Abstract
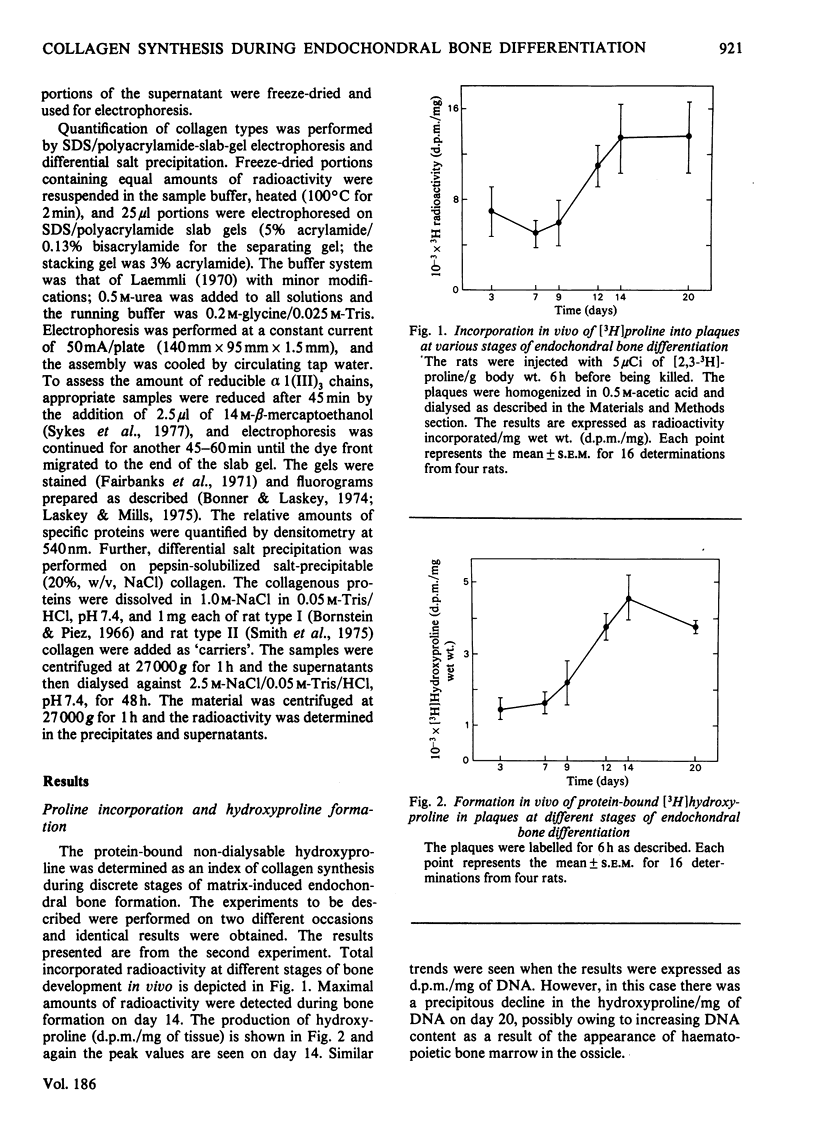
The changes in rates of hydroxyproline formation and biosynthesis of types-I and -III collagen during bone matrix-induced sequential differentiation of cartilage, bone and bone marrow in rat were investigated. Biosynthesis of types-I and -III collagen at different stages of this sequence was studied by labelling in vivo and in vitro with [2,3-3H]proline. Pepsin-solubilized collagens were separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-slab-gel electrophoresis. The results revealed that maximal amounts of type-III collagen were synthesized on day 3 during mesenchymal-cell proliferation. Thereafter, there was a gradual decline in type-III collagen synthesis. On days 9--20 during bone formation predominantly type-I collagen was synthesized. Similar results were obtained by the use of labelling techniques both in vivo and in vitro.
