Abstract
BACKGROUND:
In the contemporary healthcare environment, optimizing patient care strategies is of importance, particularly in neurosurgical environments. While traditional nursing methods have the foundation of patient care, there exists a growing recognition of the potential benefits of comprehensive nurse management. Despite this acknowledgment, there remains a gap in understanding the comparative effectiveness of comprehensive nurse management versus traditional approaches in reducing postoperative psychological stress, enhancing patient satisfaction, and promoting adherence in neurosurgical patients.
OBJECTIVE:
This study compares the efficacy of comprehensive nurse management against traditional methods in facilitating the postoperative recovery of neurosurgical patients.
METHODS:
Taking the traditional nursing management and detailed nursing management of neurosurgical patients in a municipal neurosurgical hospital from March 2021 to March 2022 as an example, the neurosurgery was divided into 50 patients in the detailed nursing management group and 50 patients in the traditional nursing management group. In the clear nursing management group, there were 50 patients, 20 male patients, with an average age of 58.7 3.8 years, and 30 female patients, with an average age of 60.4 4.3 years; In the traditional nursing management group, there were 50 patients, 26 male patients, with an average age of 59.7 3.7 years, and 24 female patients, with an average age of 59.4 3.9 years; Among the 100 patients, there were 60 cases of cerebral infarction, 25 cases of intracerebral hemorrhage and 15 cases of other neurosurgical diseases.
RESULTS:
Hundred neurosurgical patients were divided into two groups: comprehensive nursing management group and traditional nursing management group. The results showed that the comprehensive treatment effect of patients with detailed nursing management was better than that of the routine nursing group. At the same time, the complications were reduced, and the patient’s satisfaction was higher.
CONCLUSION:
Through retrospective analysis and investigation of patients, this paper discusses the clinical application of a detailed nursing management model in neurosurgery, which can reduce the probability of infection and other complications and improve the quality of life and treatment effect of patients.
Keywords: Detailed nursing management intervention, neurosurgery, quality of life, cerebrovascular diseases, treatment effect
1. Introduction
With the improvement of living standards and the extension of the human life cycle, people are overwhelmed by the emergence of various diseases. In particular, neurosurgical diseases, including brain tumors, cerebrovascular diseases, epilepsy, and other brain neurological diseases, have the characteristics of acute onset and rapid development of symptoms. Headaches, seizures, altered cognition, motor dysfunction, sensory abnormalities, visual disturbances, difficulties with speech and language, imbalance, changed behavior, and disturbed sleep are all frequently brought on by neurosurgical illnesses. Depending on the ailment, these symptoms might differ and call for medical intervention. Therefore, timely intervention measures are needed once they occur, which will not lead to severe consequences. Therefore, patients with the disease generally have severe psychological anxiety and panic, which easily harms the development of the disease. With the improvement of medical levels, many diseases have been well treated, and the life cycle of patients has been prolonged. However, the negative psychological emotions brought by the disease itself cannot be eradicated in time, which has a particular impact on the recovery of the disease. To make patients more fully understand their situation and trust in medical staff, patients are intervened through detailed nursing management methods, which help recover the patient’s condition, as well as psychological counseling. Quantitative and qualitative measures assess Patient care efficacy by evaluating nursing management strategies. Metrics such as tracking health indicators, doing clinical evaluations, reviewing medicine administration, assessing adherence to treatment plans, evaluating hospital stays, evaluating patient education, and evaluating the efficacy of teamwork are among them. Lihua [1] argues that postoperative nursing of patients can increase the success rate of surgery and improve the enthusiasm of patients, which is conducive to the recovery of the disease. Especially for patients with neurosurgical diseases, which are acute and easily cause serious consequences once they occur; even if the doctor gives a successful treatment plan, the patient’s panic and pressure on the disease will increase the psychological burden of the patient, which is not conducive to the recovery of the disease. To explore the application value of detailed nursing management in neurosurgery. Through grouping comparison, the results show that the management method of complex nursing cannot only improve the environmental sanitation of the ward and the satisfaction of patients but also reduce the probability of complications in patients, which is less than that in other patients [1].
