rabbit adrenal glands. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;5(1):60–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace E. F., Krantz M. J., Lovenberg W. Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase: a tetrameric glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2253–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. The biogenesis of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):657–683. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. The composition of adrenal chromaffin granules: an assessment of controversial results. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]