Abstract
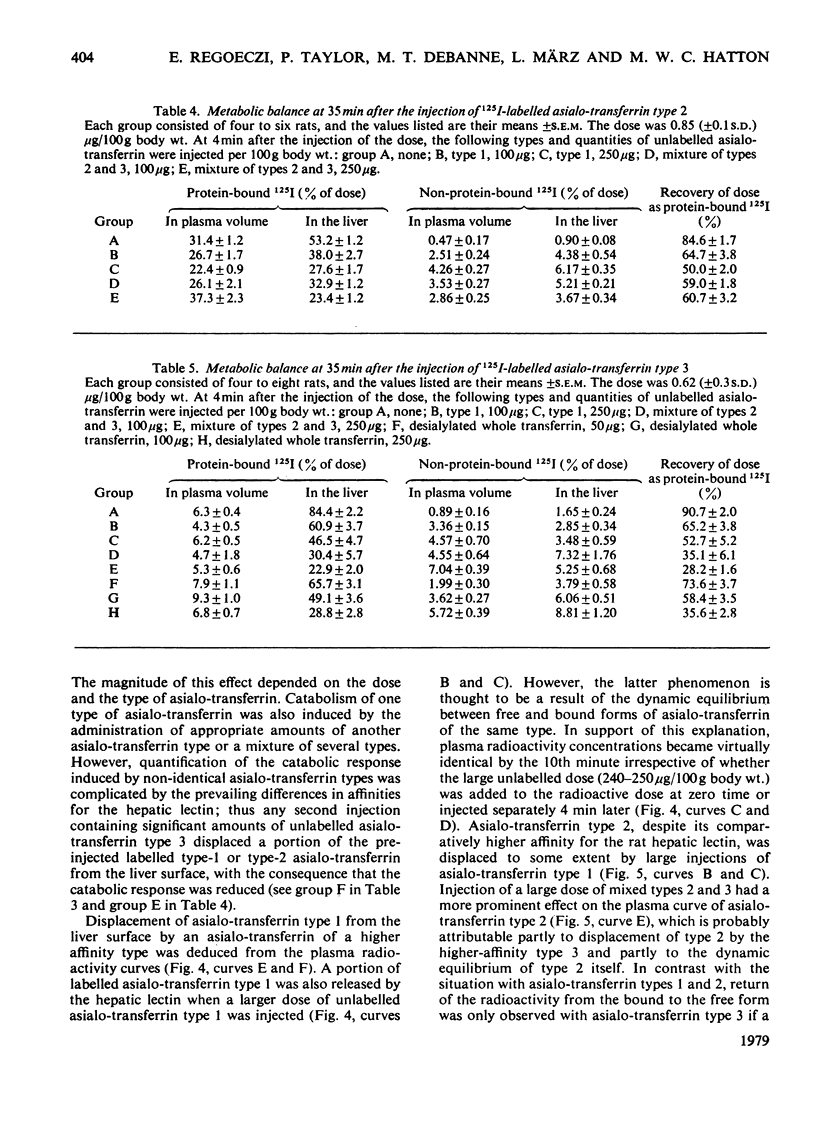
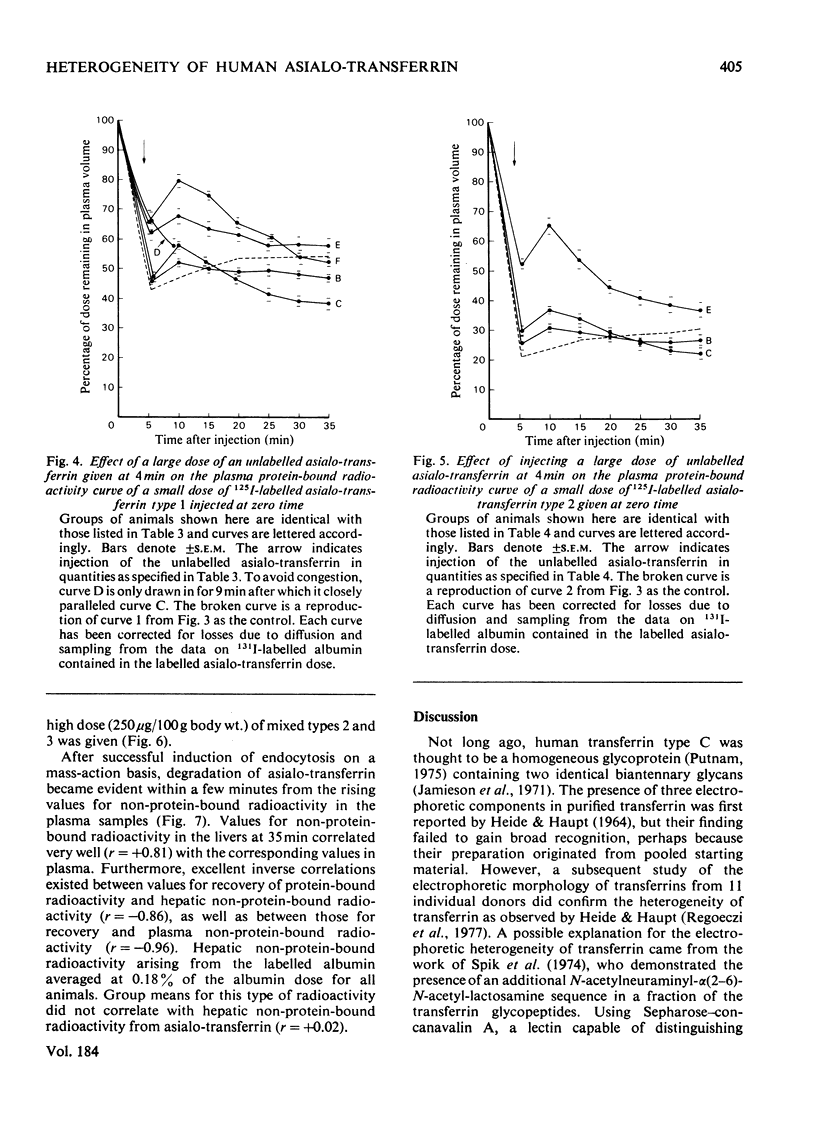
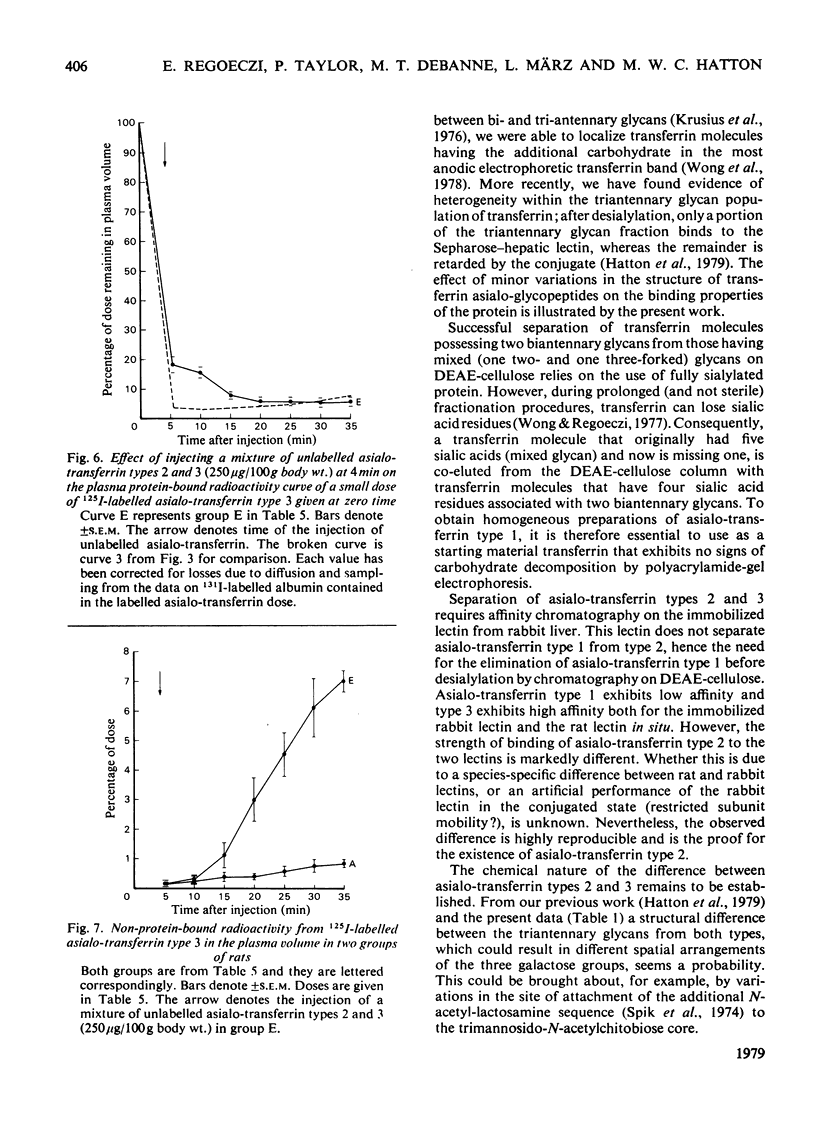
Three types of asialo-transferrin were obtained from immunologically pure human transferrin by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, followed by desialylation and affinity chromatography on a column of the immobilized asialo-glycoprotein-binding hepatic lectin from rabbit liver. Of the asialo-transferrins, type 1 was derived from the principal DEAE-cellulose chromatographic component of transferrin, i.e. the one that contains two biantennary glycans. The two other asialo-transferrins (types 2 and 3) were derived from a minor DEAE-chromatographic transferrin component, which is assumed to possess one biantennary and one triantennary glycan. The three asialo-transferrin types were indistinguishable by electrophoretic mobility, but they were readily distinguished on the basis of their binding strengths to the hepatic lectin in intact rats. Glycan structures responsible for the difference in binding strengths between asialo-transferrin types 2 and 3 are not known. Metabolic studies in rats showed that none of the individual asialo-transferrin types was capable of generating a signal for endocytosis at low doses (<1μg/100g body wt.) and, consequently, most of the injected protein was recoverable with the plasma and the liver 35min after injection. However, endocytosis and catabolism of each asialo-transferrin type was readily induced by injecting a larger dose (50–250μg/100g body wt.) of unlabelled asialo-transferrin of the same type or of a different type a short interval after the labelled dose. These findings support the view that the dose-dependent uptake of human asialo-transferrin by the hepatocyte, as established in an earlier study with asialo-transferrin made from whole transferrin [Regoeczi, Taylor, Hatton, Wong & Koj (1978) Biochem. J. 174, 171–178], also holds for these asialo-transferrin subfractions. Furthermore, the present studies indicate that asialo-transferrins of different carbohydrate compositions are capable of synergistically promoting endocytosis of each other.