Abstract
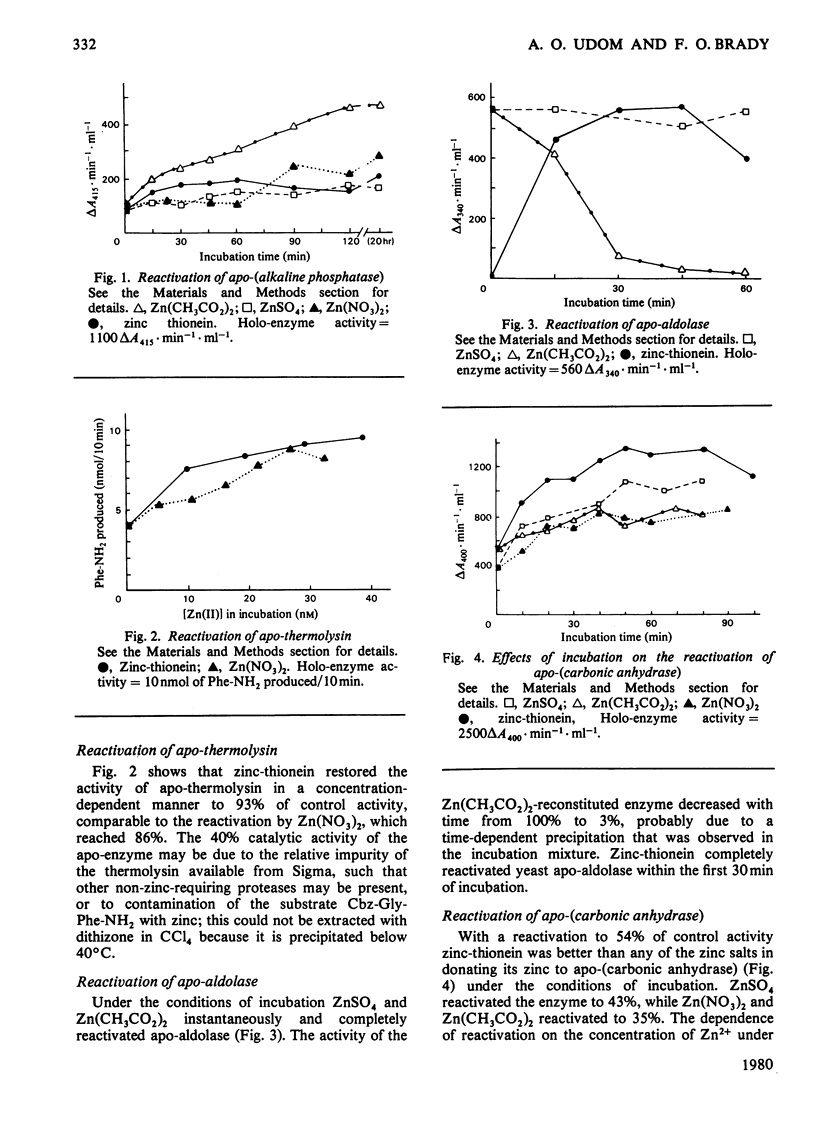
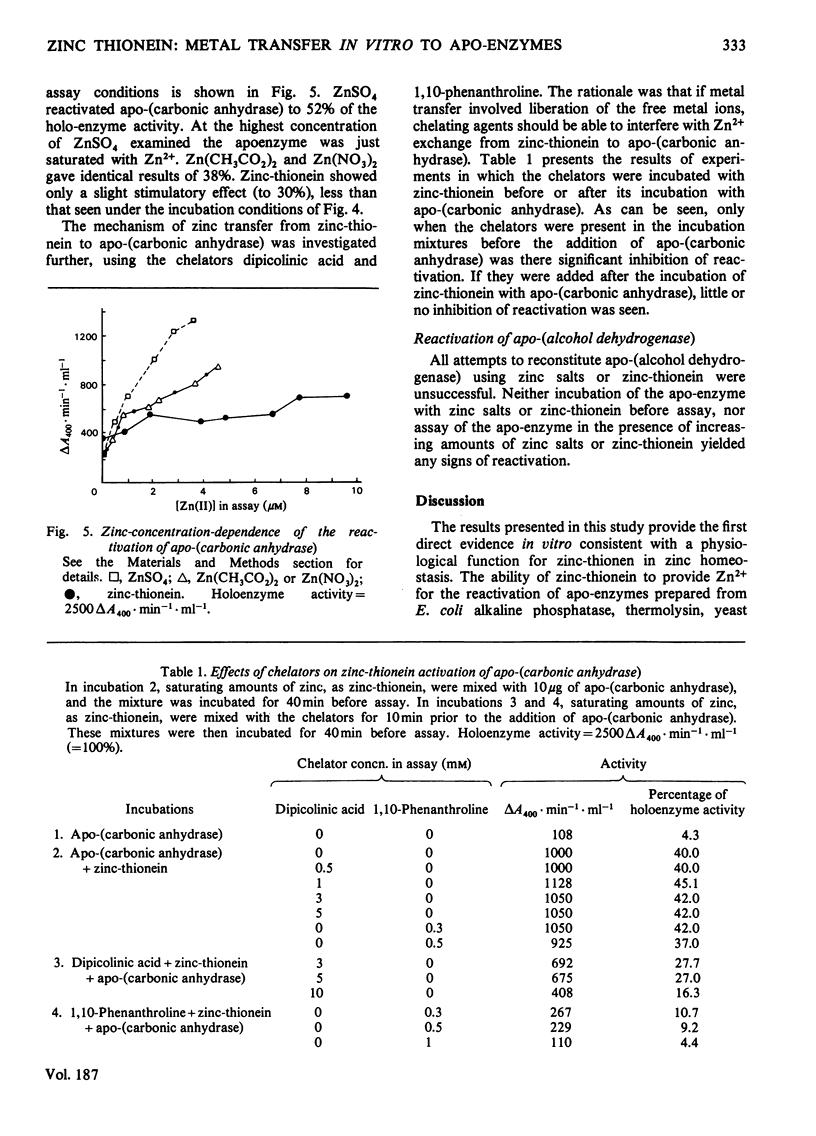
The ability of rat liver zinc-thionein to donate its metal to the apo-enzymes of the zinc enzymes horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase, yeast aldolase, thermolysin, Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase and bovine erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase was investigated. Zinc-thionein was as good as, or better than, ZnSO4, Zn(CH3CO2)2 or Zn(NO3)2 in donating its zinc to these apo-enzymes. Apo-(alcohol dehydrogenase) could not be reactivated by zinc salts or by zinc-thionein. Incubation of the other apo-enzymes with near-saturating amounts of zinc as ZnSO4, Zn(CH3CO2)2, Zn(NO3)2, or zinc-thionein resulted in reactivation of the apo-enzymes. With apo-aldolase zinc-thionein gave 100% reactivation within 30min. Reactivation by ZnSO4 and Zn(CH3CO2)2 was complete and instantaneous. Zinc-thionein was somewhat better than Zn(NO3)2 in completely reactivating apo-thermolysin. With apo-(alkaline phosphatase) 43% reactivation was obtained with Zn(CH3CO2)2 and 18% with zinc-thionein. With apo-(carbonic anhydrase) zinc-thionein was better than ZnSO4, Zn(CH3CO2)2 or Zn(NO3)2, with a maximal reactivation of 54%. That zinc was really being transferred from zinc-thionein to apo-(carbonic anhydrase) was shown by the fact that 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid and 1,10-phenanthroline had minimal effects on the reactivation of apo-(carbonic anhydrase) when added after the incubation {[apo-(carbonic anhydrase)+zinc thionein]+chelator}, but inhibited reactivation when added before the incubation {apo-(carbonic anhydrase)+[zinc-thionein+chelator]}. These observations support the idea that zinc-thionein can function in zinc homeostasis as a reservoir of zinc, releasing the metal to zinc-requiring metalloenzymes according to need.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Bosron W. F., Kennedy F. S., Vallee B. L. Role of magnesium in Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock J. L., Kowalsky A. Zinc stoichiometry in Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Studies by 31P NMR and ion-exchange chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 11;526(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner I., Davies N. T. The induction of metallothionein in rat liver by zinc injection and restriction of food intake. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):733–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1490733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R. H., Kägi J. H. Human hepatic metallothioneins. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins R. J., Barber A. K., Trout J. R. Cadmium toxicity in growing swine. J Nutr. 1973 Jul;103(7):964–972. