Abstract
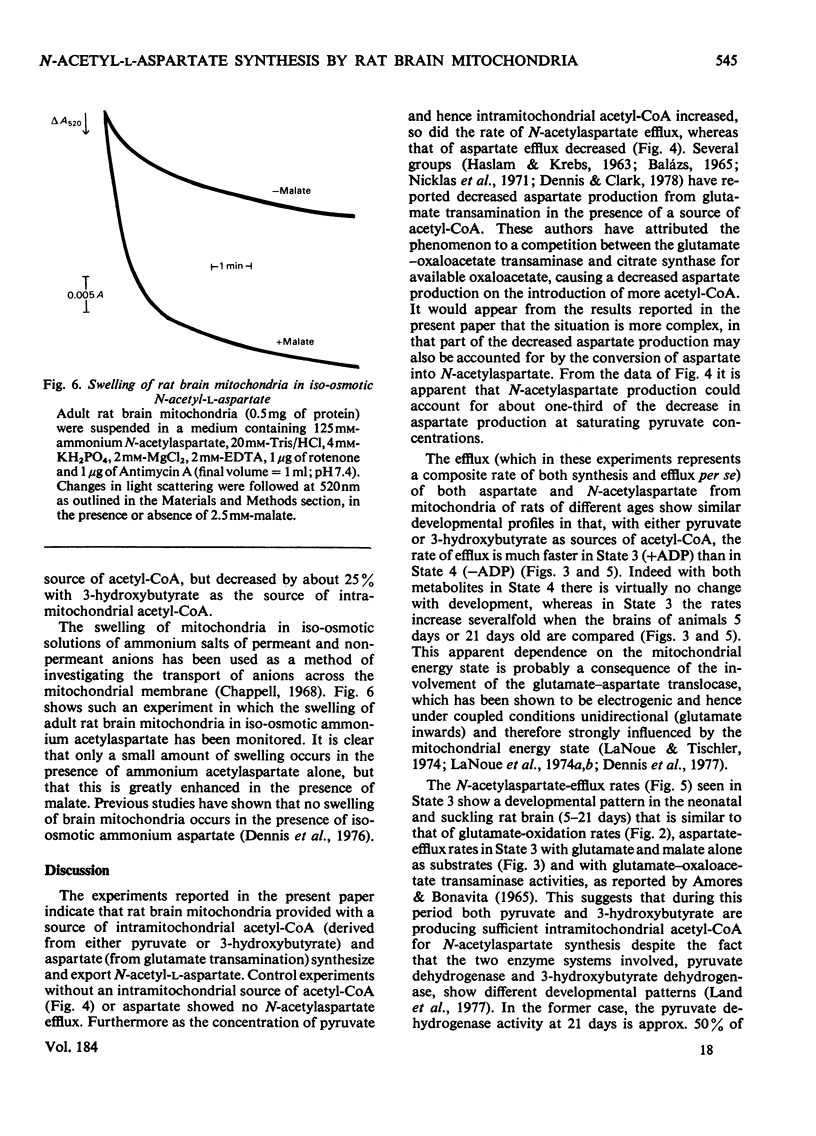
1. The synthesis and efflux of N-acetyl-l-aspartate from brain mitochondria of rats of different ages has been studied. 2. Brain mitochondrial State 3 (+ADP) respiration rate, using 10mm-glutamate and 2.5mm-malate as substrates, increases during the suckling period and reaches approx. 50% of the adult value at 17 days after birth [adult State 3 respiration rate=160±7ng-atoms of O/min per mg of mitochondrial protein(mean±s.d.; n=3)]. 3. The influence of 5mm-pyruvate or 10mm-dl-3-hydroxybutyrate on aspartate efflux from brain mitochondira from rats of different ages oxidizing glutamate and malate was studied. In all cases the aspartate efflux in State 3 was greater than in State 4, but, whereas the aspartate efflux in State 3 increased as the animals developed, that of State 4 showed only a small increase. However, the rate of aspartate efflux in the presence of pyruvate or 3-hydroxybutyrate as well as glutamate and malate was approx. 60–65% of that in the presence of glutamate and malate alone. 4. An inverse relationship between aspartate efflux and N-acetylaspartate efflux was observed with adult rat brain mitochondria oxidizing 10mm-glutamate and 2.5mm-malate in the presence of various pyruvate concentrations (0–5mm). 5. N-Acetylaspartate efflux by brain mitochondria of rats of different ages was studied in States 3 and 4, utilizing 5mm-pyruvate or 10mm-dl-3-hydroxybutyrate as acetyl-CoA sources. A similar pattern of increase during development was seen in State 3 for N-acetylaspartate efflux as for aspartate efflux (see point 3 above). Also only very small increases in N-acetylaspartate efflux occurred during development in State 4.6. Rat brain mitochondria in the presence of iso-osmotic N-acetylaspartate showed some swelling which was markedly increased in the presence of malate. 7. It is concluded that N-acetylaspartate may be synthesized and exported from both neonatal and adult rat brain mitochondria. It is proposed that the N-acetylaspartate is transported by the dicarboxylic acid translocase and may be an additional mechanism for mitochondrial/cytosolic carbon transport to that of citrate.
