Abstract
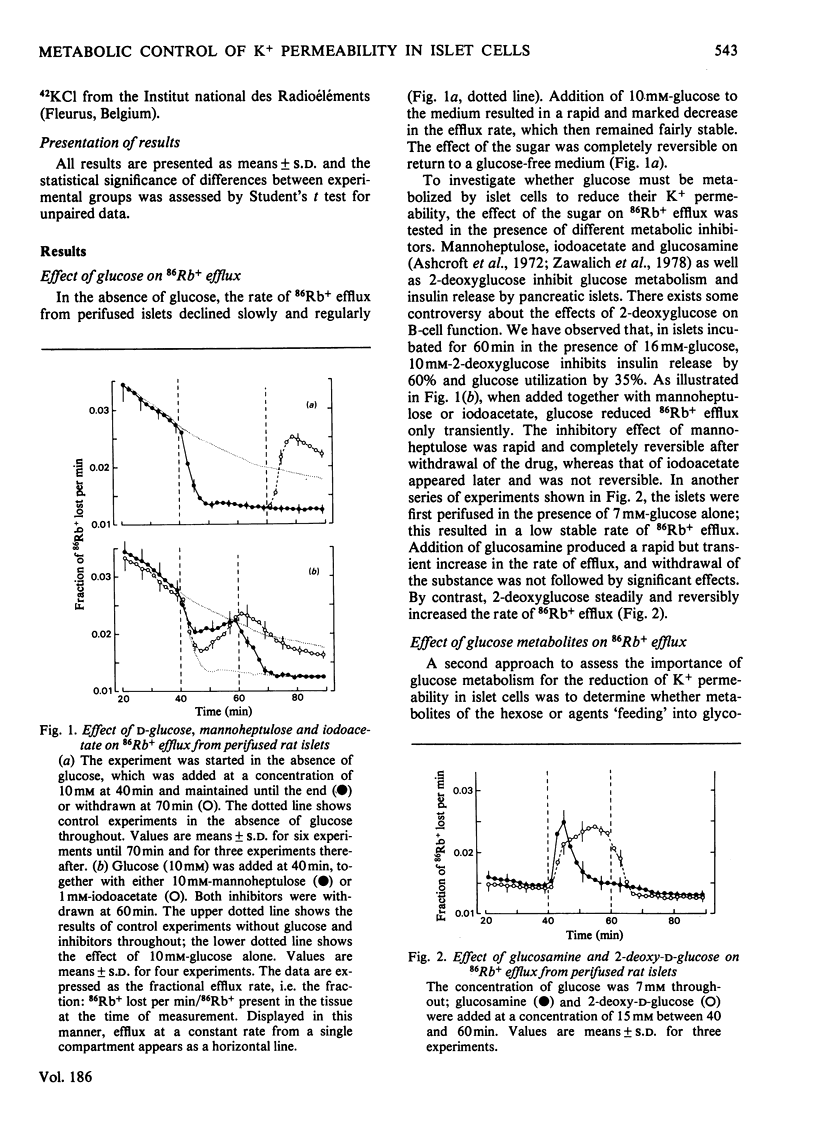
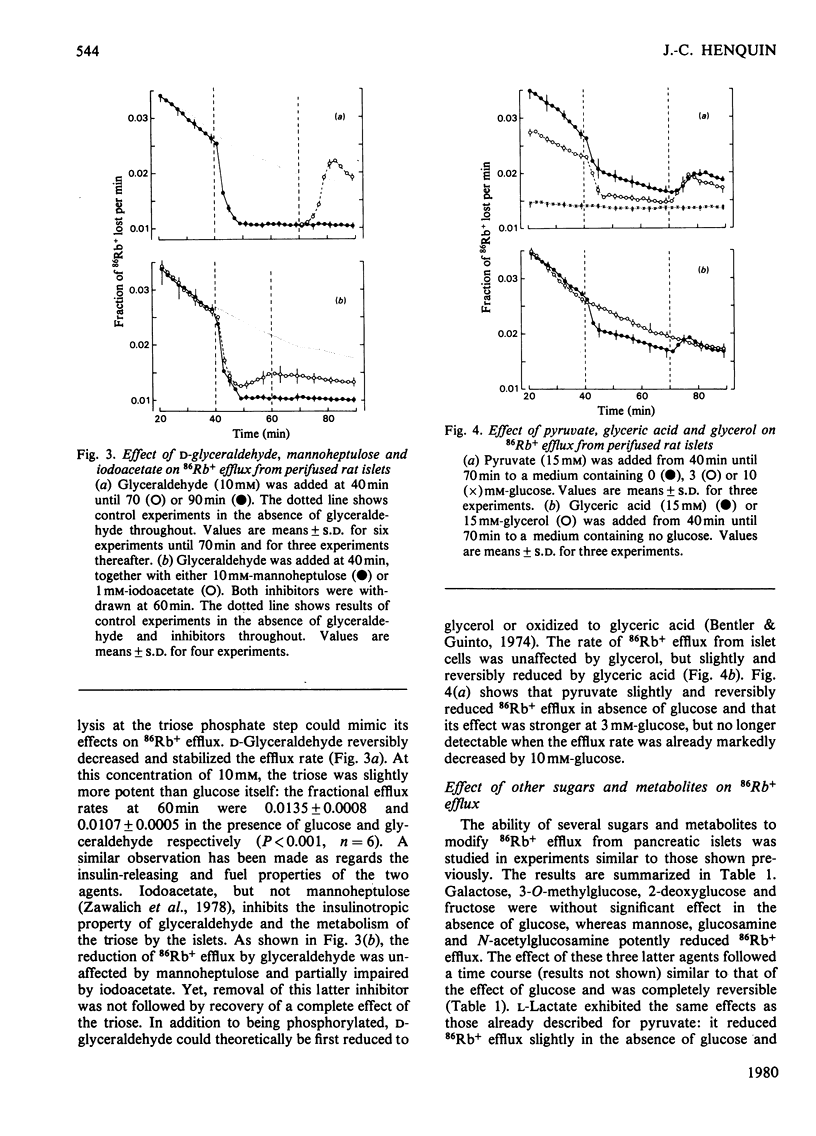
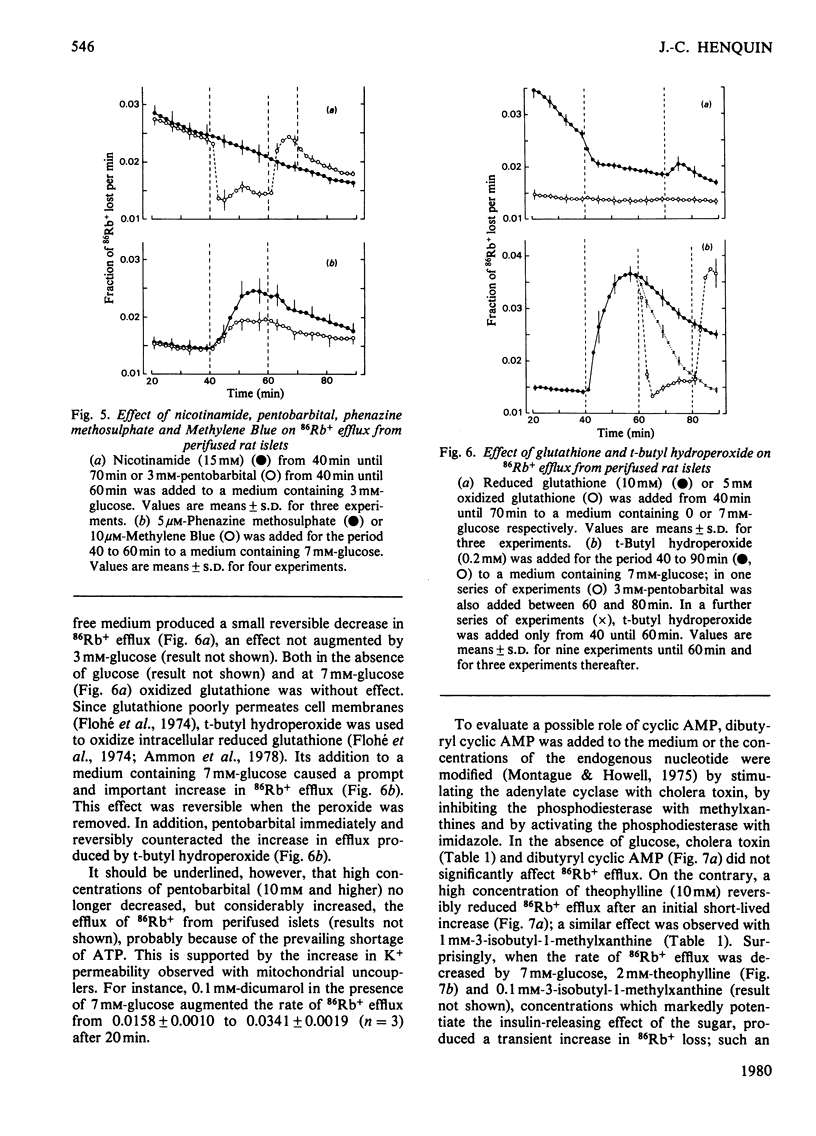
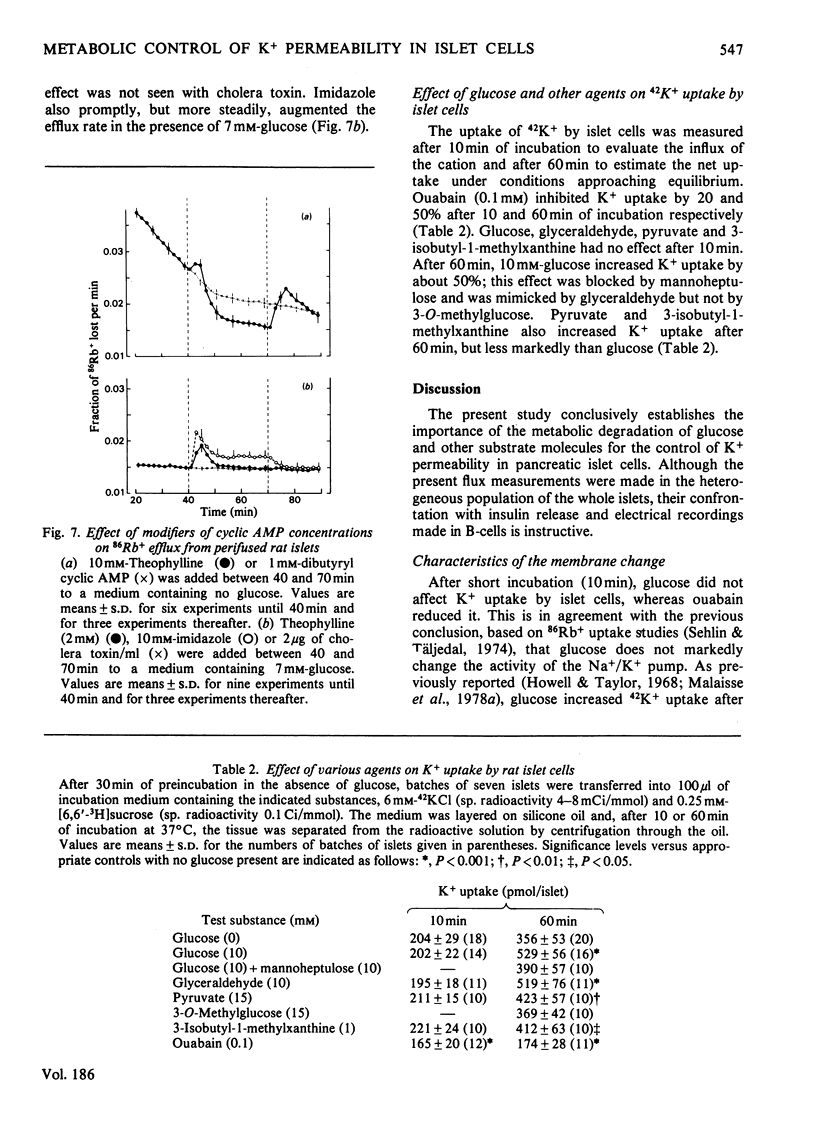
The K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells was studied by monitoring the efflux of 86Rb+ (used as tracer for K+) from perifused rat islets and measuring the uptake of 42K+. Glucose markedly and reversibly decreased 86Rb+ efflux from islet cells and this effect was antagonized by inhibitors of the metabolic degradation of the sugar, i.e. mannoheptulose, iodoacetate, glucosamine and 2-deoxyglucose. Among glucose metabolites, glyceraldehyde reduced the K+ permeability even more potently than did glucose itself; pyruvate and lactate alone exhibited only a small effect, but potentiated that of glucose. Other metabolized sugars, like mannose, glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine, also decreased 86Rb+ efflux from islet cells. Fructose was effective only in the presence of glucose. Non-metabolized sugars like galactose, 2-deoxyglucose and 3-O-methylglucose had no effect. The changes in K+ permeability by agents known to modify the concentrations of nicotinamide nucleotides, glutathione or ATP in islet cells were also studied. Increasing NAD(P)H concentrations in islet cells by pentobarbital rapidly and reversibly reduced 86Rb+ efflux; exogenous reduced glutathione produced a similar though weaker effect. By contrast, oxidizing nicotinamide nucleotides with phenazine methosulphate or Methylene Blue, or oxidizing glutathione by t-butyl hydroperoxide increased the K+ permeability of islet cells. Uncoupling the oxidative phosphorylations with dicumarol also augmented 86Rb+ efflux markedly. In the absence of glucose, but not in its presence, methylxanthines reduced 86Rb+ efflux from the islets; such was not the case for cholera toxin or dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Glucose and glyceraldehyde had no effect on 42K+ uptake after a short incubation (10min), but augmented it after 60min; the effect of glucose was suppressed by mannoheptulose and not mimicked by 3-O-methylglucose. The results clearly establish the importance of the