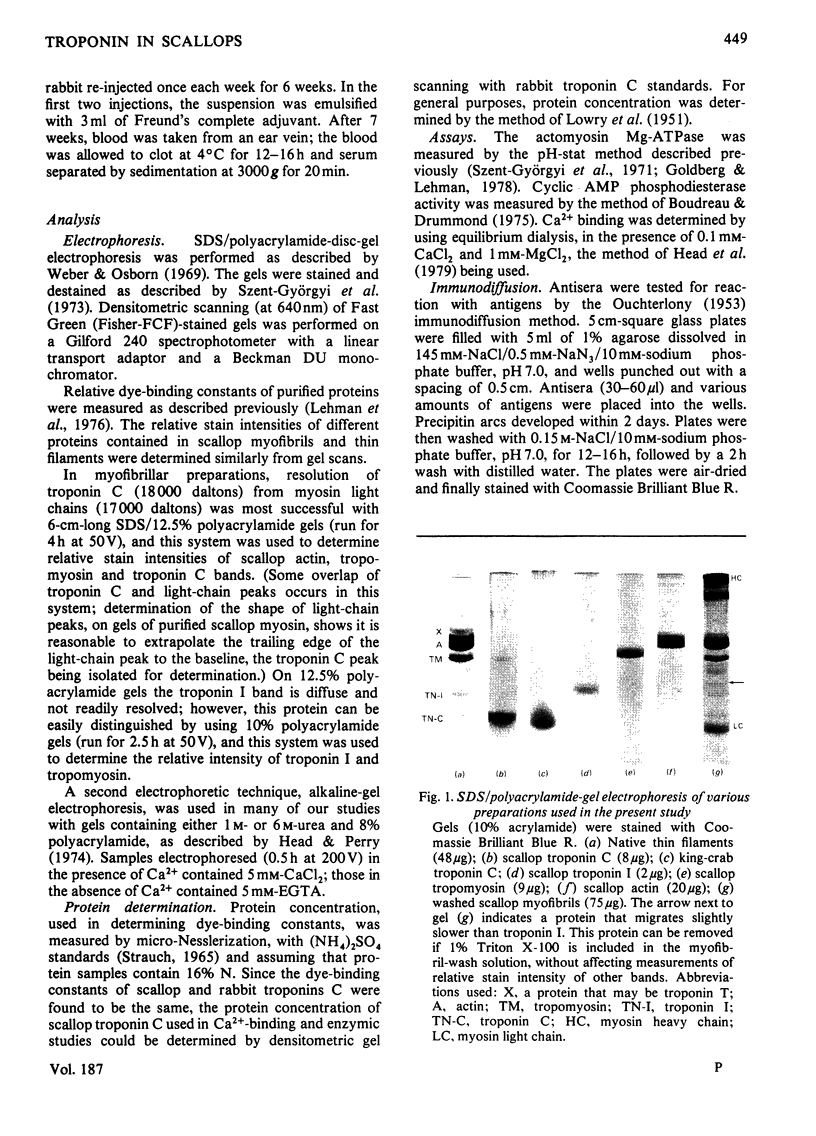
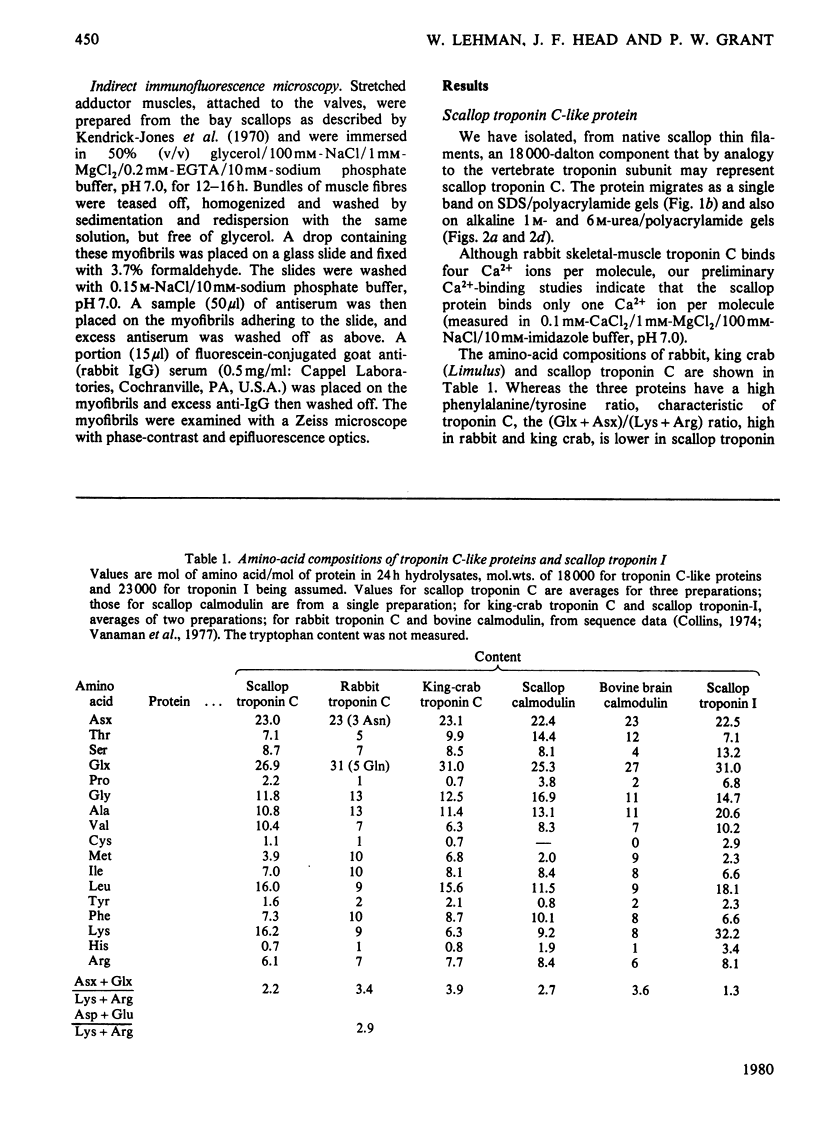
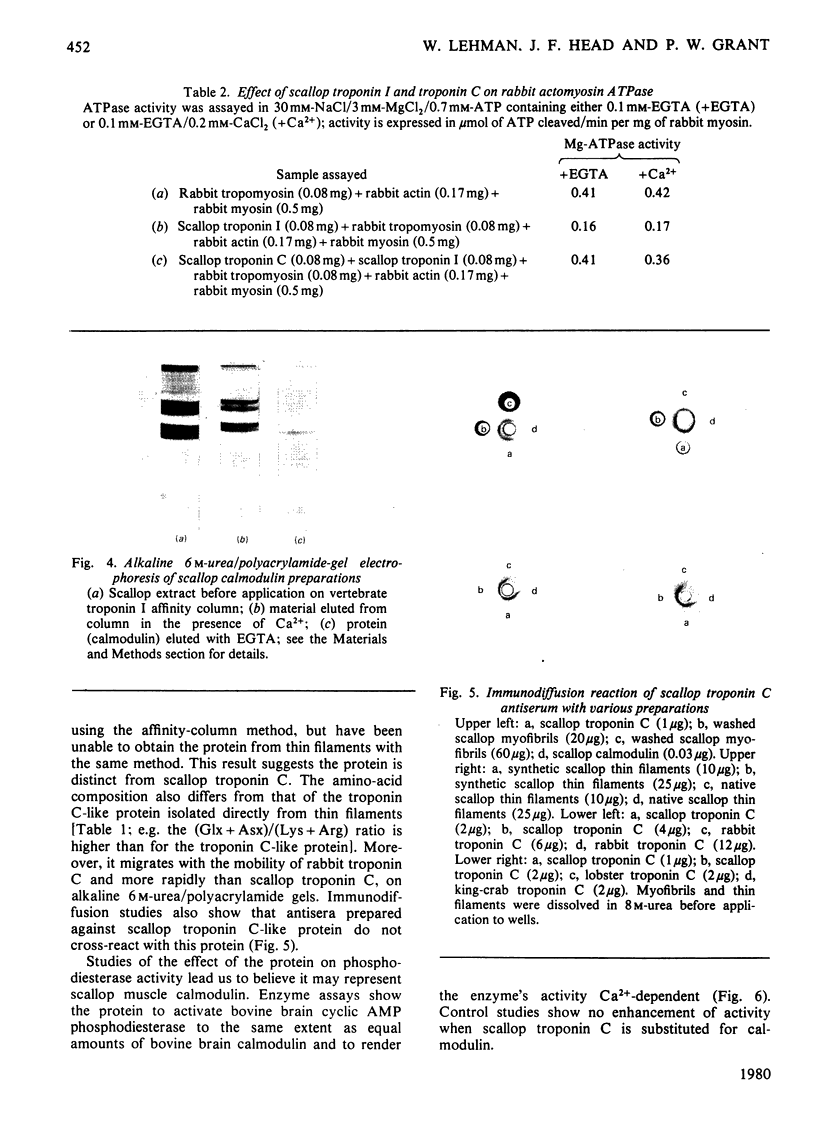
Abstract
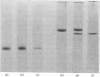
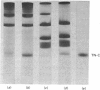
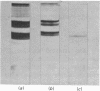
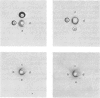
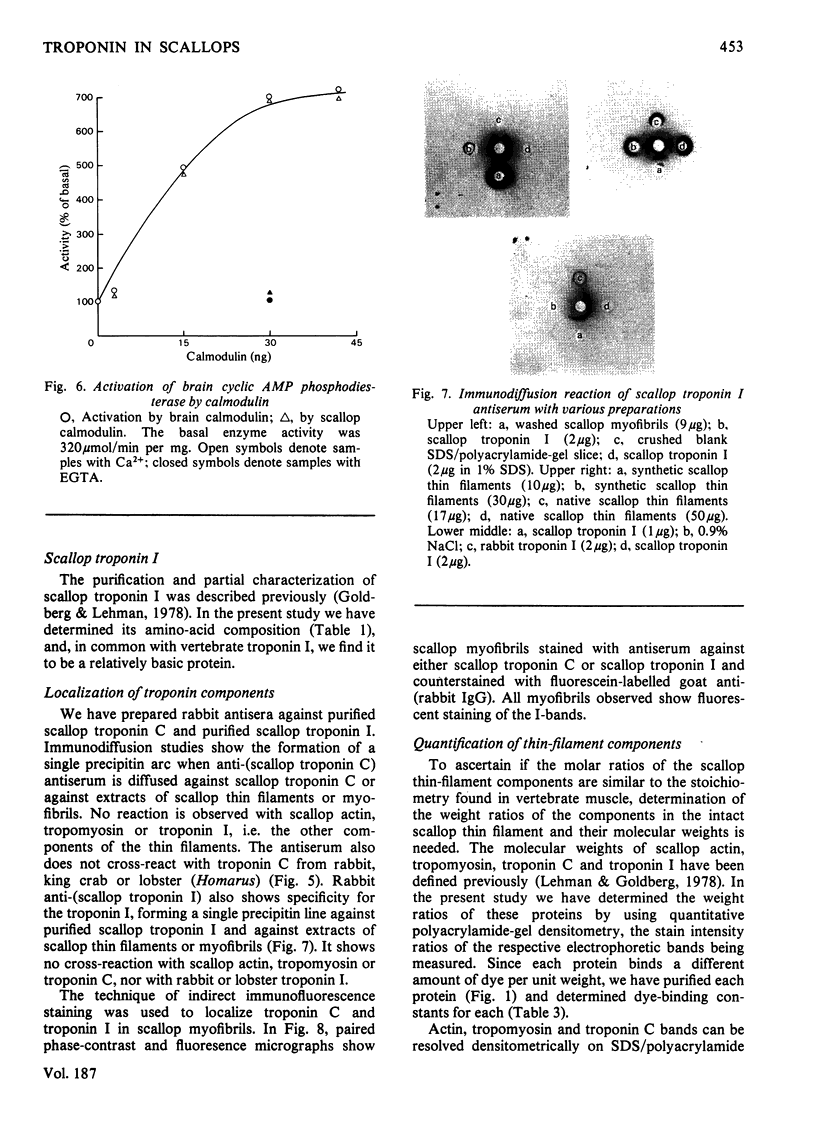
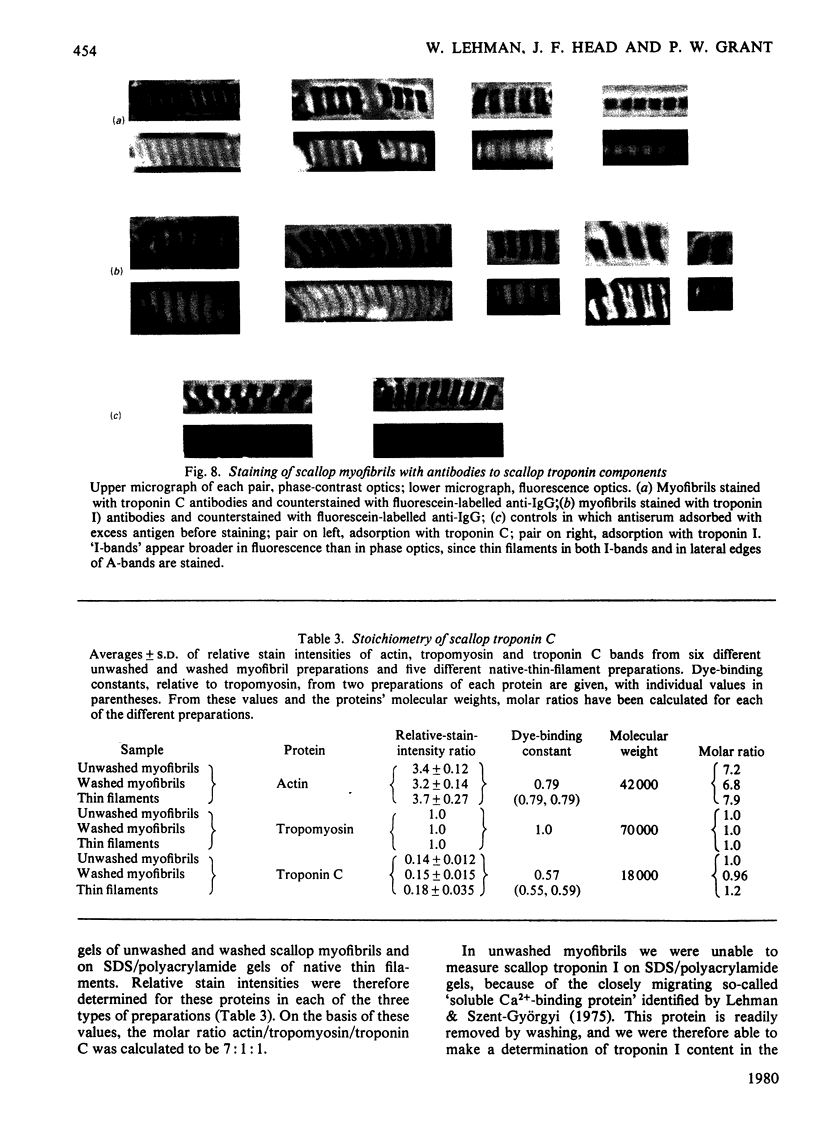
Localization and quantification studies were carried out on bay-scallop (Aequipecten irradians) striated-muscle troponin C- and troponin I-like proteins. Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy of scallop myofibrils stained with either rabbit anti-(scallop troponin I) or anti-(scallop troponin C) antibodies shows staining of all I-bands observed. The results of quantification studies using sodium dodecyl sulfate poly-acrylamide-gel electrophoresis of untreated scallop myofibrils, washed scallop myofibrils, and isolated scallop thin filaments indicate an actin/tropomyosin/troponin-C molar rationn of 7:1:1. The molar ratio for troponin I could not be determined in untreated myofibrils because of interfering bands; in washed myofibrils a value of 0.6 mol of troponin I/mol of tropomyosin was found. Purified scallop troponin C binds Ca2+ and interacts with scallop troponin I to relieve troponin I-induced inhibition