Qiong [2] states that neurosurgery generally involves patients with severe symptoms, and nursing workers need to face situations of great difficulty and high risk. The management mode of detailed nursing can improve the nursing staff’s sense of responsibility to improve patients’ dependence on the medical staff, better cooperate with medical staff, and help improve patient recovery [2]. Jiao et al. studied how well critically sick neurosurgery patients did with evidence-based enteral nutrition therapy in terms of avoiding complications. The study group was shown to have a better prognosis, higher feeding compliance, reduced incidence of complications, and lower nutritional markers. By implementing these treatments, nursing staff knowledge and patients’ nutritional status may be improved [3]. Alrashidi et al. [4] stated that according to Montreal Neurological Hospital research, just 42% of registered nurses were at ease handling EVD patients, and 37% were uneasily troubleshooting EVD malfunctions. However, comfort increased after employing a quality improvement tool, indicating the need for ongoing instruction and training [4]. Wu et al. [5] described that this research investigates comfort care strategies for patients undergoing general surgery and neurology with an emphasis on their distinctiveness, efficacy, and usefulness. According to the research, comfort nursing interventions promote clinical holistic nursing and elevate the status of clinical nursing. The study concludes that comfort nursing techniques can help patients heal [5].
The study compares thorough nurse management with traditional approaches at a municipal hospital to improve postoperative recovery, lessen psychological strain, and improve the patient experience in neurosurgical care, ultimately leading to decreased complications and increased patient satisfaction. The objective is to improve the clinical application of detailed nursing management mode in neurosurgery, alleviate the tension between doctors and patients, increase the trust between doctors and patients, and enhance the compliance of patients, which is conducive to the work of medical staff.
2. Data and methods
2.1. General information of patients
Taking the traditional nursing management and detailed nursing management of neurological patients in a municipal neurosurgery hospital from March 2021 to March 2022, the neurosurgery was divided into 50 patients in the complex nursing management group and 50 patients in the traditional nursing management group. In the clear nursing management group, there were 50 patients: 20 male patients, with an average age of 58.7 3.8 years, and 30 female patients, with an average age of 60.4 4.3 years; In the traditional nursing management group, there were 50 patients, 26 male patients, with an average age of 59.7 3.7 years, and 24 female patients, with an average age of 59.4 3.9 years; Among the 100 patients, there were 60 cases of cerebral infarction, 25 cases of intracerebral hemorrhage and 15 cases of other neurosurgical diseases.
Inclusion criteria: Patients with neurological problems diagnosed by the hospital’s neurosurgeon and their general information and physical condition meet the admission criteria. Exclusion criteria: Patients with other serious complications, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and incomplete data. There was no significant statistical difference between the two groups.
2.2. Grouping and nursing methods
2.2.1. Grouping and observation indicators
The detailed and traditional nursing management groups were assessed and scored. The assessment contents are as follows: nursing quality includes ward management, health publicity, communication ability score, nursing technology score, and nursing attitude score. Quality and complications, vital signs, pain evaluation, wound examination, and medicine delivery are examples of observational indicators in nursing. Assessing the physiological and psychological condition, identifying problems, and improving patient outcomes depend on good documentation and routine monitoring. Complications include infection, pressure ulcers, etc. Nursing satisfaction: a unified questionnaire survey was adopted, with a total score of 100. The higher the score, the higher the patient’s satisfaction with nursing.
