Abstract
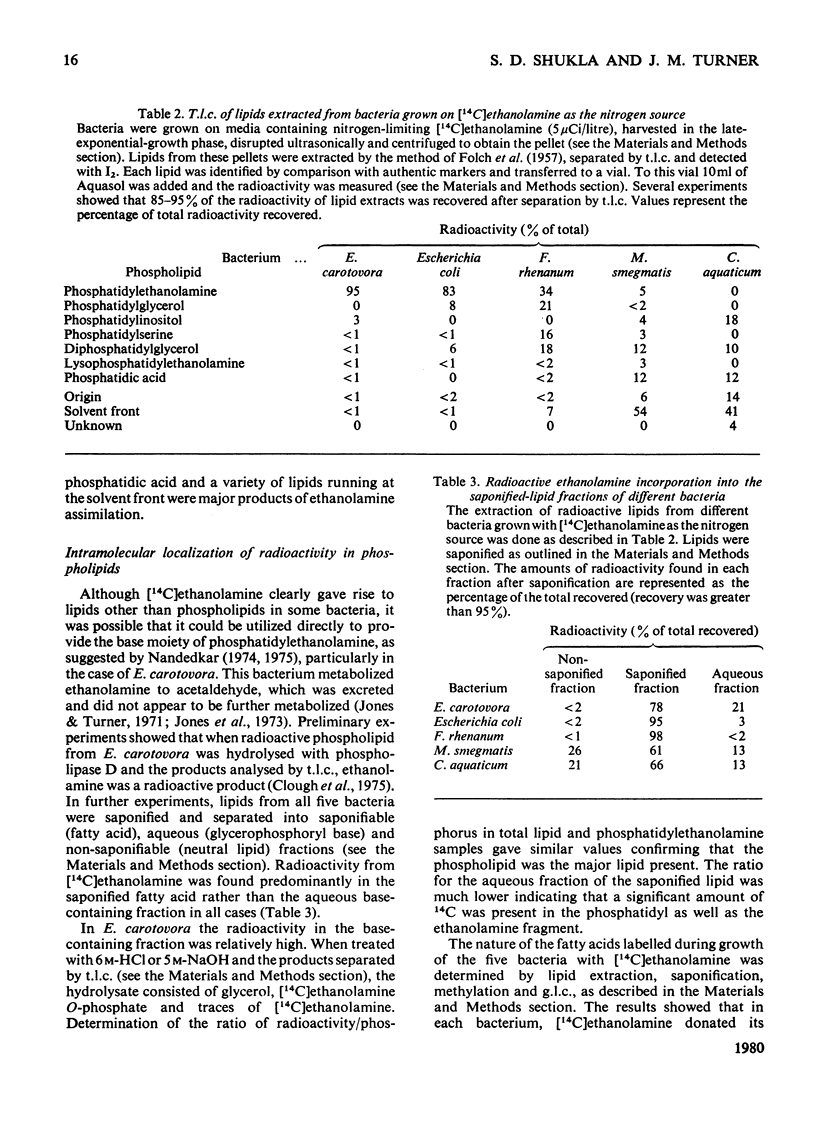
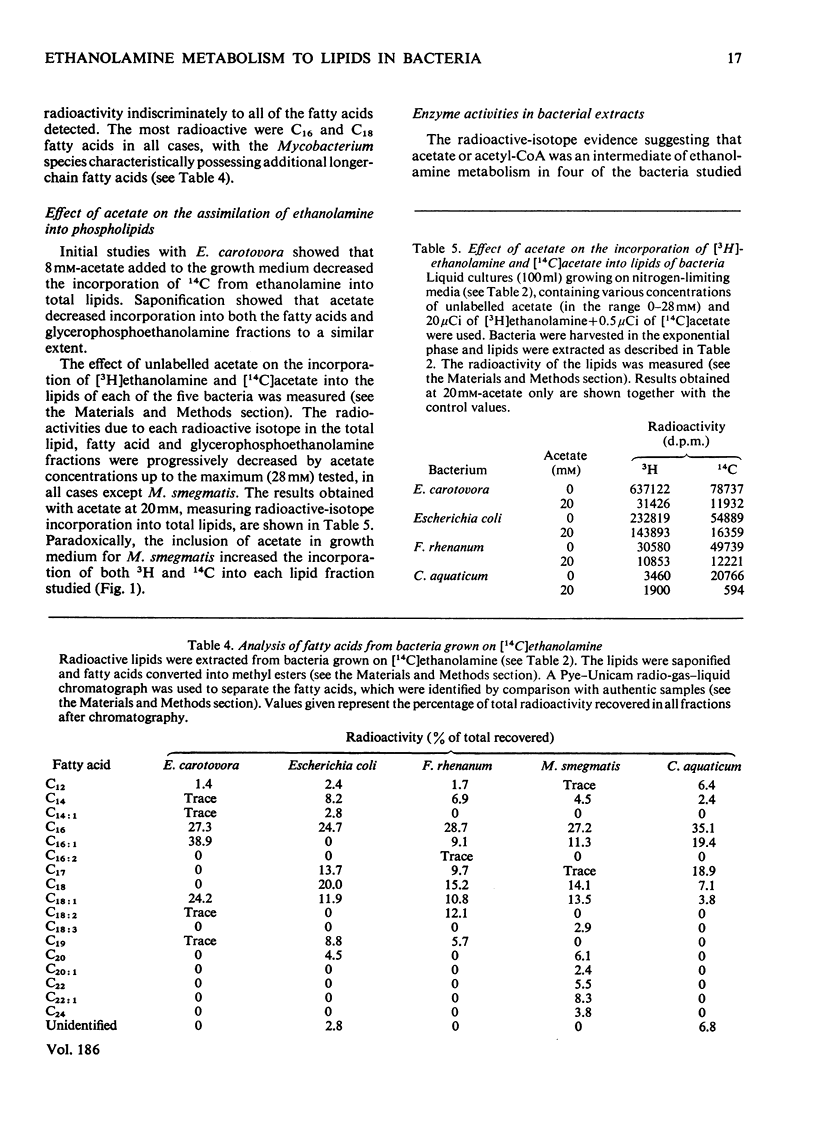
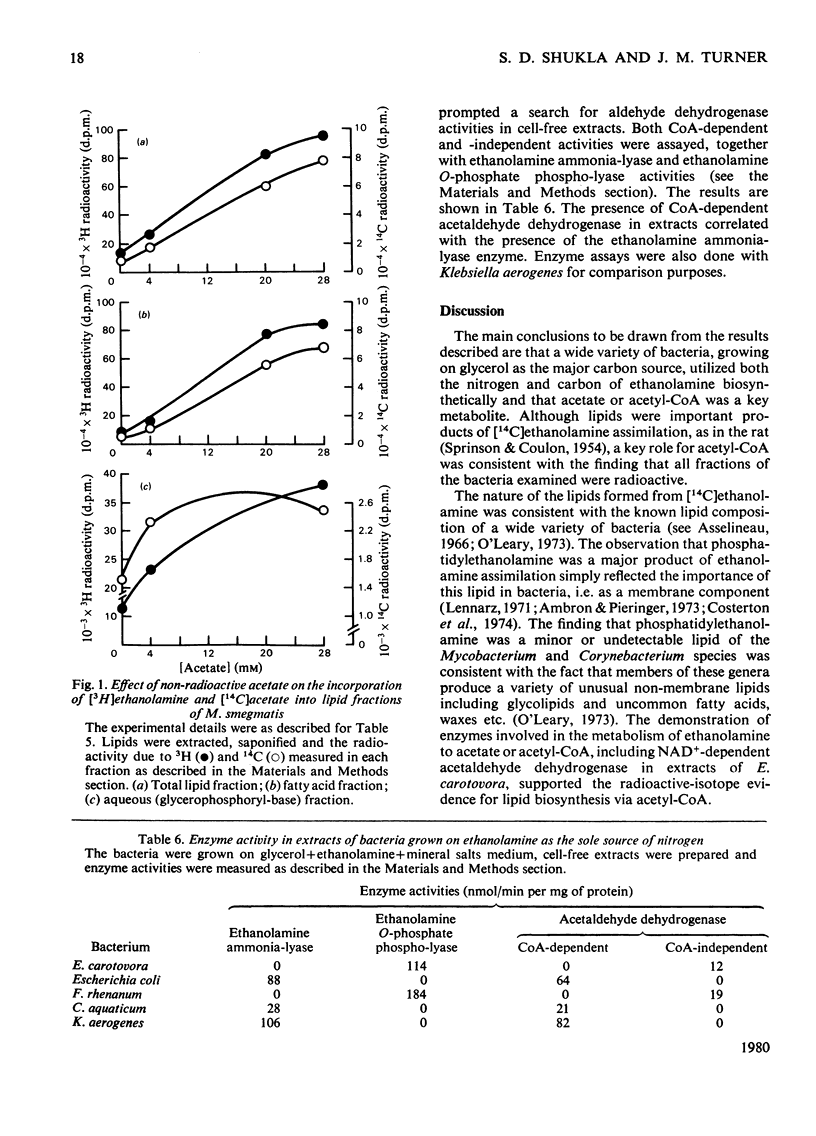
1. Ten bacteria utilizing [2-14C]ethanol-2-amine as the sole or major source of nitrogen for growth on glycerol + salts medium incorporated radioactivity into a variety of bacterial substances. A high proportion was commonly found in lipid fractions, particularly in the case of Erwinia carotovora. 2. Detailed studies of [14C]ethanolamine incorporation into lipids by five bacteria, including E. carotovora, showed that all detectable lipids were labelled. Even where phosphatidylethanolamine was the major lipid labelled, radioactivity was predominantly in the fatty acid rather than the base moiety. The labelled fatty acids were identified in each case. 3. The addition of acetate to growth media decreased the incorporation of radioactivity from ethanolamine into both fatty acid and phosphatidyl-base fragments of lipids from all the bacteria except Mycobacterium smegmatis. Experiments with [3H]ethanolamine and [14C]acetate confirmed that unlabelled acetate decreased the incorporation of both radioactive isotopes into lipids, except in the case of M. smegmatis. 4. Enzyme studies suggested one of two metabolic routes between ethanolamine and acetyl-CoA for each of four bacteria. A role for ethanolamine O-phosphate was not obligatory for the incorporation of [14C]ethanolamine into phospholipids, but correlated with CoA-independent aldehyde dehydrogenase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell C. M., Scarlett F. A., Turner J. M. Ethanolamine catabolism by bacteria, including Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(3):495–497. doi: 10.1042/bst0040495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. M., Scarlett