Abstract
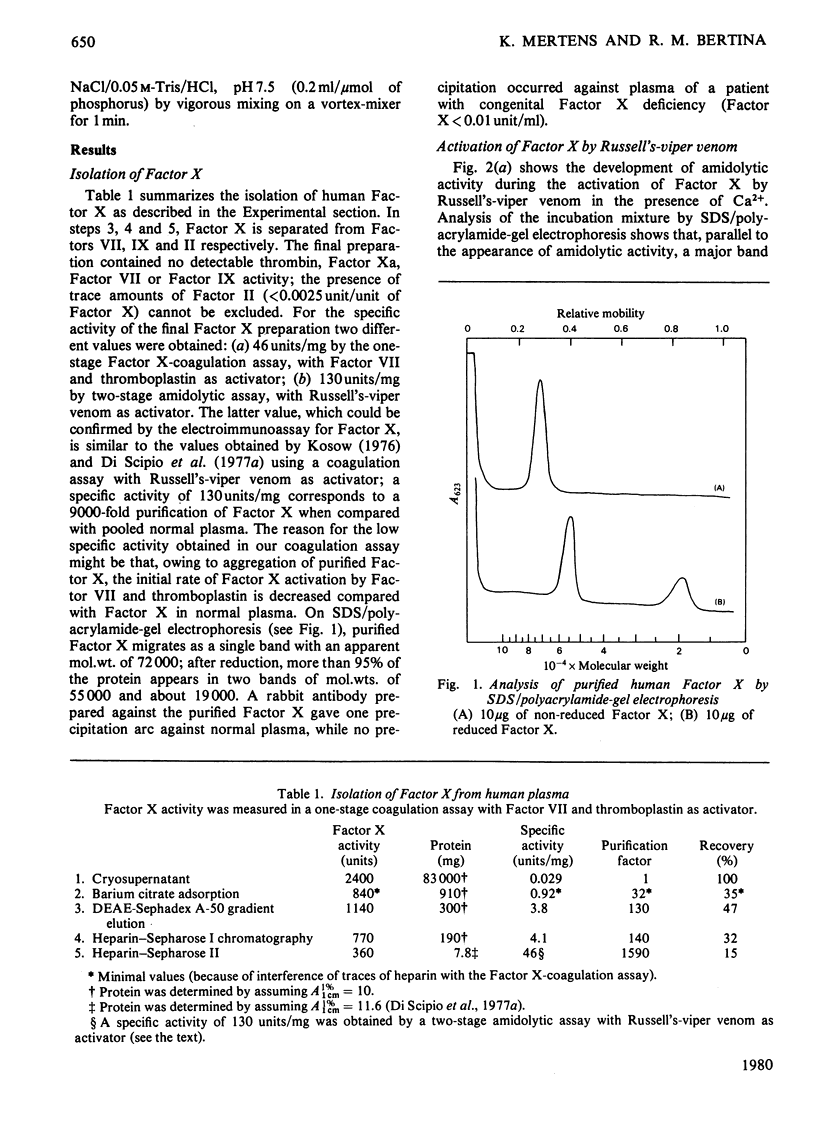
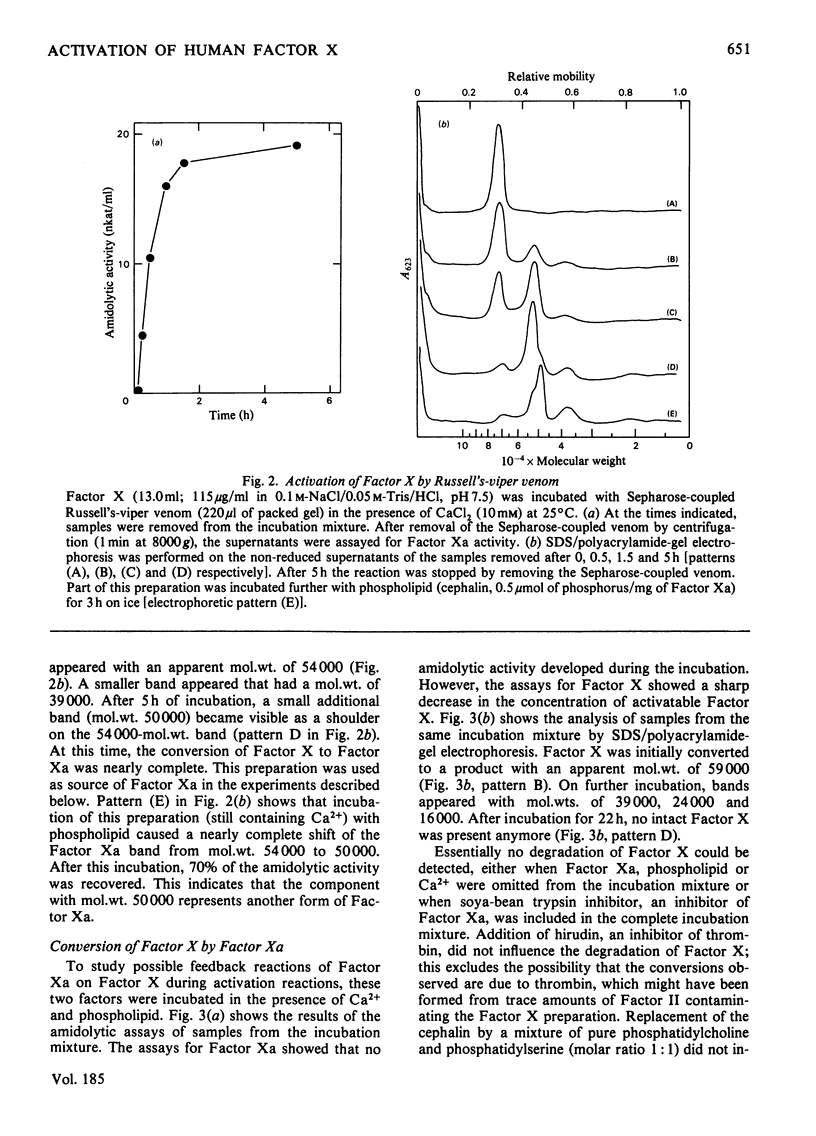
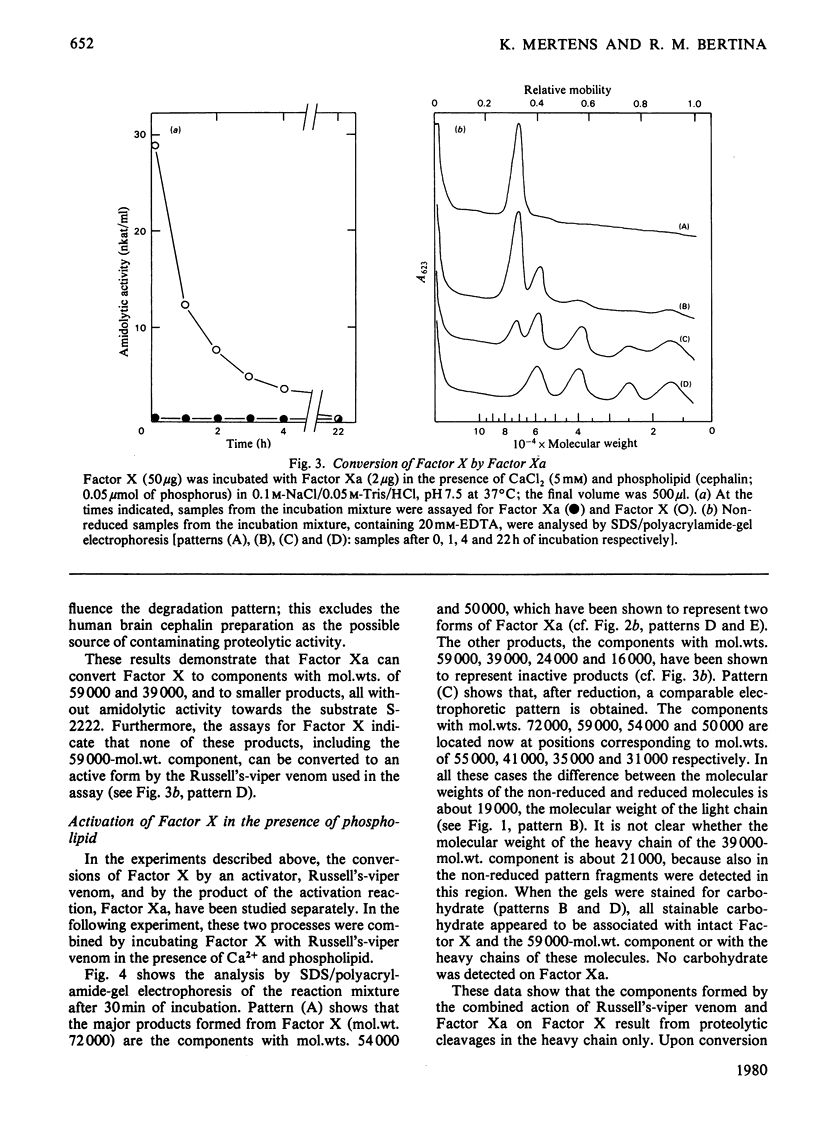
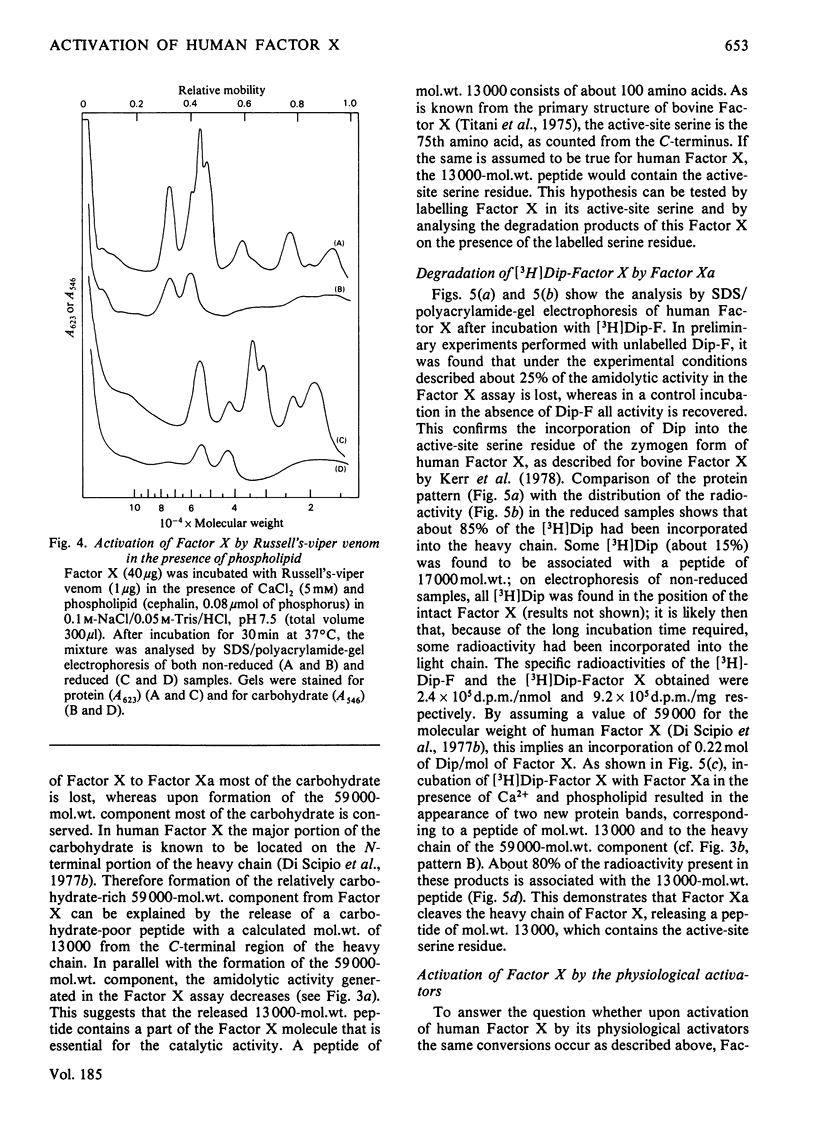
Purified human Factor X (apparent mol.wt. 72000), which consists of two polypeptide chains (mol.wt. 55000 and 19000), was activated by both Russell's-viper venom and the purified physiological activators (Factor VII/tissue factor and Factor IXa/Factor VIII). They all convert Factor X to catalytically active Factor Xa (mol.wt. 54000) by cleaving the heavy chain at a site on the N-terminal region. In the presence of Ca2+ and phospholipid, the Factor Xa formed catalyses (a) the cleavage of a small peptide (mol.wt. 4000) from the C-terminal region of the heavy chain of Factor Xa, resulting in a second active form (mol.wt. 50000), and (b) the cleavage of a peptide containing the active-site serine residue (mol.wt. 13000) from the C-terminal region of the heavy chain of Factor X, resulting in an inactivatable component (mol.wt. 59000). A nomenclature for the various products is proposed.
