Abstract
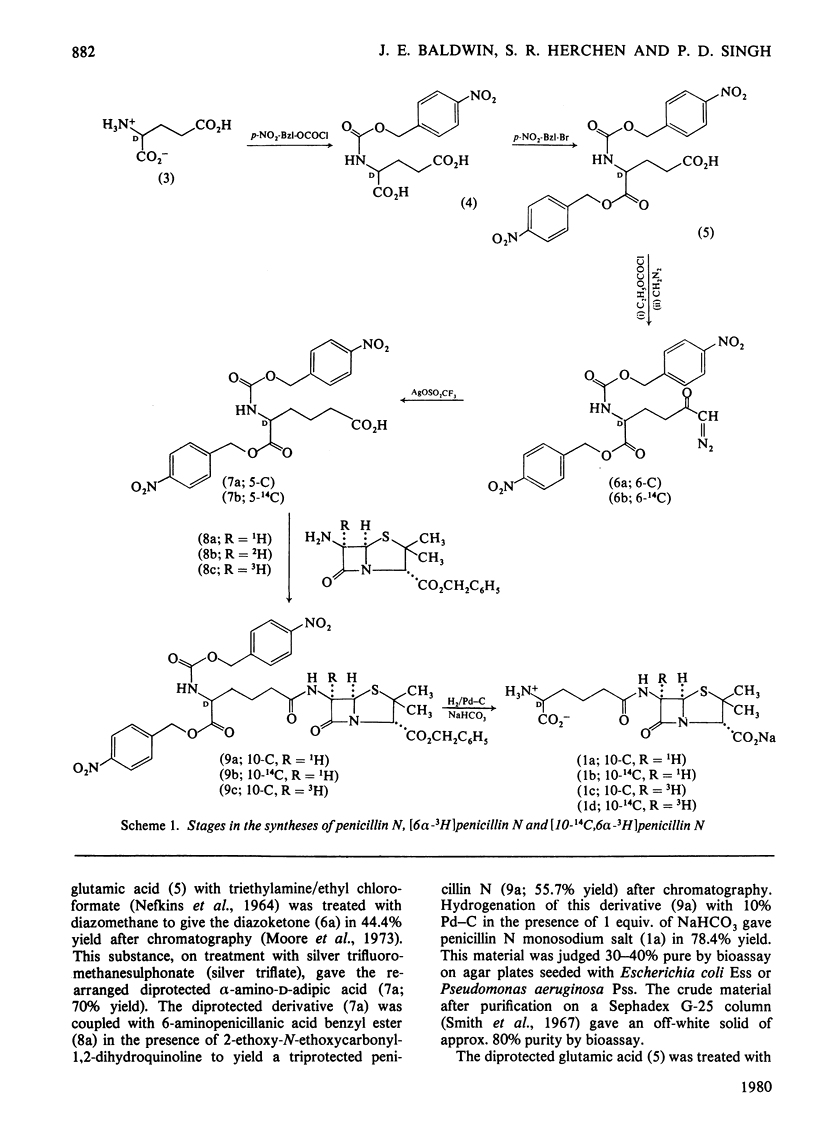
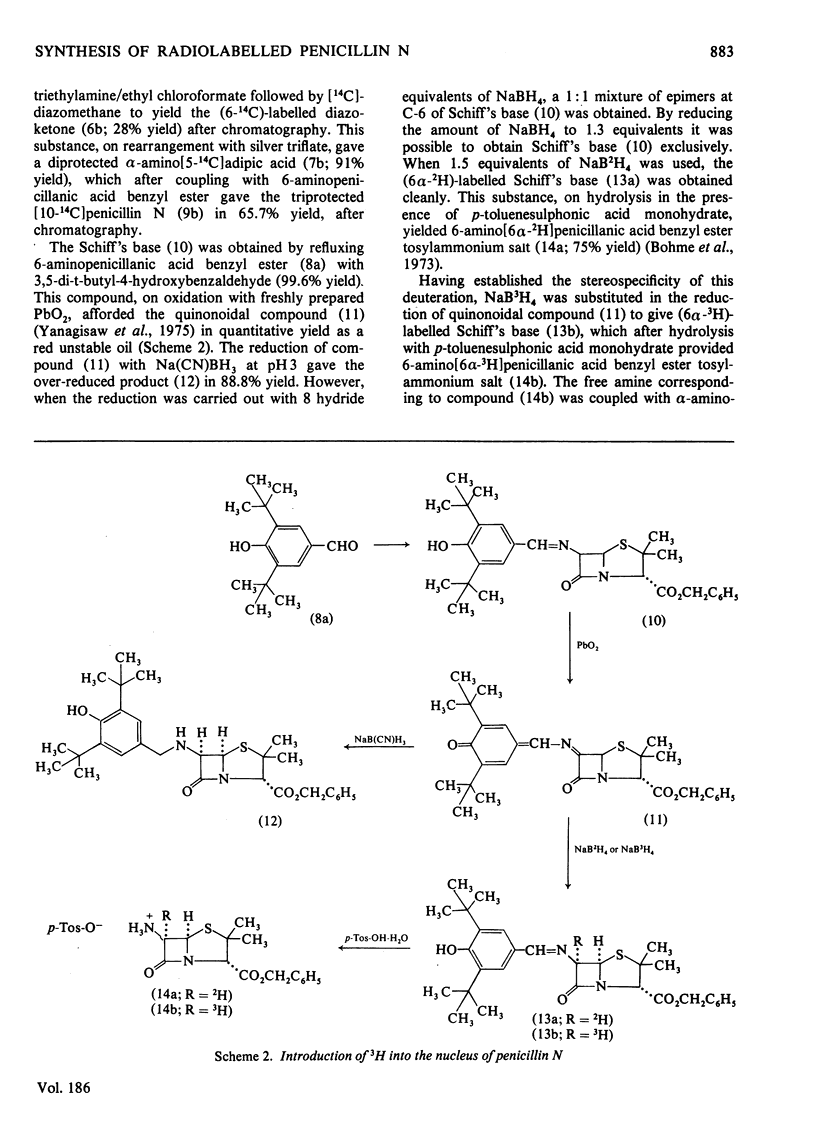
1. Penicillin N was synthesized by coupling alpha-amino-alpha-p-nitrobenzyl-N-p-nitro-benzyloxycarbonyl-D-adipate with 6-aminopenicillanic acid benzyl ester, followed by removal of the protecting groups through hydrogenolysis. 2. alpha-Amino-alpha-p-nitrobenzyl-N-p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-D-[5-14C]adipate was prepared by treating alpha-p-nitrobenzyl-N-p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-D-glutamic acid with [14C]diazomethane followed by rearrangement with silver trifluoromethanesulphonate. 3. Coupling of alpha-amino-alpha-p-nitrobenzyl-N-p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-D-[5-14C]adipate with 6-aminopenicillanic acid benzyl ester gave triprotected [10-14C]penicillin N. 4. 3H was introduced at C-6 of the Schiff's base derivative (10) by oxidation followed by reduction with NaB3H4. 5. The so-derived (6 alpha-3H)-labelled Schiff's base was hydrolysed to give 6-amino [6 alpha-3H]penicillanic acid benzyl ester p-toluenesulphonic acid salt, which after coupling as the free amine with alpha-amino-alpha-p-nitrobenzyl-N-pnitrobenzyloxycarbonyl-D-adipate and then hydrogenolysis, yielded [6alpha-3H]penicillin N. 6. Triprotected [10-14C]penicillin N and triprotected [6alpha-3H]penicillin N in admixture were hydrogenolysed to give [10-14C,6alpha-3H]penicillin N.