F. A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Control of formation and stability of partially purified ethanolamine ammonia-lyase in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):133–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. M., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Purification and properties of coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):555–563. doi: 10.1042/bj1750555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough H. B., Shukla S. D., Turner J. M. Biosynthetic utilization of ethanolamine by Erwinia carotovora. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):769–772. doi: 10.1042/bst0030769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Aminoacetone metabolism via 1-aminopropan-2-ol in Pseudomonas sp. N.C.I.B. 8858. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):263–276. doi: 10.1042/bj1380263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAKOBY W. B. Aldehyde oxidation. I. Dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):75–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A., Faulkner A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Metabolism of ethanolamine and 1-aminopropan-2-ol in species of Erwinia and the roles of amino alcohol kinase and amino alcohol o-phosphate phospho-lyase in aldehyde formation. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):959–968. doi: 10.1042/bj1340959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols via aldehydes. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Aug;67(3):379–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-67-3-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. 1-Aminopropan-2-ol and ethanolamine metabolism via propionaldehyde and acetaldehyde in a species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):167–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1340167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANFER J., KENNEDY E. P. METABOLISM AND FUNCTION OF BACTERIAL LIPIDS. II. BIOSYNTHESIS OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1720–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. The linkage of pyrophosphorylethanolamine to heptose in the core of Salmonella minnesota lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandedkar A. K. Biosynthesis of phosphatidyl ethanolamine in Mycobacterium 607. Biochem Med. 1975 Feb;12(2):116–122. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandedkar A. K. Report on the utilization of ethanolamine-1-14C by Mycobacterium 607. Biochem Med. 1974 Sep;11(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph F. B., Purich D. L., Fromm H. J. Coenzyme A-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. I. Partial purification, properties, and kinetic studies of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5539–5545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRINSON D. B., COULON A. The precursors of sphingosine in brain tissue. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett F. A., Turner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino alcohols. Ethanolamine catabolism mediated by coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jul;95(1):173–176. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. M., Lambert P. A., Poxton I. R. The uptake of choline by Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Dec;109(2):313–317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuner J. M. Microbial metabolism of amino ketones. Aminoacetone formation from 1-aminopropan-2-ol by a dehydrgenase in Escerichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj0990427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