2.2.2. Nursing methods
The control group used traditional nursing methods. In research studies, standard nursing procedures are employed to determine extra advantages, address ethical problems, and create a baseline level of care. They also help evaluate the efficacy of new therapies and guarantee their application in real-world healthcare settings. After admission, the patients closely monitored their respiratory rate and heart rate index and regularly monitored their pulse and blood pressure. Patients should be given oral cleaning and pipeline care on time daily, secretions in the pipeline, the pipeline kept unobstructed, medication guidance strengthened, and health publicity increased. Identifying pulse spots, palpating fingers, counting beats, and using a cuff and stethoscope are some methods to monitor blood pressure and pulse. It’s essential to follow control protocols, standards, and moral principles. An unobstructed pipeline guarantees prompt diagnosis, treatment, prevention, management of chronic diseases, emergency care, psychosocial well-being, control of diseases, public health, a reduction in healthcare inequalities, and the promotion of health equity. The observation group implemented detailed nursing management methods, which were divided into nurses’ and patients’ management. The management methods of nurses were as follows: (1) quality management of nursing staff: new nurses need to receive strict anatomical training. Nursing quality management includes standard compliance, ongoing education, implementing clinical protocols, measuring performance, keeping an eye on patient safety, patient communication, working as a healthcare team, using technology, conducting routine audits, and using risk management techniques. After mastering excellent professional knowledge and technology, clarify the responsibilities and obligations of nursing staff and formulate nursing objectives according to the actual needs of patients. In rare instances, the following strategies can help to improve communication: promote a collaborative culture, set up interdisciplinary meetings, use EHRs, create clear protocols, apply structured tools, offer training, promote two-way communication, standardize documentation, hold debriefings, and facilitate joint patient rounds. The doctor explained the rare cases to the nursing staff so that the nursing staff could clarify the causes, treatment procedures, precautions, and risk prevention of the cases. “Nursing staff meetings” shall be held regularly in the Department to solve nursing problems. (2) Strengthen the ideological education of nurses, make nurses realize the importance of “detailed nursing,” apply the idea of “paying attention to details” to daily nursing work, and ensure that each nursing detail can be completed qualitatively and quantitatively. Nurses get an ideological education that emphasizes values, ethics, and professionalism. It also emphasizes patient-centered care, cultural competency, effective communication, teamwork, advocacy, critical thinking, and social responsibility as pillars of compassionate care. Nurses should be good at discovering possible risks in nursing links and try their best to reduce them. To help patients eliminate their usual bad habits, nurses should develop the habit of “details determine success or failure.” Nurses can recognize and manage risks in nursing processes using various techniques, including risk assessments, root cause analysis, monitoring systems, incident reporting, staff training, communication protocols, patient involvement, audits, medication safety, standardization, emergency response plans, and regulatory compliance. Through ideological education and action education, patients feel that they are patient-centered in heart and behavior and are provided with comprehensive, detailed nursing services.
2.3. Statistical methods
The data were processed using SPSS 20.0 statistical software. The measurement data were expressed by (), and a -test was performed. The counting data were described by [ (%)], and the -test was performed test, 0.05; the difference was statistically significant. An independent samples -test for separate groups and a paired samples -test for related groups are the two primary forms of -tests, statistical methods used to compare the means of two groups. It is predicated on variance homogeneity, independence of observations, and a normal distribution of data. -tests increase precision and patient outcomes in healthcare research by helping to evaluate therapy efficacy, diagnostic accuracy, personalized medicine, quality improvement, resource allocation, risk assessment, and risk stratification.
3. Results
3.1. Comparative analysis of nursing efficiency
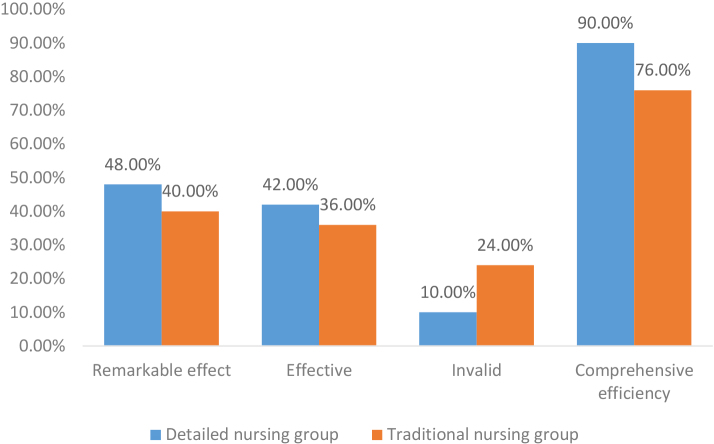
The practice has proved that in the detailed nursing group, integrating the transparent, high-quality nursing mode can improve the psychological state of patients, significantly improve the nursing quality, and achieve satisfactory results. In a supportive setting, high-quality nursing treatments may dramatically enhance patients’ psychological states, encouraging general well-being and better health outcomes. These interventions include effective communication, sympathetic care, patient education, pain management, and holistic approaches. Improved communication, safety precautions, continuity, standardized procedures, patient assessments, tailored care plans, evidence-based practices, effective workflows, professional development, patient involvement, outcome assessment, and quality improvement programs are all components of a superior nursing model that improves patient care. Suitable nursing measures are of great significance to enhance the treatment effect. Detailed nursing fully embodies the advanced concept of “people-oriented” and has been widely praised by doctors and patients in clinical practice. To further improve the intervention level of Neurosurgical Nursing and apply the detailed nursing method to clinical practice, the overall effect is satisfactory. This study uses two nursing modes: complex nursing and traditional nursing; in order to verify the comprehensive efficiency of the two modes, the above two nursing modes were recorded and analyzed according to the obvious effect, effectiveness, and ineffectiveness. The chart was made by comparing the results of the comprehensive efficiency data, and the following Table 1 was obtained.
