Abstract
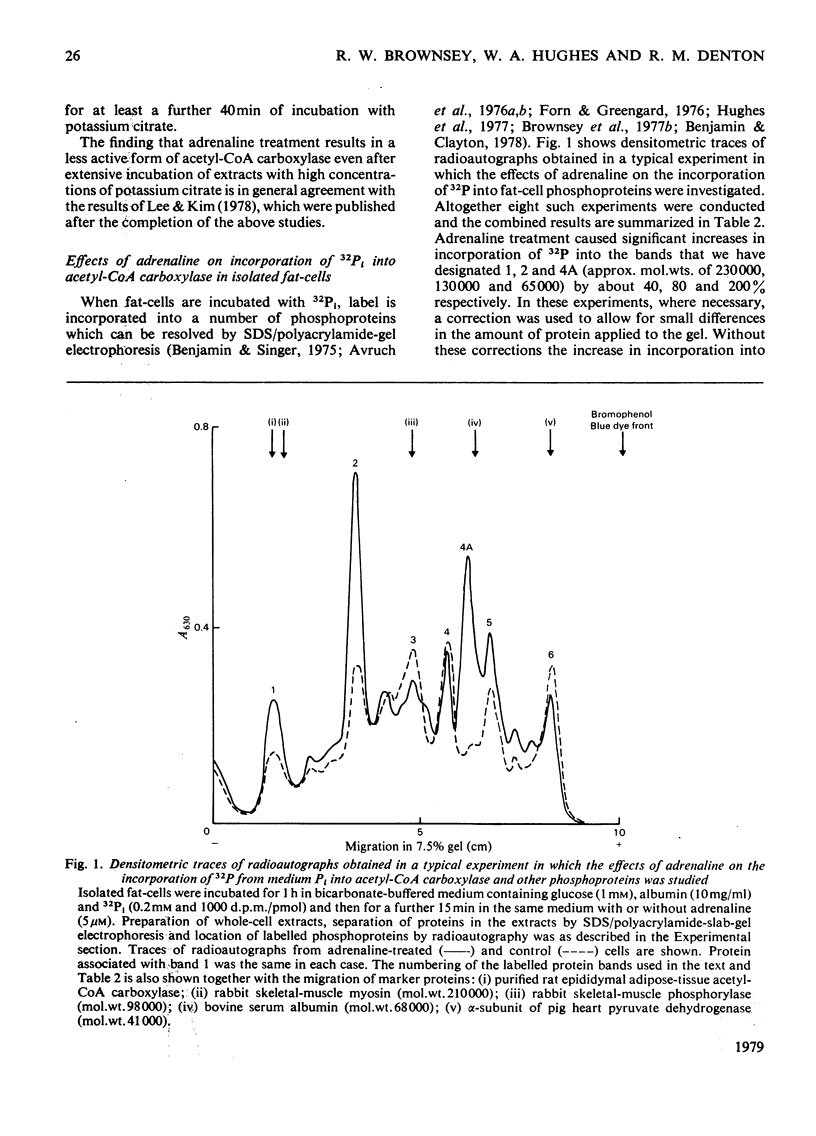
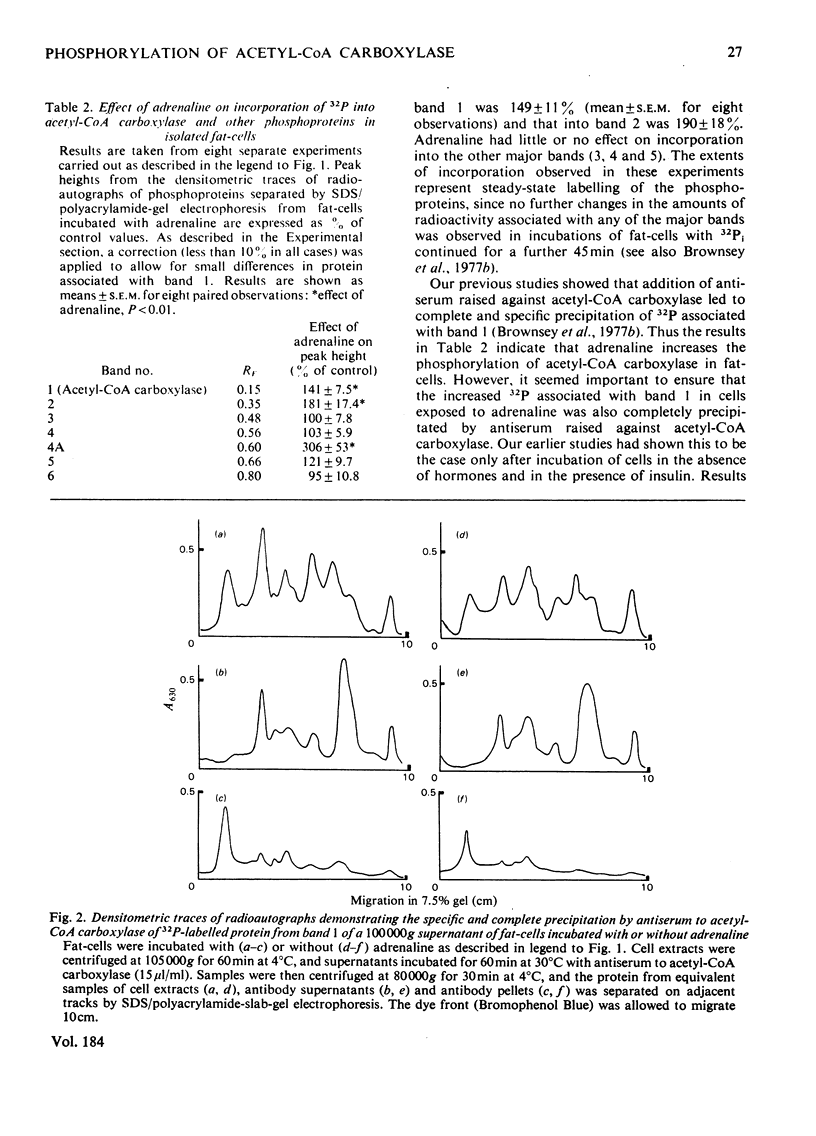
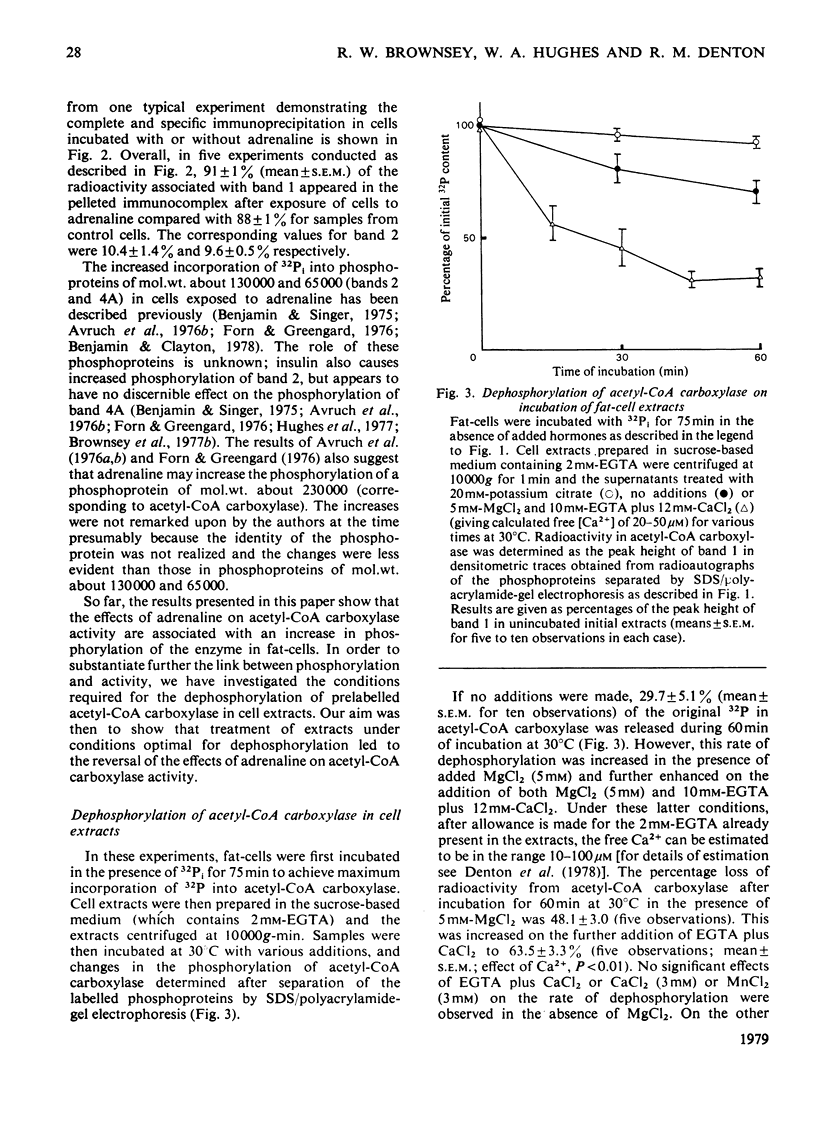
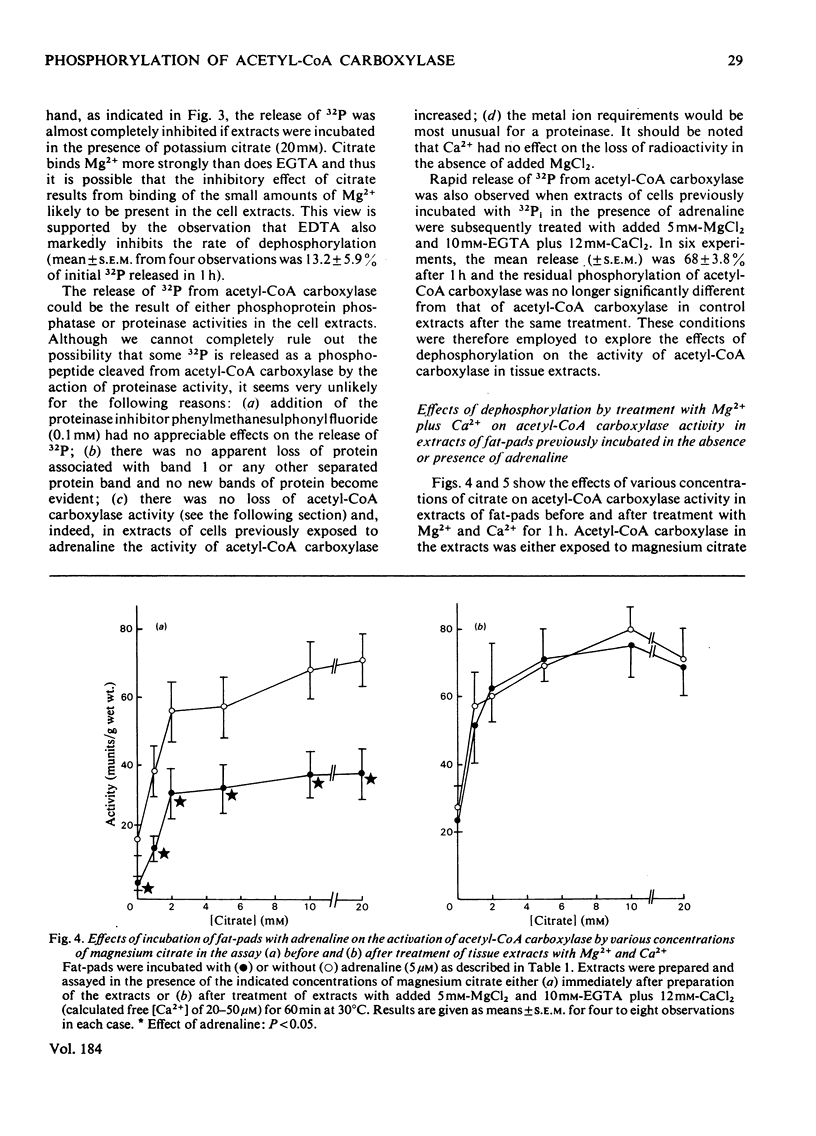
1. Exposure of rat epididymal fat-pads or isolated fat-cells to adrenaline results in a decrease in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity measured both in initial extracts and in extracts incubated with potassium citrate; in addition the concentration of citrate required to give half-maximal activation may also be increased. 2. Incorporation of 32Pi into acetyl-CoA carboxylase within intact fat-cells was investigated and evidence is presented that adrenaline increases the extent of phosphorylation of the enzyme. 3. Dephosphorylation of 32P-labelled acetyl-CoA carboxylase was studied in cell extracts. The rate of release of 32P is increased by 5mM-MgCl2 plus 10--100 microM-Ca2+, whereas it is inhibited by the presence of bivalent metal ion chelators such as EDTA and citrate. 4. The effects of adrenaline on the kinetic properties of acetyl-CoA carboxylase disappear if pad or cell extracts are treated with Mg2+ and Ca2+ under conditions that also lead to dephosphorylation of the enzyme. 5. The results of this study represent convincing evidence that adrenaline inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase in adipose-tissue preparations by increasing the degree of phosphorylation of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Leone G. R., Martin D. B. Effects of epinephrine and insulin on phosphopeptide metabolism in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1511–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Leone G. R., Martin D. B. Identification and subcellular distribution of adipocyte peptides and phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1505–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. B., Clayton N. L. Action of insulin and catecholamines on the phosphorylation of proteins