Abstract
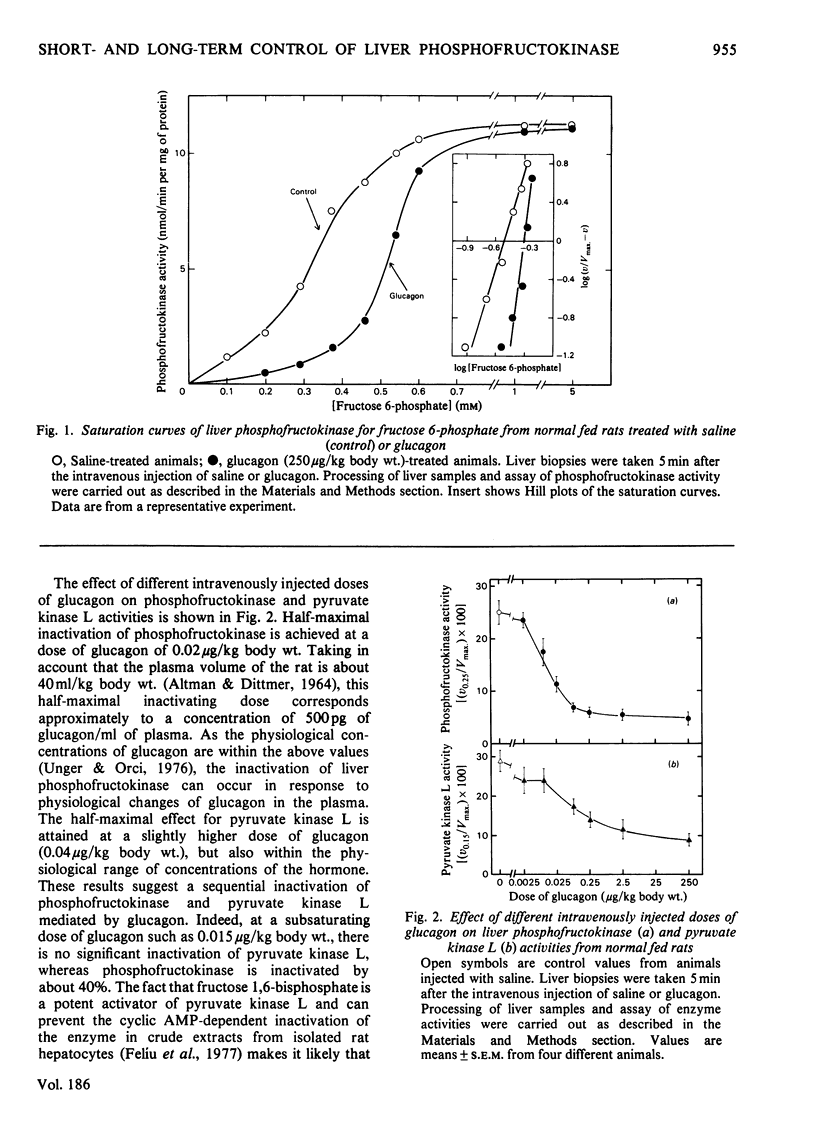
Glucagon (250 microgram/kg body wt.) intravenously injected into normal fed rats produces within 5 min a marked inactivation of liver phosphofructokinase, only observed when the enzyme activity is measured at subsaturating concentrations of fructose 6-phosphate. Since half-maximal inactivation is observed at a dose of glucagon of 0.32 microgram/body wt., a dose within the range of the physiological concentrations of the hormone, the inactivation of phosphofructokinase can occur in vivo in response to physiological changes in the concentration of glucagon. In gluconeogenic conditions (starved rats or high-protein-diet-fed rats), there is a marked inactivation of liver phosphofructokinase at subsaturating concentrations of fructose 6-phosphate similar to that found in normal fed rats after glucagon treatment. In these gluconeogenic conditions a 50% decrease in the Vmax. of the enzyme is also observed. No significant changes in phosphofructokinase activity either at subsaturating concentrations of fructose 6-phosphate or in the Vmax. of the enzyme are observed when rats are fed on a high-carbohydrate diet. In the last dietary condition, glucagon treatment produces similar effects to that described in the normal fed rats. Similar results have been obtained in the above condtions for pyruvate kinase L activity when measured at subsaturating concentrations of phosphoenolpyruvate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand I. A., Müller M. K., Unger C., Söling H. D. In vivo and in vitro interconversions of active and inactive forms of phosphofructokinase in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 1;68(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80451-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Nieto A., Felíu J. E. Inactivation of phosphofructokinase by glucagon in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5576–5579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway G. A., Jr, Weber G. Effects of hormonal and nutritional changes on rates of synthesis and degradation of hepatic phosphofructokinase isozymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felíu J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Regulation in vitro and in vivo of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent inactivation of rat-liver pyruvate kinase type L. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagimoto T., Uyeda K. Hormone-stimulated phosphorylation of liver phosphofructokinase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5584–5587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., POTTER V. R., MORRIS H. P. Metabolic adaptations in rat hepatomas. I. The effect of dietary protein on some inducible enzymes in liver and hepatoma 5123. Cancer Res. 1961 Sep;21:1001–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestaña A. Dietary and hormonal control of enzymes of amino acid catabolism in liver. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):400–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S., Schlumpf J., Pilkis J., Claus T. H. Regulation of phosphofructokinase activity by glucagon in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):960–967. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapag-Hagar M., Lagunas R., Sols A. Apparent unbalance between the activities of 6-phosphogluconate and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 4;50(1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz H. J., Müller M. J., Krone W., Tarnowski W. Coordinate control of intermediary metabolism in rat liver by the insulin/glucagon ratio during starvation and after glucose refeeding. Regulatory significance of long-chain acyl-CoA and cyclic AMP. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):647–663. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Physiology and pathophysiology of glucagon. Physiol Rev. 1976 Oct;56(4):778–826. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.4.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


