Abstract
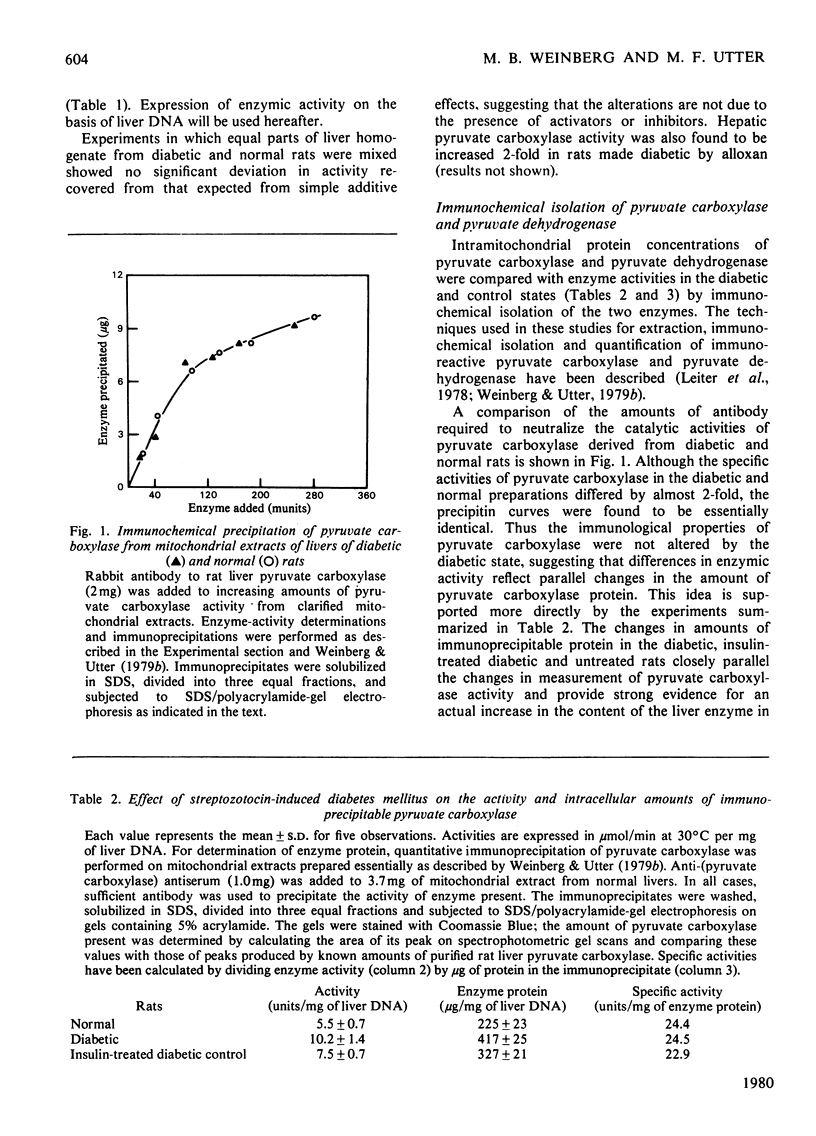
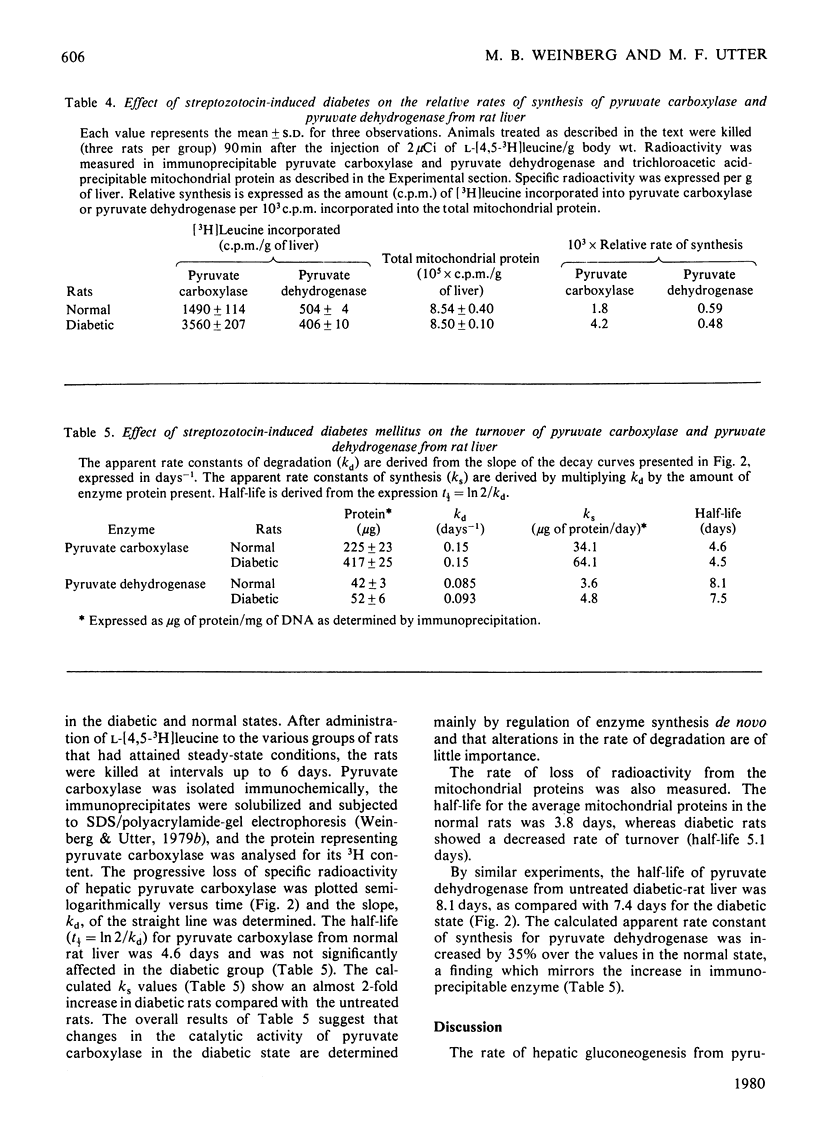
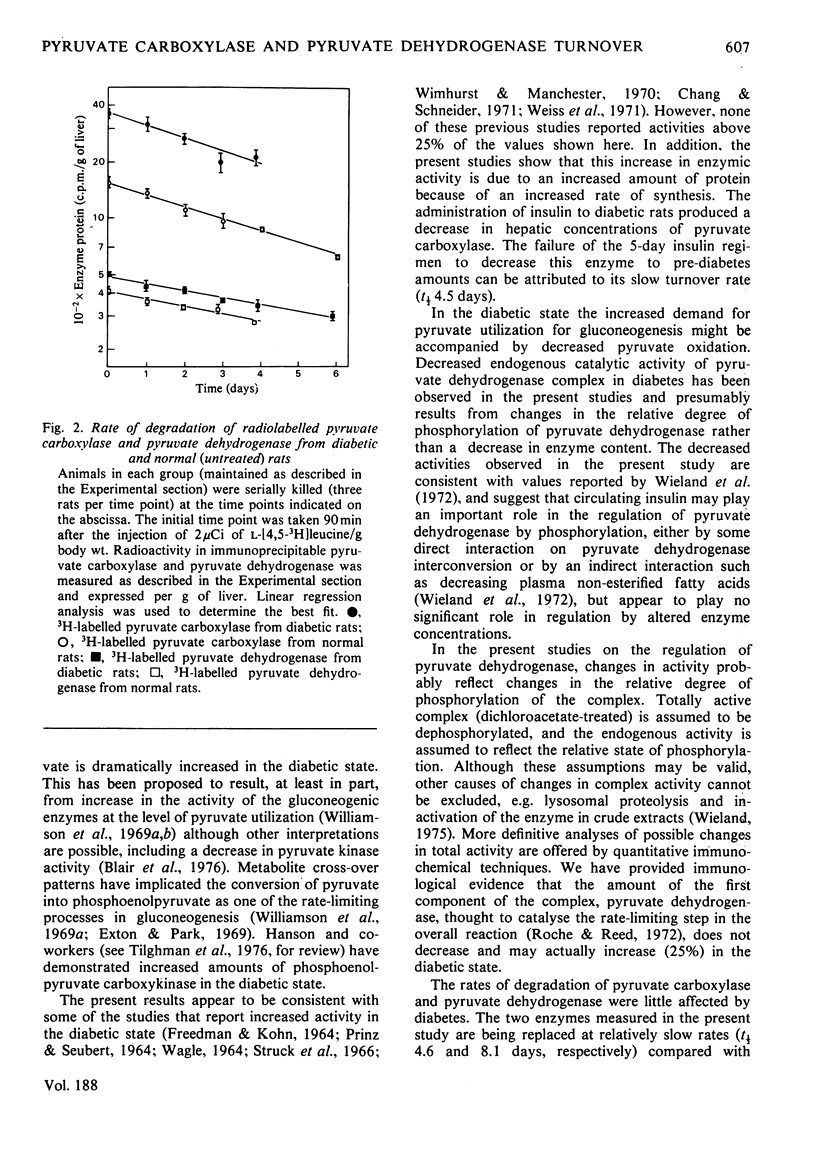
Immunochemical techniques were used to study the effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the amounts of pyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase and on their rates of synthesis and degradation. Livers from diabetic rats had twice the pyruvate carboxylase activity of livers from normal rats when expressed in terms of DNA or body weight. The changes in catalytic activity closely paralleled changes in immunoprecipitable enzyme protein. Relative rates of synthesis determined by pulse-labelling studies showed that the ratio of synthesis of pyruvate carboxylase to that of average mitochondrial protein was increased 2.0-2.5 times in diabetic animals over that of control animals. Other radioisotopic studies indicated that the rate of degradation of this enzyme was not altered significantly in diabetic rats, suggesting that the increase in this enzyme was due to an increased rate of synthesis. Similar experiments with pyruvate dehydrogenase, the first component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, showed that livers from diabetic rats had approximately the same amount of immunoprecipitable enzyme protein as the control animals, but a larger proportion of the enzyme was in its inactive state. The rates of synthesis and degradation of pyruvate dehydrogenase were not affected significantly by diabetes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias I. M., Doyle D., Schimke R. T. Studies on the synthesis and degradation of proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3303–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and pyruvate carboxylase in developing rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):866–871. doi: 10.1042/bj1040866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. B., Cimbala M. A., Foster J. L., Morgan R. A. Hepatic pyruvate kinase. Regulation by glucagon, cyclic adenosine 3'-5'-monophosphate, and insulin in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3756–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brech W., Shrago E., Wilken D. Studies on pyruvate carboxylase in rat and human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 24;201(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90288-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. Y., Schneider D. I. Hepatic enzyme activities in streptozotocin-diabetic rats before and after insulin treatment. Diabetes. 1971 Feb;20(2):71–77. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.2.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. 3. Effects of L-lactate, pyruvate, fructose, glucagon, epinephrine, and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on gluconeogenic intermediates in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1424–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN A. D., KOHN L. PYRUVATE METABOLISM AND CONTROL: FACTORS AFFECTING PYRUVIC CARBOXYLASE ACTIVITY. Science. 