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. The physicochemical and chemical properties of alpha 1-acid glycoproteins from mammalian and avian plasmas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 26;453(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A., Regoeczi E., Hatton M. W. Hepatic uptake and degradation of trace doses of asialofetuin and asialoorosomucoid in the intact rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 1;585(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., März L., Berry L. R., Debanne M. T., Regoeczi E. Bi-and tri-antennary human transferrin glycopeptides and their affinities for the hepatic lectin specific for asialo-glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):633–638. doi: 10.1042/bj1810633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Jamieson G. A., DeBernardo S. L. The carbohydrate sequence of the glycopeptide chains of human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3686–3693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Finne J., Rauvala H. The structural basis of the different affinities of two types of acidic N-glycosidic glycopeptides for concanavalin A--sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80911-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S. DEAE-cellulose chromatography of human transferrin: the effect of increasing iron saturation and copper(II) binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 27;243(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnhardt W. F., Winzler R. J. Determination of neutral sugars in glycoproteins by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1968 May 7;34(4):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E. Hepatic uptake of asialoglycoproteins in vivo: quantification using a dual-isotope technique. J Nucl Biol Med. 1975 Jul-Sep;19(3):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Taylor P., Hatton M. W., Wong K. L., Koj A. Distinction between binding and endocytosis of human asialo-transferrin by the rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1740171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Wong K. L., Ali M., Hatton M. W. The molecular components of human transferrin type C. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;10(1):17–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Bayard B., Fournet B., Strecker G., Bouquelet S., Montreuil J. Studies on glycoconjugates. LXIV. Complete structure of two carbohydrate units of human serotransferrin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):296–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H. Mammalian hepatic lectin. Science. 1974 Oct 25;186(4161):365–366. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4161.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Hamer C. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. IX. The role of galactosyl residues in the clearance of ceruloplasmin from the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4397–4402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Debanne M. T., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. Human transferrin, asialotransferrin and the intermediate forms. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Jul;12(1):27–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Regoeczi E. Some observations on the carbohydrate composition of purified transferrin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(4):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb03487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