metabolic degradation of glucose and other substrates for the control of the K+ permeability in pancreatic islet cells and support the concept that a decrease in the K+ permeability represents a major step of the B-cell response to physiological stimulation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. P., Patel T. N., Steinke J. The role of the pentose phosphate shunt in glucose induced insulin release: in vitro studies with 6-aminonicotinamide, methylene blue, NAD + , NADH, NADP + , NADPH and nicotinamide on isolated pancreatic rat islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):352–367. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Hedeskov C. J., Randle P. J. Glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):143–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1180143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. The control of insulin release by sugars. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;41:117–139. doi: 10.1002/9780470720233.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. The pentose cycle and insulin release in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1260525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Randle P. J. Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1320223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-converting enzymes and adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase in some tissues and organs of New Zealand obese mice with special reference to the enzyme pattern of the pancreatic islets. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Sep;23(9):660–665. doi: 10.1177/23.9.240882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Guinto E. The reduction of glyceraldehyde by human erythrocytes. L-hexonate dehydrogenase activity. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1258–1264. doi: 10.1172/JCI107672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. Diabetes mellitus--a disorder of cellular information transmission? Horm Metab Res. 1970 Jul;2(4):246–249. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Lawecki J., Pictet R., Grodsky G. M. Insulin secretion. Interrelationships of glucose, cyclic adenosine 3:5-monophosphate, and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6134–6140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):66–78. doi: 10.1042/bj0930066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Pancreatic islet cells: effects of monosaccharides, glycolytic intermediates and metabolic inhibitors on membrane potential and electrical activity. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):459–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Production of highly purified choleragen and choleragenoid. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):63+–63+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODSKY G. M., BATTS A. A., BENNETT L. L., VCELLA C., MCWILLIAMS N. B., SMITH D. F. EFFECTS OF CARBOHYDRATES ON SECRETION OF INSULIN FROM ISOLATED RAT PANCREAS. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:638–644. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Cerasi E. Effect of hexoses and mannoheptulose on cyclic AMP accumulation and insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):36–50. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Cerasi E. Stimulation by D-glucose of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate accumulation and insulin release in isolated pancreatic islets of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4196–4201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Danielsson A. Adenosine triphosphate levels of mammalian pancreatic B cells after stimulation with glucose and hypoglycemic sulfonylureas. Diabetes. 1969 Aug;18(8):509–516. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.8.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Idahl L. A., Lernmark A., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic beta-cell recognition of insulin secretagogues: does cyclic AMP mediate the effect of glucose? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3405–3409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cationic environment and dynamics of insulin secretion. III. Effect of the absence of potassium. Diabetologia. 