of actomyosin ATPase. Although scallop troponin C is an acidic protein, it appears to be less acidic than troponin C from higher organisms. A calmodulin-like protein has been isolated from scallop striated muscle that activates bovine brain phosphodiesterase to the same extent as does brain calmodulin. Its amino acid composition and its electrophoretic mobility on alkaline 6 M-urea/polyacrylamide gels differs from that of scallop troponin C, and it appears not to be associated with thin filaments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boudreau R. J., Drummond G. I. A modified assay of 3':5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):388–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H. Homology of myosin light chains, troponin-C and parvalbumins deduced from comparison of their amino acid sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90927-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Sherry J. M., Aromatorio D. K., Hartshorne D. J. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):253–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A., Lehman W. Troponin-like proteins from muscles of the scallop, Aequipecten irradians. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):413–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1710413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4226–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Mader S., Kaminer B. Calcium-binding modulator protein from the unfertilized egg of the sea urchin Arbacia punctulata. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):211–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Perry S. V. The interaction of the calcium-binding protein (troponin C) with bivalent cations and the inhibitory protein (troponin I). Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):145–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1370145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation in molluscan muscles. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno K. Two calcium regulation systems in squid (Ommastrephes sloani pacificus) muscle. Preparation of calcium-sensitive myosin and troponin-tropomyosin. J Biochem. 1978 Dec;84(6):1431–1440. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W. Calcium ion-dependent myosin from decapod-crustacean muscles. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):291–296. doi: 10.1042/bj1630291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Regenstein J. M., Ransom A. L. The stoichiometry of the components of arthropod thin filaments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation of muscular contraction. Distribution of actin control and myosin control in the animal kingdom. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi G. Activation of the adenosine triphosphatase of Limulus polyphemus actomyosin by tropomyosin. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):375–387. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. Calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase of rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1790089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
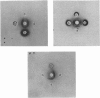
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. IV. Types of reactions in coordinated systems of diffusion. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(2):230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C., Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. II. Native filaments: isolation and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Szentkiralyi E. M., Kendrick-Jonas J. The light chains of scallop myosin as regulatory subunits. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Kaneko T., Matsumoto J. J. Calcium sensitivity of mantle muscle of squid. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):1191–1193. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]