Abstract
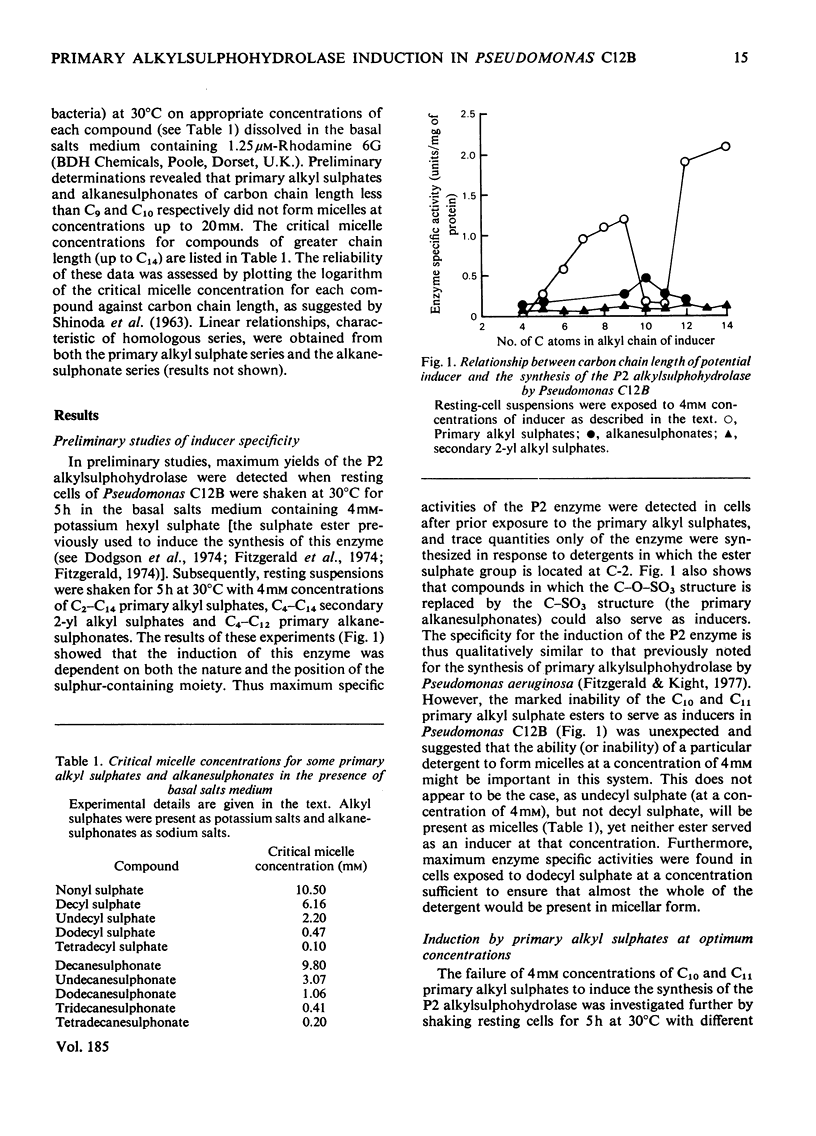
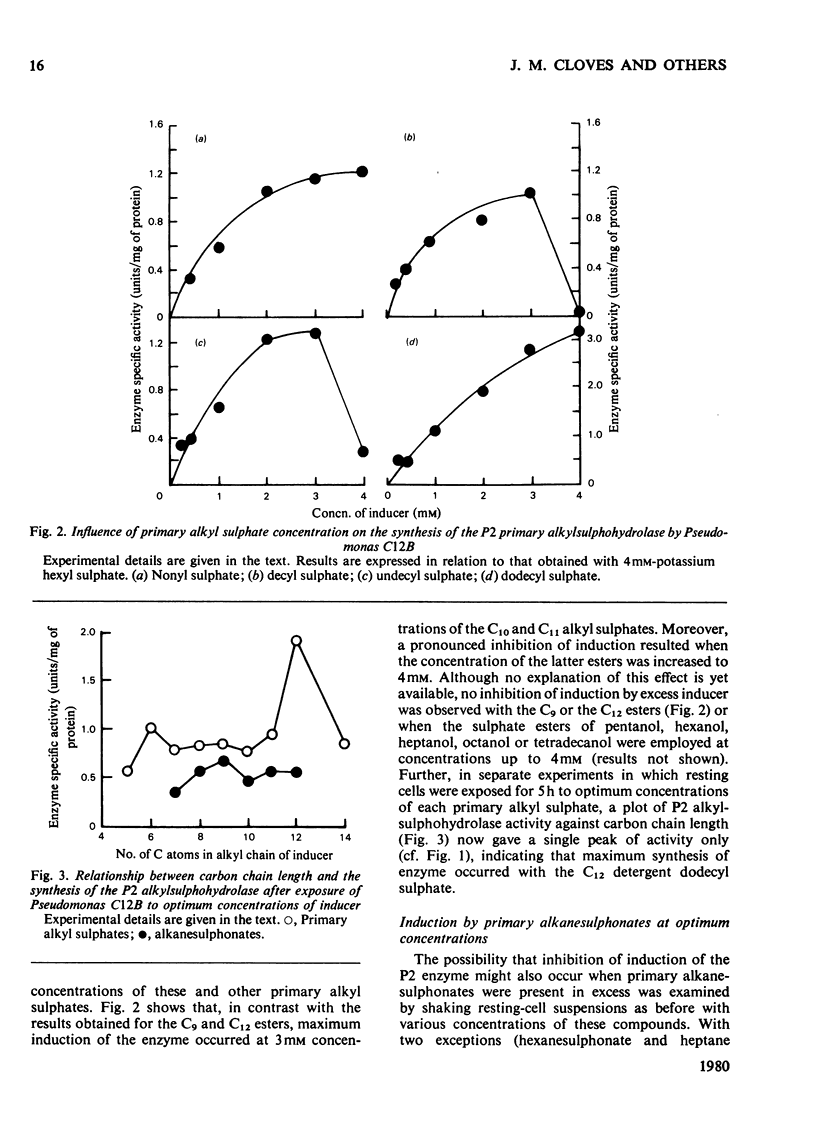
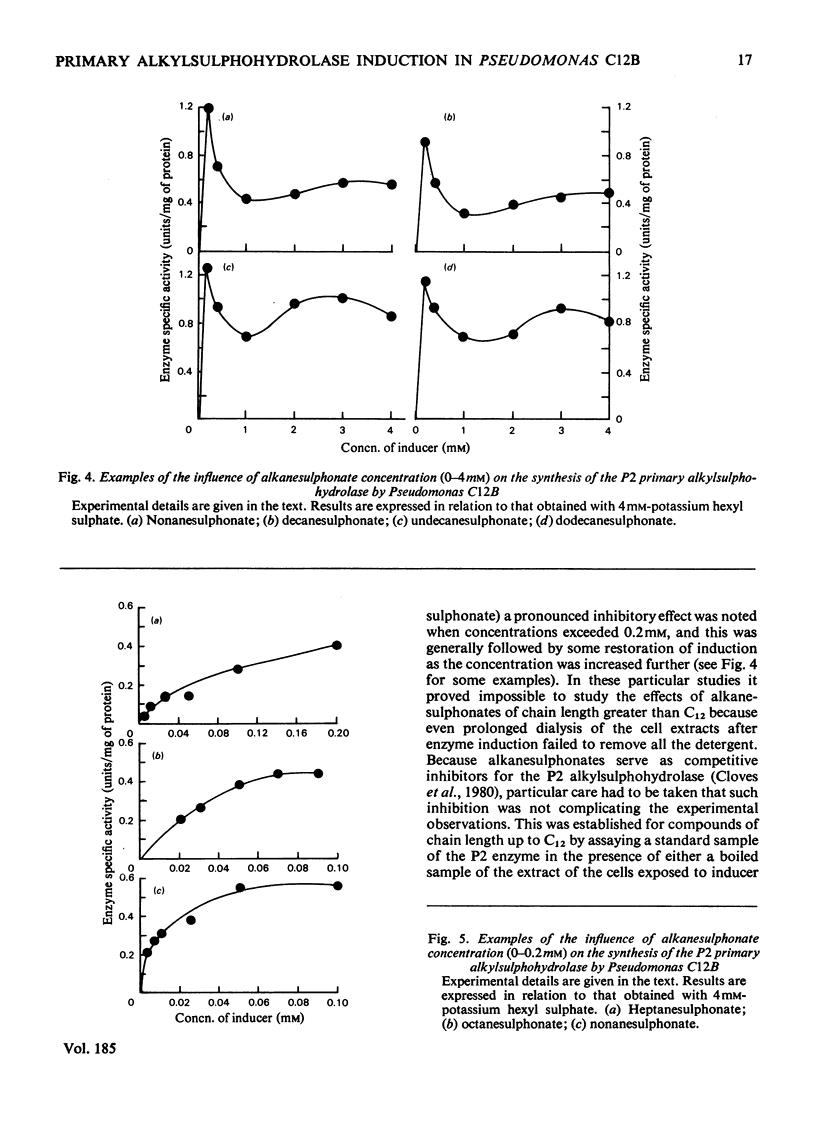
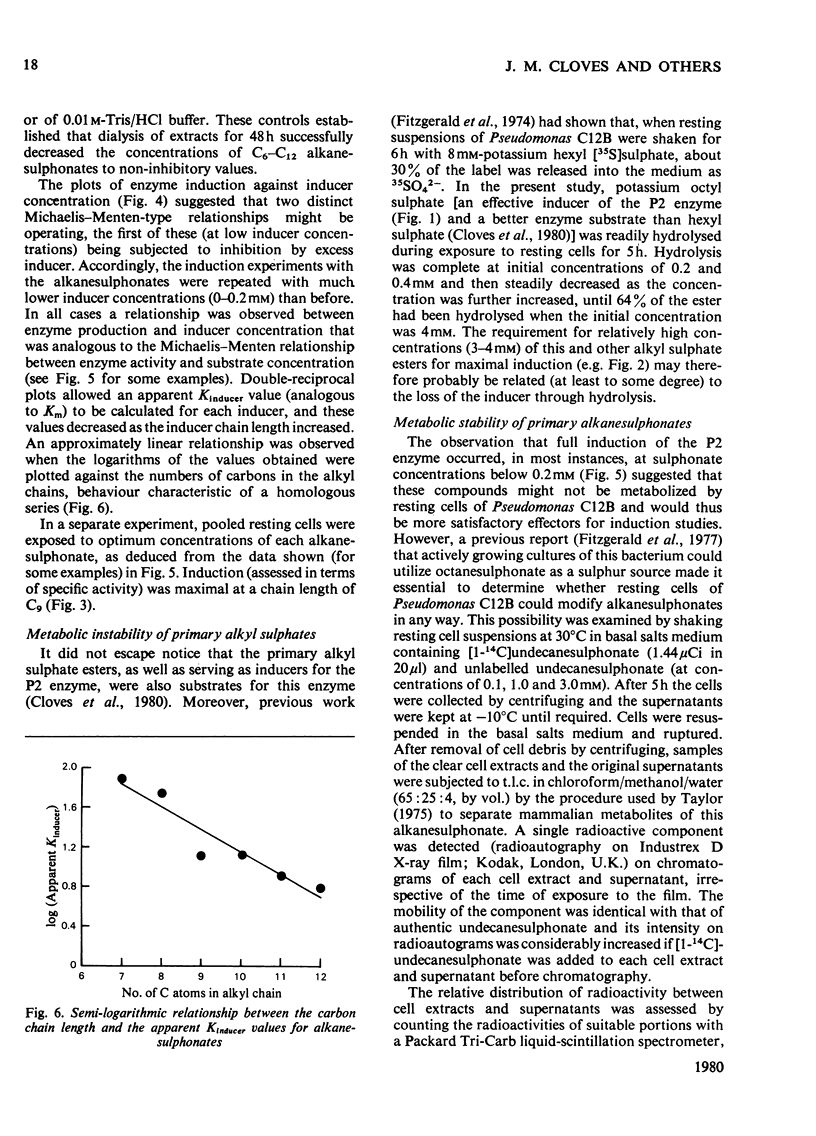
Primary alkanesulphonates were shown to serve as non-metabolizable (gratuitous) inducers of the P2 primary alkylsulphohydrolase enzyme in resting cell suspensions of Pseudomonas C12B. The effects of increasing concentrations of inducer on the production of enzyme were complex and suggestive of a multiphasic phenomenon. However, it was possible to determine Kinducer constants (analogous to Km or Ki) for alkanesulphonates of chain length from C7 to c12. these decreased with increasing chain length in a manner characteristic of an homologous series. Primary alkyl sulphates also served as good inducers of alkylsulphohydrolase, but valid kinetic values could not be obtained because these esters are good substrates for the enzyme and are therefore appreciably hydrolysed during the induction period. Small amounts of enzyme were also produced when cyprinol sulphate, dodecyltriethoxy sulphate C12H23-[O-CH2-CH2]3-O-SO3-Na+), Crag herbicide and some secondary alkyl sulphates were tested as inducers.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOSTROM H., VESTERMARK A. Studies on ester sulphates. 7. On the excretion of sulphate conjugates of primary aliphatic alcohols in the urine of rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Jan 30;48:88–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton A., Surdin-Kerjan Y. Sulfate uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: biochemical and genetic study. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.224-232.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. Micellar properties of dihydroxy and trihydroxy bile salts: effects of counterion and temperature. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1969 Nov;31(3):382–396. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(69)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Young F. E. Active transport of D-alanine and related amino acids by whole cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1085–1092. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1085-1092.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloves J. M., Dodgson K. S., White G. F., Fitzgerald J. W. Purification and properties of the P2 primary alkylsulphohydrolase of the detergent-degrading bacterium pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):23–31. doi: 10.1042/bj1850023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson K. S., Fitzgerald J. W., Payne W. J. Chemically defined inducers of alkylsulphatases present in Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;138(1):53–62. doi: 10.1042/bj1380053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Dodgson K. S., Payne W. J. Induction of primary alkysulphatases and metabolism of sodium hexan-1-yl sulphate by Pseudomonas C12B. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;138(1):63–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1380063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Kight L. C. Physiological control of alkylsulfatase synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effects of glucose, glucose analogs, and sulfur. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Oct;23(10):1456–1464. doi: 10.1139/m77-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Laslie W. W. Loss of primary alkylsulfatase and secondary alkylsulfatases (S-1 and S-2) from Pseudomonas C12B: effect of culture conditions, cell-washing procedures, and osmotic shock. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):59–68. doi: 10.1139/m75-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Payne W. J. Induction in a Pseudomonas species of sulphatases active on short chain alkylsulphates. Microbios. 1972 Mar-Apr;5(18):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J. Transport systems for L-methionine in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):232–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.232-241.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kight-Olliff L. C., Fitzgerald J. W. Inhibition of enzyme induction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by exogenous nucleotides. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jul;24(7):811–817. doi: 10.1139/m78-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem P. Q., Laur M. H. Les alcools aliphatiques sulfatés: nouveaux lipides polaires isolés de diverses fucacées. Biochimie. 1976;58(11-12):1381–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matcham G. W., Dodgson K. S. Preparation and characterization of substrates suitable for the study of stereospecific secondary alkylsulphohydrolases of detergent-degrading micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):717–722. doi: 10.1042/bj1670717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE W. J., FEISAL V. E. Bacterial utilization of dodecyl sulfate and dodecyl benzene sulfonate. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jul;11:339–344. doi: 10.1128/am.11.4.339-344.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J., Fitzgerald J. W., Dodgson K. S. Methods for visualization of enzymes in polyacrylamide gels. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):154–158. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.154-158.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J., Painter B. G. Resolution by acrylamide gel electrophoresis of alkyl sulphatases and alcohol dehydrogenase. Microbios. 1971 Apr;3(12):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J., Williams J. P., Mayberry W. R. Primary alcohol sulfatase in a Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Sep;13(5):698–701. doi: 10.1128/am.13.5.698-701.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer B. Endogenous sulphate acceptors in rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77(2):294–304. doi: 10.1042/bj0770294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J., PAYNE W. J. ENZYMES INDUCED IN A BACTERIUM BY GROWTH ON SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:360–362. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.360-362.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