Table 1.
Comparison of comprehensive, effective rates of patients with different nursing modes
| Group | Remarkable effect | Effective | Invalid | Comprehensive efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detailed nursing group | 50 | 48.00% | 42.00% | 10.00% | 90.00% |
| Traditional nursing group | 50 | 40.00% | 36.00% | 24.00% | 76.00% |
| value | / | 3.624 | 3.257 | 3.304 | 3.331 |
| -value | / | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.031 | 0.021 |
In Table 1, through the comparison of the comprehensive, effective rates of two different nursing modes, it is found that the difference between the detailed nursing group and the traditional nursing group increases significantly in the ineffective rate. When the patients receive complex nursing, the clinical symptoms are improved considerably, showing that detailed nursing intervention can effectively monitor the patients’ postoperative situation. Nursing interventions are a team-based method of caring for patients with mental, emotional, and physical needs. They also encourage health literacy, interdisciplinary coordination, self-care, transition readiness, and ongoing quality improvement.
To better observe and analyze the comprehensive, practical effects of different nursing modes after the operation, the patient data in the above table are visualized, as shown in Fig. 1. As can be seen, visualization is carried out according to the data results of patients’ comprehensive, effective rate after the operation. Compared with the traditional nursing group, the total effective rate of the detailed nursing group is as high as 90%, and the comprehensive effective rate of the complex nursing group is significantly better than that of the traditional nursing group, which directly opens the gap between the two nursing modes. Therefore, the use of detailed nursing can achieve better nursing effects. Nursing effectiveness is increased when attention to detail is given to patient safety, timely intervention, risk mitigation, individualized patient care, effective communication, high-quality documentation, critical thinking, efficient workflow, professional accountability, and ongoing improvement.
Figure 1.
Comparison of comprehensive, effective rates of patients with different nursing modes.
3.2. Patient complication rates and outcomes
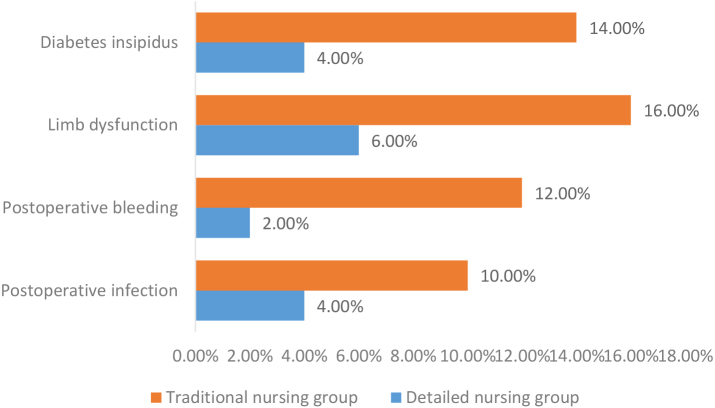
Neurosurgical patients are often in critical condition and carry out surgical rescue. Many patients are prone to postoperative infection, postoperative bleeding, limb dysfunction, and diabetes insipidus after surgery, mainly because of the damage to neurological function. The brain and spinal cord are the primary organs affected by neurosurgical procedures; therefore, improved outcomes necessitate brain mapping, minimally invasive approaches, advanced anesthesia, postoperative monitoring, rehabilitation services, multidisciplinary collaboration, technology advancements, and patient education. The occurrence of postoperative complications cannot be avoided. Detailed nursing intervention subdivides the nursing work, carries out the nursing intervention, helps patients control their condition, accelerates their recovery, and reduces or avoids postoperative complications. Patient safety, optimal recovery, financial savings, increased satisfaction, avoidable nature, decreased morbidity, professional responsibility, evidence-based practice, ethical principles, improving patient outcomes, and upholding moral obligations are all prioritized in preventing postoperative complications. To analyze and study the complications of postoperative infection, postoperative bleeding, limb dysfunction, and diabetes insipidus in neurosurgical patients, the nursing effects of patients in different complications are observed and discussed (Table 2).
Table 2.
