Abstract
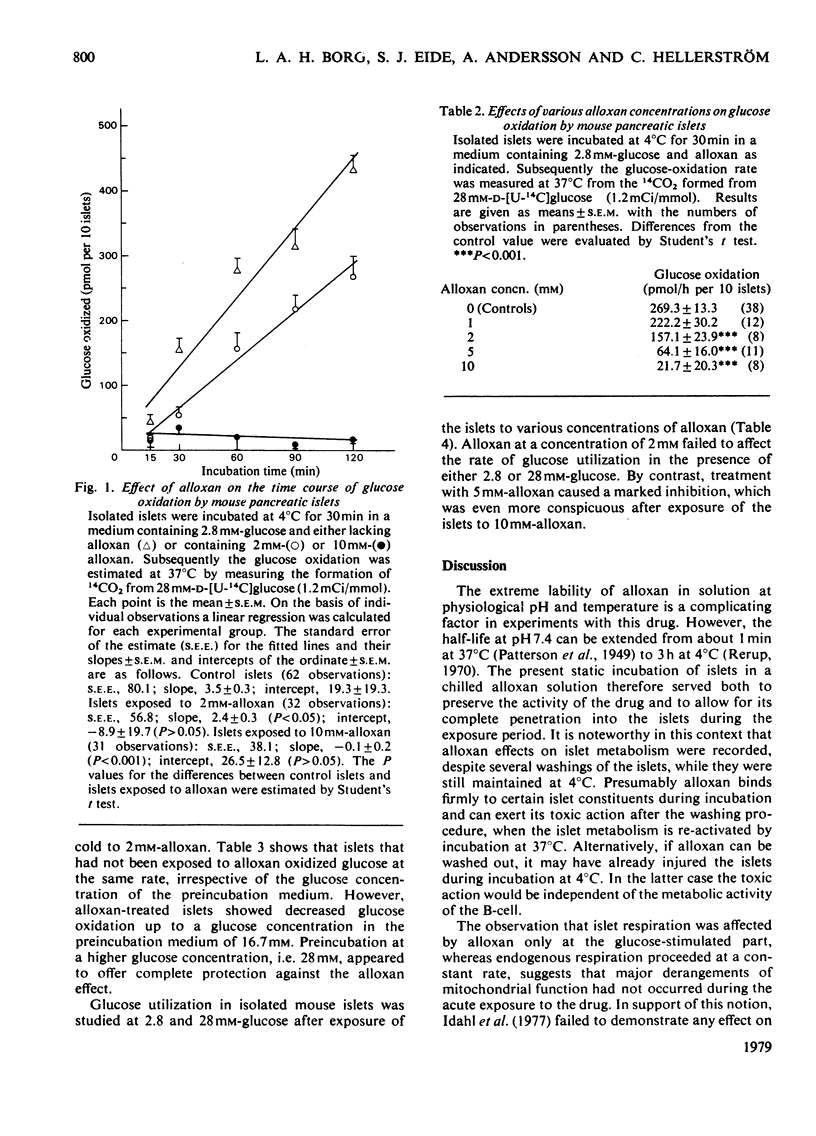
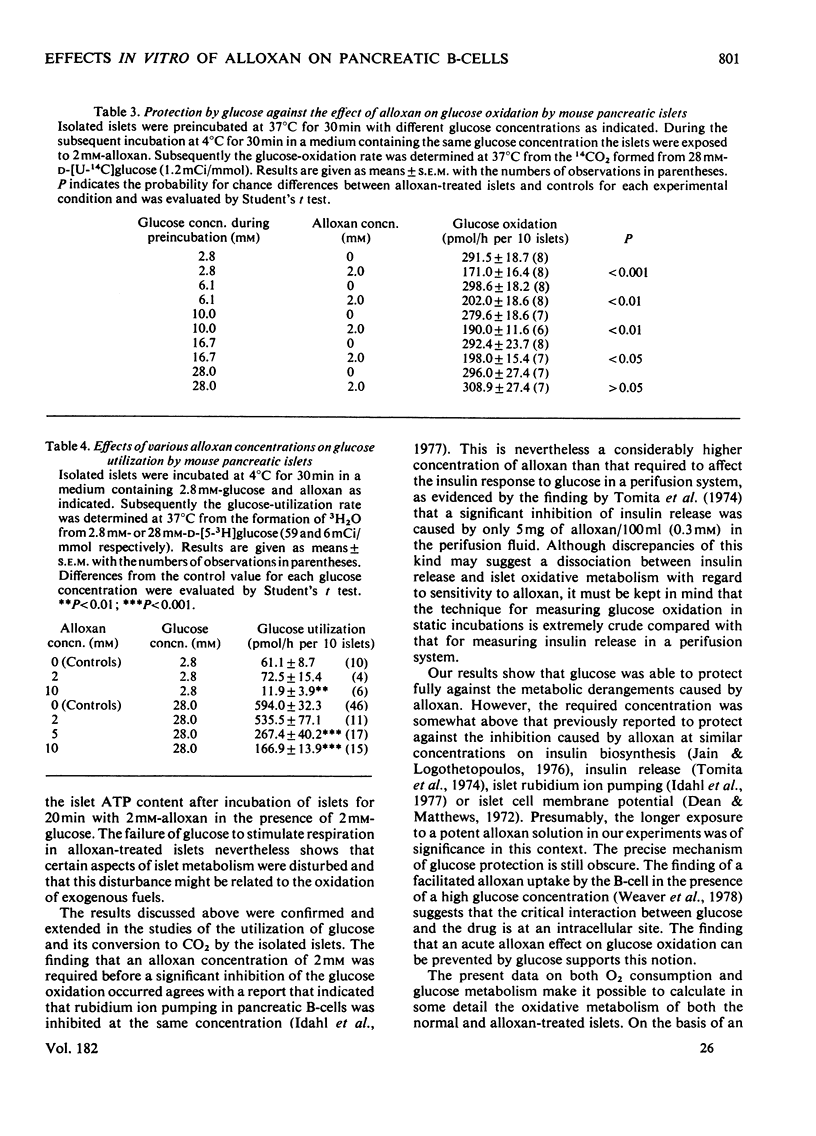
To facilitate detailed studies of the B-cytotoxic action of alloxan we developed a model using isolated pancreatic islets of normal mice. An essential feature of this model is the low temperature employed during exposure to alloxan, which minimizes the degradation of the drug. The islets were incubated with alloxan for 30min at 4°C and subsequently various aspects of their metabolism were studied. The O2 consumption was measured by the Cartesian-diver technique. Islets exposed to 2mm-alloxan and control islets had the same endogenous respiration, whereas the O2 uptake of the alloxan-treated islets was inhibited and that of the control islets stimulated when they were incubated with 28mm-glucose as an exogenous substrate. The islet glucose oxidation was estimated by measurement of the formation of 14CO2 from [U-14C]glucose at 37°C. Compared with the controls, alloxan-treated islets showed a decrease in the glucose-oxidation rate in a dose-dependent manner. Pretreatment of the islets with 28mm-glucose for 30min at 37°C completely protected against this effect, whereas preincubations at glucose concentrations below 16.7mm failed to exert any protective effect. The glucose utilization was estimated as the formation of 3H2O from [5-3H]glucose. Alloxan (2mm) failed to affect islet glucoseutilization rate in the presence of either 2.8 or 28mm-glucose. In contrast, islets exposed to 5 or 10mm-alloxan exhibited lowered glucose utilization. It is concluded that in vitro alloxan has an acute inhibitory effect on the islet glucose metabolism, and that this action can be prevented by previous exposure to a high glucose concentration. The results are consistent with the idea that the B-cytotoxicity of alloxan reflects an interaction with intracellular sites involved in the oxidative metabolism of the B-cell.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. The pentose cycle and insulin release in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1260525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILLIE L. A. Determination of liquid scientillation counting efficiency by pulse height shift. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1960 May;8:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(60)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA G. On the protection against alloxan diabetes by hexoses. Science. 1954 Nov 19;120(3125):841–843. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3125.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquist L. The endocrine pancreas in early alloxan diabetes. Including study of the alloxan inhibitory effect of feeding and some hexoses. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977 Mar;85A(2):219–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. The bioelectrical properties of pancreatic islet cells: effects of diabetogenic agents. Diabetologia. 1972 Jul;8(3):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01212257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson R., Hellerström C. Acute effects of alloxan on the metabolism and insulin secretion of the pancreatic B-cell. Horm Metab Res. 1973 Nov;5(6):404–409. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerström C. Effects of carbohydrates on the oxygen consumption of isolated pancreatic islets of mice. Endocrinology. 