Abstract
Exopenicillinase of Bacillus cereus 569/H was cross-linked with toluene 2,4-diisocyanate in the presence of cephalothin, cloxacillin or no substrate. The derivatives show significant differences in susceptibility to inactivation by heat, urea, iodination or proteolysis. Such differences can be predicted from the contrasting effects of these substrates on the conformation of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF
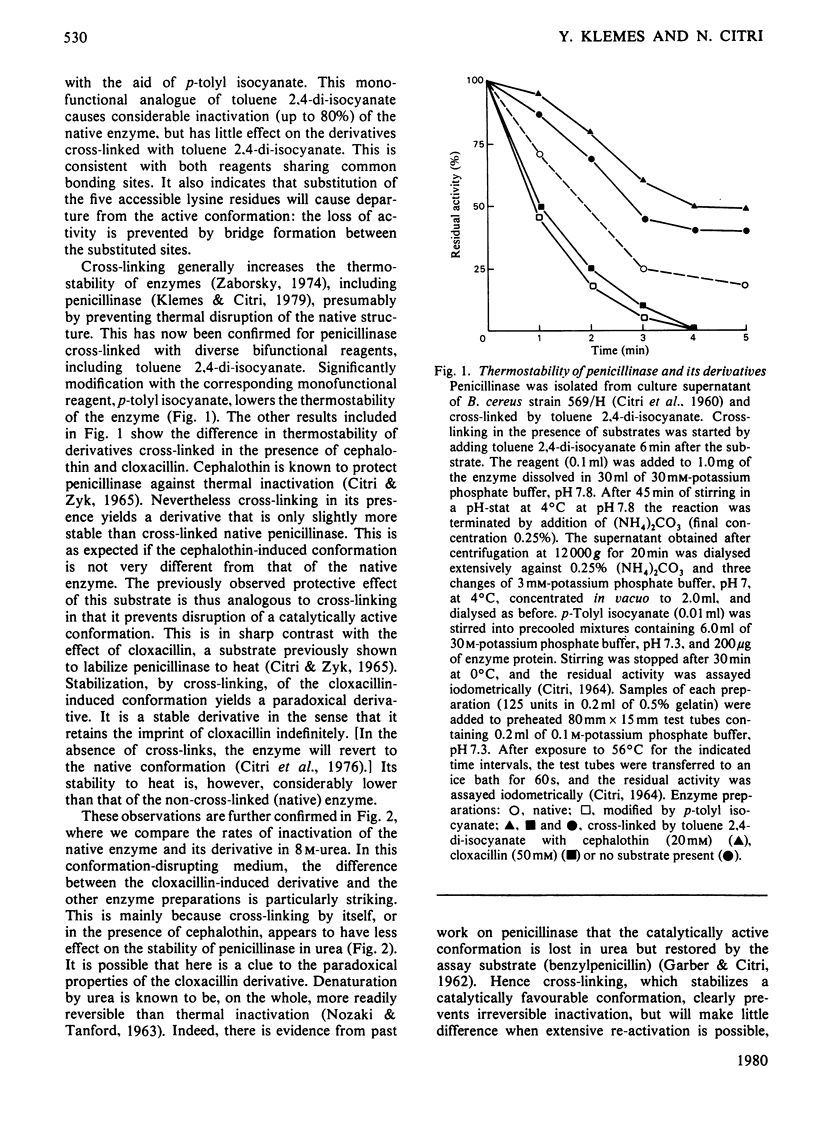
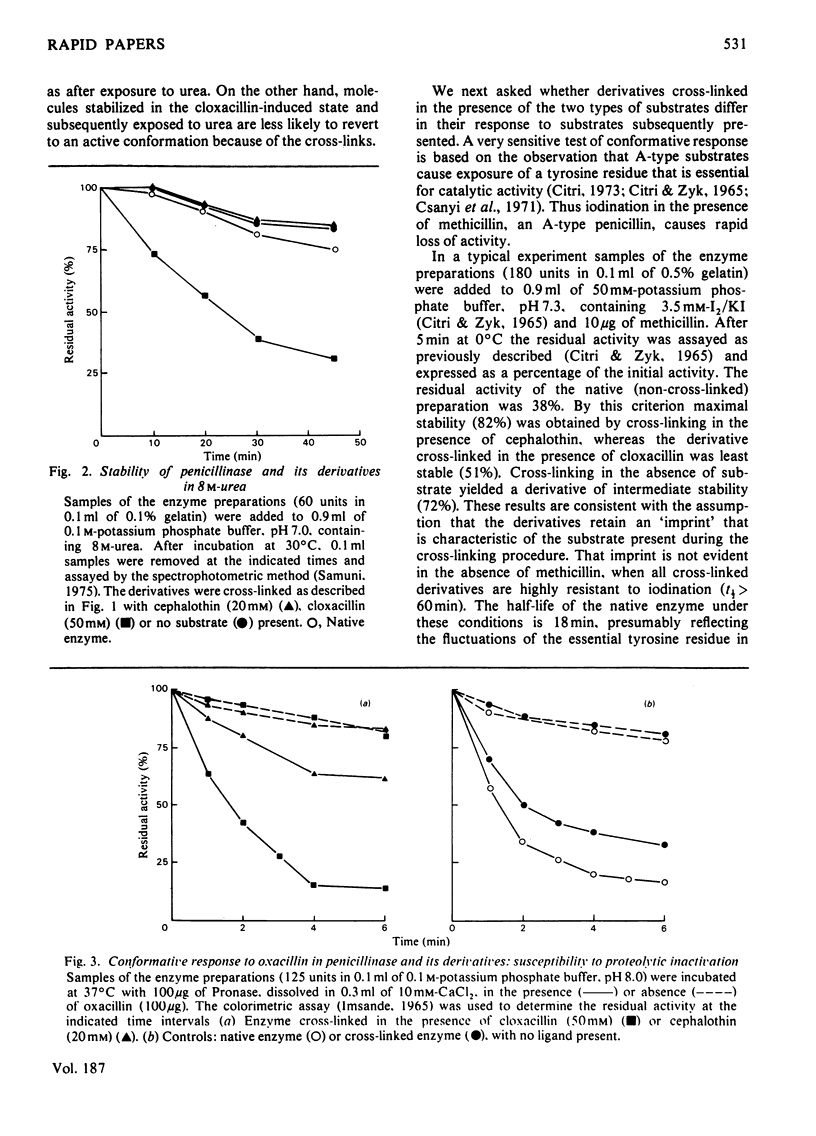

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CITRI N. DETERMINATION OF PENICILLINASE ACTIVITY. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:221–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITRI N., GARBER N., SELA M. The effect of urea and guanidine hydrochloride on activity and optical rotation of penicillinase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3454–3459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N. Conformational adaptability in enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;37:397–648. doi: 10.1002/9780470122822.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Samuni A., Zyk N. Acquisition of substrate-specific parameters during the catalytic reaction of penicillinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1048–1052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Zyk N. The interaction of penicillinase with penicillins. IV. Structural aspects of catalytic and non-catalytic interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 22;99(3):427–441. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csányi V., Ferencz I., Mile I. Chemical nature of the inactivation of Bacillus cereus penicillinase by iodine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 29;236(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARBER N., CITRI N. The interaction of penicillinase with penicillins. I. Effect of substrates and of a competitive inhibitor on native and urea-treated enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 13;62:385–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMSANDE J. NEW ASSAY FOR PENICILLINASE AND SOME RESULTS ON PENICILLINASE INDUCTION. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1322–1327. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1322-1327.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemes Y., Citri N. Catalytic and conformational properties of cross-linked derivatives of penicillinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 12;567(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E. Application of a Theory of Enzyme Specificity to Protein Synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):98–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOZAKI Y., TANFORD C. THE SOLUBILITY OF AMINO ACIDS AND RELATED COMPOUNDS IN AQUEOUS UREA SOLUTIONS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:4074–4081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHICK A. F., SINGER S. J. On the formation of covalent linkages between two protein molecules. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2477–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A. A direct spectrophotometric assay and determination of Michaelis constants for the beta-lactamase reaction. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