Comparison of nursing effects of postoperative complications in patients with different nursing modes
| Classification of complications | Detailed nursing group | Traditional nursing group | value | -value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative infection | 2 (4%) | 5 (10%) | 5.367 | 0.032 |
| Postoperative bleeding | 1 (2%) | 6 (12%) | 5.201 | 0.025 |
| Limb dysfunction | 3 (6%) | 8 (16%) | 5.074 | 0.031 |
| Diabetes insipidus | 2 (4%) | 7 (14%) | 5.335 | 0.026 |
Table 2 shows the incidence and effect of postoperative complications in the two groups of patients with different nursing modes. It is evident that the incidence of postoperative complications of postoperative infection, postoperative bleeding, limb dysfunction, and diabetes insipidus in the detailed nursing group is significantly lower than that in the traditional nursing group, and the comparison difference between the two groups is evident, 10.000, 0.05, which has apparent statistical significance.
To better compare the incidence of complications in patients with different nursing modes, the patient data in the above table are visualized, as shown in Fig. 2. The figure shows the visual comparison of the incidence of postoperative complications between the detailed nursing group and the traditional nursing group, which intuitively indicates that the incidence of postoperative complications in the conventional nursing group is higher and indirectly shows that the detailed nursing is more conducive to the postoperative recovery of patients, can reduce the incidence of postoperative complications and better restore health.
Figure 2.
Incidence of postoperative complications in patients with different nursing modes.
3.3. Scoring results of various evaluation scales of patients
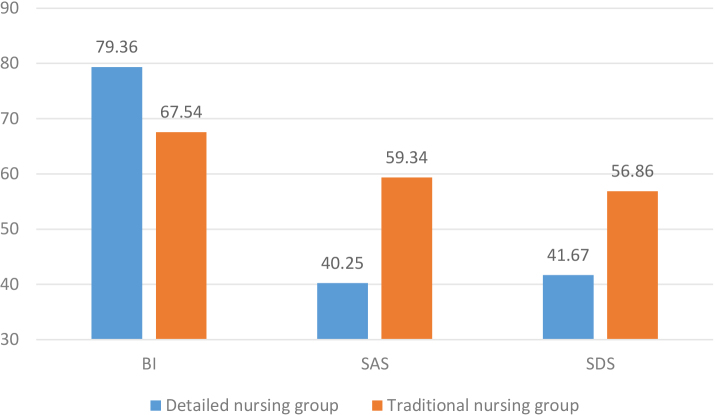
When the patient wakes up after the operation, he has safely passed the anesthesia and dangerous period. However, there are still psychological obstacles, so the patient will have various psychological states. Now, according to the subtle psychological reactions of the patient after the operation, based on clinical nursing, it is necessary to score each patient with the Barthel index (BI), self-rating Depression Scale (SDS), and self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS). Traditional nursing groups’ postoperative anxiety and depression symptoms exhibit a gap, reflecting the surgical reaction of the patient. To raise these patients’ quality of life and overall well-being, focused therapies, constant monitoring, and psychological support are required. Giving targeted nursing intervention measures can further improve the quality of nursing and restore the patients’ daily living ability. In order to provide excellent patient outcomes, targeted nursing interventions enhance nursing quality through the following methods: patient involvement, continuous monitoring, evidence-based practices, risk reduction, rapid response, individualized care, and effective communication. In this study, the patients in the detailed nursing group and the traditional nursing group were scored. The above two nursing groups were recorded and analyzed according to Bi, SAS, and SDS (Table 3).
Table 3.
Comparison of postoperative scoring indexes of patients with different nursing modes
| Scoring index | Detailed nursing group | Traditional nursing group | value | -value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI | 79.36 3.67 | 67.54 4.28 | 4.257 | 0.021 |
| SAS | 40.25 3.64 | 59.34 4.57 | 4.363 | 0.018 |
| SDS | 41.67 3.55 | 56.86 4.48 | 2.671 | 0.015 |
Table 3 shows the comparative effect of the two nursing groups on the postoperative scoring indicators. The comparison indicates that the detailed nursing group has a higher postoperative BI score, mild dependence on others, and little or no care from others, and the symptoms of SAS and SDS are also lighter than those of the traditional nursing group, which shows that the detailed nursing is more conducive to supervising the postoperative situation of patients.
