Abstract
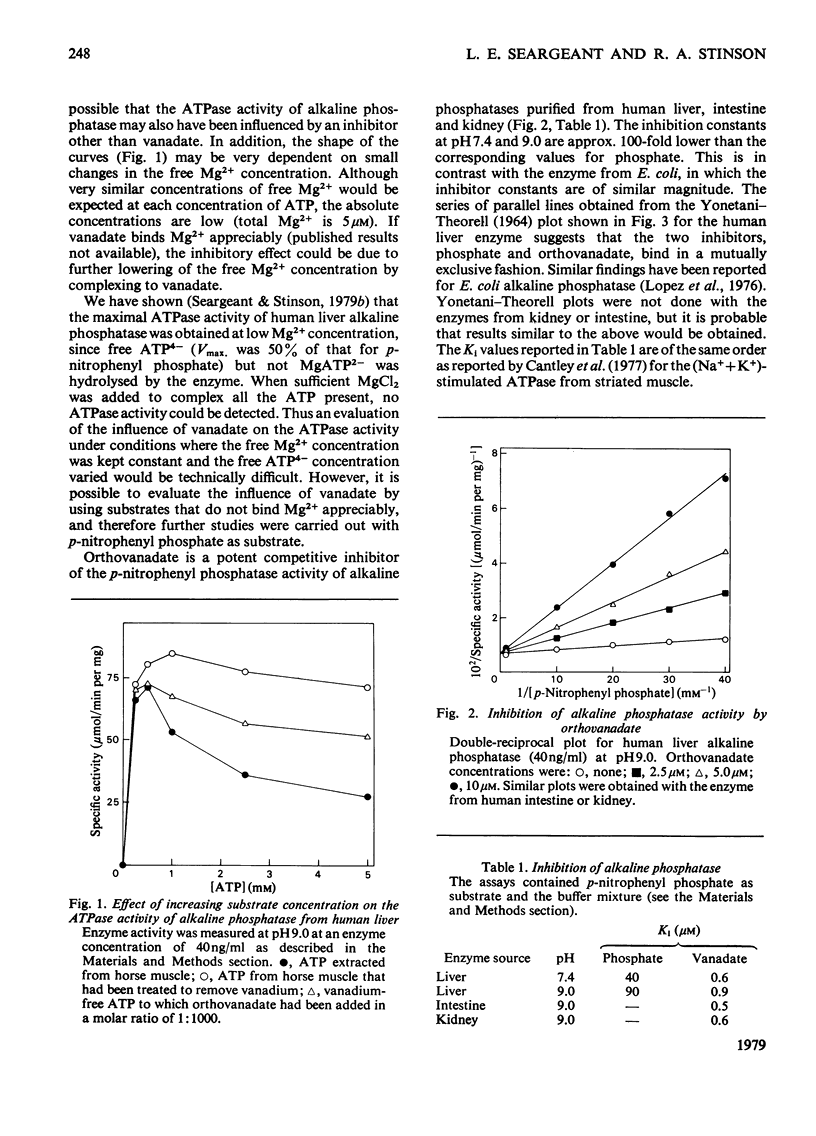
Orthovanadate was shown to be a potent competitive inhibitor (Ki less than 1 microM) of purified alkaline phosphatase from human liver, intestine of kidney. Inhibition was reversed and full enzymic activity restored in the presence of 1mM-adrenaline. Phosphate and vanadate competed for the same binding site on the enzyme.
