Abstract
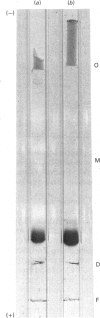
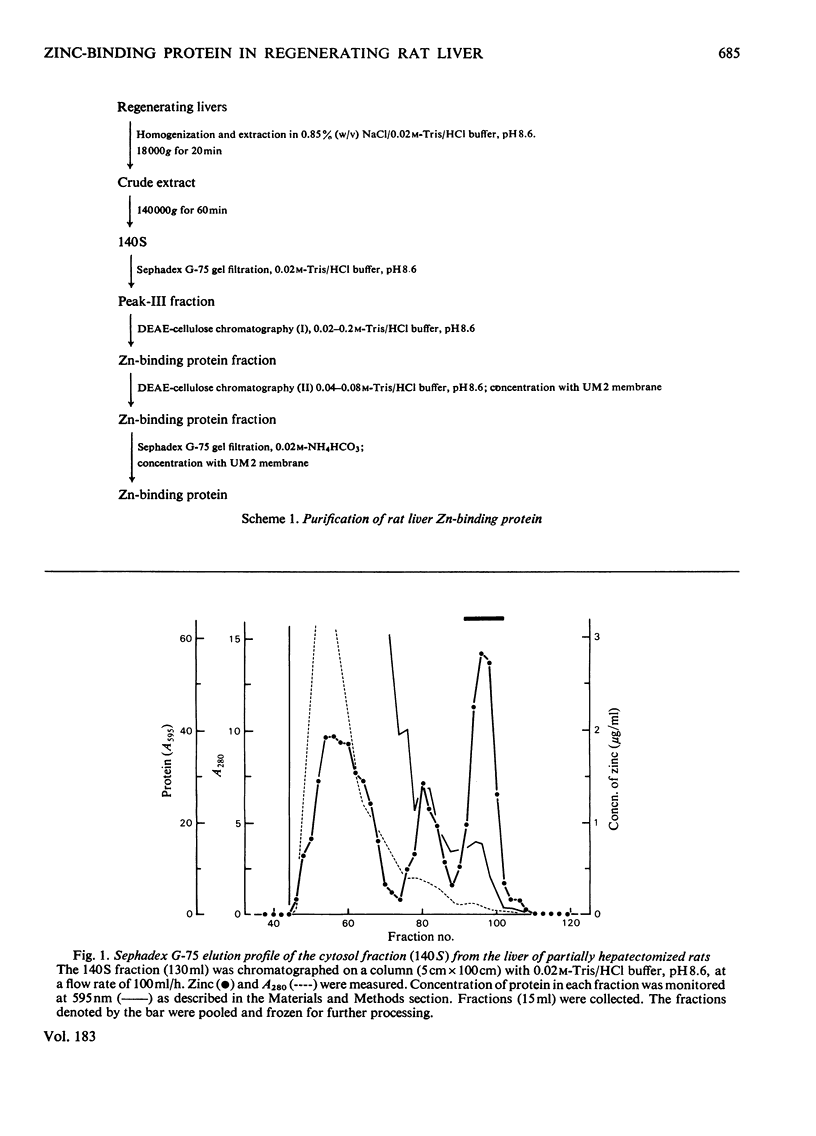
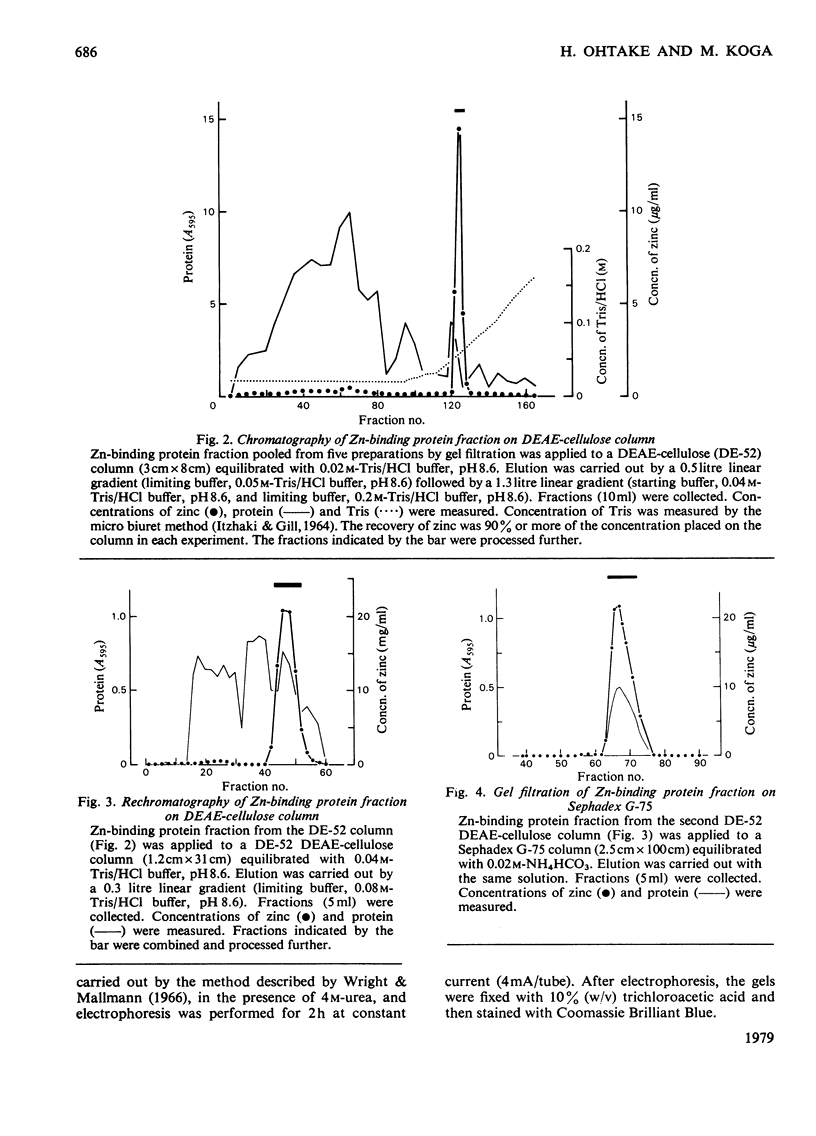
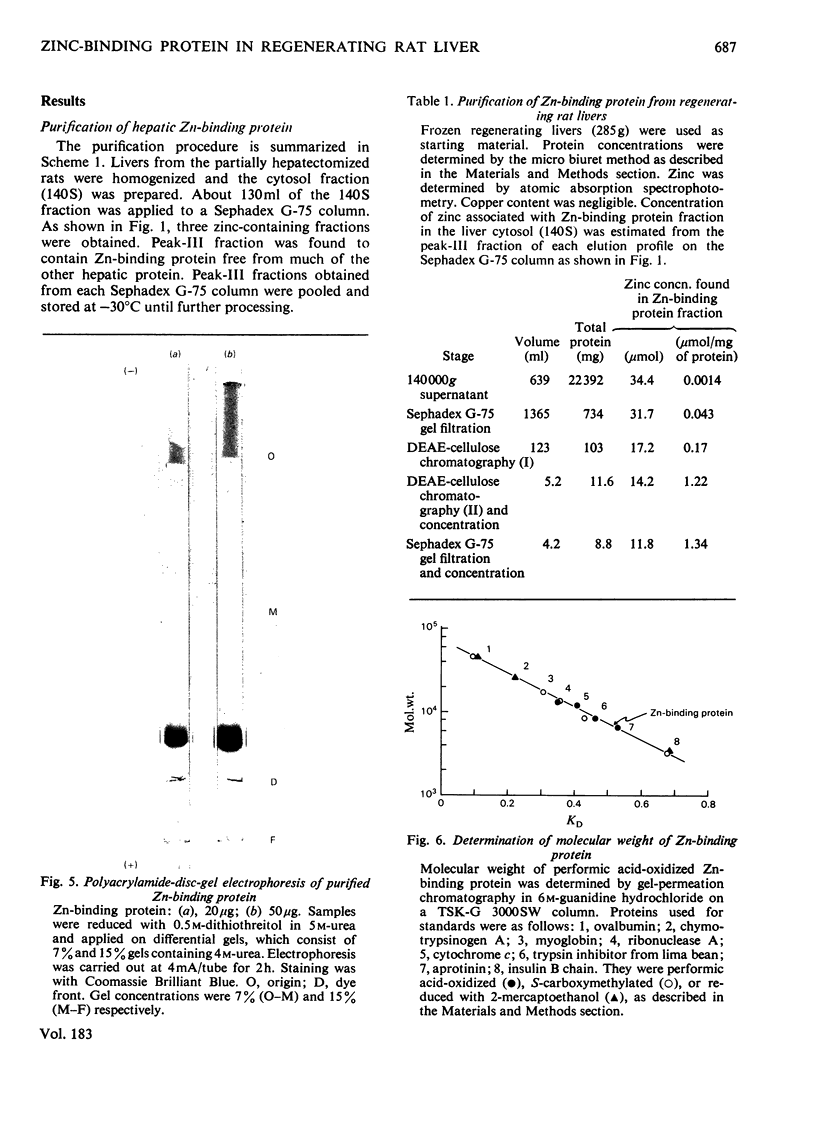
Zn-binding protein in liver of the partially hepatectomized rat was purified by column chromatography on Sephadex G-75 and DEAE-cellulose. Homogeneity was judged by polyacrylamide-disc-gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight determined by gel-permeation chromatography in 6 M-guanidine hydrochloride was 6700. This value is in good agreement with the molecular weight calculated from the amino acid composition, which was 6073. Zn-binding protein was composed of 61 amino acid residues, and the distinctive features include an extremely high content of cysteine, which accounted for one-third of the total amino acid residues, and an absolute absence of aromatic amino acids as well as of histidine, leucine and arginine. The amino acid composition was similar to that of the metallothioneins previously isolated from rat liver and mouse liver. These observations suggest that the Zn-binding protein can be classified as a type of metallothionein. Zn-binding protein contained 8.2g-atoms of zinc per mol and traces of copper, but no cadmium. The molar ratio of thiol groups to zinc was calculated to be 2.5:1. Possible roles of this Zn-binding protein in the transport and storage of zinc in the liver are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchmeier W., Christen P. Chemical evidence for syncatalytic conformational changes in aspartate aminotransferase. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80446-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner I., Davies N. T. The induction of metallothionein in rat liver by zinc injection and restriction of food intake. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):733–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1490733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R. H., Kägi J. H. Human hepatic metallothioneins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. Alkylation and identification of the histidine residues at the active site of ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino F. J., Barker R. Examination of the dissociation of multichain proteins in guanidine hydrochloride by membrane osmometry. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2207–2217. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters J. K. The role of zinc ions in the transformation of lymphocytes by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):133–139. doi: 10.1042/bj1300133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIOKA M., LIEBERMAN I. A ZN++ REQUIREMENT FOR SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1164–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. L., Cousins R. J. Degradation of hepatic zinc-thionein after parenteral zinc administration. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj1600583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuwa K., Wacker W. E., Druyan R., Bartholomay A. F., Vallee B. L. NUCLEIC ACIDS AND METALS, II: TRANSITION METALS AS DETERMINANTS OF THE CONFORMATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Oct;46(10):1298–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.10.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H. A method for determining the sedimentation constant of material of low molecular weight: studies on oxidation products of insulin. Biochem J. 1949;44(2):163–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S. AMINO-ACID SEQUENCE OF BOVINE CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN-A. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1284–1287. doi: 10.1038/2011284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITZHAKI R. F., GILL D. M. A MICRO-BIURET METHOD FOR ESTIMATING PROTEINS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Konishi K., Yokoyama M., Konishi K. High-speed gel filtration of polypeptides in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biochem. 1979 Sep;86(3):639–642. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3460–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Berger C., Vallee B. L., Kägi J. H. Amino-acid sequence of equine renal metallothionein-1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Himmelhoch S. R., Whanger P. D., Bethune J. L., Vallee B. L. Equine hepatic and renal metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3537–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN I., OVE P. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and its inhibition in mammalian cells cultured from the animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1634–1642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. H., Deagen J. T., Whanger P. D., Weswig P. H. Biological function of metallothionein. V. Its induction in rats by various stresses. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E282–E285. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake H., Hasegawa K., Koga M. Zinc-binding protein in the livers of neonatal, normal and partially hepatectomized rats. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):999–1005. doi: 10.1042/bj1740999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido P., Kägi J. H., Vallee B. L. Isolation and some properties of human metallothionein. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1768–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Mammalian zinc homeostasis: requirement for RNA and metallothionein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in animal cells by ethylene diamine tetraacetate, and its reversal by zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH D. G., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. The sequence of amino acid residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease: revisions and confirmations. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstead H. H., Rinaldi R. A. Impairment of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by dietary zinc deficiency in the rat. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Feb;73(1):81–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh Z. A., Lucis O. J. Isolation of cadmium-binding proteins. Experientia. 1971 Sep 15;27(9):1024–1025. doi: 10.1007/BF02138857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobocinski P. Z., Canterbury W. J., Jr, Mapes C. A., Dinterman R. E. Involvement of hepatic metallothioneins in hypozincemia associated with bacterial infection. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):E399–E406. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.4.E399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo H., Kino K., Nakajima H., Hata A., Huang I. Y., Yoshida A. Mouse liver metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4172–4174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTLEY J., LAMBETH J. Protein determination on the basis of copper-binding capacity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:364–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. Binding of cadmium ions by rat liver and kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2751–2765. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Rajagopalan K. V. Purification and some properties of Cd-binding protein from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. L., Jr, Mallmann W. L. Differential disc electrophoresis of serum proteins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):22–27. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]