To better compare and analyze the scoring indexes of patients after adopting different nursing modes, it is visualized according to the patient data, as shown in Fig. 3. The Figure compares patients’ postoperative scoring indicators with different nursing modes. The detailed nursing group and the traditional nursing group have opened a significant gap in the symptoms of postoperative SAS and SDS. Complex nursing can alleviate the patient’s mood and restore the patient’s condition to improve the patient’s self-care ability. Postoperative care nurses employ targeted treatments to mitigate patients’ feelings of anxiety and despair. They include evaluations, therapeutic communication, patient education, pain management, sleep hygiene, emotional support, counseling, medication management, and continuous care to provide a supportive atmosphere.
Figure 3.
Comparison of postoperative scoring indexes of patients with different nursing modes.
3.4. Satisfaction survey results of patients and their families
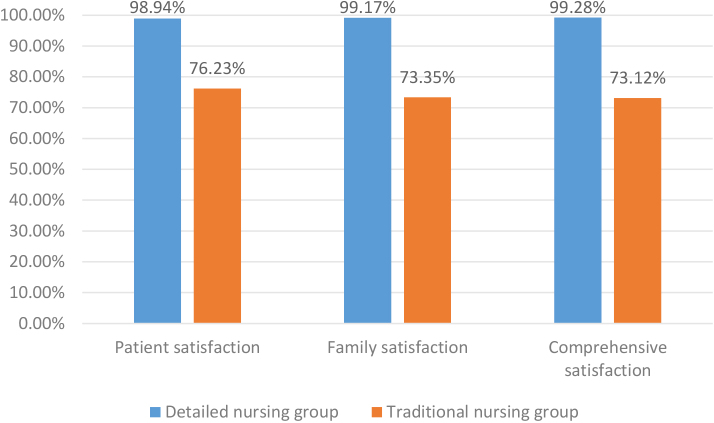
Detailed nursing intervention can make targeted nursing after the operation. Paying attention to the management of details can significantly reduce patients’ pain and improve the nursing effect. Carry out all-around care and nursing for the physiology and psychology of patients during treatment, further give play to the role of detailed nursing, and effectively restore the postoperative physical condition of patients to improve the satisfaction of patients and their families. Now, according to the results of the detailed and traditional nursing groups, the satisfaction of patients and their families is investigated (Table 4).
Table 4.
Comparison of satisfaction of patients and their families in different nursing groups
| Group | Patient satisfaction | Family satisfaction | Comprehensive satisfaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detailed nursing group | 50 | 98.94% | 99.17% | 99.28% |
| Traditional nursing group | 50 | 76.23% | 73.35% | 73.12% |
| value | / | 3.641 | 3.217 | 3.321 |
| -value | / | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.004 |
Table 4 shows the data results of the satisfaction of patients and their families in the detailed nursing group and the traditional nursing group. The results show that in the complex nursing group, the comprehensive satisfaction of patients and their families is as high as 99%, which indicates that detailed nursing in neurosurgical nursing can achieve better nursing results.
To more vividly understand patients, family members, and comprehensive satisfaction, visualization is now carried out according to the data, as shown in Fig. 4. The figure shows the evaluation of the satisfaction of patients and their families with different nursing modes after the operation. The patients, their families, and the comprehensive satisfaction of the detailed nursing group are better than those of the traditional nursing group. From the satisfaction of up to 99%, it is more intuitive to show that this high-quality nursing mode using detailed nursing can give practical nursing to patients and has high application value.
Figure 4.
Comparison of satisfaction of patients and their families in different nursing groups.
4. Discussion
Nursing intervention can be tailored to the condition of surgical patients to improve the treatment effect. Moreover, the physical and mental health of patients after surgery are relatively fragile, and they are prone to infection risk. Strict hand hygiene, aseptic procedures, antibiotics, preoperative screening, skin antisepsis, wound care, and infection control measures are necessary to prevent postoperative infections in surgical patients. These tactics use a multidisciplinary team approach and are intended to avoid difficulties. Planning comprehensive evaluations, patient education, therapeutic communication, pain management, and cultural sensitivity in nursing intervention plans for surgical patients take mental health issues into account. It fosters a kind, emotional care environment. They have high requirements for the environmental sanitation of the ward, poor self-care ability, and emotional excitement. Nurses not only give action care but also need to give emotional comfort and psychological counseling, patiently communicate with patients, and cooperate with the work of medical staff, which is conducive to the prognosis of patients. Nurses offer psychological and emotional support through therapeutic approaches, information sharing, active listening, sympathetic communication, and a welcoming atmosphere. They work with mental health specialists, create customized treatment programs, and monitor symptoms.
