Abstract
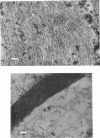
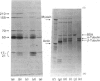
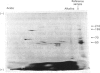
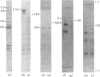
Brain 10 nm filaments were isolated from bovine, rabbit and rat brains by a modification of an existing procedure. The overall polypeptide composition of these preparations was similar to that previously reported for brain neurofilaments. In addition to the major polypeptide component, which has mol. wt. approx. 50 000, three other polypeptides with chain mol. wts. approx. 210 000, 155 000 and 70 000, which correspond to peripheral-nerve neurofilament polypeptides, were consistently found to be present. The mol. wt.-50 000 species was found to be heterogeneous and may contain a component derived from the mol. wt. 70 000 polypeptide. The three higher-molecular-weight polypeptides did not appear to be obviously homologous or to be homologous with myosin or Myxicola neurofilament polypeptides. These same three higher-molecular-weight components were shown to be identical with the polypeptides probably responsible for the 10 nm filaments formed during the early cycles of the tubulin-purification protocol.
Full text
PDF


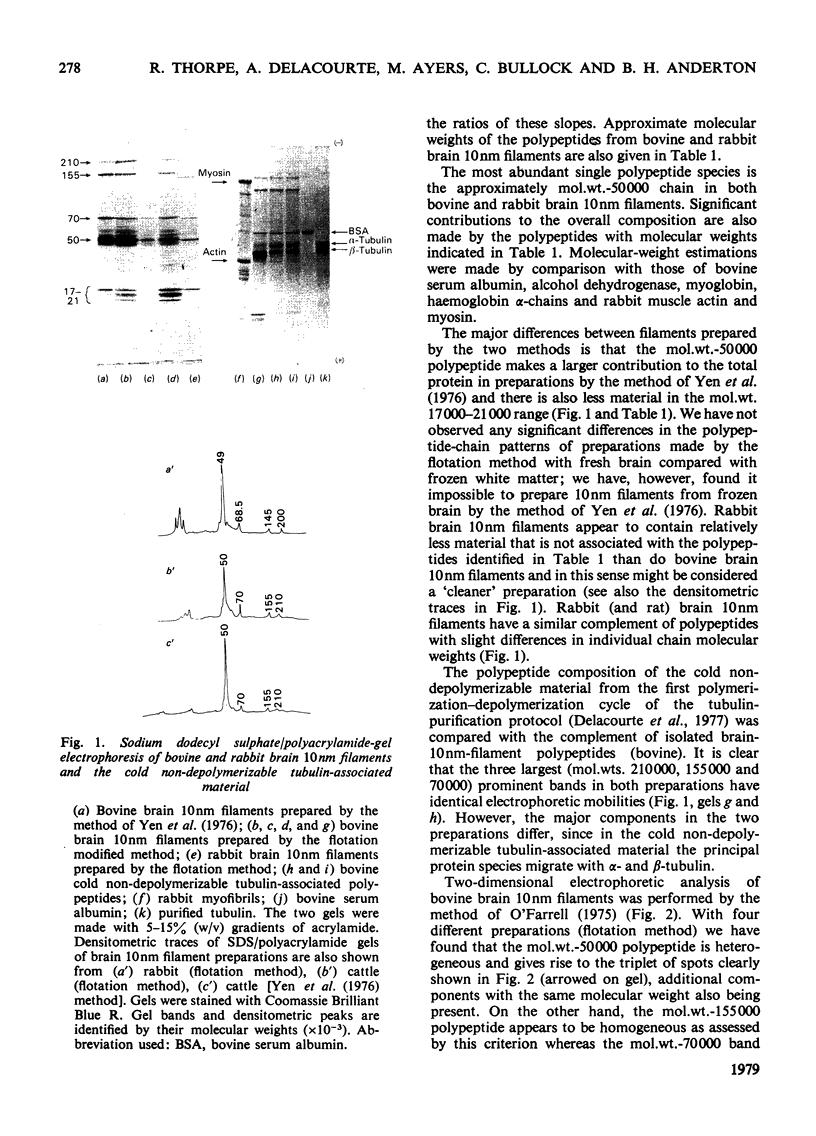
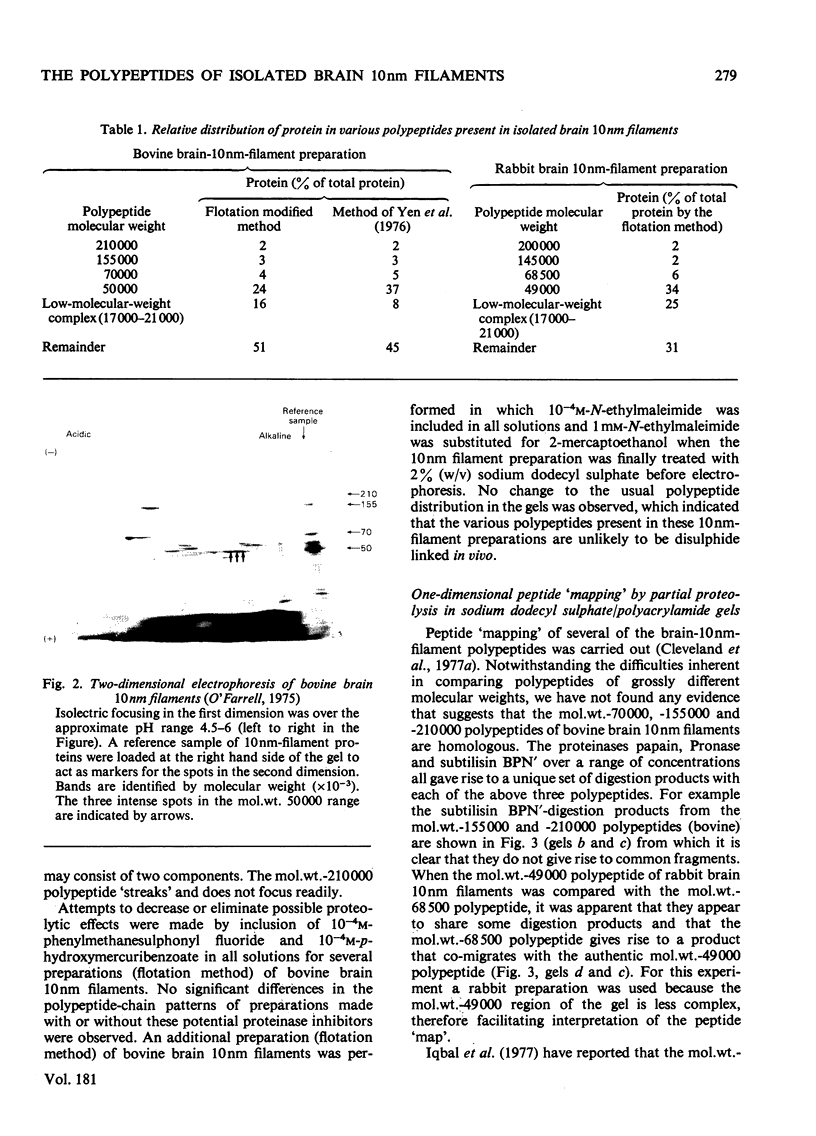





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderton B. H., Ayers M., Thorpe R. Neurofilaments from mammalian central and peripheral nerve share certain polypeptides. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton B. H., Bell C. W., Newby B. J., Gilbert D. S. Neurofilaments. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(4):544–548. doi: 10.1042/bst0040544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benitz W. E., Dahl D., Williams K. W., Bignami A. The protein composition of glial and nerve fibers. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. A., Katagiri J., Binder H. K., Williams R. C., Jr Separation and characterization of microtubule proteins from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5610–5617. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Purification of tau, a microtubule-associated protein that induces assembly of microtubules from purified tubulin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):207–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Hong B. S. Sturctural homologies in mammalian neurofilament proteins. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Winslow B. The protein subunit of calf brain neurofilament. J Neurobiol. 1974;5(2):119–133. doi: 10.1002/neu.480050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries G. H., Eng L. F., Lewis D. L., Hadfield M. G. The protein composition of bovine myelin-free axons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 19;439(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVries G. H., Norton W. T., Raine C. S. Axons: isolation from mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1972 Mar 24;175(4028):1370–1372. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4028.1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Plancot M. T., Han K. K., Hildebrand H., Biserte G. Investigation of tubulin fibers formed during microtubule polymerization cycles. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 1;77(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Shelanski M. L. Microtubules and intermediate filaments. Essays Biochem. 1976;12:115–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S., Newby B. J. Neurofilament disguise, destruction and discipline. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):586–589. doi: 10.1038/256586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. H., Brabec R. K., Byrsk M. M., Bernstein I. A. Immunocytochemical localization of a protein in tonofilaments as a morphologic marker for epidermal differentiation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Oct;25(10):1127–1139. doi: 10.1177/25.10.72096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huneeus F. C., Davison P. F. Fibrillar proteins from squid axons. I. Neurofilament protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Wisniewski H. M., Terry R. D. Chemical relationship of the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's dementia to normal human neurofilaments and neurotubules. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 24;142(2):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Wisniewski H. M., Terry R. D. On neurofilament and neurotubule proteins from human autopsy tissue. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keates R. A., Hall R. H. Tubulin requires an accessory protein for self assembly in microtubules. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):418–421. doi: 10.1038/257418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micko S., Schlaepfer W. W. Protein composition of axons and myelin from rat and human peripheral nerves. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1041–1049. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Hsu D. W., Schoonmaker G., Bignami A. Ultrastructural localization of glial fibrillary acidic protein in mouse cerebellum by immunoperoxidase labeling. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):67–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Freeman L. A. Neurofilament proteins of rat peripheral nerve and spinal cord. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):653–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schook W. J., Norton W. T. Neurofilaments account for the lipid in myelin-free axons. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 24;118(3):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Albert S., DeVries G. H., Norton W. T. Isolation of filaments from brain. Science. 1971 Dec 17;174(4015):1242–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4015.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheterline P. Phosphorylation of pig brain microtubule proteins. General properties and partial characterization of endogenous substrate and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):533–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1680533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Microtubule-associated proteins and the stimulation of tubulin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4497–4505. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the function and composition of the 10-NM(100-A) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:243–268. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Brown W. E., Goldman A. E., Goldman R. D. Biochemical and immunological analysis of rapidly purified 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):93–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Goldman R. D. Isolation and preliminary characterization of 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Dahl D., Schachner M., Shelanski M. L. Biochemistry of the filaments of brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]