associated with the cytosol, membranes, and "fat cake" of rat fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1700–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. B., Singer I. Actions of insulin, epinephrine, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate on fat cell protein phosphorylations. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate dependent and independent mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3301–3309. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Demonstration of the phosphorylation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase within intact rat epididymal fat-cells. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj1680441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Kim K. H. Differential effects of metabolites on the active and inactive forms of hepatic acetyl CoA carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):490–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Kim K. H. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):478–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. A., Nielsen R. C., Hawkins R. A., Mehlman M. A., Lakshmanan M. R., Veech R. L. Effect of glucagon on hepatic malonyl coenzyme A concentration and on lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4421–4424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Richards D. A., Chin J. G. Calcium ions and the regulation of NAD+-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from the mitochondria of rat heart and other tissues. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1760899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R., Bridges B., Brownsey R., Evans G., Hughes W., Stansbie D. Regulation of the conversion of glucose into fat in white adipose tissue by insulin [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):894–900. doi: 10.1042/bst0050894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Regulation by lipolytic and antillipolytic compounds of the phosphorylation of specific proteins in isolated intact fat cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Oct;176(2):721–733. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of adipose-tissue acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase by changes in the polymeric state of the enzyme. The role of long-chain fatty acyl-Coenzyme A thioesters and citrate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):365–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1420365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Insulin and the regulation of adipose tissue acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1320509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. Purification and physicochemical properties of fatty acid synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):25–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis: simple procedure for the purification of acetyl CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland, and its phosphorylation by endogenous cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent protein kinase activities. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 1;91(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. D., Moss J., Polakis S. E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):139–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Effect of epinephrine on acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat epididymal fat tissue. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8157–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Evidence for interconversion between active and inactive forms of enzyme by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1748–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lent B. A., Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Stimulation of phosphorylation and subsequent inactivation of liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase by cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and effect on the structure of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8149–8156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiwara H., Tanabe T., Nikawa J., Numa S. Inhibition of rat-liver acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase by palmitoyl-coenzyme A. Formation of equimolar enzyme-inhibitor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekala P. H., Meredith M. J., Tarlow D. M., Lane M. D. Multiple phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in chick liver cells. A cyclic AMP-independent process. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5267–5269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Denton R. M., Bridges B. J., Randle P. J. Exchangeable and total calcium pools in mitochondria of rat epididymal fat-pads and isolated fat-cells. Role in the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):209–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1540209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Brownsey R. W., Crettaz M., Denton R. M. Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1600413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Betts S. A., Manning R., Mayer R. J. Absorption of antisera for studies on specific enzyme turnover. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):355–362. doi: 10.1042/bj1590355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. A., Tarlow D. M., Lane M. D. Mechanism for acute control of fatty acid synthesis by glucagon and 3':5'-cyclic AMP in the liver cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1497–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Kowaloff E. M., Avruch J. Glucagon regulation of protein phosphorylation. Identification of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase as a substrate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


