Abstract
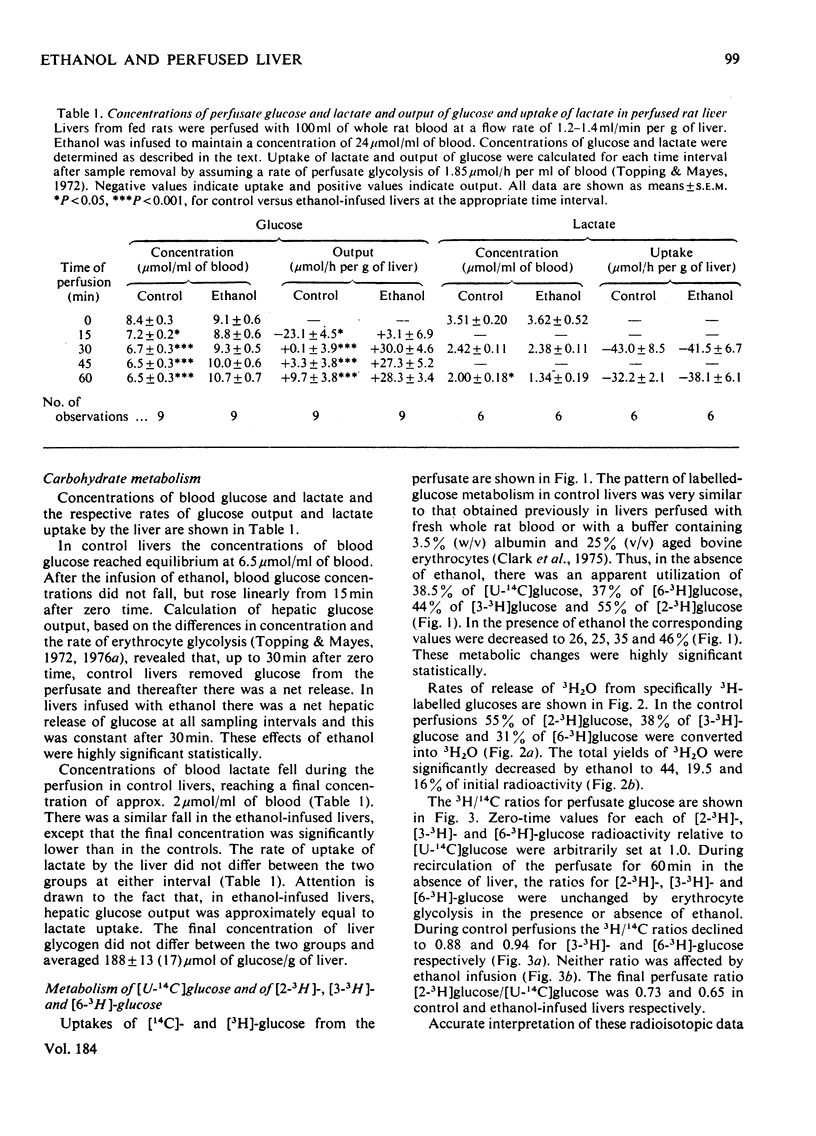
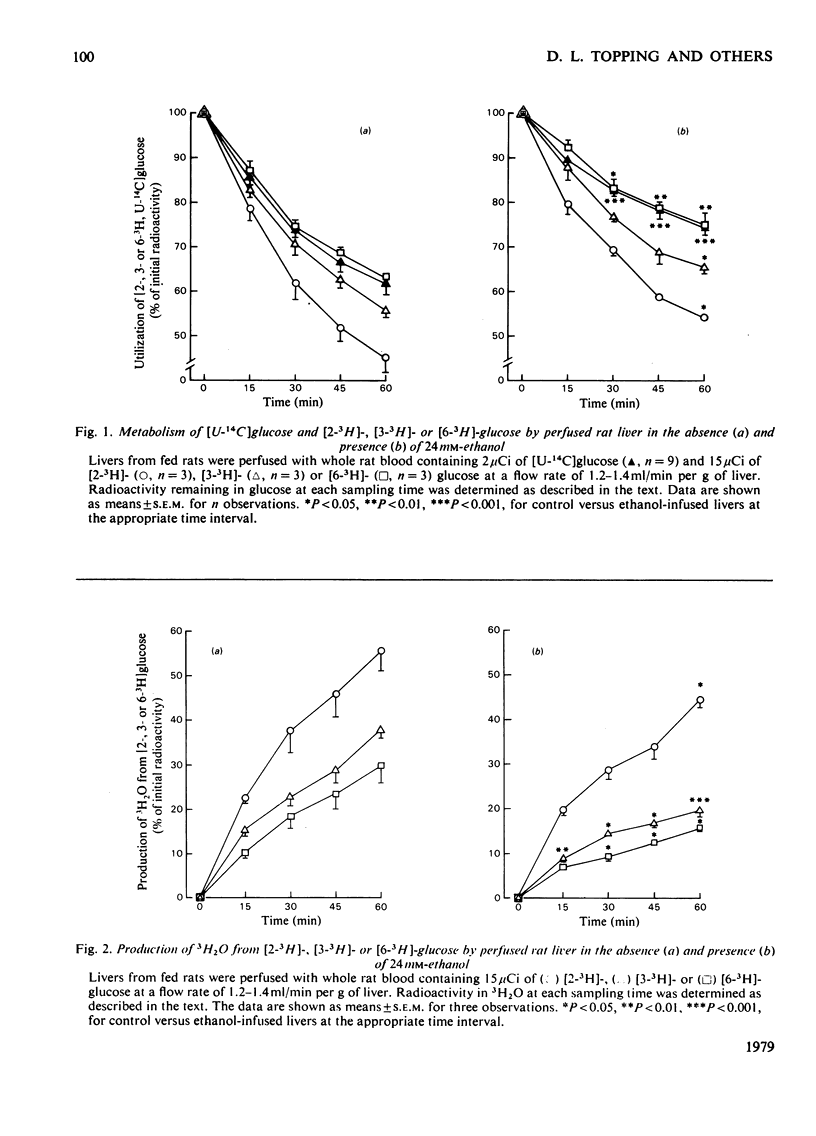
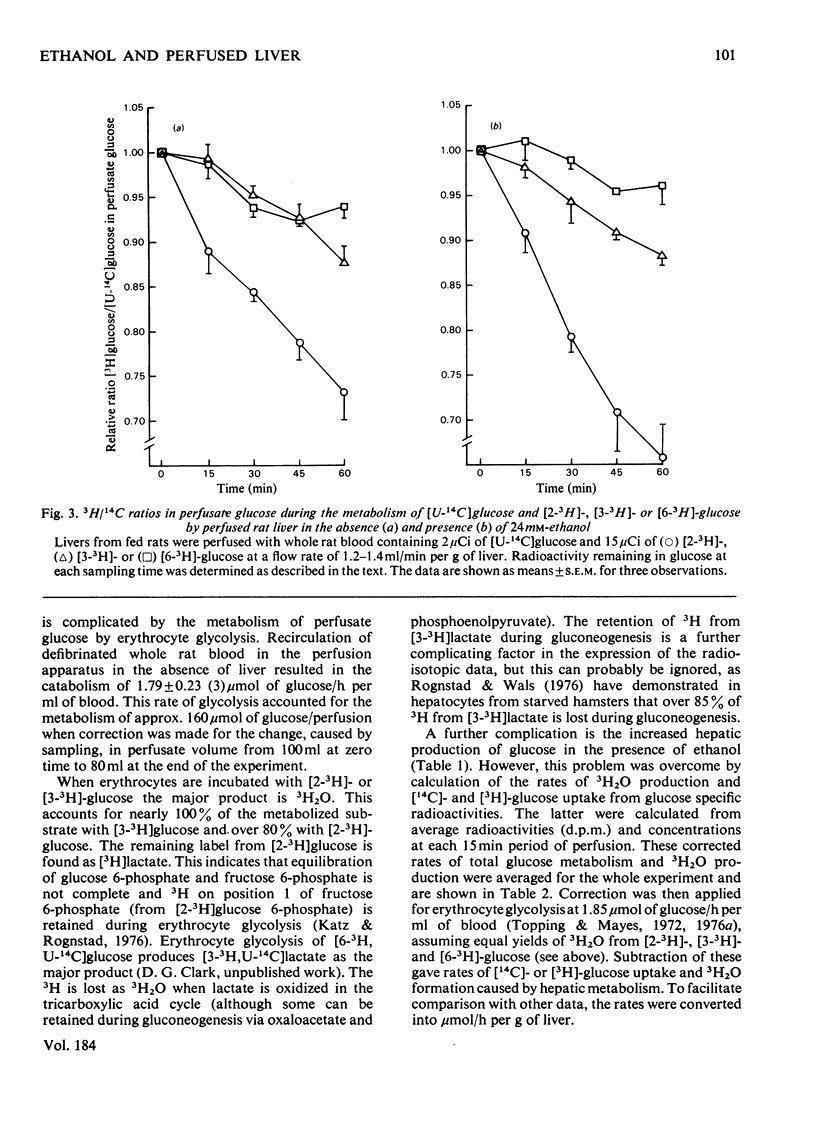
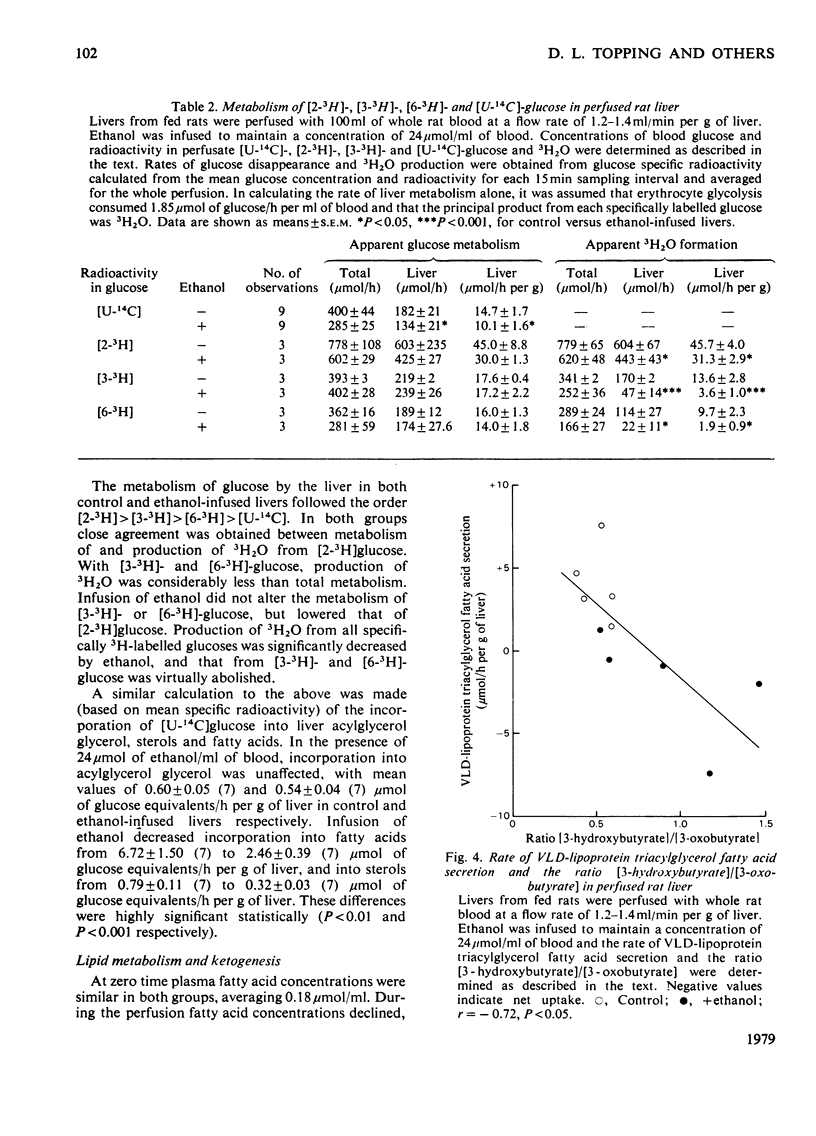
1. Livers from fed rats were perfused in situ with whole rat blood containing glucose labelled uniformly with 14C and specifically with 3H at positions 2, 3 or 6. 2. When ethanol was infused at a concentration of 24μmol/ml of blood the rate of utilization was 2.8μmol/min per g of liver. 3. Ethanol infusion raised perfusate glucose concentrations and caused a 2.5-fold increase in hepatic glucose output. 4. Final blood lactate concentrations were decreased in ethanol-infused livers, but the mean uptake of lactate from erythrocyte glycolysis was unaffected. 5. Production of ketone bodies (3-hydroxybutyrate+3-oxobutyrate) and the ratio [3-hydroxybutyrate]/[3-oxobutyrate] were raised by ethanol. 6. Formation of 3H2O from specifically 3H-labelled glucoses increased in the order [6-3H]<[3-3H]<[2-3H]. Production of 3H2O from [2-3H]glucose was significantly greater than that from [3-3H]glucose in both control and ethanol-infused livers. Ethanol significantly decreased 3H2O formation from all [3H]glucoses. 7. Liver glycogen content was unaffected by ethanol infusion. 8. Production of very-low-density lipoprotein triacylglycerols was inhibited by ethanol and there was a small increase in liver triacylglycerols. Very-low-density-lipoprotein secretion was negatively correlated with the ratio [3-hydroxybutyrate]/[3-oxobutyrate]. Perfusate fatty acid concentrations and molar composition were unaffected by perfusion with ethanol. 9. Ethanol decreased the incorporation of [U-14C]glucose into fatty acids and cholesterol. 10. The concentration of total plasma amino acids was unchanged by ethanol, but the concentrations of alanine and glycine were decreased and ([glutamate]+[glutamine]) was raised. 11. It is proposed that the observed effects of ethanol on carbohydrate metabolism are due to an increased conversion of lactate into glucose, possibly by inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase. The increase in gluconeogenesis is accompanied by diminished substrate cycling at glucose–glucose 6-phosphate and at fructose 6-phosphate–fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams M. A., Cooper C. Mechanism of increased hepatic uptake of unesterified fatty acid from serum of ethanol-treated rats. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):47–54. doi: 10.1042/bj1560047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams M. A., Cooper C. Quantitative analysis of metabolism of hepatic triglyceride in ethanol-treated rats. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):33–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1560033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Rognstad R., Katz J. Isotopic evidence for futile cycles in liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1141–1148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90811-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Rognstad R., Katz J. Lipogenesis in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2028–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D., Lee D., Rognstad R., Katz J. Futile cycles in isolated perfused rat liver and in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):212–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. G., Bloxham D. P., Holland P. C., Lardy H. A. Estimation of the fructose 1,6-diphosphatase-phosphofructokinase substrate cycle and its relationship to gluconeogenesis in rat liver in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):279–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse J. R., Gerson C. D., DeCarli L. M., Lieber C. S. Role of acetate in the reduction of plasma free fatty acids produced by ethanol in man. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):509–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Hughes W. A. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and the hormonal regulation of fat synthesis in mammalian tissues. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(8):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Bridges B. J., Cooper R. H., Kerbey A. L., Pask H. T., Severson D. L., Stansbie D., Whitehouse S. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Oct 31;9(1):27–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01731731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Corbin J. G., Harper S. C. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. V. Effects of fasting, diabetes, and glucagon on lactate and endogenous metabolism in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4996–5003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Gluconeogenesis. Metabolism. 1972 Oct;21(10):945–990. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD J. B., WILLIAMS H. E., MORTIMORE G. E. Studies on the mechanism of ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:497–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI104738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Singer D. L., Arky R. A., Bleicher S. J., Anderson J. B., Silbert C. K. ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA. I. CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM OF PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL ALCOHOL HYPOGLYCEMIA AND THE EXPERIMENTAL REPRODUCTION OF THE SYNDROME WITH PURE ETHANOL. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42(7):1112–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI104797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. S., Mayes P. A. Comparison of the metabolism of chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants by the perfused liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):47–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1700047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunnet N., Quistorff B., Thieden H. I. Rate-limiting factors in ethanol oxidation by isolated rat-liver parenchymal cells. Effect of ethanol concentration, fructose, pyruvate and pyrazole. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Muñoz R., Santamaría A., García-Sáinz J. A., Piña E., Chagoya de Sánchez V. On the mechanism of ethanol-induced fatty liver and its reversibility by adenosine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauhonen V. P., Savolainen M. J., Hiltunen J. K., Hassinen I. E. Adaptive changes in gluconeogenic enzymes in rat liver and kidney during long-term ethanol ingestion. Metabolism. 1978 Oct;27(10):1557–1565. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Dunn A., Chenoweth M., Golden S. Determination of synthesis, recycling and body mass of glucose in rats and rabbits in vivo 3H-and 14C-labelled glucose. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;142(1):171–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1420171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondrup J., Grunnet N. The effect of acute and prolonged ethanol treatment on the contents of coenzyme A, carnitine and their derivatives in rat liver. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1320373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Freedland R. A., Hems R., Stubbs M. Inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by ethanol. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1120117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., DeCarli L. M. Hepatic microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system. In vitro characteristics and adaptive properties in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2505–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYES P. A. Absence of a relation between lipogenesis and ketogenesis in vivo. Nature. 1959 Feb 21;183(4660):540–541. doi: 10.1038/183540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie S. L., Tenaschuk D. Gas-liquid chromatography of N-heptafluorobutyryl isobutyl esters of amino acids. J Chromatogr. 