Abstract
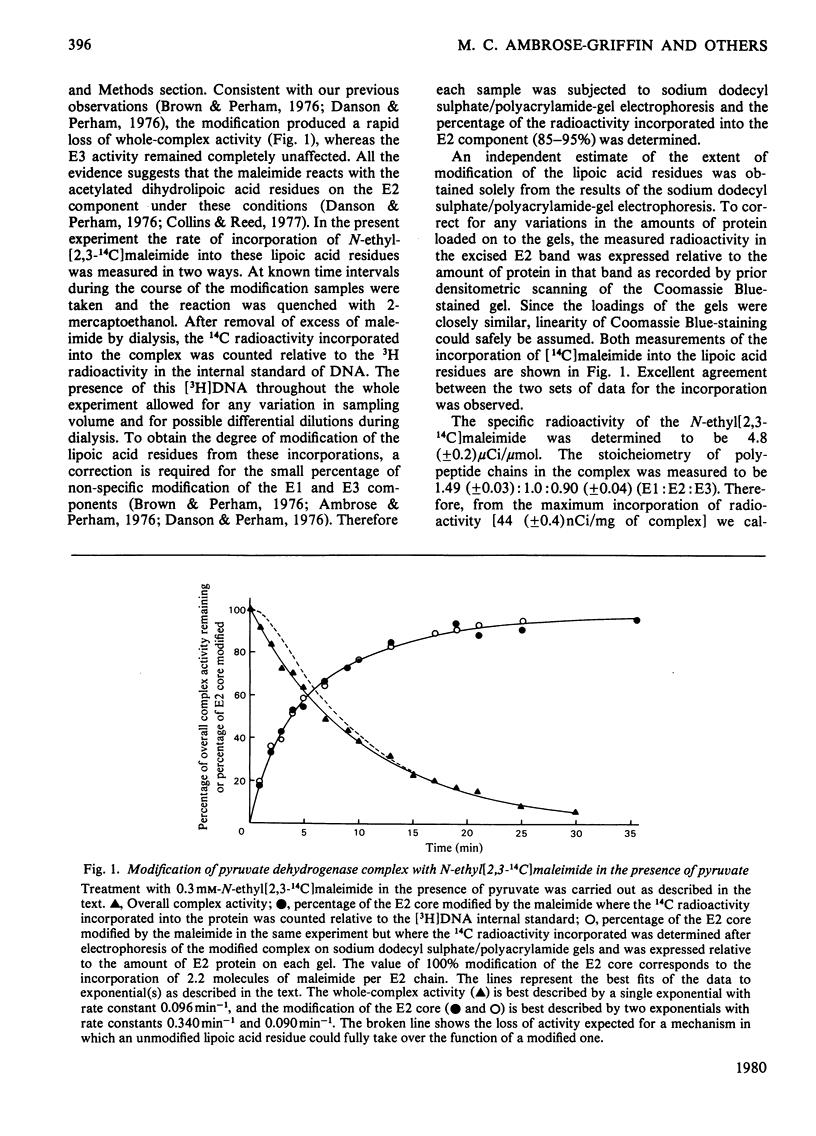
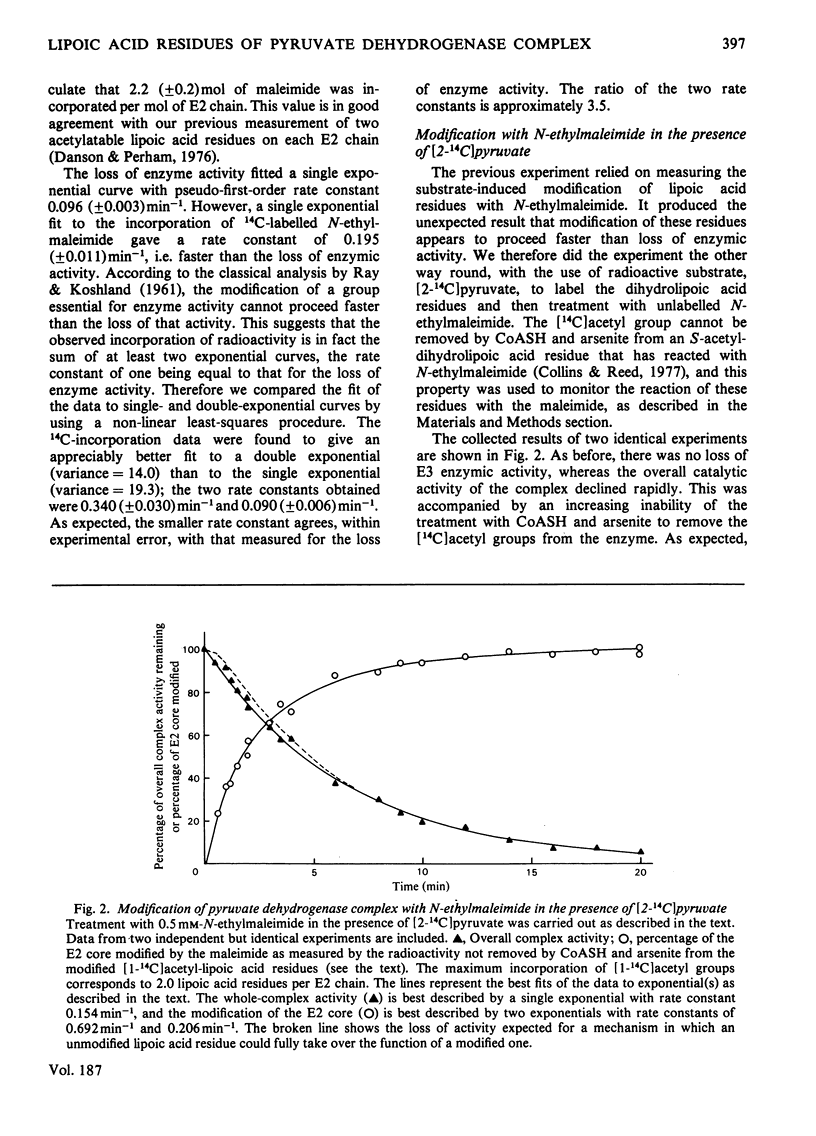
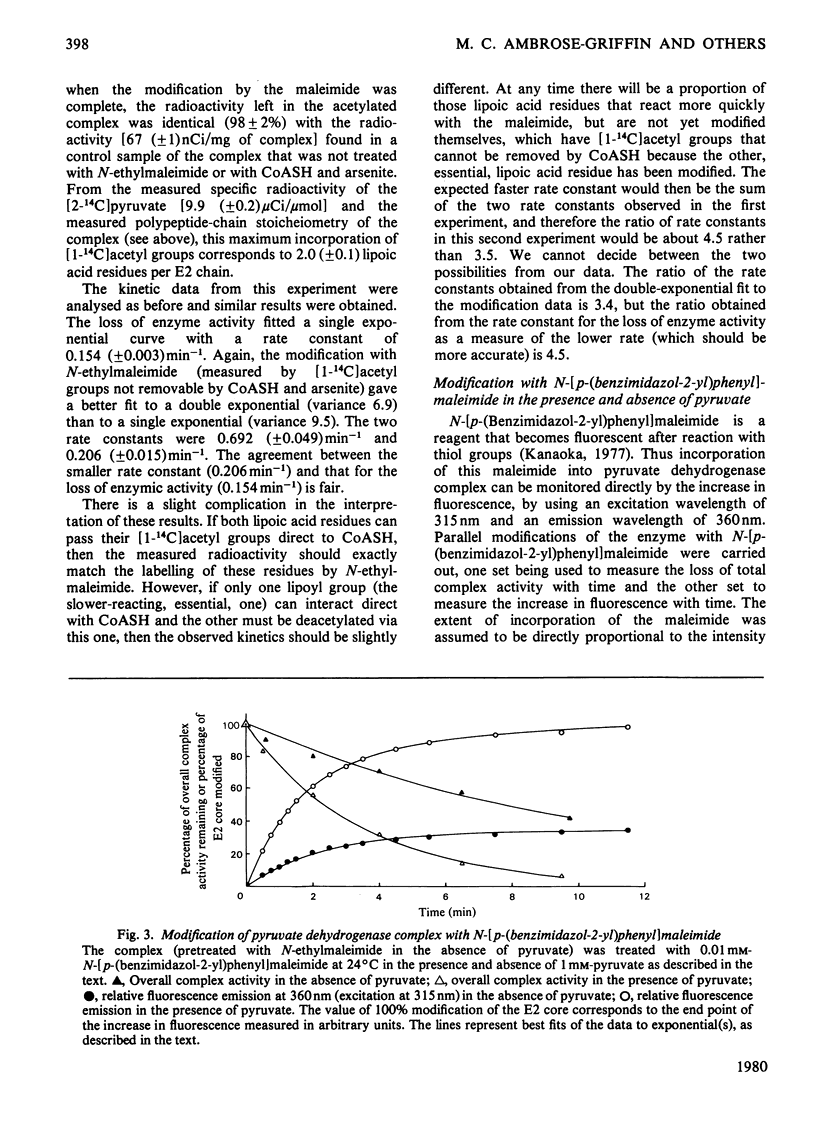
The catalytic roles of the two reductively acetylatable lipoic acid residues on each lipoate acetyltransferase chain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli were investigated. Both lipoyl groups are reductively acetylated from pyruvate at the same apparent rate and both can transfer their acetyl groups to CoASH, part-reactions of the overall complex reaction. The complex was treated with N-ethylmaleimide in the presence of pyruvate and the absence of CoASH, conditions that lead to the modification and inactivation of the S-acetyldihydrolipoic acid residues. Modification was found to proceed appreciably faster than the accompanying loss of enzymic activity. The kinetics of the modification were fitted best by supposing that the two lipoyl groups react with the maleimide at different rates, one being modified at approximately 3.5 times the rate of the other. The loss of complex activity took place at a rate approximately equal to that calculated for the modification of the more slowly reacting lipoic acid residue. The simplest interpretation of this result is that only this residue is essential in the overall catalytic mechanism, but an alternative explanation in which one lipoic acid residue can take over the function of another was not ruled out. The kinetics of inactivation could not be reconciled with an obligatory serial interaction between the two lipoic acid residues. Similar experiments with the fluorescent N-[p-(benzimidazol-2-yl)phenyl]maleimide supported these conclusions, although the modification was found to be less specific than with N-ethylmaleimide. The more rapidly modified lipoic acid residue may be involved in the system of intramolecular transacetylation reactions that couple active sites in the lipoate acetyltransferase component.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrose M. C., Perham R. N. Spin-label study of the mobility of enzyme-bound lipoic acid in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):429–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1550429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelides K. J., Hammes G. G. Fluorescence studies of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1223–1229. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelides K. J., Hammes G. G. Mechanism of action of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4877–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Danson M. J., Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Self-assembly and catalytic activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):313–316. doi: 10.1038/268313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Harrison R. A., Perham R. N. The stoichiometry of polypeptide chains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of E. coli determined by a simple novel method. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Perham R. N. Selective inactivation of the transacylase components of the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1550419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Reed L. J. Acyl group and electron pair relay system: a network of interacting lipoyl moieties in the pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4223–4227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Fersht A. R., Perham R. N. Rapid intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli: mechanism for rate enhancement in a multimeric structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5386–5390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hale G., Johnson P., Perham R. N., Smith J., Spragg P. Molecular weight and symmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):603–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj1750193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Perham R. N. Evidence for two lipoic acid residues per lipoate acetyltransferase chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1590677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Ikeda B. H., Gavino G. R., Speckhard D. C., Wong S. S. Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Site coupling in electron and acetyl group transfer pathways. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. E., ODA T. On the unit of mitochondrial structure and function. J Biochem. 1961 Jun;49:742–757. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande H. J., Van Telgen H. J., Veeger C. Symmetry and asymmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from Azotobacter vinelandii and Escherichia coli as reflected by fluorescence and spin-label studies. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. C., Griffin W. G., Perham R. N. Electron-spin-resonance studies of the lipoamide 'swinging arm' of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):225–226. doi: 10.1042/bst0060225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Bates D. L., Perham R. N. Subunit exchange in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 15;104(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80848-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Amidination of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli under denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):136–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1770136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Limited proteolysis of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Polypeptide-chain stoicheiometry and lipoic acid content of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj1770129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Primary structure of the swinging arms of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Perham R. N., Finch J. T. Structure and symmetry of B. stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex and implications for eucaryote evolution. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIKE M., REED L. J., CARROLL W. R. alpha-Keto acid dehydrogenation complexes. IV. Resolution and reconstitution of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenation complex. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaoka Y. Organic fluorescence reagents in the study of enzymes and proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1977 Mar;16(3):137–147. doi: 10.1002/anie.197701371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. A., Jr, Lerner D. A., Hammes G. G. Fluorescence energy transfer between the thiamine diphosphate and flavine adenine dinucleotide binding sites on the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2552–2557. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N. Self-assembly of biological macromolecules. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 6;272(915):123–136. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Thomas J. O. The subunit molecular weights of the alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 2;15(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY W. J., Jr, KOSHLAND D. E., Jr A method for characterizing the type and numbers of groups involved in enzyme action. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1973–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED L. J., KOIKE M., LEVITCH M. E., LEACH F. R. Studies on the nature and reactions of protein-bound lipoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):143–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. B., Papadakis N. Fluorescence energy-transfer measurements between coenzyme A and flavin adenine dinucleotide binding sites of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2888–2893. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speckhard D. C., Ikeda B. H., Wong S. S., Frey P. A. Acetylation stoichiometry of Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):708–713. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