Full text
PDF

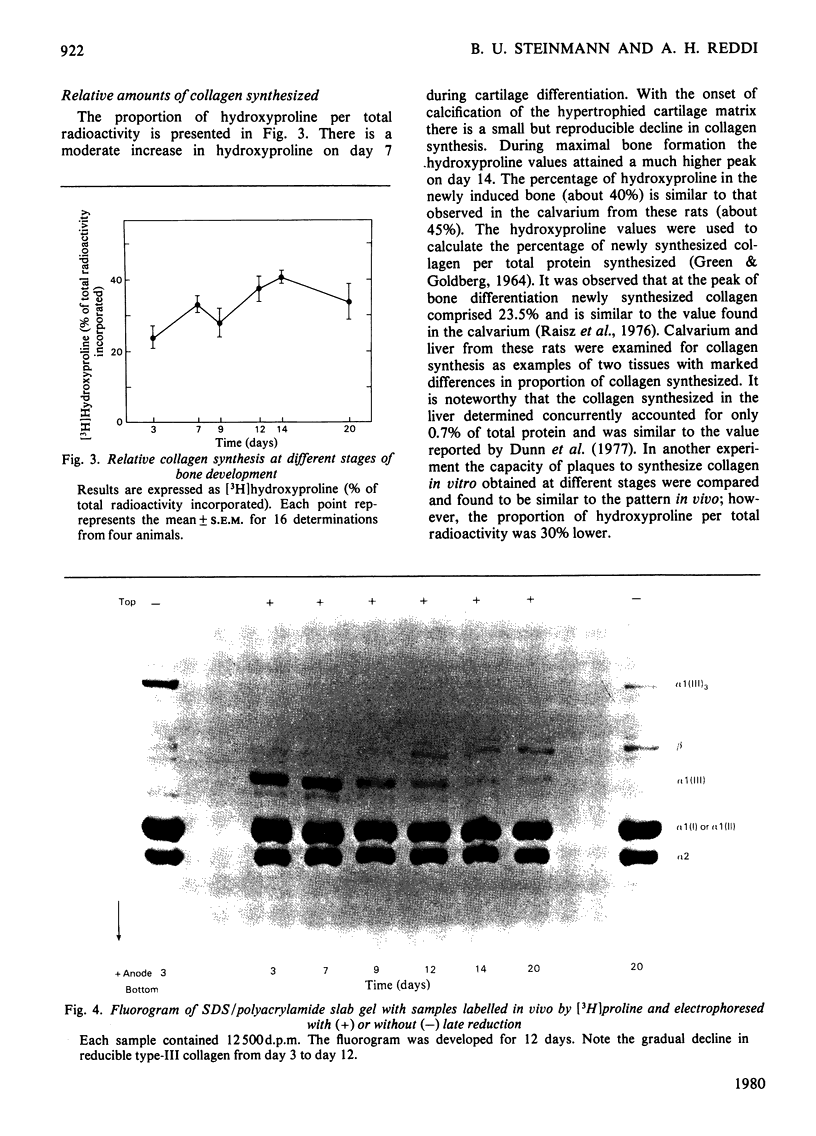


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Steinmann B. U., Wahl L. M., Martin G. R. High cell density alters the ratio of type III to I collagen synthesis by fibroblasts. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):442–444. doi: 10.1038/279442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes M. J., Morton L. F., Bennett R. C., Bailey A. J., Sims T. J. Presence of type III collagen in guinea-pig dermal scar. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):263–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1570263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum B. J., Moss J., Breul S. D., Crystal R. G. Association in normal human fibroblasts of elevated levels of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate with a selective decrease in collagen production. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3391–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Piez K. A. The nature of the intramolecular cross-links in collagen. The separation and characterization of peptides from the cross-link region of rat skin collagen. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3460–3473. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley K. H., McConnell S. D., Crystal R. G. Lung collagen composition and synthesis. Characterization and changes with age. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2674–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutroneo K. R., Guzman N. A., Liebelt A. G. Elevation of peptidylproline hydroxylase activity and collagen synthesis in spontaneous primary mammary cancers of inbred mice. Cancer Res. 1972 Dec;32(12):2828–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. A., Rojkind M., Warren K. S., Hait P. K., Rifas L., Seifter S. Liver collagen synthesis in murine schistosomiasis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):666–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI108685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., GOLDBERG B. COLLAGEN AND CELL PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY AN ESTABLISHED MAMMALIAN FIBROBLAST LINE. Nature. 1964 Oct 24;204:347–349. doi: 10.1038/204347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein L., ChandraRajan J. Collagen degradation in rat skin but not in intestine during rapid growth: effect on collagen types I and III from skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Toole B. P., Trelstad R. L. Temporal and spatial transitions in collagen types during embryonic chick limb development. Dev Biol. 1973 Dec;35(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. K., Raisch K., Matzen K., Gay S. Presence of type III collagen in bone from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Apr 26;125(1):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00470603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Dietrich J. W., Canalis E. M. Factors influencing bone formation in organ culture. Isr J Med Sci. 1976 Feb;12(2):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath N. C., Reddi A. H. Collagenous bone matrix is a local mitogen. Nature. 1979 Apr 26;278(5707):855–857. doi: 10.1038/278855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Anderson W. A. Collagenous bone matrix-induced endochondral ossification hemopoiesis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):557–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Gay R., Gay S., Miller E. J. Transitions in collagen types during matrix-induced cartilage, bone, and bone marrow formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5589–5592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Huggins C. B. Formation of bone marrow in fibroblast-transformation ossicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2212–2216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Huggins C. Biochemical sequences in the transformation of normal fibroblasts in adolescent rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1601–1605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Martin G. R., Miller E. J., Dorfman A., Swarm R. Nature of the collagen synthesized by a transplanted chondrosarcoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Francis M. J., Smith R. Altered relation of two collagen types in osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 26;296(21):1200–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705262962104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H. Immunological and biochemical studies of collagen type transition during in vitro chrondrogenesis of chick limb mesodermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):736–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]