1974 Oct 9;97(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes P. A., Felts J. M. Effect of haematocrit value and pO2 on the redox state and metabolism of the perfused liver. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):685–689. doi: 10.1042/bj1560685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes P. A., Topping D. L. Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by plasma free fatty acids: simultaneous studies on lipoprotein secretion, cholesterol synthesis, ketogenesis and gluconeogenesis. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;140(1):111–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1400111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mørland J., Flengsrud R., Prydz H., Svendsen L. Hepatic amino acid levels in rats after long-term ethanol feeding. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(3):423–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Crabtree B. Substrate cycles in metabolic regulation and in heat generation. Biochem Soc Symp. 1976;(41):61–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Gevers W. Control of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver and kidney cortex. Vitam Horm. 1967;25:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Marks V. Lunchtime gin and tonic a cause of reactive hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1977 Jun 18;1(8025):1286–1288. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R., Katz J. Effects of hormones and of ethanol on the fructose 6-P-fructose 1,6-P2 futile cycle during gluconeogenesis in the liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognstad R., Wals P. The metabolism of l-[3-3h]lactate by isolated hamster liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. D., Hems R., Krebs H. A. The rate of gluconeogenesis from various precursors in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):942–951. doi: 10.1042/bj1020942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D. M., Bowen N. L., Hems D. A. Synthesis of fatty acids in the perused mouse liver. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):611–618. doi: 10.1042/bj1420611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmer J., Grunnet N. Ethanol metabolism and lipid synthesis by isolated liver cells from fed rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 25;428(1):123–137. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess E. A., Brocks D. G., Wieland O. H. Distribution of metabolites between the cytosolic and mitochondrial compartments of hepatocytes isolated from fed rats. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jul;359(7):785–798. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess E. A., Wieland O. H. Phosphorylation state of cytosolic and mitochondrial adenine nucleotides and of pyruvate dehydrogenase in isolated rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):91–102. doi: 10.1042/bj1560091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen T. L., Hartling O., Trap-Jensen J. Effect of adrenergic beta receptor blockade on ethanol elimination and on ethanol-induced changes in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May 17;13(2):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00609751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROUT D. L., ESTES E. H., Jr, FRIEDBERG S. J. Titration of free fatty acids of plasma: a study of current methods and a new modification. J Lipid Res. 1960 Apr;1:199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolman E. L., Schworer C. M., Jefferson L. S. Effects of hypophysectomy on amino acid metabolism and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4552–4560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Mayes F. A. Regulation of lipogenesis by insulin and free fatty acids in perfused rat liver. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(4):717–717. doi: 10.1042/bst0040717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Mayes P. A. Comparative effects of fructose and glucose on the lipid and carbohydrate metabolism of perfused rat liver. Br J Nutr. 1976 Jul;36(1):113–126. doi: 10.1079/bjn19760062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Mayes P. A. The concentration of fructose, glucose and lactate in the splanchnic blood vessels of rats absorbing fructose. Nutr Metab. 1971;13(6):331–338. doi: 10.1159/000175352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping D. L., Mayes P. A. The immediate effects of insulin and fructose on the metabolism of the perfused liver. Changes in lipoprotein secretion, fatty acid oxidation and esterification, lipogenesis and carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):295–311. doi: 10.1042/bj1260295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton P. D., Rodrigues L. M., Hems D. A. Stimulation by acetate of gluconeogenesis in hepatocyte suspensions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):85–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Scholz R., Browning E. T., Thurman R. G., Fukami M. H. Metabolic effects of ethanol in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5044–5054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