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.7.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csopak H. The specific binding of zinc(II) to alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(2):186–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day F. A., Coles B. J., Brady F. O. Postinductive actinomycin D effects on the concentrations of cadmium thionein, zinc thionein, and copper chelatin in rat liver. Bioinorg Chem. 1978;8(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J., Garrett L. R., Kochavi D. Studies on the inhibition of neutral proteases by 1,10-phenanthroline. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 12;235(2):370–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES J. E., Jr, VELICK S. F. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: molecular weight, coenzyme binding, and reaction equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):225–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES T. R., KLOTZ I. M. Analysis of metal-protein complexes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:265–299. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Metal substitutions and inhibition of thermolysin: spectra of the cobalt enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4601–4607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. B., Rhee M. J., Storm C. B. A rapid and convenient preparation of apocarbonic anhydrase. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):614–617. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Sawauchi K. Inhibitory effects on cadmium-induced testicular damage by pretreatment with smaller cadmium dose. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1966 May;42(2):107–117. doi: 10.2535/ofaj1936.42.2-3_107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3460–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobes R. D., Simpson R. T., Vallee R. L., Rutter W. J. A functional role of metal ions in a class II aldolase. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):585–588. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Berger C., Vallee B. L., Kägi J. H. Amino-acid sequence of equine renal metallothionein-1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Himmelhoch S. R., Whanger P. D., Bethune J. L., Vallee B. L. Equine hepatic and renal metallothioneins. Purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3537–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSKOG S. Effects of pH and inhibitors on some properties related to metal binding in bovine carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 1963 Mar;238:945–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSKOG S., MALMSTROM B. G. Metal binding and catalytic activity in bovine carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1129–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Kobes R. D., Rutter W. J. Magnetic resonance studies of the role of the divalent cation in the mechanism of yeast aldolase. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1191–1204. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. Amino acid analysis: aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent for the ninhydrin reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6281–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg G. F., Piscator M., Lind B. Distribution of cadmium among protein fractions of mouse liver. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1971;29(5):456–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1971.tb00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer H. L., Green R. W., McKay R. H. Function of zinc in horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):552–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocker Y., Stone J. T. The catalytic versatility of erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase. 3. Kinetic studies of the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):668–678. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido P., Kägi J. H., Vallee B. L. Isolation and some properties of human metallothionein. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1768–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Influence of parenteral zinc and actinomycin D on tissue zinc uptake and the synthesis of a zinc - binding protein. Bioinorg Chem. 1975 Apr;4(3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Mammalian zinc homeostasis: requirement for RNA and metallothionein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughton F. J., Booth V. H. The effect of substrate concentration, pH and other factors upon the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Biochem J. 1946;40(2):319–330. doi: 10.1042/bj0400319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph R., Gerschitz J., Jaenicke R. Effect of zinc(II) on the refolding and reactivation of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Synthesis of metallothionein in a polysomal cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):806–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weser U., Rupp H., Donay F., Linnemann F., Voelter W., Voetsch W., Jung G. Characterization of Cd, Zn-thionein (metallothionein) isolated from rat and chicken liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Premakumar R., Rajagopalan K. V. Metal-induced formation of metallothionein in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):242–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Rajagopalan K. V. Purification and some properties of Cd-binding protein from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