1974 Dec;10(6):789–794. doi: 10.1007/BF01219542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cobalt inhibition of insulin secretion and calcium uptake by isolated rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1669–1677. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P., Preissler M. 9-Aminoacridine- and tetraethylammonium-induced reduction of the potassium permeability in pancreatic B-cells. Effects on insulin release and electrical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 1;587(4):579–592. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Valinomycin inhibition of insulin release and alteration of the electrical properties of pancreatic B cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Tetraethylammonium potentiation of insulin release and inhibition of rubidium efflux in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):551–556. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Potassium ions and the secretion of insulin by islets of Langerhans incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):17–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1080017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C. The stimulus secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVII. Effect of glucose on K+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Mar 20;373(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00580830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Koser M., Herchuelz A. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Metabolism of alpha- and beta-D-glucose in isolated islets. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5936–5943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquié G. Preventive effect of gliclazide on experimental atherosclerosis in rabbits. Diabetologia. 1978 Apr;14(4):269–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01219427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Ellerman J. E., Krzanowski J., Kotler-Brajtburg J., Landgraf R., Fertel R. The dual function of glucose in islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1007–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Weaver D. C., Roth C. E., Fink C. J., Swanson J. A., Lacy P. E. Characterization of the uptake of the methylxanthines theophylline and caffeine in isolated pancreatic islets and their effect on D-glucose transport. Endocrinology. 1977 Dec;101(6):1701–1708. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-6-1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P. Electrical characteristics of the beta-cells in pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):757–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Howell S. L. Cyclic AMP and the physiology of the islets of Langerhans. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:201–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Christians J., von Kriegstein E., Poser W., Hasselblatt A. Effect of carbohydrates upon fluorescence of reduced pyridine nucleotides from perifused isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00461692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Taljedal I. B. Glucose-induced decrease in Rb+ permeability in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):635–636. doi: 10.1038/253635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of rubidium and sodium in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):505–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Ashcroft S. J. Effects of phosphoenolpyruvate, other glycolytic intermediates and methylxanthines on calcium uptake by a mitochondrial fraction from rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Sep;15(3):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00421235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D., Cooperstein S. J., Lazarow A. Stimulation of insulin secretion by pyridine nucleotides. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1380–1384. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Dye E. S., Rognstad R., Matschinsky F. M. On the biochemical nature of triose- and hexose-stimulated insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2027–2034. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Karl R. C., Ferrendelli J. A., Matschinsky F. M. Factors governing glucose induced elevation of cyclic 3'5' AMP levels in pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00422327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