Zhang and Zhang [6] stated that neurosurgery nursing work is relatively complex, with a large workload, which often needs to be understood by patients and increases the workload. However, patients feel that the attitude of nursing staff could be better and that service awareness needs to be more significant. The two are often at the two ends of the contradiction and do not cooperate, resulting in safety accidents. The detailed nursing management model can solve this dispute and fundamentally solve the contradiction between medical staff and patients, Improving patient compliance and satisfaction [6]. The nursing management model strongly emphasizes tailored care plans, open communication, patient involvement, ongoing observation, comprehensive support, cultural competency, and compassionate care to mitigate any conflicts between medical personnel and patients. Ding [7] argued that, generally speaking, patients in neurosurgery have severe symptoms, which brings some difficulties to the development of nursing work, and patients will also have an infection and other complications after the operation, which makes patients feel anxious because of their condition. They often take a non-cooperative attitude towards the work of nursing staff, which increases the difficulty of nursing and dramatically reduces the treatment effect [7]. Many practical techniques are used to assess how well nursing staff manages attitudes that are not cooperative, such as patient feedback surveys, incident reports, observations, training evaluations, team debriefings, peer reviews, assessments of communication skills, patient advocacy, and so on. Patient dissatisfaction, higher expenses, and worse health outcomes might result from reduced treatment effectiveness. Careful observation, prompt corrections, unambiguous communication, commitment to ethics, evidence-based treatment, and continuous innovation are needed to address these effects. At this time, the comprehensive quality of nursing staff is highlighted. The detailed nursing management model can improve the work effect of nursing staff, reduce patients’ complaints, and improve patients’ self-restraint ability to enhance the treatment effect [8, 9, 10].
Surgery is originally a high-incidence area of doctor-patient disputes, especially when the postoperative recovery is not optimistic; the patients are depressed and miserable, which is not conducive to the recovery of the disease [11, 12]. In addition, the lack of medical knowledge leads to distrust of medical staff, which makes it easy to have contradictions with medical staff and intensify contradictions. By increasing the comprehensive quality of nursing staff, improving the benign communication with patients and emotional counseling, and timely and targeted early intervention on the infection risk and complications of surgery to reduce the occurrence of similar risks, it is helpful to live in harmony between doctors and patients and improve the quality of nursing and the quality of life of patients [13, 14, 15]. Surgical outcomes are improved, and patient safety is maximized with a comprehensive perioperative approach that includes quality improvement initiatives, prompt intervention, wound care, antibiotic prophylaxis, skin antisepsis, postoperative monitoring, pain management, hygiene practices, patient education, and collaboration with infectious disease specialists.
5. Necessities of applying detailed nursing management in neurosurgical nursing
With the improvement of people’s material level, people pay more and more attention to health, and the human life cycle is constantly prolonged. Still, the disease problem has become a non-negligible existence in people’s quality of life. Especially neurosurgical diseases have relatively severe symptoms. Surgery is generally used for treatment, but the occurrence of postoperative infection and complications seriously affects the expected recovery of patients. Bring physical and mental double pressure to patients; not only do they not report hope for future life, but they also have a questioning attitude towards medical staff, no longer cooperate with medical orders, and report a negative attitude to face life. This requires the comprehensive quality of our nursing staff. Although the nursing task of neurosurgery is high, based on the responsibility and mission of medical staff, we should give specific emotional care to patients who need periodic treatment and nursing and publicize relevant medical knowledge so that patients can understand that surgery is only the first step of treatment, and what risks will occur in the follow-up, so that patients have a specific right to know their symptoms, At the same time, avoid too straightforward statements, which will bring ideological burden to patients.
Strengthen detail management, enhance the sense of responsibility of nursing staff, correct the original working attitude, and give the initially dirty and tired work a sense of mission. I believe that every medical staff comes with a sacred sense of responsibility in this industry but becomes impatient in the heavy work day after day and does not disregard the anxiety and panic of patients; it’s just that they have to ignore the busy work. If every patient needs to be scolded like a baby, the work can’t be carried out, but emotional comfort is necessary. Balancing the contradiction between the two also requires nurses to explore their daily work slowly, deal with the details, and warm the patients.