Full text
PDF

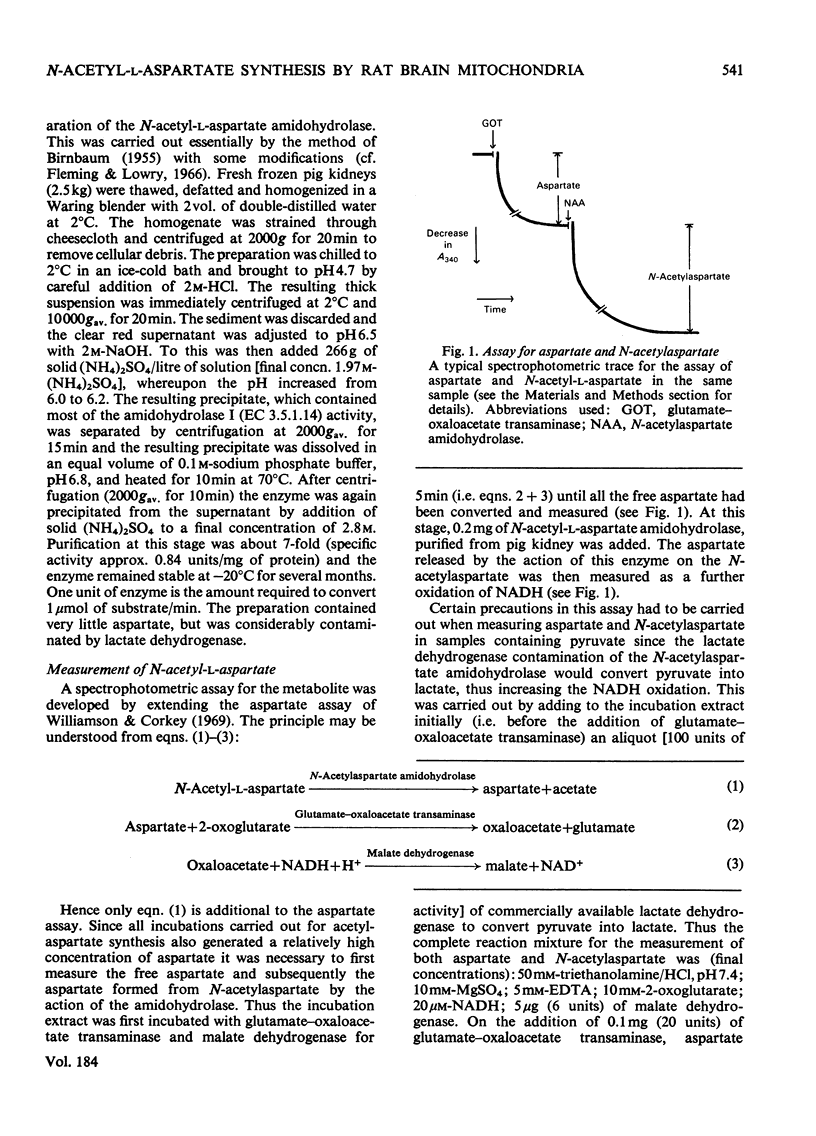
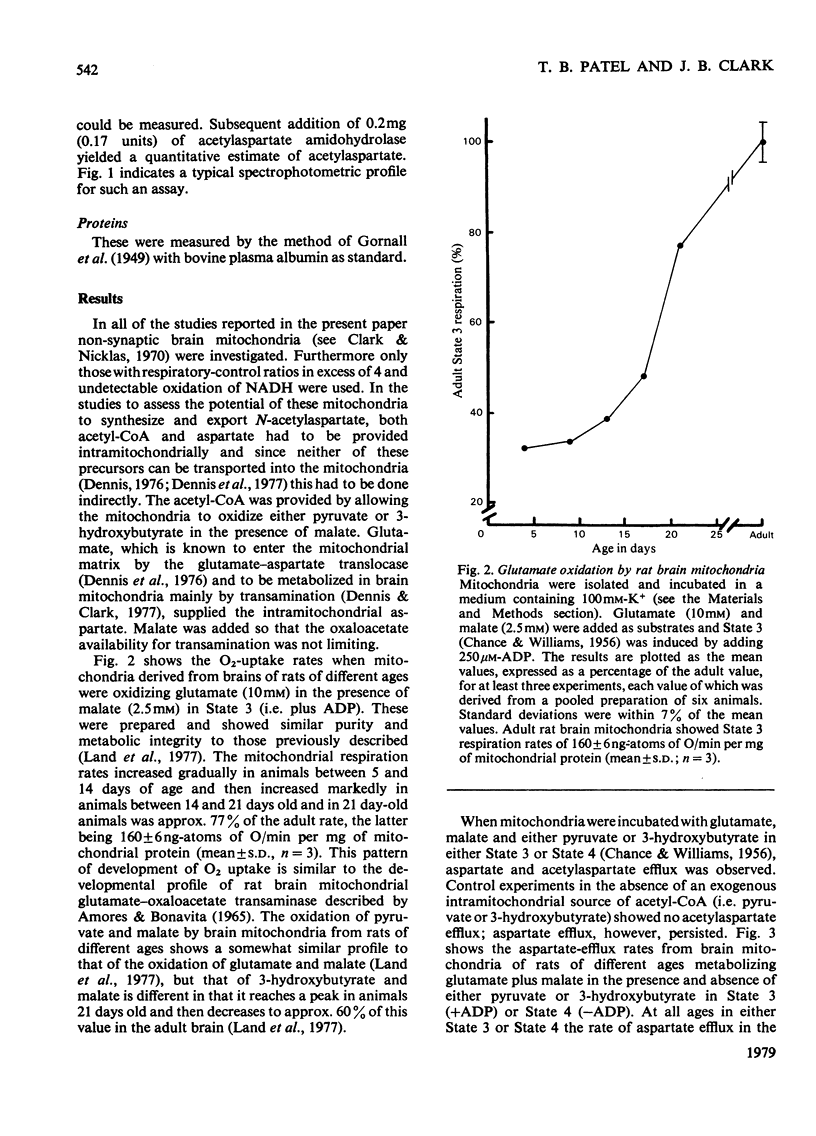
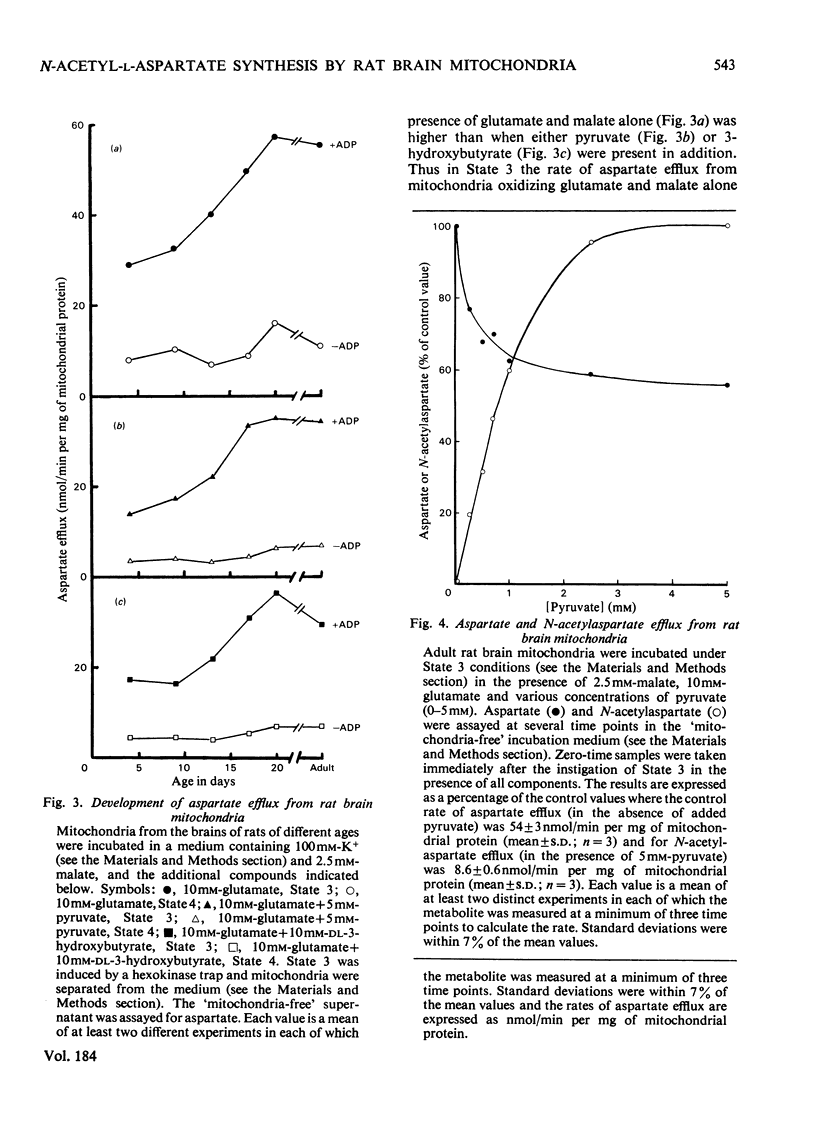
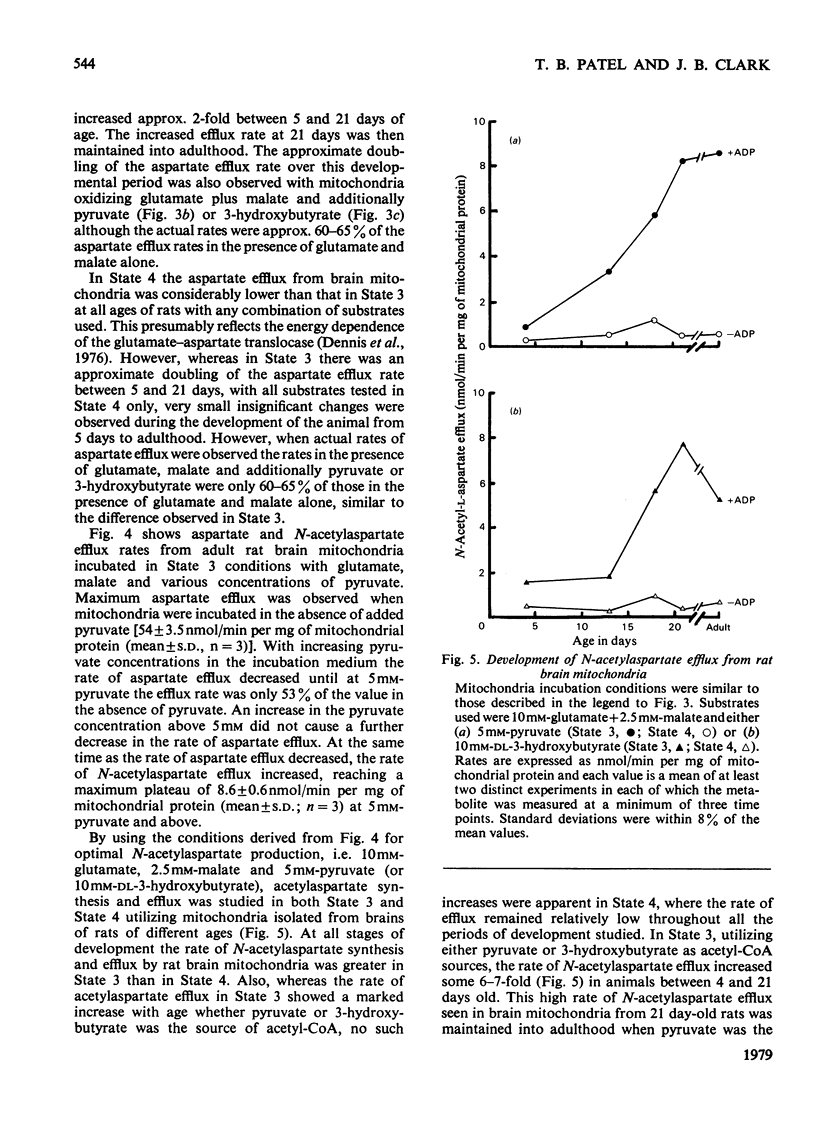

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amore G., Bonavita V. Aspartate aminotransferase in the brain of the developing rat. Life Sci. 1965 Dec;4(24):2417–2424. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALAZS R. CONTROL OF GLUTAMATE OXIDATION IN BRAIN AND LIVER MITOCHONDRIAL SYSTEMS. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:497–508. doi: 10.1042/bj0950497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benuck M., D'Adamo A. F., Jr Acetyl transport mechanisms. Metabolism of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in the non-nervous tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 1;152(3):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buniatian H. C., Hovhannissian V. S., Aprikian G. V. The participation of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in brain metabolism. J Neurochem. 1965 Aug;12(8):695–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell J. B. Systems used for the transport of substrates into mitochondria. Br Med Bull. 1968 May;24(2):150–157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. B., Nicklas W. J. The metabolism of rat brain mitochondria. Preparation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4724–4731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Adamo A. F., Jr, Gidez L. I., Yatsu F. M. Acetyl transport mechanisms. Involvement of N-acetyl aspartic acid in de novo fatty acid biosynthesis in the developing rat brain. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(4):267–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00235902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Adamo A. F., Jr, Smith J. C., Woiler C. The occurrence of N-acetylaspartate amidohydrolase (aminoacylase II) in the developing rat. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):1275–1278. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Adamo A. F., Jr, Yatsu F. M. Acetate metabolism in the nervous system. N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid and the biosynthesis of brain lipids. J Neurochem. 1966 Oct;13(10):961–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb10292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. C., Clark J. B. The pathway of glutamate metabolism in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):521–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1680521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. C., Clark J. B. The regulation of glutamate metabolism by tricarboxylic acid-cycle activity in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):155–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1720155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. C., Lai J. C., Clark J. B. Comparative studies on glutamate metabolism in synpatic and non-synaptic rat brain mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):727–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1640727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. C., Land J. M., Clark J. B. Glutamate metabolism and transport in rat brain mitochondria. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):323–331. doi: 10.1042/bj1560323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming M. C., Lowry O. H. The measurement of free and N-acetylated aspartic acids in the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):779–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein F. B. The enzymatic synthesis of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid by subcellular preparations of rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4257–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASLAM R. J., KREBS H. A. THE METABOLISM OF GLUTAMATE IN HOMOGENATES AND SLICES OF BRAIN CORTEX. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:566–578. doi: 10.1042/bj0880566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knizley H., Jr The enzymatic synthesis of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid by a water-insoluble preparation of a cat brain acetone powder. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4619–4622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Bryla J., Bassett D. J. Energy-driven aspartate efflux from heart and liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7514–7521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Meijer A. J., Brouwer A. Evidence for electrogenic aspartate transport in rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Apr 2;161(2):544–550. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaNoue K. F., Tischler M. E. Electrogenic characteristics of the mitochondrial glutamate-aspartate antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7522–7528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land J. M., Booth R. F., Berger R., Clark J. B. Development of mitochondrial energy metabolism in rat brain. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):339–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1640339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. C., Cooper J. R. Studies on the function of N-acetyl aspartic acid in brain. J Neurochem. 1965 Sep-Oct;12(9):825–835. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb10267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer A. J., Van Dam K. The metabolic significance of anion transport in mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 30;346(3-4):213–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas W. J., Clark J. B., Williamson J. R. Metabolism of rat brain mitochondria. Studies on the potassium ion-stimulated oxidation of pyruvate. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):83–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1230083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid in brain. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Studies on the free amino acids and related compounds in the tissues of the cat. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):927–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLAN H. H. Studies on the distribution of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in brain. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