Full text
PDF


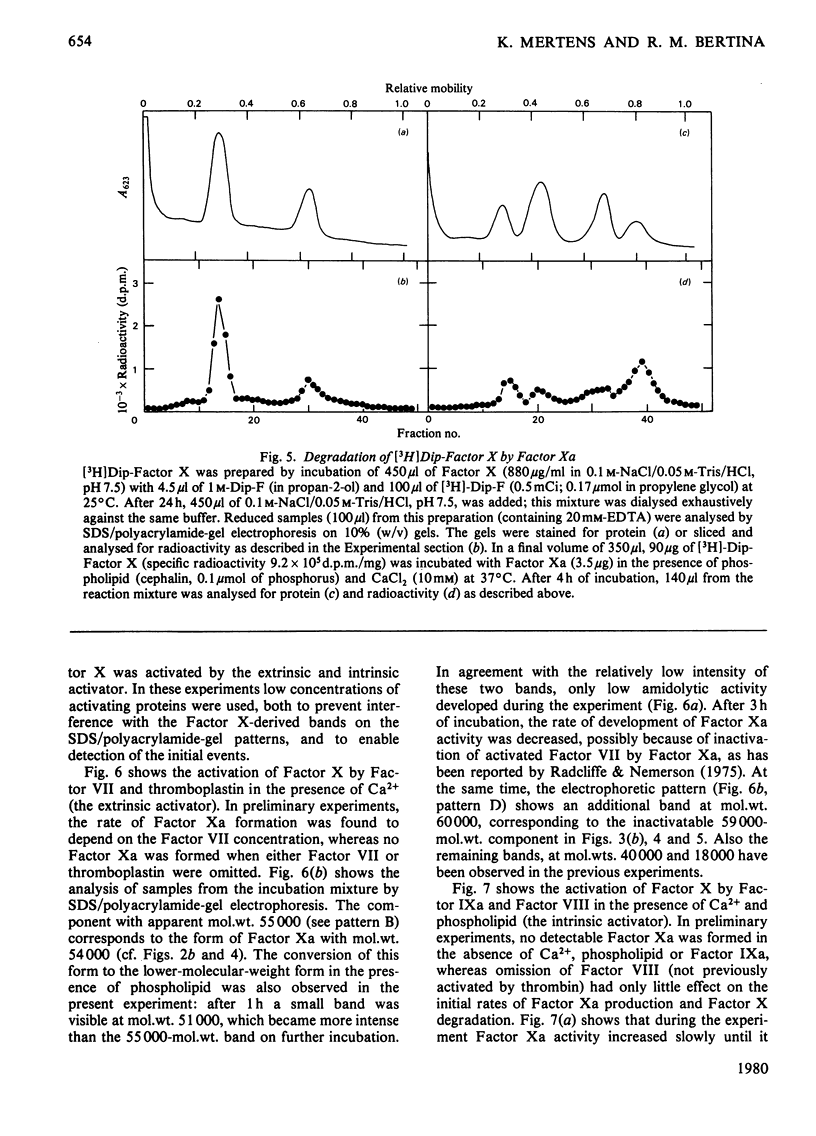
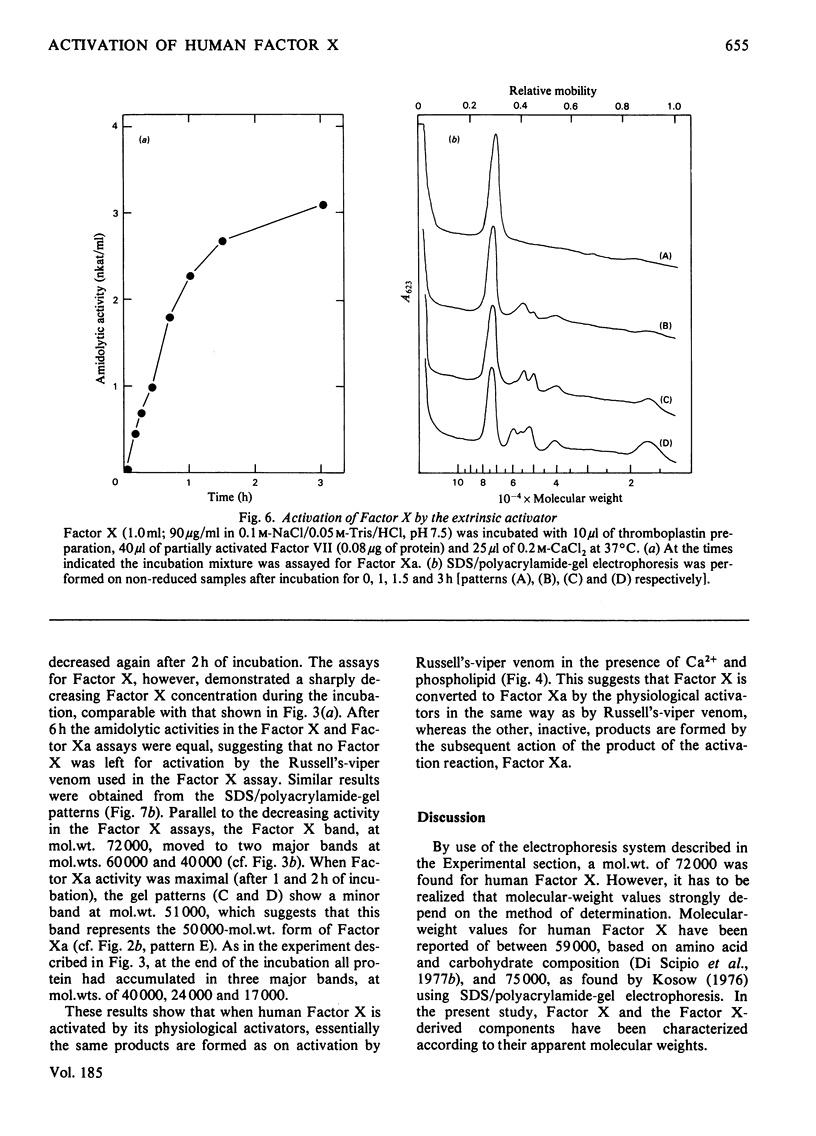
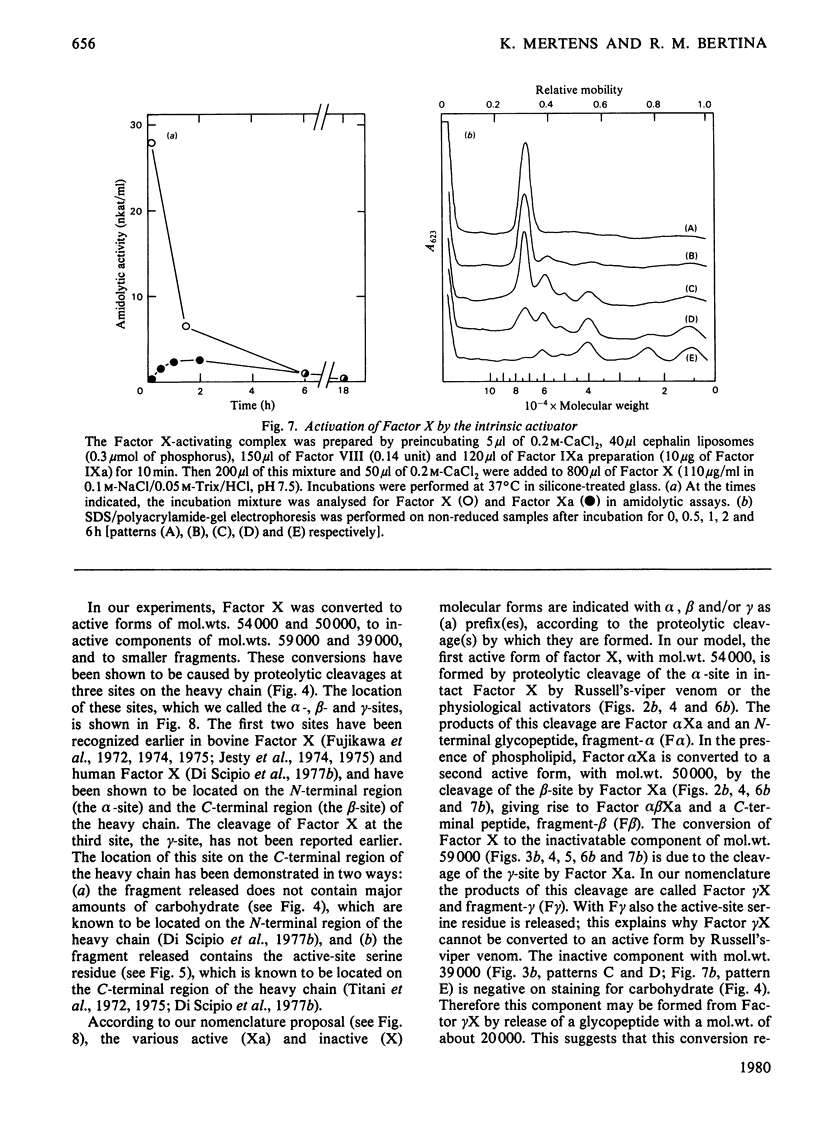
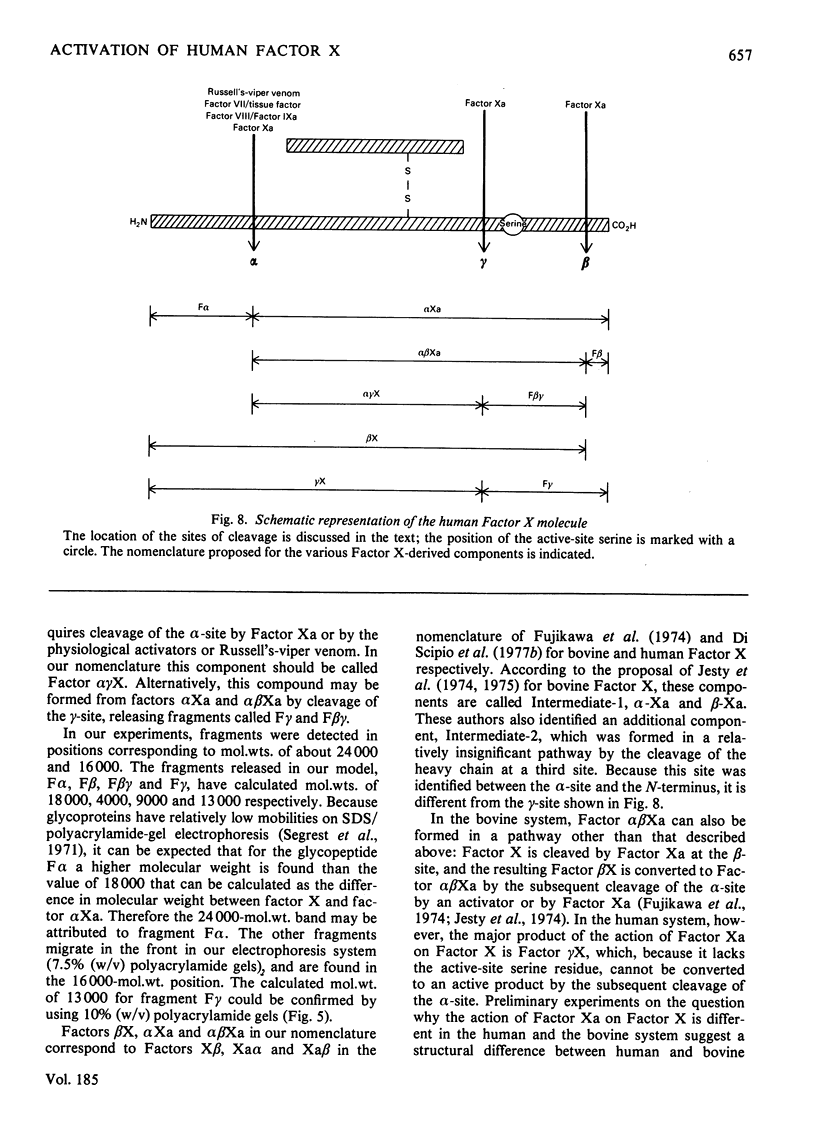

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Borg H., Miller-Andersson M. Purification and characterization of human factor IX. Thromb Res. 1975 Sep;7(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurell L., Friberger P., Karlsson G., Claeson G. A new sensitive and highly specific chromogenic peptide substrate for factor Xa. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström K., Egberg N. Determination of vitamin K sensitive coagulation factors in plasma: studies on three methods using synthetic chromogenic substrates. Thromb Res. 1978 Mar;12(3):531–547. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Orlando M., Tiedemann-Alderkamp G. H. Preparation of a human factor VII deficient plasma. Thromb Res. 1978 Sep;13(3):537–541. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Veltkamp J. J. The abnormal factor IX of hemophilia B+ variants. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Oct 31;40(2):335–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., van der Linden I. K. Inhibitor-neutralisation assay and electro-immuno assay of human factor IX (Christmas factor). Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jun 15;77(3):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Baugh R. F., Hougie C. Substrate inhibition of the intrinsic generation of activated factor X (Stuart factor). Thromb Res. 1978 Nov;13(5):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor X (Stuart factor) by a protease from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5253–5260. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor) by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5290–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1 (Stuart factor). Mechanism of activation by protein from Russell's viper venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4892–4899. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Titani K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor): conversion of factor Xaalpha to factor Xabeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3359–3363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemker H. C., Swart A. C., Alink A. J. Artificial reagents for factor VII and factor X, a computer programme for obtaining reference tables for one-stage determinations in the extrinsic system. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):205–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Esnouf M. P. The preparation of activated factor X and its action on prothrombin. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):791–799. doi: 10.1042/bj1310791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Nemerson Y. Purification of Factor VII from bovine plasma. Reaction with tissue factor and activation of Factor X. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Spencer A. K., Nakashima Y., Nemerson Y., Konigsberg W. The activation of coagulation factor X. Identity of cleavage sites in the alternative activation pathways and characterization of the COOH-terminal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4497–4504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Spencer A. K., Nemerson Y. The mechanism of activation of factor X. Kinetic control of alternative pathways leading to the formation of activated factor X. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5614–5622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Grahn D. T., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor)--analogy with pancreatic zymogen-enzyme systems. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2645–2648. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosow D. P. Purification and activation of human factor X: cooperative effect of Ca++ on the activation reaction. Thromb Res. 1976 Dec;9(6):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILSTONE J. H. The problem of the lipoid thromboplastins. Yale J Biol Med. 1950 Jul;22(6):675–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMENCLATURE of blood clotting factors; four factors, their characterization and international number. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 May 16;170(3):325–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Nemerson Y. Activation and control of factor VII by activated factor X and thrombin. Isolation and characterization of a single chain form of factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):388–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Jackson C. M. Prothrombin structure, activation, and biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):1–70. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Fujikawa K., Enfield D. L., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Bovine factor X1 (Stuart factor): amino-acid sequence of heavey chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Hermodson M. A., Fujikawa K., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1a (activated Stuart factor). Evidence of homology with mammalian serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4899–4903. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltkamp J. J., Drion E. F., Loeliger E. A. Detection of the carrier state in hereditary coagulation disorders. I. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):279–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