Full text
PDF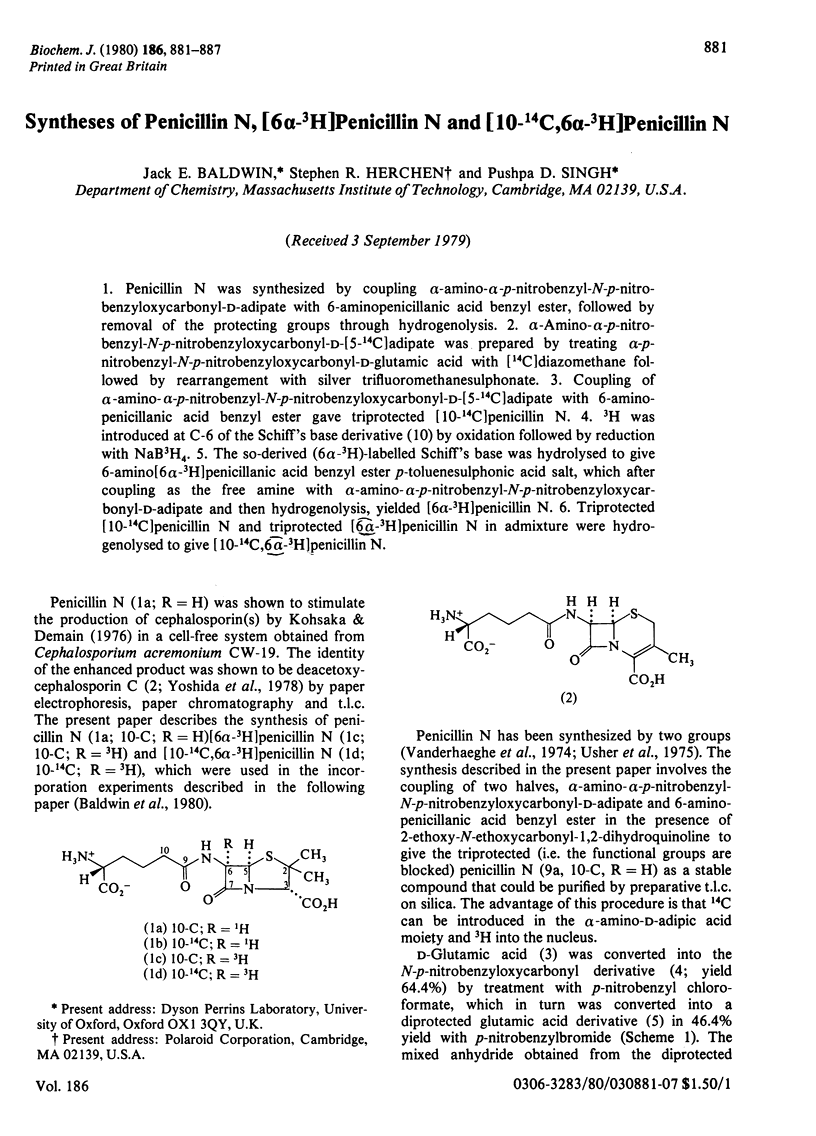




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. E., Singh P. D., Yoshida M., Sawada Y., Demain A. L. Incorporation of 3H and 14C from (6 alpha-3H)penicillin N and (10-14C,6 alpha-3H) penicillin N into deacetoxycephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):889–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1860889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohme E. H., Applegate H. E., Ewing J. B., Funke P. T., Puar M. S., Dolfini J. E. 6-ALKYL PENICILLINS AND 7 ALKYL CEPHALOSPORINS. J Org Chem. 1973 Jan 26;38(2):230–236. doi: 10.1021/jo00942a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohsaka M., Demain A. L. Conversion of penicillin N to cephalosporin(s) by cell-free extracts of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Warren S. C., Newton G. G., Abraham E. P. Biosynthesis of penicillin N and cephalosporin C. Antibiotic production and other features of the metabolism of Cephalosporium sp. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):877–890. doi: 10.1042/bj1030877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher J. J., Loder B., Abraham E. P. Synthesis of tritium-labelled isopenicillin N, penicillin N and 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):729–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1510729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghe H., Vlietinck A., Claesen M., Parmentier G. Preparation of penicillin N and isopenicillin N. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Mar;27(3):169–177. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Konomi T., Kohsaka M., Baldwin J. E., Herchen S., Singh P., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free ring expansion of penicillin N to deacetoxycephalosporin C by Cephalosporium acremonium CW-19 and its mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6253–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