Active patient involvement in symptom communication, respiratory care, vaccinations, hand hygiene, isolation precautions, education, and decision-making make the hospital environment safer by limiting the spread of infections and enhancing overall health. The management of details is added in the daily nursing work, which can stabilize the patient’s mood and cooperate with the work of nursing staff in daily work to reduce the risk of infection and complications and is conducive to the harmonious development of the doctor-patient relationships.
6. Conclusions
With the improvement of medical levels, some diseases still perplex the life safety of patients, especially in neurosurgery. Experts in the medical field have not given up any patients and are also paying attention to the psychology of patients. Therefore, detailed nursing is proposed to manage patients. Nursing is no longer the routine nursing and detection of physical signs. Still, it starts from the environment and health of the ward and the emotions of patients and their families so that patients can get the care of medical staff in the long treatment process. Both sides work together to reduce patients’ complications to improve the comprehensive treatment effect for patients. Although detailed nursing management only pays more attention to humanistic care and plays no decisive role in the disease, it is believed that people will know more about the disease and reduce the panic about the unknown. To improve neurosurgical nursing, it will evaluate long-term results, incorporate technology, encourage patient-centered care, foster teamwork, create educational materials, carry out cost-effectiveness evaluations, put patient safety procedures into place, and look at the influence on the nursing workforce.
Funding
No funds or grants were received by any of the authors.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the design and methodology of this study, the assessment of the outcomes, and the writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
References
- [1]. Lihua C. Application of detailed nursing management in Neurosurgical Nursing. Medical Diet Therapy and Health. 2021; 19(01): 158-159. [Google Scholar]
- [2]. Qiong H. Application of detailed nursing management intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. Chinese Community Physician. 2020; 36(18): 142-143. [Google Scholar]
- [3]. Jiao J, Chen Y, Yang L, Li W, Zhou Z, Li L, Xiao Y, Zhao J, Li L, Xia Y. Nursing practice based on evidence-based concepts to prevent enteral nutrition complications for critically ill neurosurgical patients. Frontiers in Surgery. 2022. Mar 18; 9: 857877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4]. Alrashidi Q, Al-Saadi T, Alhaj AK, Diaz RJ. The role of nursing care in the management of external ventricular drains on the neurosurgical ward: A quality improvement project. World Neurosurgery. 2023. Aug 1; 176: 265-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5]. Wu L, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yu H. Review on comfort nursing interventions for patients undergoing neurosurgery and general surgery. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2022. Aug 10; 2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Retracted]
- [6]. Zhang J, Zhang J. Application of detailed nursing management in Neurosurgical Nursing. Medical Diet Therapy and Health. 2020; 18(10): 134-136. [Google Scholar]
- [7]. Ding X. Application effect of detailed nursing management in Neurosurgical Nursing. Compilation of national scientific research theory and academic research achievements. 2020; 463-465.
- [8]. Liu R, Xiaojun J, Jing L, Yan S, Fen H. Clinical effect of detailed nursing management intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. China’s Health Industry. 2020; 17(10): 20-22. [Google Scholar]
- [9]. Xia Z, Zhaowei C, Yumiao Y. Application and experience of detailed nursing management concept in Neurosurgical Nursing. China’s Health Industry. 2020; 17(09): 11-12+17. [Google Scholar]
- [10]. Jinhui Z, Lingyue S, Jieshu G. Application of detailed nursing management in Neurosurgical Nursing. Psychological Monthly. 2020; 15(04): 136. [Google Scholar]
- [11]. Fangying W. Application of detail nursing in surgical nursing management. Electronic Journal of General Stomatology. 2019; 6(35): 127-146. [Google Scholar]
- [12]. Huiwen J. Application of detailed nursing management intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. Chinese Medical Guidelines. 2019; 17(26): 271-272. [Google Scholar]
- [13]. Juan X, Shuang N, Jie Y. Application of detailed nursing intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. Electronic Journal of Practical Clinical Nursing. 2019; 4(23): 137. [Google Scholar]
- [14]. Jixia Z, Bowen W. Application of detailed nursing management intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. China’s Health Industry. 2019; 16(05): 48-49. [Google Scholar]
- [15]. Xiaoyu X. Application of detailed nursing management intervention in Neurosurgical Nursing. Capital Food and Medicine. 2019; 26(02): 100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript.