Abstract
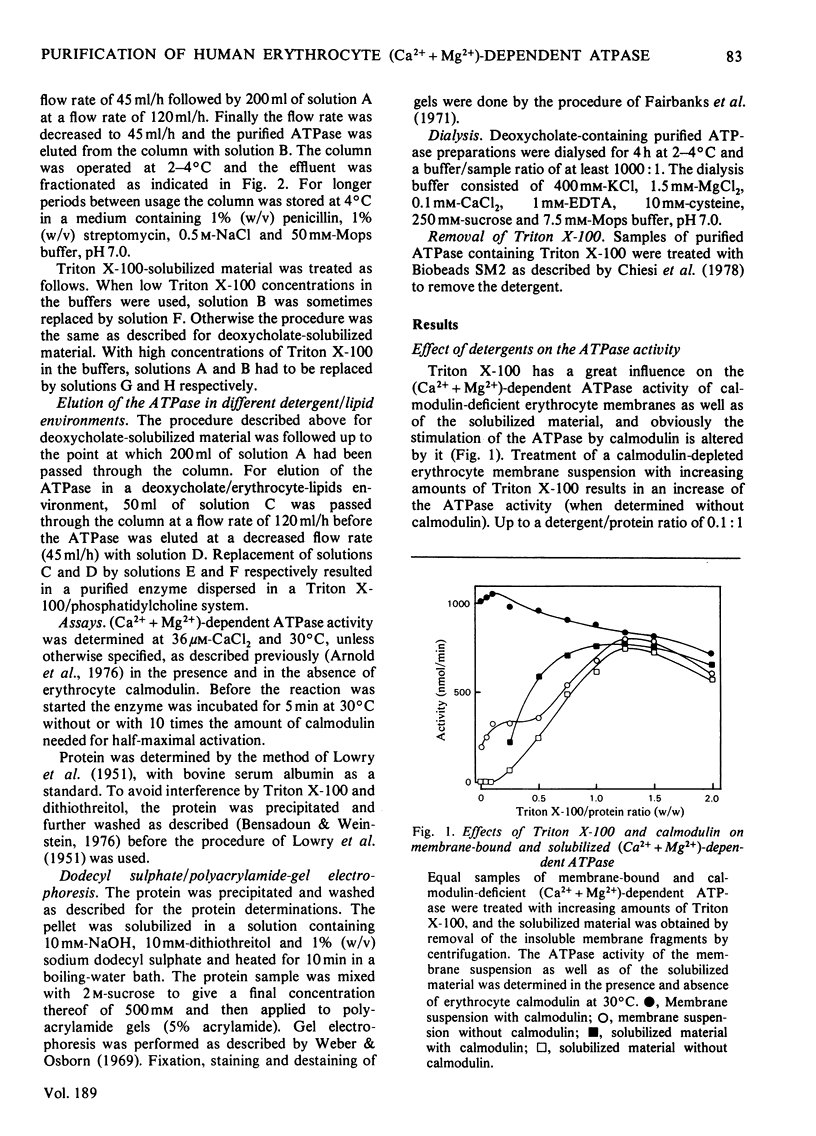
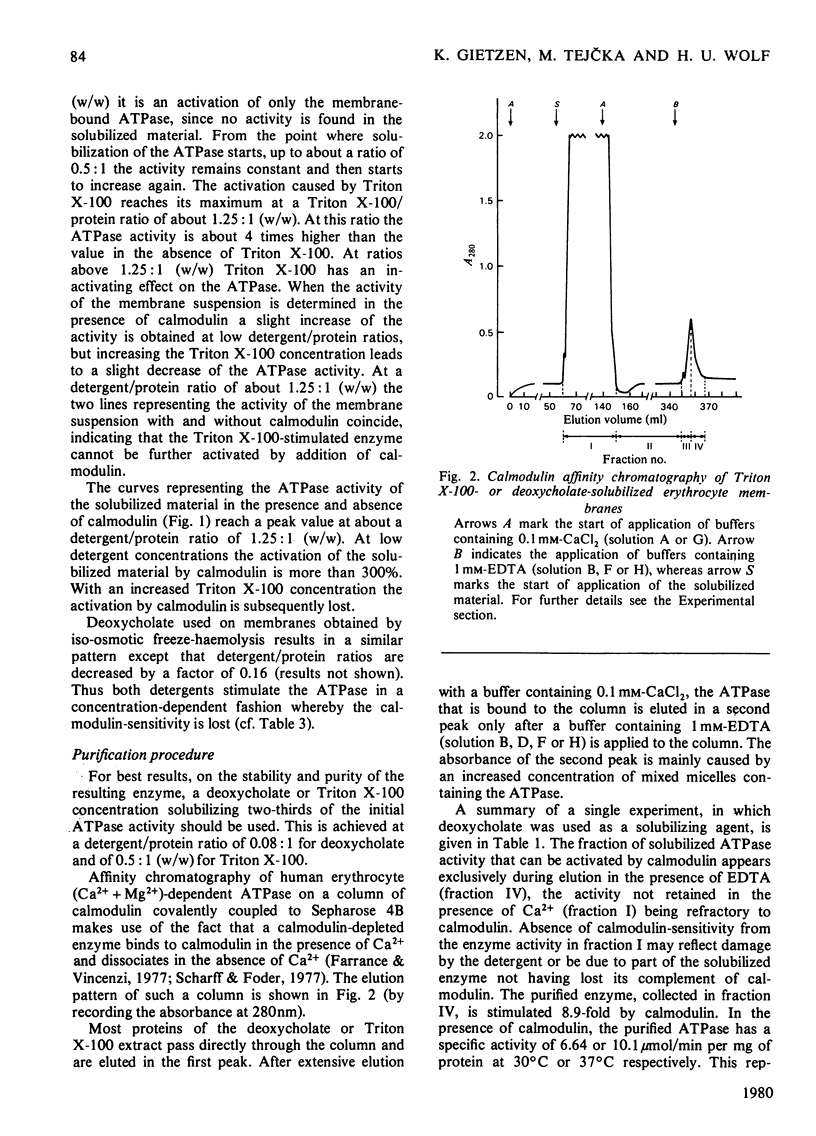
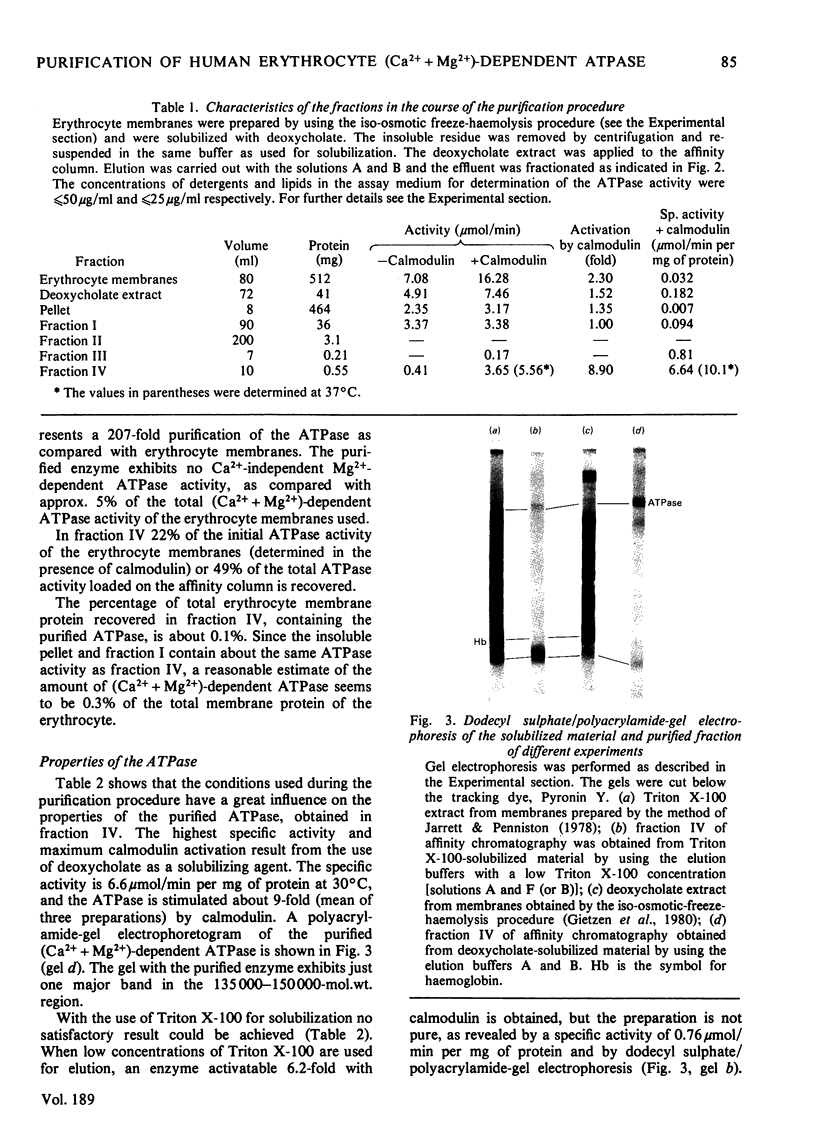
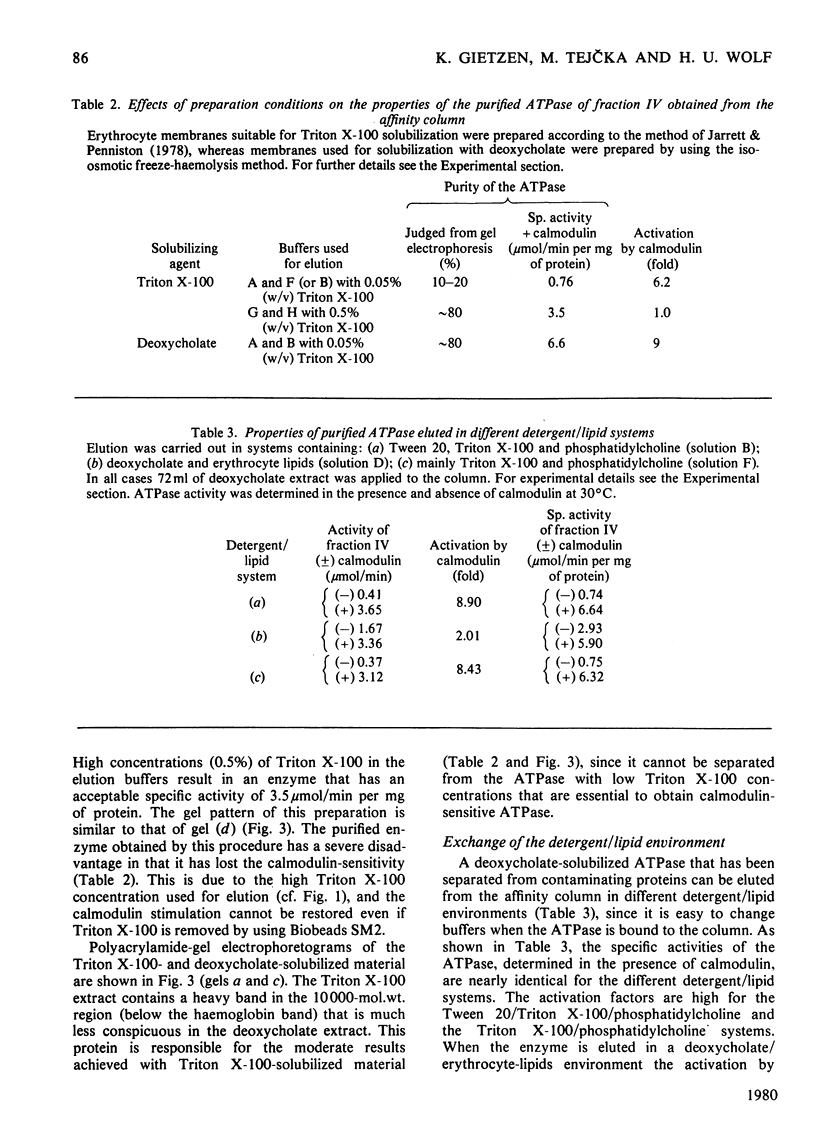
The (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase of human erythrocyte membranes was solubilized with deoxycholate and purified by calmodulin affinity chromatography to yield a functional enzyme. The method gave an enzyme purified 207-fold as compared with that of the erythrocyte membranes. The molecular weight of the ATPase was in the range 135 000-150 000, as revealed by a single major band after electrophoresis on dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels. The isolated enzyme was highly sensitive to calmodulin, since the activity was increased about 9-fold. At 37 degrees C and in the presence of calmodulin the purified ATPase had a specific activity of 10.1 mumol/min per mg of protein. Triton X-100 or deoxycholate stimulated the calmodulin-deficient enzyme in a concentration-dependent fashion whereby the calmodulin-sensitivity was lost. The purification method is suitable for studying the lipid-sensitivity of the ATPase, since the lipids can easily be exchanged without a significant loss of activity. A purification procedure described by Niggli, Penniston & Carafoli [(1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 9955-9958] resulted in an enzyme that indeed was pure but was lacking a predominant feature, namely the modulation by calmodulin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Peterson S. W., Acuto O. Reconstitution of a Ca2+-transporting ATPase system from triton X-100-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jul;189(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrance M. L., Vincenzi F. F. Enhancement of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity of human erythrocyte membranes by hemolysis in isosmotic imidazole buffer. II. Dependence on calcium and a cytoplasmic activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Seiler S., Fleischer S., Wolf H. U. Reconstitution of the Ca2+-transport system of human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):47–54. doi: 10.1042/bj1880047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath R. M., Vincenzi F. F. Phosphodiesterase protein activator mimics red blood cell cytoplasmic activator of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J., Taverna R. D., Flynn D. D., Ekholm J. E. The interaction of Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase activator protein and Ca2+ with human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):1009–1015. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91684-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds T. R., Larsen F. L., Vincenzi F. F. Plasma membrane Ca2+ transport: stimulation by soluble proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):455–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett H. W., Penniston J. T. Purification of the Ca2+-stimulated ATPase activator from human erythrocytes. Its membership in the class of Ca2+-binding modulator proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4676–4682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Fleischer S. Dissociation and reconstitution of functional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Purification of the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase from human erythrocyte membranes using a calmodulin affinity column. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9955–9958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orringer E. P., Parker J. C. Ion and water movements in red blood cells. Prog Hematol. 1973;8:1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen B., Schatzmann H. J. The lipid requirement of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase in the human erythrocyte membrane, as studied by various highly purified phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):17–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronner P., Gazzotti P., Carafoli E. A lipid requirement for the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-activated ATPase of erythrocyte membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):578–583. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O., Foder B. Reversible shift between two states of Ca2+-ATPase in human erythrocytes mediated by Ca2+ and a membrane-bound activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 4;509(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. Dependence on calcium concentration and stoichiometry of the calcium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):551–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Harrelson W. G., Jr, Keller P. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. Structural similarities between the Ca2+-dependent regulatory proteins of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. U., Dieckvoss G., Lichtner R. Purification and properties of high-affinity Ca2+-ATPase of human erythrocyte membranes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(5-6):847–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. U., Gietzen K. Proceedings: The solubilization of high-affinity Ca-2+-ATPase of human erythrocyte membranes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Oct;355(10):1272–1272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