1967 Jul;81(1):105–112. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Potassium ions and the secretion of insulin by islets of Langerhans incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):17–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1080017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idahl L. A., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Alloxan cytotoxicity in vitro. Inhibition of rubidium ion pumping in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):9–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1620009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain K., Logothetopoulos J. Proinsulin biosynthesis by pancreatic islets of the rat and the study of alloxan cytotoxicity in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 18;435(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEEN H., FIELD J. B., PASTAN I. H. A simple method for in vitro metabolic studies using small volumes of tissue and medium. Metabolism. 1963 Feb;12:143–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Anderson S., Fink J., Roth C., Lacy P. E. Effect of alloxan on permeability and hexose transport in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1975 Jul;97(1):68–75. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Ellerman J., Hover B. A., Stillings S. N., Matschinsky F. M. Multiple metabolic functions of glucose in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):476–488. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rerup C. C. Drugs producing diabetes through damage of the insulin secreting cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Dec;22(4):485–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Täljedal I. B. On the mechanism of glucose protection against alloxan toxicity. Diabetologia. 1971 Aug;7(4):252–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01211877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Measurement of lactic acid in nanomolar amounts. Reliability of such a method as an index of glycolysis in pancreatic islets. Biochem Med. 1976 Feb;15(1):34–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Lacy P. E., Natschinsky F. M., McDaniel M. L. Effect of alloxan on insulin secretion in isolated rat islets perifused in vitro. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):517–524. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON J. R., LACY P. E. Electron microscopy of islet cells in alloxan-treated rabbits. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 Jan;67(1):102–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., McDaniel M. L., Lacy P. E. Alloxan uptake by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1847–1855. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellmann K. F., Volk B. W., Lazarus S. S. Ultrastructural pancreatic beta-cell changes in rabbits after small and large doses of alloxan. Diabetes. 1967 Apr;16(4):242–251. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.4.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Karl R. C., Matschinsky F. M. Effects of alloxan on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, glucose metabolism, and cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate levels in rat isolated islets of langerhans. Diabetologia. 1979 Feb;16(2):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01225460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


