Abstract
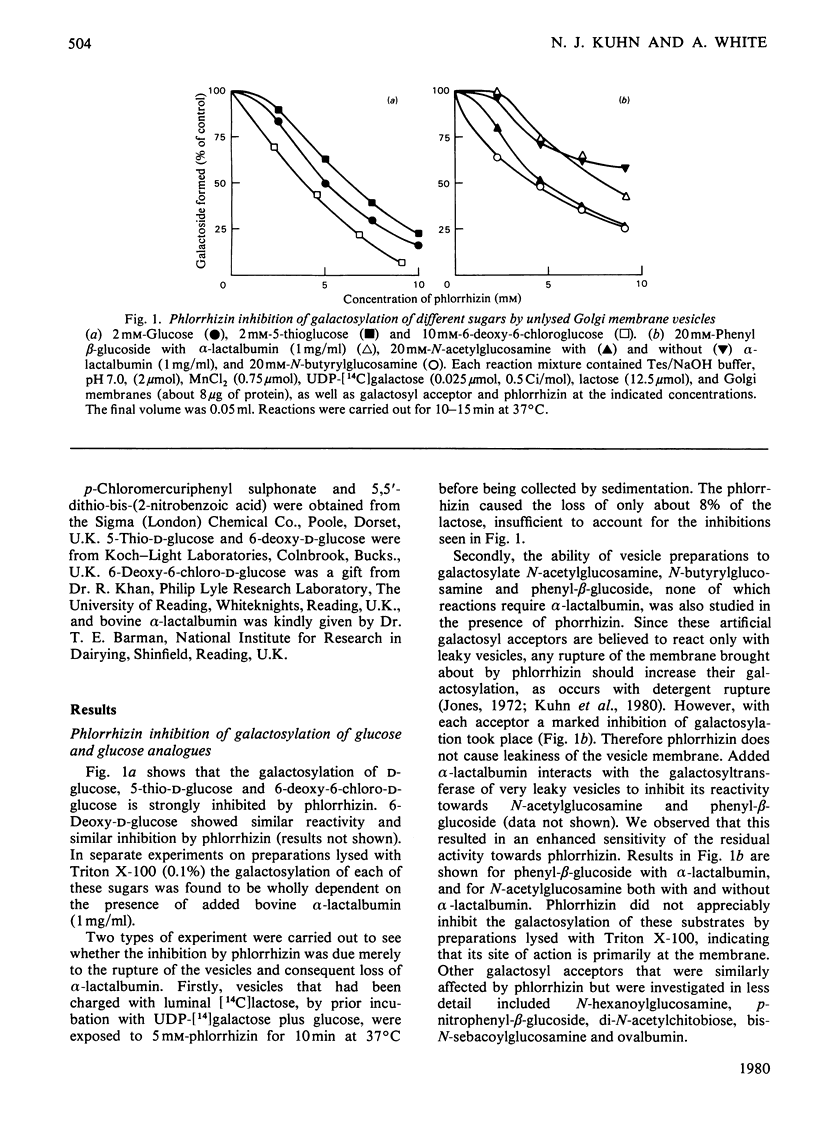
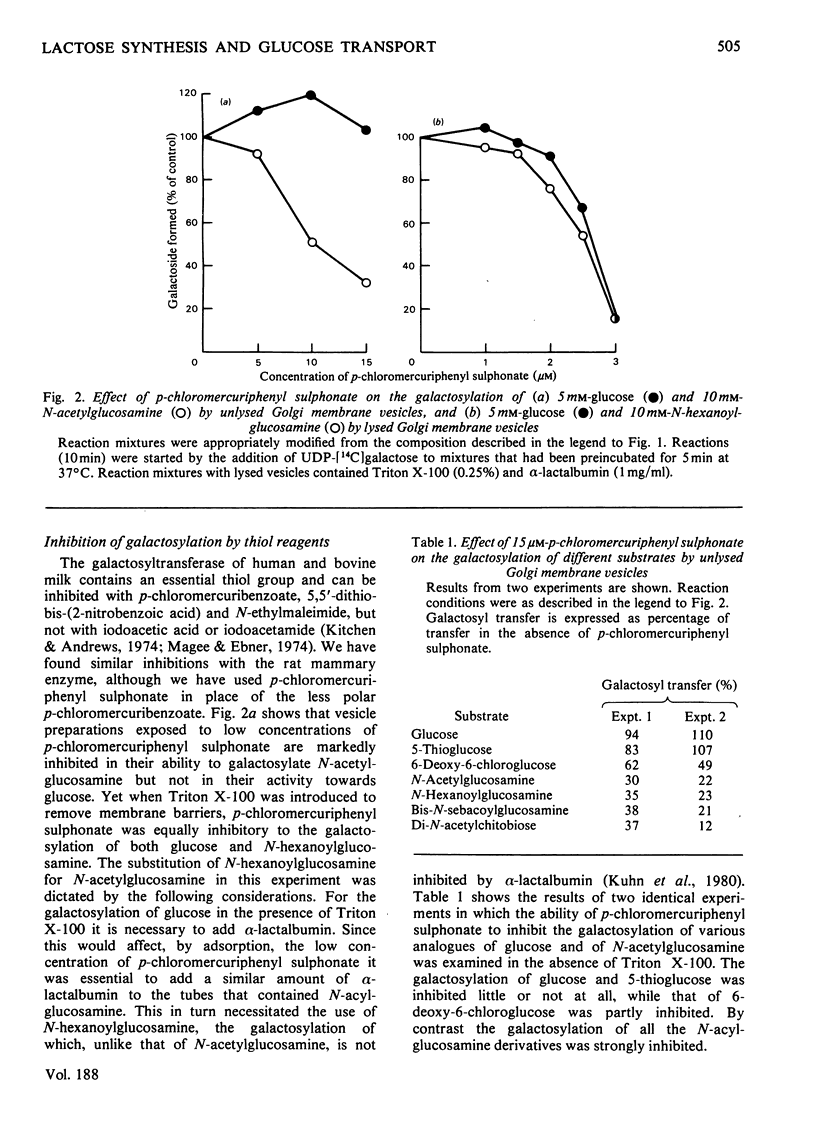
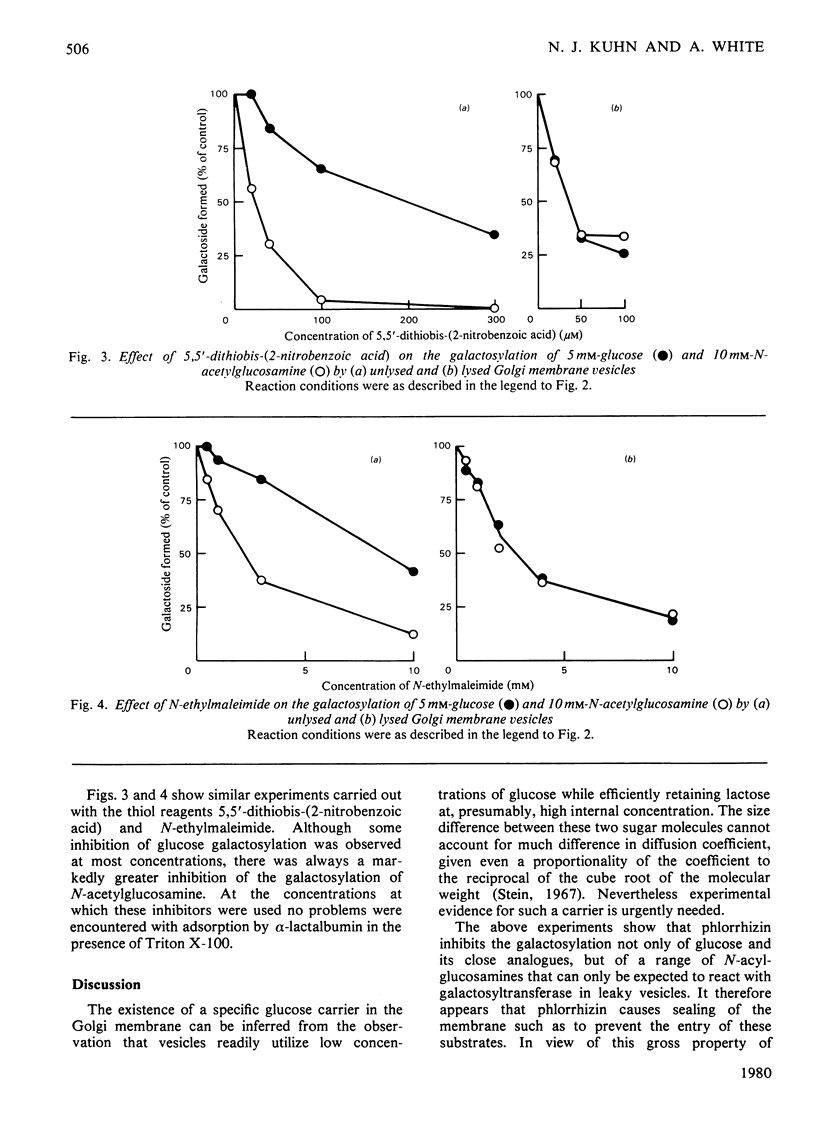
1. The ability of phlorrhizin to inhibit the galactosylation of glucose was re-examined with Golgi membrane vesicles purified from rat mammary gland, and extended to the galactosylation of several glucose analogues and N-acylglucosamines. 2. The inhibition is ascribed, contrary to previous conclusions, to a general annealing of leaky membranes comprising a minority of the vesicles. 3. Three thiol reagents were able to inhibit the galactosylation of N-acylglucosamines with less, or no, inhibition of galactosylation of glucose. This demonstrates the existence of a Golgi membrane carrier that distinguishes between glucose and N-acylglucosamines.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. The role of alpha-lactalbumin and the A protein in lactose synthetase: a unique mechanism for the control of a biological reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):491–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodbeck U., Ebner K. E. Resolution of a soluble lactose synthetase into two protein components and solubilization of microsomal lactose synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):762–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodbeck U., Ebner K. E. The subcellular distribution of the A and B proteins of lactose synthetase in bovine and rat mammary tissue. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5526–5532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. G., Reithel F. J. The lactose synthetase particles of lactating bovine mammary gland. Characteristics of the particles. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):177–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1090177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. G., Reithel F. J. The lactose synthetase particles of lactating bovine mammary gland. Preparation of particles with intact lactose synthetase. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):169–176. doi: 10.1042/bj1090169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A. Studies on the particulate lactose synthetase of mouse mammary gland and the role of -lactalbumin in the initiation of lactose synthesis. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):67–78. doi: 10.1042/bj1260067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen B. J., Andrens P. Studies on the thiol group of lactose synthetase A protein from human milk and on the binding of uridine diphosphate galactose to the enzyme. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):173–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1410173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen B. J., Andrews P. The effect of temperature on a reaction catalysed by lactose synthetase A protein. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80605-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., White A. The role of nucleoside diphosphatase in a uridine nucleotide cycle associated with lactose synthesis in rat mammary-gland Golgi apparatus. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1680423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., White A. The topography of lactose synthesis. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):77–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1480077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., Wooding F. B., White A. Properties of galactosyltransferase-enriched vesicles of Golgi membranes from lactating-rat mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):377–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee S. C., Ebner K. E. Inactivation of soluble bovine milk galactosyltransferase (lactose synthetase) by sulfhydryl reagents and trypsin. Protection by substrates and products. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6992–6998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D., Steggall M., Eyring E. M. The effect of phloretin on red cell nonelectrolyte permeability. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(1):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01869971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanbacher F. L., Ebner K. E. Galactosyltransferase acceptor specificity of the lactose synthetase A protein. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5057–5061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


