Abstract
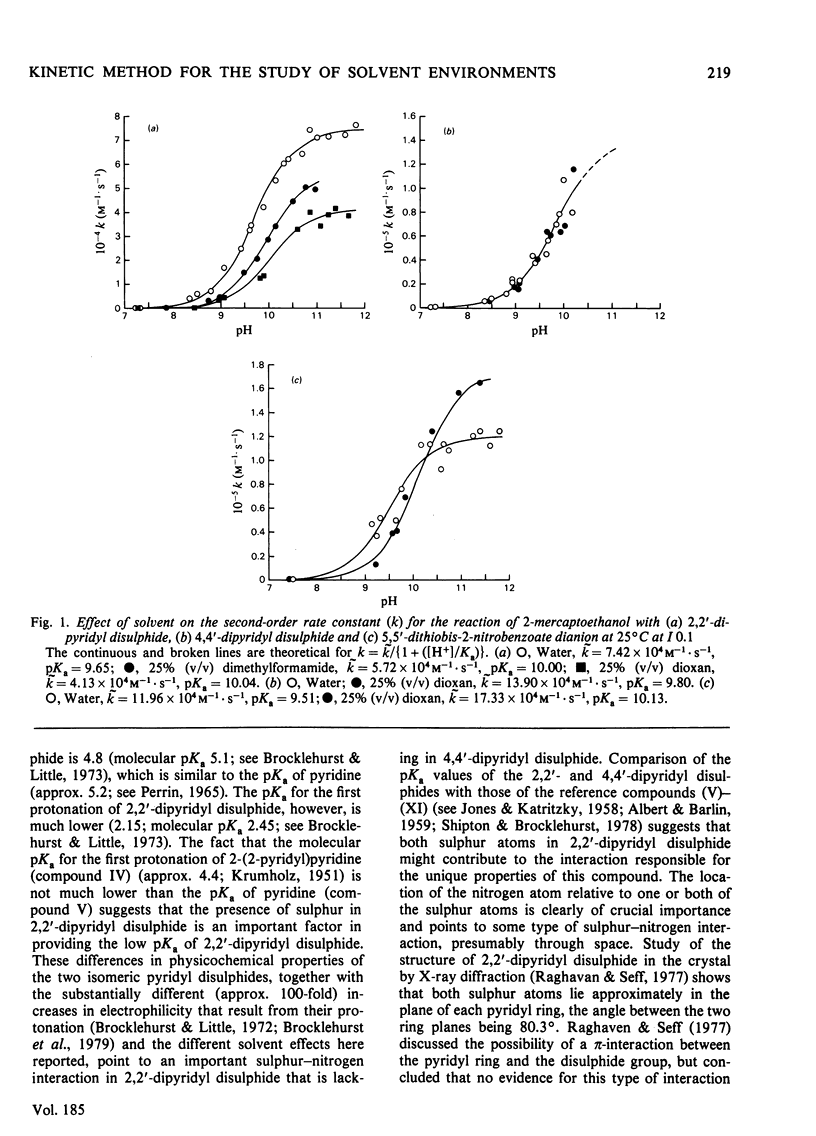
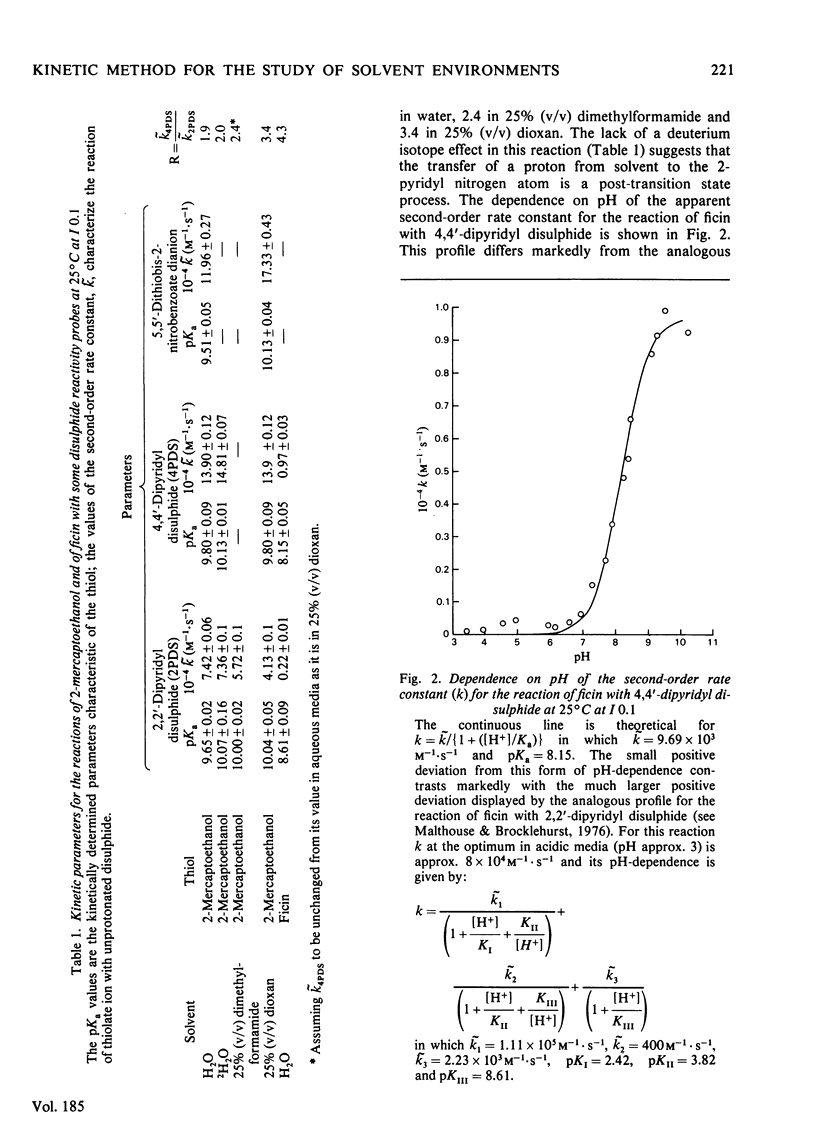
1. Whereas the second-order rate constants for the reaction of the thiolate ion of 2-mercaptoethanol with 4,4'-dipyridyl disulphide (k4PDS) and with 5,5'-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoate dianion increase with decreasing dielectric constant of the solvent, or remain unchanged, the rate constant for the analogous reaction with 2,2'-dipyridyl disulphide (k2PDS) decreases. This anomalous solvent effect and other unusual physicochemical properties of 2,2'-dipyridyl disulphide are discussed. 2. The differential effect of solvent on the reactions of thiolate ion with the 2,2'- and 4,4'-dipyridyl disulphides is shown to provide a method of characterizing solvent environments of thiol groups in proteins by a reactivity-probe method that should not suffer from the usual drawback associated with the existence of steric or binding effects of unknown magnitude. Application of the method to ficin (EC 3.4.22.3) suggests that its active-centre thiol group resides in a relatively hydrophobic environment. 3. The pH-k profile for the reaction of ficin with 4,4'-dipyridyl disulphide is reported.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brocklehurst K., Little G. Reactions of papain and of low-molecular-weight thiols with some aromatic disulphides. 2,2'-Dipyridyl disulphide as a convenient active-site titrant for papain even in the presence of other thiols. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):67–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1330067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K., Little G. Reactivities of the various protonic states in the reactions of papain and of L-cysteine with 2,2'- and with 4,4'- dipyridyl disulphide: evidence for nucleophilic reactivity in the un-ionized thiol group of the cysteine-25 residue of papain occasioned by its interaction with the histidine-159-asparagine-175 hydrogen-bonded system. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):471–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1280471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K. Specific covalent modification of thiols: applications in the study of enzymes and other biomolecules. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(4):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K., Stuchbury T., Malthouse J. P. Reactivities of neutral and cationic forms of 2,2'-dipyridyl disulphide towards thiolate anions. Detection of differences between the active centres of actinidin, papain and ficin by a three-protonic-state reactivity probe. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):233–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1830233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. L., Kallen R. G. Coenzyme B 12 model studies. Equilibria and kinetics of axial ligation of methylaquocobaloxime by thiols. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Mar 22;94(6):1894–1901. doi: 10.1021/ja00761a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthouse J. P., Brocklehurst K. Preparation of fully active ficin from Ficus glabrata by covalent chromatography and characterization of its active centre by using 2,2'-depyridyl disulphide as a reactivity probe. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):221–234. doi: 10.1042/bj1590221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipton M., Brochlehurst K. Characterization of the papain active centre by using two-protonic-state electrophiles as reactivity probes. Evidence for nucleophilic reactivity in the un-interrupted cysteine-25-histidine-159 interactive system. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):385–401. doi: 10.1042/bj1710385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