Full text
PDF
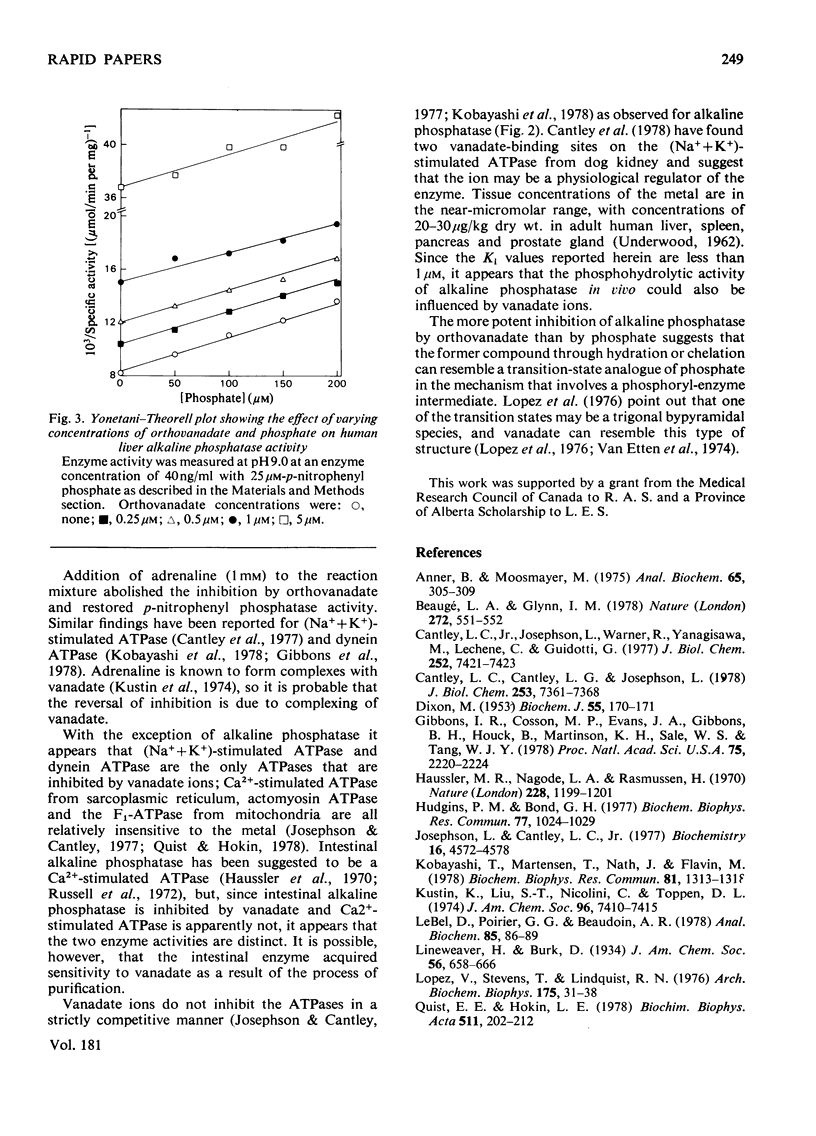

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anner B., Mossmayer M. Rapid determination of inorganic phosphate in biological systems by a highly sensitive photometric method. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Commercial ATP containing traces of vanadate alters the response of (Na+ + K+) ATPase to external potassium. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):551–552. doi: 10.1038/272551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Cantley L. G., Josephson L. A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na,K)-ATPase. Mechanistic and regulatory implications. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7361–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Cosson M. P., Evans J. A., Gibbons B. H., Houck B., Martinson K. H., Sale W. S., Tang W. J. Potent inhibition of dynein adenosinetriphosphatase and of the motility of cilia and sperm flagella by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M., Nagode L. A., Rasmussen H. Induction of intestinal brush border alkaline phosphatase by vitamin D and identity with ca-ATPase. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1199–1201. doi: 10.1038/2281199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgins P. M., Bond G. H. (Mg2+ + K+)-dependent inhibition of NaK-ATPase due to a contaminant in equine muscle ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson L., Cantley L. C., Jr Isolation of a potent (Na-K)ATPase inhibitor from striated muscle. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4572–4578. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Martensen T., Nath J., Flavin M. Inhibition of dynein ATPase by vanadate, and its possible use as a probe for the role of dynein in cytoplasmic motility. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 28;81(4):1313–1318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Poirier G. G., Beaudoin A. R. A convenient method for the ATPase assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez V., Stevens T., Lindquist R. N. Vanadium ion inhibition of alkaline phosphatase-catalyzed phosphate ester hydrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quist E. E., Hokin L. E. The presence of two (Na+ + K+)-ATPase inhibitors in equine muscle ATP: vanadate nad a dithioerythritol-dependent inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 4;511(2):202–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Monod A., Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H. Relation between alkaline phosphatase and Ca 2+ -ATPase in calcium transport. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 22;240(99):126–127. doi: 10.1038/newbio240126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seargeant L. E., Stinson R. A. Affinity elution from a phosphonic acid-Sepharose derivative in the purification of human liver alkaline phosphatase. J Chromatogr. 1979 May 11;173(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80449-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trépanier J. M., Seargeant L. E., Stinson R. A. Affinity purification and some molecular properties of human liver alkaline phosphatase. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):653–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1550653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanEtten R. L., Waymack P. P., Rehkop D. M. Letter: Transition metal ion inhibition of enzyme-catalyzed phosphate ester displacement reactions. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Oct 16;96(21):6782–6785. doi: 10.1021/ja00828a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T., THEORELL H. STUDIES ON LIVER ALCOHOL HYDROGENASE COMPLEXES. 3. MULTIPLE INHIBITION KINETICS IN THE PRESENCE OF TWO COMPETITIVE INHIBITORS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:243–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