1964 Jul 3;145(3627):58–60. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3627.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filsell O. H., Jarrett I. G., Taylor P. H., Keech D. B. Effects of fasting, diabetes and glucocorticoids on gluconeogenic enzymes in the sheep. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan J. C., Jeffay H. Origins and metabolism of the intracellular amino acid pools in rat liver and muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):448–459. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY C. D., LAYNE S. Bacteria found in the air over Canada and the American Arctic. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;3(3):447–455. doi: 10.1139/m57-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A. The regulation of the release of ketone bodies by the liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:339–354. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter A. B., Weinberg M., Isohashi F., Utter M. F. Relationshiop between phosphorylation and activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat liver mitochondria and the absence of such a relationship for pyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2716–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlman M. A., Tobin R. B., Johnston J. B. Metabolic control of enzymes in normal, diabetic, and diabetic insulin-treated rats utilizing 1,3 butanediol. Metabolism. 1971 Feb;20(2):149–167. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niejadlik D. C., Dube A. H., Adamko S. M. Glucose measurements and clinical correlations. JAMA. 1973 Jun 25;224(13):1734–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz W., Seubert W. Effect of insulin on pyruvate carboxylase in alloxan diabetic animals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Aug 11;16(6):582–585. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Garland P. B., Hales C. N., Newsholme E. A., Denton R. M., Pogson C. I. Interactions of metabolism and the physiological role of insulin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1966;22:1–48. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9825-5.50004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche T. E., Reed L. J. Function of the nonidentical subunits of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 21;48(4):840–846. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90684-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D., Snyder S. H. Amine synthesis in rapidly growing tissues: ornithine decarboxylase activity in regenerating rat liver, chick embryo, and various tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1420–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Control of enzyme levels in mammalian tissues. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;37:135–187. doi: 10.1002/9780470122822.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Doyle D. Control of enzyme levels in animal tissues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:929–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrago E., Lardy H. A. Paths of carbon in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. II. Conversion of precursors to phosphoenolpyruvate in liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck E., Ashmore J., Wieland O. Pyruvatcarboxylase-Aktivität und Glucoseneubildung in der isoliert perfundierten Rattenleber. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1966;7(1):38–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagle S. R. Studies on pyruvate carboxylase activity in alloxan diabetic and normal animals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:533–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg M. B., Utter M. F. Effect of thyroid hormone on the turnover of rat liver pyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9492–9499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland O. H. On the mechanism of irreversible pyruvate dehydrogenase inactivation in liver mitochondrial extracts. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):44–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland O. H., Patzelt C., Löffler G. Active and inactive forms of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat liver. Effect of starvation and refeeding and of insulin treatment on pyruvate-dehydrogenase interconversion. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 11;26(3):426–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland O., Von Jagow-Westermann B., Stukowski B. Kinetic and regulatory properties of heart muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Mar;350(3):329–334. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1969.350.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Browning E. T., Scholz R. Control mechanisms of gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis. I. Effects of oleate on gluconeogenesis in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4607–4616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Browning E. T., Thurman R. G., Scholz R. Inhibition of glucagon effects in perfused rat liver by (+)decanoylcarnitine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5055–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. A comparison of the effects of diabetes induced with either alloxan or streptozotocin and of starvation on the activities in rat liver of the key enzymes of gluconeogenesis. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):95–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1200095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


